APPLICATION OF INSULATION BOARD IN ROAD ENGINEERING IN PERMAFROST REGIONS OF INNER MONGOLIA
-
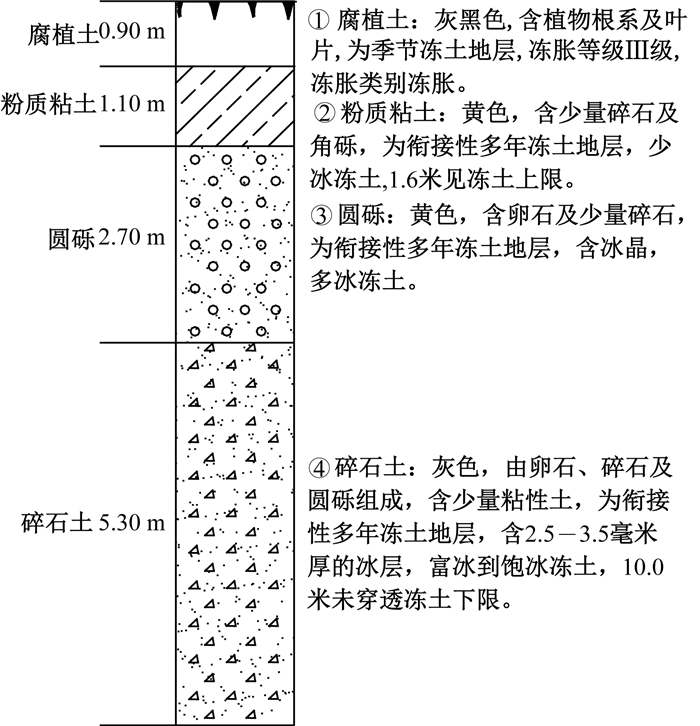
摘要: 根据博—牙高速沿线气象工程地质资料、观测资料、设计资料,借助有限元软件构建了路基温度场数值计算模型,着重对不同路基填筑高度条件下XPS板对温度场的影响进行了研究。研究发现:路基填筑高度的增加和XPS保温板的应用对冻土都起到了积极的保护作用,相同路堤填筑高度下,道路运营到第20年时,XPS保温板路基多年冻土温度比碎石路基降低了约0.19℃;XPS保温板的存在使得冻土上限上移更加明显,相同路基高度下,冻土上限平均抬升量约为1.23 m,在规范规定年限内,XPS保温板路基的冻土上限均位于换填碎石中;但XPS保温板的存在加剧了阴阳坡效应的发展,综合考虑,在本段落若采用碎石路堤建议路堤高度应保持在3 m以上;若采用XPS保温板路基,建议路堤高度不超过2 m。Abstract: Based on the meteorological engineering geological data, observation data and design data along the Bo-Ya expressway, a numerical calculation model of the roadbed temperature field was constructed by means of finite element software, and the influence of XPS insulation board on temperature field under different subgrade filling height was studied emphatically. The results show that, the increase of the subgrade height and the application of XPS insulation board both play a positive role in protecting permafrost. With the same embankment filling height, the temperature of permafrost of the subgrade with XPS insulation board reduces by about 0.19℃ than that of the subgrade with crushed rocks when the road runs to its twentieth years. XPS insulation board makes the upper limit of permafrost obviously raised, and the average uplift of the upper limit of permafrost is about 1.23 m under the same subgrade height. The upper limit of permafrost of subgrade with XPS insulation board is located in the replaced crushed rocks during the specified years of the designing code. However; the application of XPS insulation board aggravates the development of sunny-shady slope effect, the subgrade height with crushed rock should be kept above 3 m, and the subgrade height with XPS insulation board should be kept no more than 2 m.
