THE CALCULATION METHOD FOR OSMOTIC SUCTION OF SALINE SOLUTION
-
摘要: 膨润土垫层在高放废料处置库环境中与围岩接触,力学性能会受到围岩裂隙中所含盐溶液的影响。盐溶液的渗透吸力会在膨润土上产生类似于竖向荷载作用的附加应力,量化盐溶液对膨润土力学性能的影响对评估地下处置库的安全性具有重要意义。溶液渗透吸力系数作为计算渗透吸力的关键,目前需要通过较为复杂的实验测得,对工程实际应用造成了阻碍。通过引入Debye-Hückel公式,提出含单价离子电解质、2-2型电解质及混合电解质溶液的渗透吸力系数及渗透吸力的计算方法。基于Debye-Hückel公式,分析溶剂种类和温度对渗透吸力系数的影响,结果表明:溶剂极性越大,渗透吸力系数越大;温度越高,渗透吸力系数越小。
-
关键词:
- 膨润土 /
- 盐溶液 /
- 渗透吸力 /
- Debye-Hückel公式
Abstract: When bentonite cushion contacts with surrounding rocks in a disposal repository of highly radioactive waste, its mechanical properties will be affected by the saline solution contained in surrounding rock cracks, and the osmotic suction of salt solution will add additional stress similar to vertical load on bentonite. Therefore, quantifying the effect of saline solution on the mechanical properties of bentonite is of great significance for evaluating the safety of underground repository. Osmotic coefficients as the key to calculate the osmotic suction are usually obtained by complex tests, which obstructs the practical engineering applications. The Debye-Hückel formula are introduced to calculate the osmotic coefficients and osmotic suction for monovalent ion electrolyte, 2-2 type electrolyte and mixed electrolyte solutions. The impact of various factors on solution suction coefficients, such as solvent type, solute type, solute concentration and temperature are analyzed. Then the calculation method of osmotic suctions of different solutions are obtained. Based on the Debye-Hückel formula, the influence of solvent type and temperature on the osmotic suction coefficient is analyzed. The results show that the larger the solvent polarity, the larger the osmotic suction coefficient; the higher the temperature, the smaller the osmotic suction coefficient.-
Key words:
- bentonite /
- saline solution /
- osmotic suction /
- Debye-Hücke formula
-
表 1 不同种类含单价离子电解质的渗透吸力系数
Table 1. Osmotic suction coefficients of different monovalent ionic electrolytes
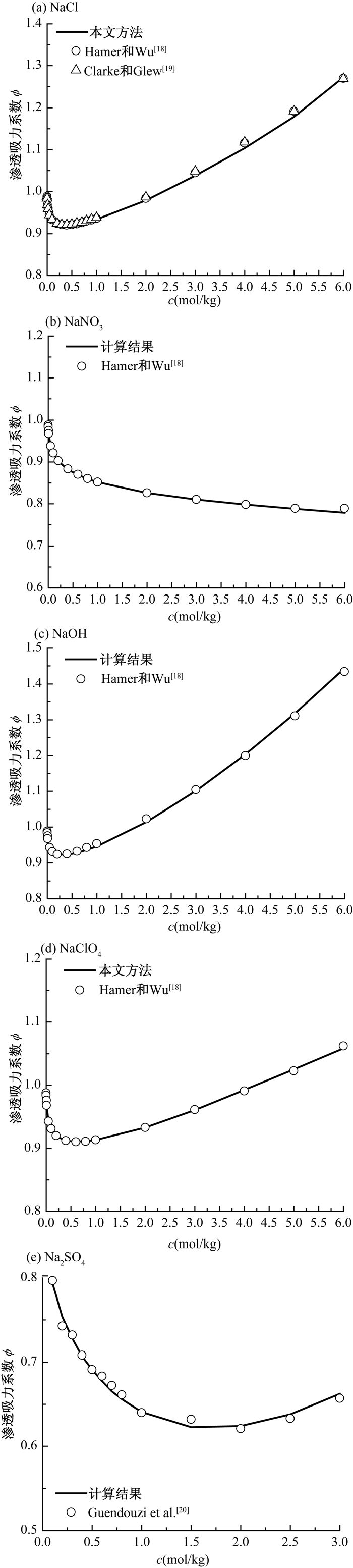
c(mol/kg) 1-1型 2-1型 3-1型 1-2型 1-3型 1-4型 1-5型 KCl Ca(NO3)2 CaCl2 AlCl3 Na2SO4 K3PO4 Na4P2O7 Na5P3O4 0.01 0.967 0.904 0.907 0.842 0.898 0.819 0.739 0.667 0.05 0.940 0.850 0.864 0.810 0.828 0.738 0.644 0.576 0.1 0.926 0.831 0.856 0.819 0.793 0.708 0.589 0.510 0.2 0.913 0.820 0.862 0.850 0.754 0.680 0.520 0.432 0.3 0.906 0.818 0.876 0.891 0.728 0.667 0.489 0.397 0.4 0.902 0.819 0.895 0.942 0.707 0.662 0.483 0.376 0.5 0.900 0.823 0.916 1.002 0.691 0.661 0.496 - 0.7 0.898 0.836 0.964 1.143 0.665 0.666 - - 1 0.898 0.861 1.048 1.390 0.641 - - - 1.6 0.905 0.917 1.243 1.953 0.622 - - - 2 0.913 0.951 1.386 - 0.624 - - - 2.5 0.924 0.904 1.572 - 0.638 - - - 3 0.937 0.850 - - 0.662 - - - 4 0.965 0.831 - - 0.734 - - - 4.8 0.989 0.820 - - - - - - 表 2 不同溶质的渗透吸力系数
Table 2. Osmotic suction coefficients of different solutes
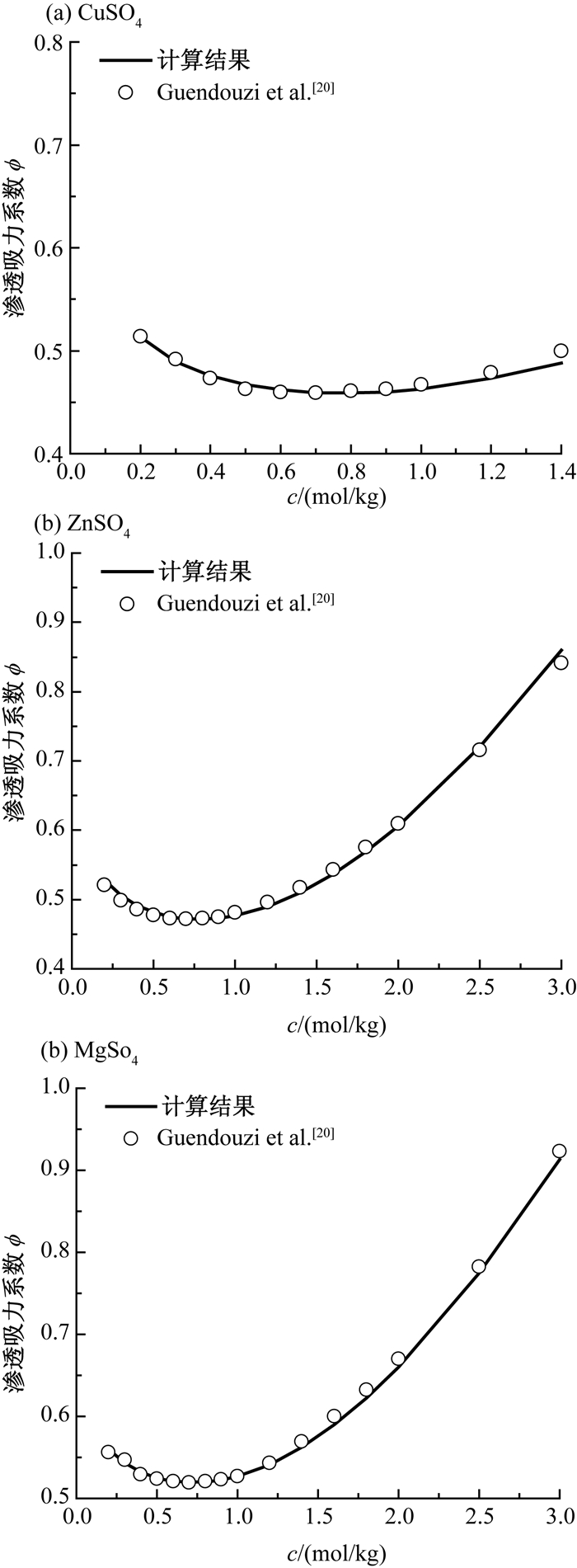
c(mol/kg) MgSO4 ZnSO4 CuSO4 CaSO4 0.001 0.894 0.895 0.888 0.910 0.005 0.791 0.793 0.778 0.792 0.01 0.741 0.741 0.725 - 0.05 0.635 0.623 0.611 - 0.1 0.595 0.573 0.560 - 0.5 0.525 0.482 0.467 - 1 0.527 0.477 0.463 - 1.4 0.562 0.510 0.488 2 0.660 0.606 - - 3 0.913 0.860 - - 3.5 - 1.022 - 表 3 不同溶质的Debye-Hückel系数
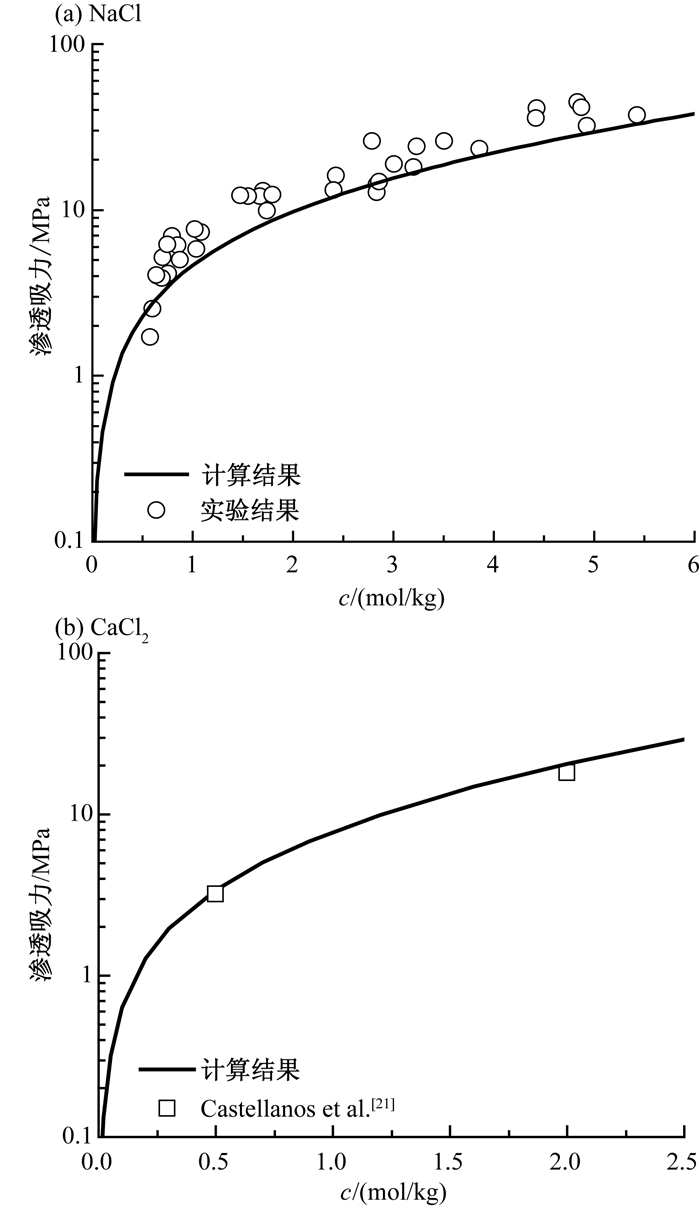
Table 3. Debye-Hückel coefficients of different solvents
溶剂 εr ρsl(kg/m3) A 水 78.4 1000 0.393 甲醇 32.63 786.6 1.297 乙醇 24.35 785 2.009 丙酮 20.7 784.35 2.562 乙酸乙酯 6.02 894.5 17.447 苯 2.28 873.6 73.974 表 4 水在不同温度中的D-H系数
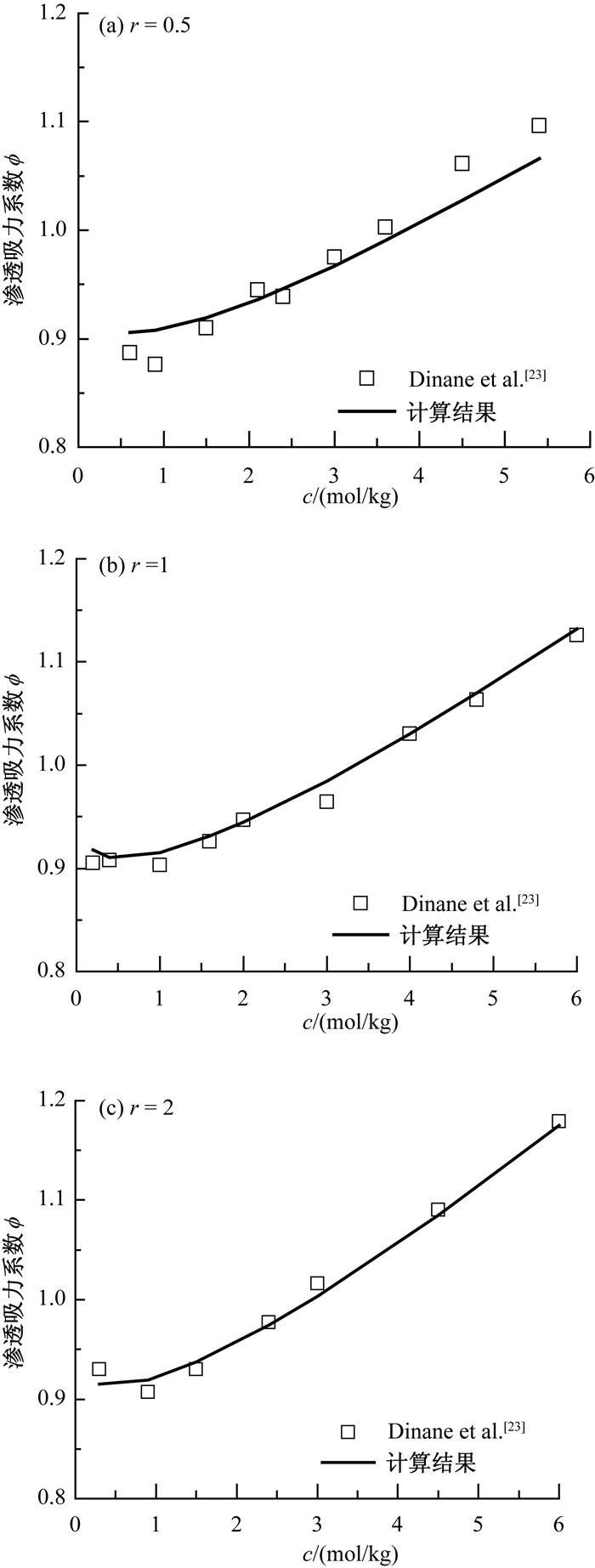
Table 4. Debye-Hückel coefficients of water under different temperatures
温度/K 相对介电常数εr 参数A 273 87.74 0.3781 278 85.76 0.3808 283 83.83 0.3836 288 81.95 0.3866 293 80.1 0.3899 294 79.73 0.3906 296 79.02 0.3918 298 78.3 0.3933 300 77.6 0.3946 303 76.55 0.3968 308 74.83 0.4006 313 73.15 0.4046 318 71.15 0.4119 323 69.91 0.4131 -
[1] 王驹, 陈伟明, 苏锐, 等.高放废物地质处置及其若干关键科学问题[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 4(25):801~812. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb200604015WANG Ju, CHEN Weiming, SU Rui, et al. Geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste and its key scientific issues[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechancis and Engineering, 2006, 4(25):801~812. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb200604015 [2] 孙德安, 张龙.盐溶液饱和高庙子膨润土膨胀特性及预测[J].岩土力学, 2013, 34(10):2790~2795. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201310007SUN Dean, ZHANG Long. Swelling characteristics of Gaomiaozi bentonite saturated by salt solution and their prediction[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(10):2790~2795. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201310007 [3] Sun Z M, Yu J, Zheng S L, et al. Effect of salt in aqueous solution on the swelling and water-retention capacity of bentonite[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 194~196:2039~2045. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.194-196 [4] Alawaji H A. Swell and compressibility characteristics of sand-bentonite mixtures inundated with liquids[J]. Applied Clay Science, 1999, 15(3/4):411~430. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=11109b69d94d9eb124098a127c33ed9b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [5] Zhang L, Sun D A, Jia D. Shear strength of GMZ07 bentonite and its mixture with sand saturated with saline solution[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2016, 132~133:24~32. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2016.08.004 [6] Tabiatnejad B, Siddiqua S, Siemens G. Impact of pore fluid salinity on the mechanical behavior of unsaturated bentonite-sand mixture[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(22):1434. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6246-5 [7] Maio D C. Shear strength of clays and clayey soils: the influence of pore fluid composition[A]. Loret B, Huyghe J M. Chemo-Mechanical Couplings in Porous Media Geomechanics and Biomechanics[M]. Vienna: Springer, 2004, 45~55. [8] Rao S M, Thyagaraj T. Swell-compression behaviour of compacted clays under chemical gradients[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2007, 44(5):520~532. doi: 10.1139/t07-002 [9] Barbour S L, Fredlund D G. Mechanisms of osmotic flow and volume change in clay soils[J]. Canadian Geotechnial Journal, 1989, 26(4):551~562. doi: 10.1139/t89-068 [10] Xu Y F, Xiang G S, Jiang H, et al. Role of osmotic suction in volume change of clays in salt solution[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2014, 101:354~361. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2014.09.006 [11] Miller D J, Nelson J D. Osmotic suction in unsaturated soil mechanics[A]. Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Unsaturated Soils[C]. Arizona:American Society of Civil Engineers, 2006, 1382~1393. [12] Apelblat A, Dov M, Wisniak J, et al. The vapour pressure of water over saturated aqueous solutions of malic, tartaric, and citric acids, at temperatures from 288 K to 323 K[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 1995, 27(1):35~41. doi: 10.1006/jcht.1995.0004 [13] Wijmans J G, Baker R W. The solution-diffusion model:a review[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 1995, 107(1~2):1~21. doi: 10.1016/0376-7388(95)00102-I [14] Fernández D P, Goodwin A R H, Lemmon E W, et al. A formulation for the static permittivity of water and steam at temperatures from 238 K to 873 K at pressures up to 1200 MPa, including derivatives and Debye-Hückel coefficients[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1997, 26(4):1125~1166. doi: 10.1063/1.555997 [15] Scatchard G. Excess free energy and related properties of solutions containing electrolytes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1968, 90(12):3124~3127. doi: 10.1021/ja01014a027 [16] Pitzer K S, Mayorga G. Thermodynamics of electrolytes. Ⅱ. activity and osmotic coefficients for strong electrolytes with One or both ions univalent[J]. Pitzer, 1973, 77(19):2300~2308. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ026170697/ [17] Pitzer K S, Mayorga G. Thermodynamics of electrolytes. Ⅲ. activity and osmotic coefficients for 2~2 electrolytes[J]. Journal of Solution Chemistry, 1974, 3(7):539~546. doi: 10.1007/BF00648138 [18] Hamer W J, Wu Y C. Osmotic coefficients and mean activity coefficients of uni-univalent electrolytes in water at 25℃[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1972, 1(4):1047~1099. doi: 10.1063/1.3253108 [19] Clarke E C W, Glew D N. Evaluation of the thermodynamic functions for aqueous sodium chloride from equilibrium and calorimetric measurements below 154℃[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1985, 14(2):489~610. doi: 10.1063/1.555730 [20] Guendouzi M E L, Mounir A, Dinane A. Water activity, osmotic and activity coefficients of aqueous solutions of Li2SO4, Na2SO4, K2SO4, (NH4)2SO4, MgSO4, MnSO4, NiSO4, CuSO4, and ZnSO4 at T=298.15 K[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2003, 35(2):209~220. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9614(02)00315-4 [21] Castellanos E, Villar M V, Romero E, et al. Chemical impact on the hydro-mechanical behaviour of high-density FEBEX bentonite[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 2008, 33(S1):S516-S526. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223791226_Chemical_impact_on_the_hydro-mechanical_behavior_of_high-density_FEBEX_bentonite [22] Pitzer K S, Kim J J. Thermodynamics of electrolytes. Ⅳ. Activity and osmotic coefficients for mixed electrolytes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1974, 96(18):5701~5707. doi: 10.1021/ja00825a004 [23] Dinane A, El Guendouzi M, Mounir A. Hygrometric determination of water activities, osmotic and activity coefficients of (NaCl+KCl)(aq) at T=298.15 K[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2002, 34(4):423~441. doi: 10.1006/jcht.2001.0845 -





 下载:
下载: