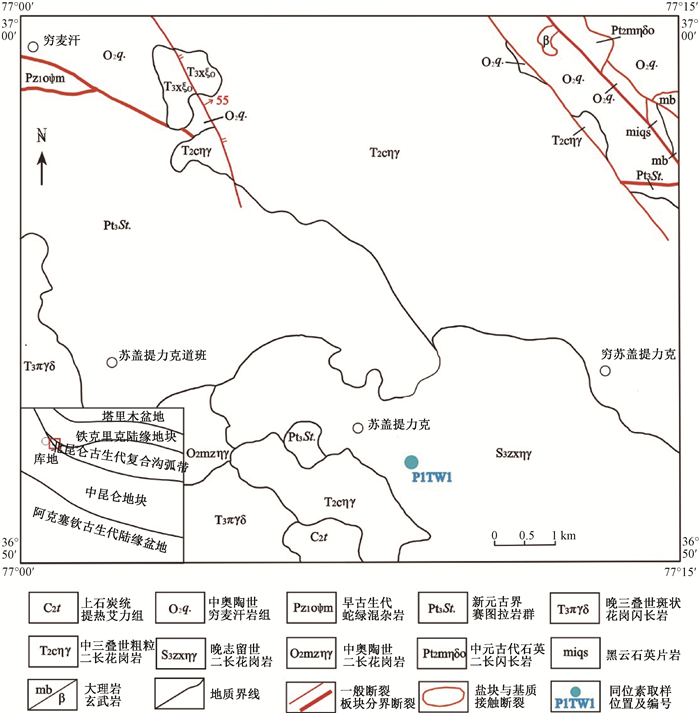
ZIRCON U-Pb AGES AND GEOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SUGAITILIKE LATE SILURIAN GRANITES IN SOUTHERN KUDI, XINJIANG AND ITS GEOTECTONIC SIGNIFICANCE
-
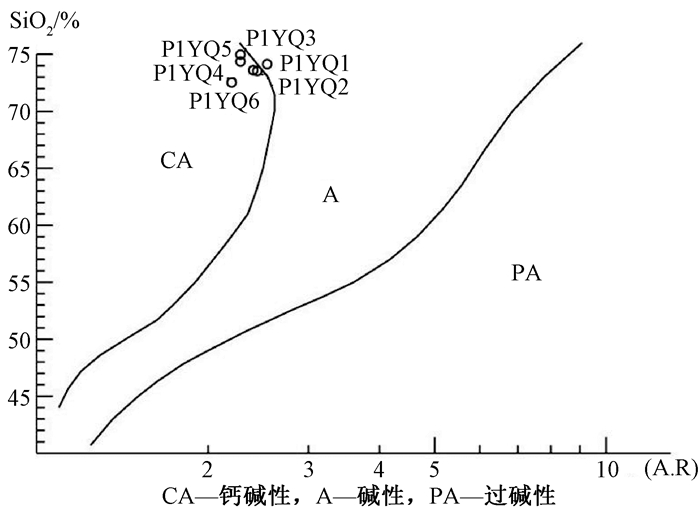
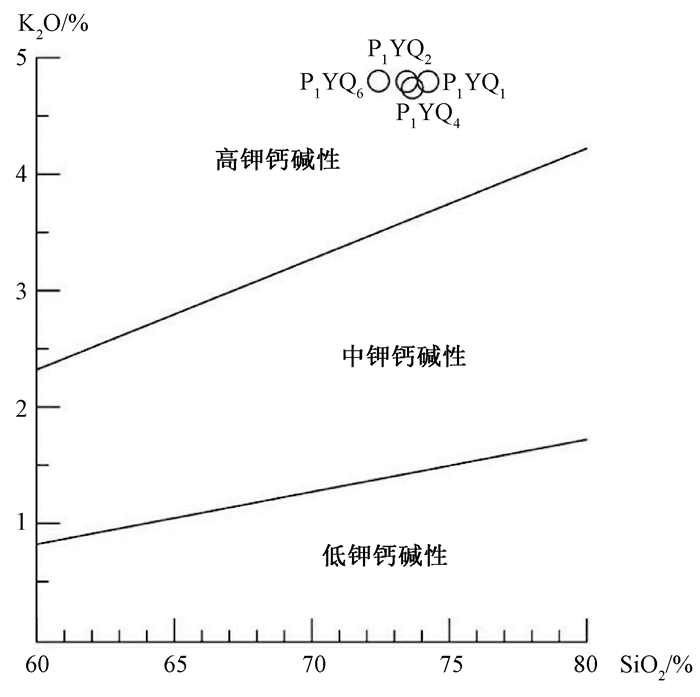
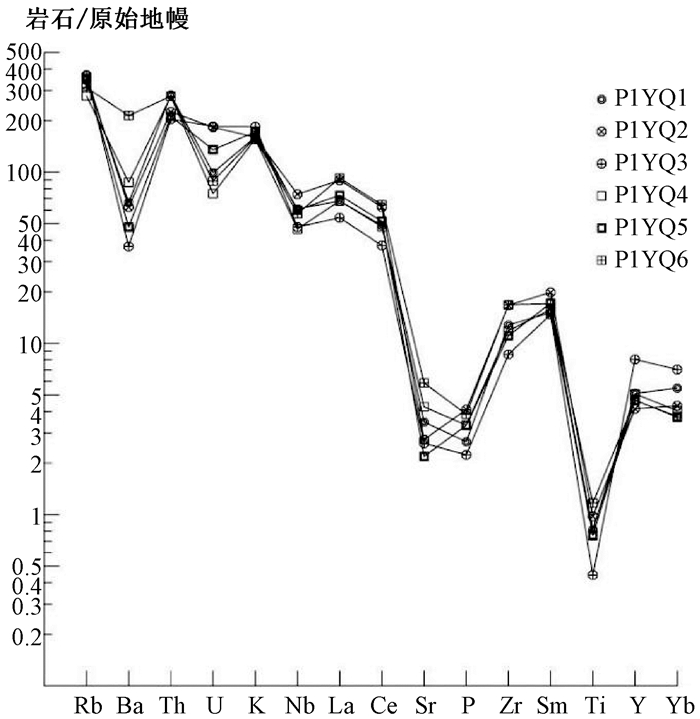
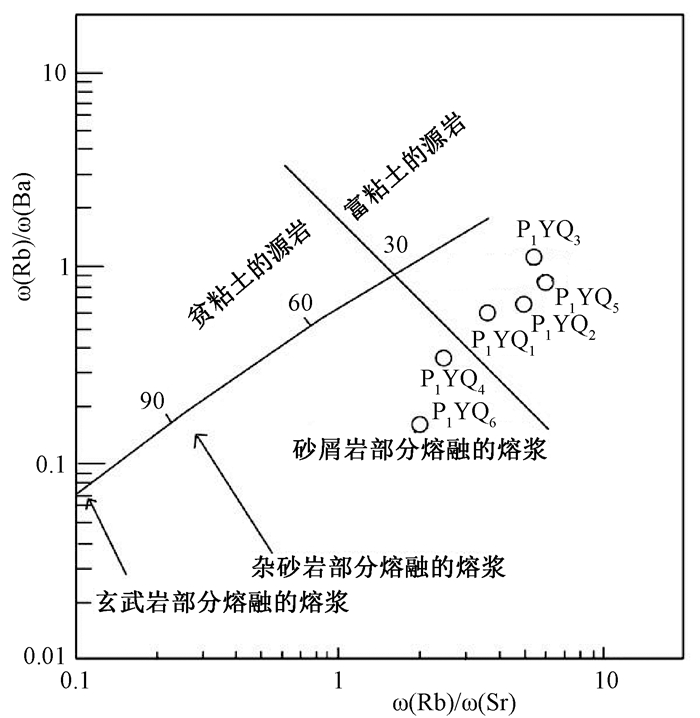
摘要: 西昆仑地区早古生代原特提斯洋的后碰撞阶段划分存在分歧,通过对库地蛇绿岩南侧苏盖提力克花岗岩开展区域地质调查、岩石学、地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学等方面研究,从而为原特提斯洋构造演化及闭合时限提供地质依据。研究表明,苏盖提力克花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄(LA-ICP-MS)为(422.5±2.5)Ma,属于晚志留世岩浆活动产物。苏盖提力克花岗岩含有典型矿物白云母,A/CNK=1.07~1.11,刚玉分子含量为1.07%~1.56%,属于S型花岗岩。地球化学上,该岩体富硅、碱,贫钙、镁,富K、Rb、Nb、Th,贫Sr、Ti、P,Rb/Sr比值高;结合区域地质背景及地球化学特征综合分析表明,苏盖提力克花岗岩是原特提斯洋闭合后碰撞阶段的产物,因而晚志留世是原特提斯洋由消减闭合到陆陆碰撞—碰撞后伸展转换时期。Abstract: There are different opinions about the division of post-collisional stages of the Early Paleozoic Proto-Tethys Ocean in the West Kunlun area. In this paper, researches including regional geological survey, petrology, geochemistry, zircon U-Pb chronology, etc. were carried out on Sugaitilike granites, south side of Kudi ophiolite, which provide a geological basis for the tectonic evolution and closing time limit of the Proto-Tethys Ocean. The results show that, the age of zircon U-Pb(LA-ICP-MS) is 422.5±2.5 Ma, making granites products of the late Silurian magma activities. Sugaitilike granite contains typical mineral muscovite, A/CNK=1.07~1.11, and the content of corundum is 1.07~1.56%, belonging to S-type granite. Geochemically, the rock body is rich in silicon, alkali, calcium-depleted, magnesium-rich, rich in K, Rb, Nb, Th, lean in Sr, Ti, P, and high in Rb/Sr ratio. The comprehensive analysis of the geological background and geochemical characteristics of the Sugeitik granite area shows that granites are the products of the collision phase of the Proto-Tethys Ocean. Therefore, the late Silurian is the transition period from the closing of the Proto-Tethys Ocean to the collision of land and land-the period of post-collisional extension transformation.
-
Key words:
- west Kunlun area /
- Proto-Tethys Ocean /
- zircon U-Pb age /
- Late Silurian granite /
- S-type granite
-
表 1 二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb分析结果
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data of monzonite granite