-
Key words:
- road engineering /
- permafrost /
- XPS insulation board /
- numerical simulation /
- temperature field
-
表 1 材料热参数
Table 1. Thermal parameters of subgrade and pavement materials
结构层 密度ρ/(kg/m3) 融土比热Cu/(J/(kg·℃)) 冻土比热Cf/(J/(kg·℃)) 融土导热系数λu/(W/(m·℃)) 冻土导热系数λf/(W/(m·℃)) 沥青路面 2358 1680 1680 1.05 1.05 水稳碎石 2277 920 920 1.5 1.5 水稳砂砾 2233 920 920 2.04 2.04 砂垫层 1500 1010 1010 0.58 0.58 路堤碎石 1900 1730 1580 1.06 1.6 换填碎石 1900 1730 1580 1.06 1.6 XPS保温板 45 5346 5346 0.029 0.029 泥炭土 800 3814 2425 0.8 1.55 季冻土 1600 2208 1900 0.77 1.12 冻土 1900 1800 1600 0.93 1.16 表 2 路基土焓值
Table 2. Enthalpy of subgrade soil
温度/(℃) -10 -5 -2 -1 -0.5 0 15 泥炭土 wu/% 3 4.5 7.3 10.7 16.2 50 50 H/(MJ/m3) 19.40 23.41 30.91 31.82 46.53 136.98 182.75 季冻土 wu/% 2.7 4.18 7.46 11.6 13.8 22 22 H/(MJ/m3) 30.40 38.32 55.88 78.03 89.81 133.69 204.35 多年冻土 wu/% 0.29 0.45 0.78 1.19 1.82 10 10 H/(MJ/m3) 30.4 39.28 45.99 49.93 54.31 101.53 132.46 表 3 太阳日辐射总量和长波有效辐射量
Table 3. Total daily solar radiation and long wave effective radiation
月份 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 太阳日总辐射量Q/(MJ/m2·d) 4.17 7.17 13.67 16.67 19.5 20.83 19.5 17.0 10.93 6.67 3.67 2.83 有效辐射F/(MJ/m2·d) 2.67 3.33 4.17 3.00 3.00 3.00 2.83 3.00 2.67 2.67 2.33 1.53 表 4 坡面系数取值
Table 4. Slope coefficient
月份 北偏西 阳坡 阴坡 1 1.61 0.3 2 1.43 0.39 3 1.24 0.5 4 1.07 0.68 5 0.93 0.78 6 0.9 0.81 7 0.93 0.78 8 1.07 0.68 9 1.24 0.5 10 1.43 0.39 11 1.61 0.3 12 1.72 0.28 表 5 博克石地区月蒸发量
Table 5. Monthly evaporation in Bokeshi
月份 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 蒸发量/mm 10.1 22.6 60.0 145.8 246.2 184.7 166.6 130.6 117.4 73.7 24.5 9.3 表 6 不同高度碎石路堤多年冻土温度
Table 6. Permafrost temperature for crushed rock subgrade with different heights
多年冻土温度/℃ 1a 5a 10a 15a 20a 碎石路堤-1 m -3.05 -1.38 -0.91 -0.71 -0.55 碎石路堤-2 m -3.07 -1.46 -0.96 -0.78 -0.63 碎石路堤-3 m -3.11 -1.54 -1.02 -0.84 -0.70 碎石路堤-4 m -3.13 -1.61 -1.09 -0.89 -0.76 表 7 不同高度XPS保温板路基多年冻土温度
Table 7. Permafrost temperature for subgrade with XPS insulation board with different heights
多年冻土温度/℃ 1a 5a 10a 15a 20a XPS路堤-1 m -3.10 -1.61 -1.07 -0.88 -0.73 XPS路堤-2 m -3.13 -1.69 -1.16 -0.94 -0.81 XPS路堤-3 m -3.14 -1.76 -1.25 -1.00 -0.87 XPS路堤-4 m -3.13 -1.82 -1.33 -1.06 -0.93 -
[1] 宇德忠, 程培峰, 季成, 等.岛状多年冻土地区桥梁桩基回冻后承载力的静载与动测对比试验研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(S1):2845~2853. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=YSLX2015S1031&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQYU Dezhong, CHENG Peifeng, JI Chen, et al. Static and dynamic contrast test for bearing capacity of refrozen bridge pile foundation in patchy permafrost regions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(S1):2845~2853. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=YSLX2015S1031&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [2] 孙志忠, 马巍, 党海明, 等.青藏铁路多年冻土区路基变形特征及其来源[J].岩土力学, 2013, 34(9):2667~2671. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201309036SUN Zhizhong, MA Wei, DANG Haiming, et al. Characteristics and causes of embankment deformation for Qinghai-Tibet Railway in permafrost regions[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(9):2267~2671. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201309036 [3] 黄仁达, 李丽, 吴会军, 等.夏热冬冷地区不同墙体结构的保温层厚度分析[J].硅酸盐通报, 2018, 37(6):1829~1835. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gsytb201806004HUANG Renda, LI Li, WU Huijun, et al. Analysis on thermal insulation thickness of different wall structures in hot summer and cold winter zone[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2018, 37(6):1829~1835. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gsytb201806004 [4] 盛煜, 张鲁新, 杨成松, 等.保温处理措施在多年冻土区道路工程中的应用[J].冰川冻土, 2002, 24(5):618~622. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2002.05.025SHENG Yu, ZHANG Luxin, YANG Chengsong, et al. Application of thermal-insulation treatment to roadway engineering in permafrost regions[J]. Journal of Glaciolgy and Geocryology, 2002, 24(5):618~622. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2002.05.025 [5] Wen Z, Sheng Y, Ma W, et al. Evaluation of EPS application to embankment of Qinghai-Tibetan railway[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2005, 41(3):235~247. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2004.11.001 [6] Tai B W, Liu J K, Fang J H, et al. Calculation model of permafrost table of XPS insulated board subgrade in warm permafrost regions[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 37(4):1~11. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xagljtdx201704001 [7] 董元宏, 朱东鹏, 张会建, 等.应用于冻土路基的XPS保温板力学性能[J].中国公路学报, 2015, 28(12):64~68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2015.12.009DONG Yuanhong, ZHU Dongpeng, ZHANG Huijian, et al. Mechanical properties of XPS thermal insulation board applied in permafrost embankment[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2015, 28(12):64~68. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2015.12.009 [8] Johansen N I, Lynch D F, Sengupta M. Notes on Norwegian arctic road construction techniques[J]. Northern Engineer, 1988, 20(1):26~29. [9] Li D Q, Wu Z W, Fang J H, et al. Heat stability analysis of embankment on the degrading permafrost district in the East of the Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 1998, 28(3):183~188. doi: 10.1016/S0165-232X(98)00018-4 [10] 盛煜, 温智, 马巍.青藏铁路北麓河试验段路基保温材料处理措施初步分析[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2003, 22(S2):2659~2663. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb2003z2025SHENG Yu, WEN Zhi, MA Wei. Preliminary analysis on insulation treatment of embankment at Beiluhe test section of Qinghai-Tibet railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 22(S2):2659~2663. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb2003z2025 [11] 温智, 盛煜, 马巍, 等.保温法保护多年冻土的长期效果分析[J].冰川冻土, 2006, 28(5):760~765. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2006.05.020WEN Zhi, SHENG Yu, MA Wei, et al. Long-term effect of insulation on permafrost on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2006, 28(5):760~765. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2006.05.020 [12] 邰博文, 刘建坤, 房建宏, 等.高温冻土区高速公路特殊结构路基地温分布特征及降温效果分析[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(S1):3696~3704. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20172017062100239255TAI Bowen, LIU Jiankun, FANG Jianhong, et al. Analysis on distribution characteristics of ground temperature and cooling effect of special-structured subgrade of the expressway in warm permafrost region[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(S1):3696~3704. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20172017062100239255 [13] Liu J K, Tian Y H. Numerical studies for the thermal regime of a roadbed with insulation on permafrost[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2002, 35(1):1~13. doi: 10.1016/S0165-232X(02)00028-9 [14] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. JGJ118~2011冻土地区建筑地基基础设计规范[S].北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012.People's Republic of China Ministry of Housing and Urban Rural Development. JGJ118~2011 Code for design of soil and foundation of buildings in frozen soil region[S]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2012. (in Chinese) [15] 徐斅祖, 王家澄, 张立新.冻土物理学[M].北京:科学出版社, 2010.XU Xuezu, WANG Jiacheng, ZHANG Lixin. Permafrost physics[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2010. (in Chinese) [16] 季国良, 时兴和, 高务祥.藏北高原地面加热场的变化及其对气候的影响[J].高原气象, 2001, 20(3):239~244. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0534.2001.03.003JI Guoliang, SHI Xinghe, GAO Wuxiang. The variation of surface heating field over northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its effect on climate[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2001, 20(3):239~244. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0534.2001.03.003 [17] 李双洋, 张明义, 张淑娟, 等.列车荷载下青藏铁路冻土路基动力响应分析[J].冰川冻土, 2008, 30(5):860~867. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bcdt200805020LI Shuangyang, ZHANG Mingyi, ZHANG Shujuan, et al. Analysis of the dynamic response of Qinghai-Tibetan railway embankment in permafrost regions under train load[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2008, 30(5):860~867. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bcdt200805020 -





 下载:
下载: