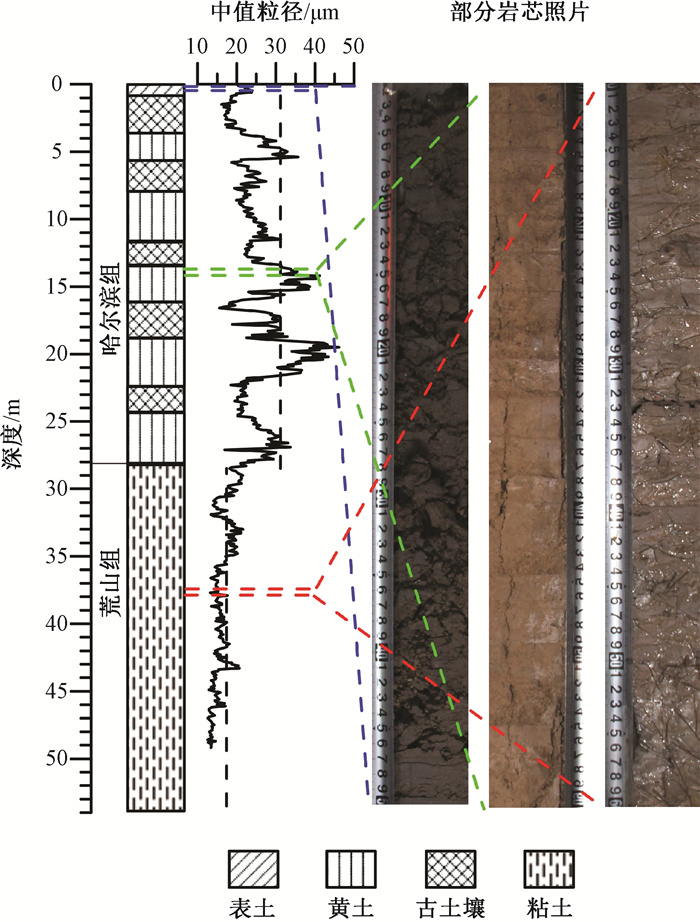
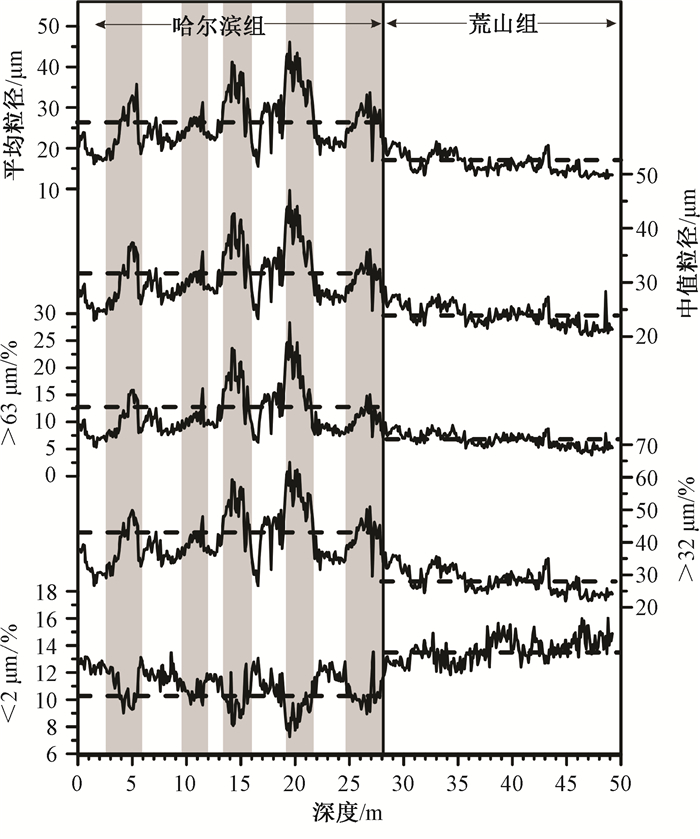
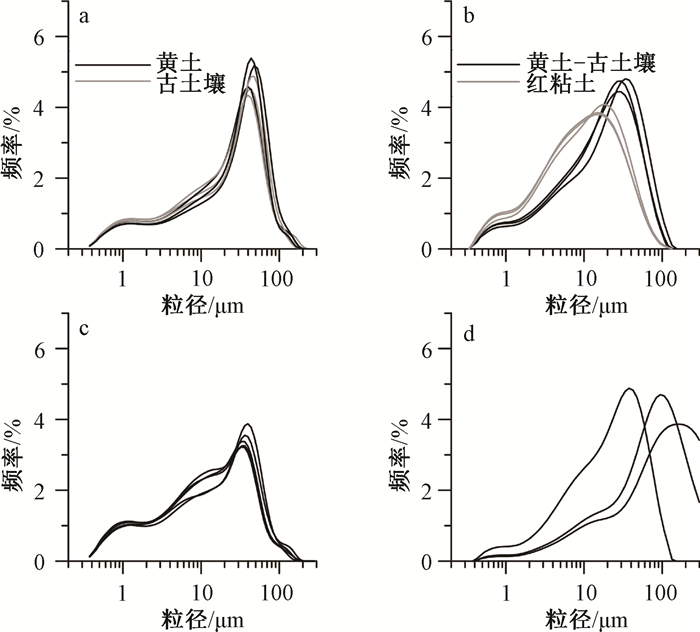
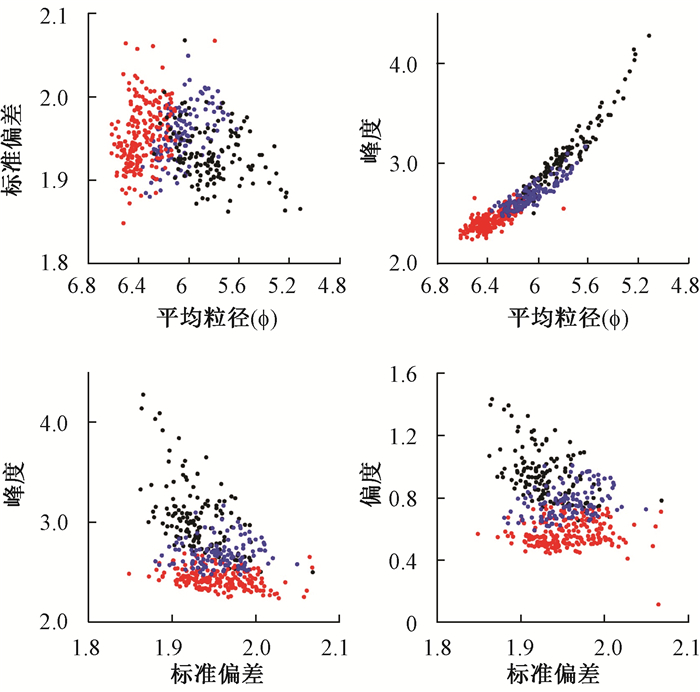
| [1] |
吴锡浩, 浦庆余, 钱方, 等.松辽平原第四纪磁性地层的初步研究[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1984, 4(2):1~13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198402000.htmWU Xihao, PU Qingyu, QIAN Fang, et al. Preliminary study on the Quaternary magnetostratigraphy of the Songliao plain in north-east China[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternaty Geology, 1984, 4(2):1~13. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198402000.htm
|
| [2] |
初本君, 高振超, 杨世生, 等.黑龙江省第四纪地质与环境[M].北京:海洋出版社, 1988.CHU Benjun, GAO Zhencao, YANG Shisheng, et al. Quaternary geology and environment of Heilongjiang province, China[M]. Beijing:Ocean Press, 1988. (in Chinese)
|
| [3] |
叶启晓.哈尔滨地区第四系[J].黑龙江地质, 1991, 2(2):17~29. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kjyqy201207136YE Qixiao. Quaternary system in Harbin area[J]. Heilongjiang Geology, 1991, 2(2):17~29. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kjyqy201207136
|
| [4] |
魏传义, 李长安, 康春国, 等.哈尔滨黄山黄土粒度特征及其对成因的指示[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(12):1945~1954. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94035X/201512/666921734.htmlWEI Chuanyi, LI Chang'an, KANG Chunguo, et al. Grain-size characteristics and genesis of the Huangshan Loess in songnen plain area[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(12):1945~1954. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94035X/201512/666921734.html
|
| [5] |
Doeglas D J. Grain-size indices, classification and environment[J]. Sedimentology, 1968, 10(2):83~100. doi: 10.1111/sed.1968.10.issue-2
|
| [6] |
Visher G S. Grain size distributions and depositional processes[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1969, 39(3):1074~1106. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/250081511_Grain_Size_Distributions_and_Depositional_Processes
|
| [7] |
Lu H Y, Vandenberghe J, An Z S. Aeolian origin and palaeoclimatic implications of the 'red clay' (north China) as evidenced by grain-size distribution[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2001, 16(1):89~97. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1417
|
| [8] |
Guo Z T, Ruddiman W F, Hao Q Z, et al. Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China[J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6877):159~163. doi: 10.1038/416159a
|
| [9] |
Yang S L, Ding Z L. Comparison of particle size characteristics of the Tertiary 'red clay' and Pleistocene loess in the Chinese Loess Plateau:implications for origin and sources of the 'red clay'[J]. Sedimentology, 2004, 51(1):77~93. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.2003.00612.x
|
| [10] |
Ding Z L, Derbyshire E, Yang S L, et al. Stacked 2.6-Ma grain size record from the Chinese loess based on five sections and correlation with the deep-sea δ18O record[J]. Paleoceanography, 2002, 17(3):1033. doi: 10.1029/2001PA000725/full
|
| [11] |
Sun D H. Monsoon and westerly circulation changes recorded in the late Cenozoic aeolian sequences of Northern China[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2004, 41(1):63~80. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2003.11.001
|
| [12] |
Guo Z T, Sun B, Zhang Z S, et al. A major reorganization of Asian climate by the early Miocene[J]. Climate of the Past, 2008, 4(3):153~174. doi: 10.5194/cp-4-153-2008
|
| [13] |
Hao Q Z, Wang L, Oldfield F, et al. Delayed build-up of Arctic ice sheets during 400, 000-year minima in insolation variability[J]. Nature, 2012, 490(7420):393~396. doi: 10.1038/nature11493
|
| [14] |
Zeng L, Lu H Y, Yi S W, et al. Long-term Pleistocene aridification and possible linkage to high-latitude forcing:New evidence from grain size and magnetic susceptibility proxies from loess-paleosol record in northeastern China[J]. Catena, 2017, 154:21~32. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.02.020
|
| [15] |
Fan M J, Song C H, Dettman D L, et al. Intensification of the Asian winter monsoon after 7.4 Ma:Grain-size evidence from the Linxia Basin, northeastern Tibetan Plateau, 13.1 Ma to 4.3 Ma[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 248(1/2):186~197. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229234756_Intensification_of_the_Asian_winter_monsoon_after_74_Ma_Grain-size_evidence_from_the_Linxia_Basin_northeastern_Tibetan_Plateau_131_Ma_to_43_Ma
|
| [16] |
Xiao J L, Chang Z G, Si B, et al. Partitioning of the grain-size components of Dali Lake core sediments:evidence for lake-level changes during the Holocene[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2009, 42(2):249~260. doi: 10.1007/s10933-008-9274-7
|
| [17] |
Jiang H C, Ding Z L. Eolian grain-size signature of the Sikouzi lacustrine sediments (Chinese Loess Plateau):Implications for Neogene evolution of the East Asian winter monsoon[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2010, 122(5~6):843~854. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/gsabulletin/article-abstract/122/5-6/843/125532/eolian-grain-size-signature-of-the-sikouzi
|
| [18] |
Yang S L, Ding Z L. Advance-retreat history of the East-Asian summer monsoon rainfall belt over northern China during the last two glacial-interglacial cycles[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 274(3~4):499~510. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X08005244
|
| [19] |
An Z S, Liu T, Lu Y C, et al. The long-term paleomonsoon variation recorded by the loess-paleosol sequence in Central China[J]. Quaternary International, 1990, 7~8:91~95. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/1040618290900423
|
| [20] |
Porter S C, An Z S. Correlation between climate events in the North Atlantic and China during the last glaciation[J]. Nature, 1995, 375(6529):305~308. doi: 10.1038/375305a0
|
| [21] |
Sun Y B, Clemens S C, An Z S, et al. Astronomical timescale and palaeoclimatic implication of stacked 3.6-Myr monsoon records from the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(1~2):33~48. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0277379105002039