样品号 含量/×10-6 同位素比值 年龄/Ma P1TW1 Pb U 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 232Th/238U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ P1TW1.1 18 247 0.0686 0.0005 0.5196 0.0096 0.0549 0.0010 0.0211 0.0002 0.6024 0.0032 427 3 425 8 410 39 P1TW1.2 90 1380 0.0694 0.0004 0.5285 0.0044 0.0553 0.0004 0.0204 0.0002 0.0922 0.0007 432 2 431 4 423 17 P1TW1.3 15 204 0.0691 0.0004 0.5201 0.0110 0.0546 0.0011 0.0192 0.0001 0.7381 0.0025 431 3 425 9 395 46 P1TW1.4 42 631 0.0687 0.0004 0.5205 0.0049 0.0550 0.0005 0.0198 0.0001 0.2140 0.0012 428 3 425 4 411 20 P1TW1.5 23 321 0.0686 0.0004 0.5360 0.0068 0.0566 0.0007 0.0197 0.0001 0.5574 0.0022 428 3 436 6 477 26 P1TW1.6 21 274 0.0687 0.0004 0.5333 0.0075 0.0563 0.0008 0.0199 0.0001 0.7047 0.0062 428 3 434 6 464 30 P1TW1.7 23 340 0.0682 0.0005 0.5264 0.0070 0.0560 0.0007 0.0201 0.0001 0.3738 0.0055 425 3 429 6 452 27 P1TW1.8 38 313 0.1244 0.0008 1.1077 0.0103 0.0646 0.0005 0.0385 0.0003 0.1954 0.0016 756 5 757 7 761 18 P1TW1.9 9 136 0.0633 0.0006 0.4739 0.0245 0.0542 0.0027 0.0219 0.0005 0.5397 0.0022 396 4 394 20 379 114 P1TW1.10 24 342 0.0671 0.0005 0.5157 0.0074 0.0557 0.0007 0.0224 0.0001 0.4178 0.0019 419 3 422 6 439 29 P1TW1.11 19 276 0.0666 0.0004 0.5077 0.0094 0.0553 0.0010 0.0232 0.0002 0.4425 0.0016 416 3 417 8 424 39 P1TW1.12 43 357 0.1230 0.0009 1.0890 0.0104 0.0642 0.0005 0.0393 0.0002 0.2244 0.0029 748 5 748 7 748 18 P1TW1.13 43 576 0.0676 0.0005 0.5270 0.0052 0.0566 0.0005 0.0199 0.0001 0.7179 0.0040 421 3 430 4 475 20 P1TW1.14 34 402 0.0664 0.0004 0.5257 0.0062 0.0574 0.0006 0.0206 0.0002 1.2851 0.1485 414 2 429 5 508 25 P1TW1.15 35 481 0.0670 0.0005 0.5238 0.0058 0.0567 0.0006 0.0195 0.0001 0.7089 0.0039 418 3 428 5 482 23 P1TW1.16 40 570 0.0669 0.0005 0.5219 0.0051 0.0566 0.0005 0.0199 0.0001 0.5597 0.0052 417 3 426 4 476 20 P1TW1.17 26 326 0.0670 0.0004 0.5514 0.0084 0.0596 0.0009 0.0202 0.0001 1.0436 0.0036 418 3 446 7 590 31 P1TW1.18 22 270 0.0681 0.0005 0.5311 0.0076 0.0566 0.0008 0.0216 0.0001 0.9443 0.0093 425 3 433 6 474 30 P1TW1.19 24 340 0.0676 0.0004 0.5281 0.0076 0.0567 0.0008 0.0211 0.0001 0.4940 0.0028 422 3 431 6 478 30 P1TW1.20 16 215 0.0675 0.0004 0.5278 0.0101 0.0567 0.0011 0.0196 0.0001 0.8569 0.0048 421 3 430 8 481 41 P1TW1.21 13 357 0.0351 0.0002 0.2554 0.0061 0.0528 0.0012 0.0115 0.0001 0.4664 0.0062 222 1 231 5 321 53 P1TW1.22 29 416 0.0672 0.0004 0.5150 0.0063 0.0556 0.0006 0.0225 0.0001 0.3992 0.0214 419 2 422 5 437 26 P1TW1.23 29 388 0.0671 0.0004 0.5312 0.0072 0.0575 0.0007 0.0208 0.0002 0.6723 0.0297 418 2 433 6 509 29 P1TW1.24 13 184 0.0670 0.0005 0.5380 0.0106 0.0583 0.0011 0.0196 0.0002 0.5327 0.0020 418 3 437 9 540 43 P1TW1.25 31 437 0.0683 0.0004 0.5208 0.0070 0.0553 0.0007 0.0190 0.0002 0.5053 0.0065 426 2 426 6 425 29 表 2 苏盖提力克花岗岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(×10-6)及相关参数
Table 2. Major elements (%) and trace elements (%) in sugaitlike granites and related parameters
样号 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 Los La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu P1YQ1 74.14 0.21 13.91 0.29 0.91 0.04 0.27 1.26 3.3 4.87 0.055 0.67 48.17 92.74 10.23 34.05 5.82 0.76 P1YQ2 73.53 0.25 14.08 0.84 0.57 0.028 0.23 1.29 3.22 4.86 0.085 0.93 63.76 118.7 13.12 43.92 7.64 0.86 P1YQ3 74.97 0.11 13.89 0.41 0.41 0.021 0.15 0.89 2.89 5.59 0.046 0.59 38.47 70.86 7.88 27.07 5.67 0.59 P1YQ4 73.61 0.19 14.09 0.32 1.08 0.035 0.35 1.35 3.18 4.74 0.069 0.9 48.23 91.21 9.95 33.12 6.08 0.7 P1YQ5 74.37 0.19 13.6 0.45 0.84 0.032 0.25 1.07 2.86 5.21 0.069 0.95 52.03 98.09 10.72 36.21 6.61 0.7 P1YQ6 72.53 0.3 14.23 0.49 1.34 0.038 0.48 1.73 3 4.82 0.08 0.85 65.54 122.4 12.67 41.38 6.56 0.93 样号 Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y Rb Sr Ba Ga Nb Ta Zr Hf Th P1YQ1 4.96 0.84 4.72 0.9 2.52 0.46 3.02 0.35 24.87 300.8 79.9 502.3 17.17 37.81 5.38 140.9 3.98 27.06 P1YQ2 6.2 0.91 4.25 0.73 1.95 0.3 2.38 0.28 20.21 313.8 63.2 472.7 20.15 46.07 4.85 183.8 5.16 21.61 P1YQ3 5.06 1.01 6.18 1.26 3.53 0.66 3.87 0.46 39.28 317.5 60.1 278.4 16.26 29.61 3.78 94.9 2.87 19.58 P1YQ4 5.01 0.82 4.32 0.82 2.23 0.38 2.22 0.29 24.72 240 98.1 658.9 17.75 28.87 3.9 130.5 3.26 26.6 P1YQ5 5.32 0.83 4.2 0.76 2.02 0.34 2.06 0.24 22.6 302.3 50.3 361.1 18.39 37.2 5.43 121.9 2.86 20.32 P1YQ6 5.47 0.77 4.02 0.78 2.13 0.36 2.04 0.23 22.69 268.2 135.1 1618 17.54 35.46 3.38 184.9 5.21 26.67 样号 V Cr Sc U AR K2O/Na2O A/CNK C Mg# ∑REE (La/Yb)N δEu (La/Sm)N (Gd/Yb)N (Ho/Yb)N Rb/Sr Rb/Ba Y/Yb P1YQ1 8.9 3.5 3.86 2.68 2.54 1.48 1.07 1.07 29 209.53 10.77 0.42 5.2 1.33 0.87 3.77 0.6 8.24 P1YQ2 14.7 4.9 3.4 4.94 2.44 1.51 1.09 1.39 25 265.04 18.07 0.37 5.25 2.1 0.9 4.97 0.66 8.5 P1YQ3 4.4 4.4 2.76 5 2.28 1.93 1.11 1.56 25 172.56 6.7 0.33 4.27 1.05 0.95 5.29 1.14 10.15 P1YQ4 11.7 5.3 3.47 2.02 2.4 1.49 1.1 1.42 32 205.37 14.64 0.38 4.99 1.82 1.07 2.45 0.36 11.12 P1YQ5 8.2 4.7 2.96 3.66 2.28 1.82 1.11 1.46 25 220.13 17.02 0.35 4.95 2.08 1.07 6.01 0.84 10.96 P1YQ6 20.3 5 3.77 2.39 2.2 1.61 1.08 1.1 32 265.27 21.66 0.46 6.29 2.16 1.12 1.99 0.17 11.12 -
[1] 王元龙, 李向东, 毕华, 等.西昆仑库地北构造带两侧地质特征对比及其大地构造意义[J].地球化学, 1997(2):53~59. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700063263WANG Yuanlong, LI Xiangdong, BI Hua, et al. Geological characteristics of northern Kudi structure belt, Western Kunlun and their geotectonic implications[J]. Geochemistry, 1997(2):53~59. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700063263 [2] 周辉, 李继亮.西昆仑库地煌斑岩的年代学及地球化学特征[J].岩石学报, 2000, 16(3):380~384. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200003010ZHOU Hui, LI Jiliang. Age and geochemical features of lamprophyres in Kuda, western Kunlun[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2000, 16(3):380~384. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200003010 [3] 肖序常, 王军, 苏犁, 等.再论西昆仑库地蛇绿岩及其构造意义[J].地质通报, 2003, 22(10):745~750. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.10.001XIAO Xuchang, WANG Jun, SU Li, et al. A further discussion of the Kuda ophiolite, West Kunlun, and its tectonic significance[J]. Regional Geology of China, 2003, 22(10):745~750. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.10.001 [4] 郝杰, 刘小汉, 方爱民, 等.西昆仑"库地蛇绿岩"的解体及有关问题的讨论[J].自然科学进展, 2003, 13(10):1116~1120. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2003.10.021HAO Jie, LIU Xiaohan, FANG Aimin, et al. Discussion on the disintegration of Kudu Ophiolitic rock in west Kunlun and discussion of related problems[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2003, 13(10):1116~1120. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2003.10.021 [5] 袁超, 孙敏, 李继亮, 等.西昆仑库地蛇绿岩的构造背景:来自玻安岩系岩石的新证据[J].地球化学, 2002, 31(1):43~48. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx200201007YUAN Chao, SUN Min, LI Jiliang, et al. Tectonic background of the Kü da ophiolite, western Kunlun:New constraints from boninite series rocks[J]. Geochemistry, 2002, 31(1):43~48. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx200201007 [6] 崔建堂, 王炬川, 边小卫, 等.西昆仑康西瓦北侧早古生代角闪闪长岩、英云闪长岩的地质特征及其锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(12):1441~1449. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.12.013CUI Jiantang, WANG Juchuan, BIAN Xiaowei, et al. Geological characteristics of Early Paleozoic amphibolite and tonalite in northern Kangxiwar, West Kunlun, China and their zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(12):1441~1449. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.12.013 [7] 黄建国, 杨瑞东, 杨剑, 等.西昆仑北缘库斯拉甫一带寒武纪中酸性岩浆活动及地质意义[J].地球化学, 2013, 42(5):454~466. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201305006HUANG Jianguo, YANG Ruidong, YANG Jian, et al. Cambrian intermediate-acid magmatic activity and its geological significance in the Kusilafu region at the north margin of the Western Kunlun[J]. Geochimica, 2013, 42(5):454~466. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201305006 [8] 高晓峰, 校培喜, 康磊, 等.西昆仑大同西岩体成因:矿物学、地球化学和锆石U-Pb年代学制约[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(9):3065~3079. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201602011GAO Xiaofeng, XIAO Peixi, KANG Lei, et al. Origin of Datongxi pluton in the West Kunlun orogen:Constraints from mineralogy, elemental geochemistry and zircon U-Pb age[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(9):3065~3079. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201602011 [9] 王超, 刘良, 何世平, 等.西昆仑早古生代岩浆作用过程:布隆花岗岩地球化学和锆石U-Pb-Hf同位素组成研究[J].地质科学, 2013, 48(4):997~1014. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2013.04.004WANG Chao, LIU Liang, HE Shiping, et al. Early Paleozoic magmatism in west Kunlun:Constraints from geochemical and zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopic studies of the Bulong granite[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2013, 48(4):997~1014. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2013.04.004 [10] 黄朝阳, 王核, 刘建平, 等.西昆仑柯岗蛇绿岩地质地球化学特征及构造意义[J].地球化学, 2014, 43(6):592~601. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201406004HUANG Chaoyang, WANG He, LIU Jianping, et al. Geological, geochemical features and structure significance of Kegang ophiolite, West Kunlun[J]. Geochimica, 2014, 43(6):592~601. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201406004 [11] 班长勇, 专少鹏, 白春东, 等.新疆库地东一带1: 50000区域地质调查报告[R].内蒙古自治区第九地质矿产勘查开发院, 2014.BAN Changyong, ZHUAN Shaopeng, BAI Chundong, et al. Geological survey report of 1: 50000 in the east of kudi, xinjiang[R]. The 9th institute of geological and mineral exploration and development, Inner Mongolia autonomous region, 2014. (in Chinese) [12] 耿建珍, 张健, 李怀坤, 等. 10μm尺度锆石U-Pb年龄的LA-MC-ICP-MS测定[J].地球学报, 2012, 33(6):877~884. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201206007GENG Jianzhen, ZHANG Jian, LI Huaikun, et al. Ten-micron-sized Zircon U-Pb Dating Using LA-MC-ICP-MS[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2012, 33(6):877~884. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201206007 [13] 王文龙, 滕学建, 刘洋, 等.内蒙古狼山乌和尔图花岗岩岩体锆石U-Pb年代学及地球化学特征[J].地质力学学报, 2017, 23(3):. 382~396. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.03.006WANG Wenlong, TENG Xuejian, LIU Yang, et al. Zircon U-Pb chronology and geochemical characteristics of the Wuheertu granite mass in Langshan, inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 23(3):382~396. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.03.006 [14] 张耀玲, 沈燕绪, 吴珍汉, 等.西藏改则地区美苏组岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J].地质力学学报, 2018, 24(1):. 128~136 http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180114&journal_id=dzlxxbZHANG Yaoling, SHEN Yanxu, WU Zhenhan, et al. Zircon U-Pb ages of magmatic rocks from Meisu formation in Gerze area in Tibet and its geological significance[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2018, 24(1):128~136. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180114&journal_id=dzlxxb [15] 邓晋福, 罗照华, 苏尚国, 等著.岩石成因、构造环境与成矿作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 2004.DENG Jinfu, LUO Zhaohua, SU Shangguo, et al. Rock Formation, Tectonic Environment and Mineralization[M]. Beijing:Geological Pulishing House, 2004. (in Chinese) [16] Peccerillo A, Taylor A R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1):63~81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745 [17] Boynton W V. Geochemistry of rate-earth elements: Meteorite studies[A]. Henderson P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry[C]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984, 63~114 [18] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[A]. Saunders A D, Norry MJ. Magmatism in Ocean Basins[M]. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1989, 42(1): 313~345. [19] 廖忠礼, 莫宣学, 潘桂堂, 等.西藏过铝花岗岩副矿物特征及岩石成因意义[J].地球学报, 2006, 27(2):115~122. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.02.003LIAO Zhongli, MO Xuanxue, PAN Guitang, et al. Characteristics of the accessory minerals from the Peraluminous granites in Tibet and their implications[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2006, 27(2):115~122. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.02.003 [20] 王德滋, 刘昌实, 沈渭洲, 等.桐庐I型和相山S型两类碎斑熔岩对比[J].岩石学报, 1993, 9(1):44~54. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1993.01.005WANG Dezi, LIU Changshi, SHEN Weizhou, et al. The contrast between Tonglu Ⅰ-type and Xiangshan S-type Clastoporphyritic lava[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1993, 9(1):44~54. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1993.01.005 [21] Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The continental crust:its composition and evolution:An examination of the geochemical record preserved in sedimentary rocks[M]. Oxford:Blackwell Science, 1985. [22] 肖庆辉, 邓晋福, 马大铨, 等.花岗岩研究思维与方法[M].北京:地质出版社, 2002.XIAO Qinghui, DENG Jinfu, MA Daquan, et al. The ways of investigation on granitoids[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2002. (in Chinese) [23] Sylvester P J. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1~4):29~44. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00024-3 [24] 计文化, 尹宗义, 李博秦, 等.麻扎-神仙湾1: 25万区域地质调查报告[R].陕西省地质调查院, 2004.JI Wengua, YIN Zongyi, LI Boqin, et al. Regional geological survey report of 10: 250, 000 people in shaza-shenxianwan[R]. Geological Survey Institute of Shanxi Province, 2004. (in Chinese) [25] Pitcher W S. The nature and origin of granite[M]. London:Blackie Academic and Professional Press, 1993, 321 [26] Bellieni G, Cavazzini G, Fioreti A M, et al. The Cima di vila (Zinsnock) Intrusion, Eastern Alps:evidence for crustal melting, acid-mafic magma mingling and Wall-rock fluid effects[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 1996, 56(1~2):125~146 doi: 10.1007/BF01162660 [27] Searle M P, Parrish R R, Hodges K V, et al. Shisha Pangma leucogranite, South Tibetan Himalaya:field relations, Geochemistry, Age, Origin, and emplacement[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1997, 105(3):295~317. doi: 10.1086/515924 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 杨少航,罗良,马诗杰,薛萌,曾联波,聂舟,犹钰玲,周杨帆. 川南长宁地区构造变形特征及对页岩气保存条件的影响. 现代地质. 2024(06): 1458-1472 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 聂舟,马诗杰,伍秋姿,田鹤,吕文雅,曾联波,罗良. 长宁地区海相页岩天然裂缝发育特征及其对含气性的影响. 断块油气田. 2022(05): 591-597 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(2)
-





 下载:
下载:




 百度学术
百度学术