|
| [22] |
鹿化煜, 安芷生.黄土高原红粘土与黄土古土壤粒度特征对比——红粘土风成成因的新证据[J].沉积学报, 1999, 17(2):226~232. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95994X/199902/3579460.htmlLU Huayu, AN Zhisheng. Comparison of grain-size distribution of red clay and loess-paleosoil deposits in Chinese loess plateau[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1999, 17(2):226~232. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95994X/199902/3579460.html
|
| [23] |
孙东怀, 鹿化煜, DAVID R, 等.中国黄土粒度的双峰分布及其古气候意义[J].沉积学报, 2000, 18(3):327~335. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199803013.htmSUN Donghuai, LU Huayu, DAVID R, et al. Bimode grain-size distribution of Chinese Loess and its paleoclimate implication[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2000, 18(3):327~335. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199803013.htm
|
| [24] |
李敬卫, 乔彦松, 王燕, 等.江西九江红土堆积的粒度特征及成因研究[J].地质力学学报, 2009, 15(1):95~104. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20090109&journal_id=dzlxxbLI Jingwei, QIAO Yansong, WANG Yan, et al. Aeolian origin of the red Earth tormation in Jiujiang city of Jiangxi province, China:evidence from grain-size analysis[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 15(1):95~104. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20090109&journal_id=dzlxxb
|
| [25] |
Friedman G M, Sanders J E. Principles of sedimentology[M]. New York:Wiley, 1978.
|
| [26] |
Folk R L, Ward W C. Brazos river bar, a study in the significance of grain size parameter[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1957, 27(1):3~26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
|
| [27] |
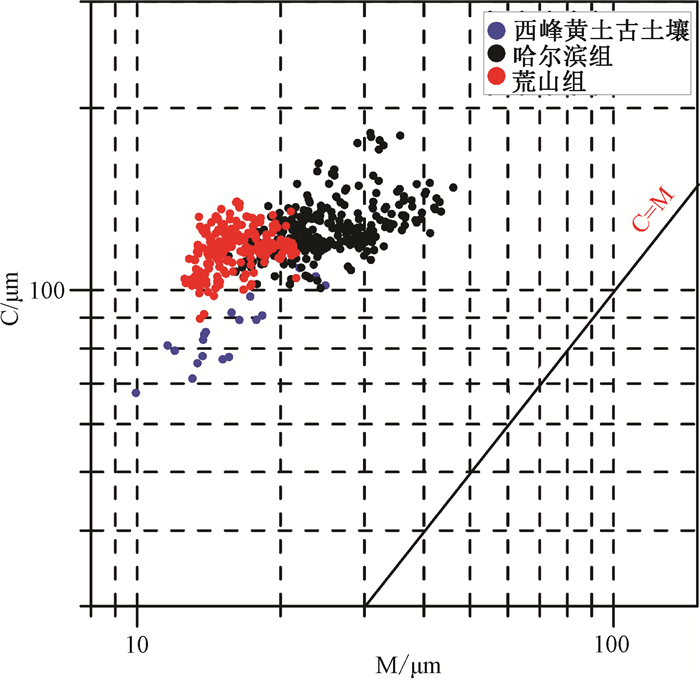
Passega R. Grain size representation by CM patterns as a geologic tool[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1964, 34(4):830~847. doi: 10.1306/74D711A4-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
|





 下载:
下载: