STUDY ON FAULT SEALING OF ORGANIC-RICH SHALE BY PRESENT STRESS: A CASE STUDY OF LONGMAXI FORMATION IN DINGSHAN AREA, SOUTHEAST SICHUAN
-
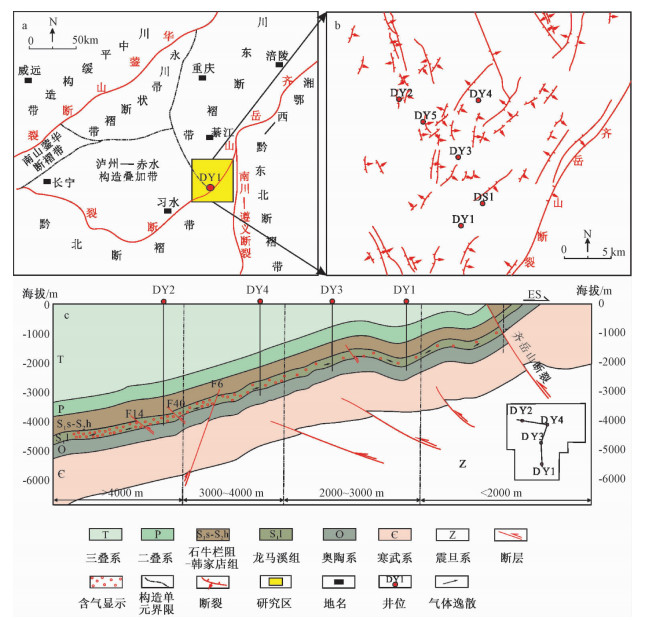
摘要: 断层的封闭性研究对油气藏的保存、评价工作及探索油气的分布规律具有重要的参考价值与指导意义。以川东南丁山地区龙马溪组页岩为例,利用FMI成像测井、震源机制解、现场水力压裂、三轴力学实验、有限元2D-σ方法等技术与方法分别对其现今地应力的方向、大小及岩石力学性质进行了分析,最后对井位附近断层封闭性进行了初步的评价。结果表明:丁山地区龙马溪组页岩现今地应力方向总体处于北东东-南西西(55°±5°)至南东东-北西西(110±5°)范围。DY2井龙马溪组页岩层现今最大主应力约145.0 MPa,断层面叠合正应力约188.4~218.3 MPa,岩石处于塑性变形阶段,破裂模式较为单一,脆性指数约41.6%~49.0%,破裂系数约0.197~0.355,断层封闭性总体较好,含气性与试气效果较好。DY1井龙马溪组页岩层现今最大主应力约52.0 MPa,断层面叠合正应力约75.8~83.1 MPa,岩石处于弹性变形阶段,破裂模式较为复杂,脆性指数约48.5%~55.0%,破裂系数约0.355~0.671,断层封闭性总体较差,含气性与试气效果较差。DY3井和DY4井龙马溪组附近断层封闭性一般。Abstract: The study of fault sealing has important reference value and guiding significance for the preservation and evaluation of oil and gas reservoirs and exploration of the distribution of oil and gas. Based on the technologies and methods of FMI imaging logging, focal mechanism solution, field hydraulic fracturing, triaxial mechanical experiment, finite element 2D-σ method and so on, the direction, intensity of the present geostress and the rock mechanical properties of the Longmaxi Formation in Dingshan area were analyzed. The sealing property of faults near well location was evaluated preliminarily. The results show that the direction of the present ground stress is generally from NEE-SWW(55°±5°)to SEE-NWW(110°±5°). The maximum principal stress of the Longmaxi Formation is about 145.0 MPa in the Well DY2, and the superimposed normal stress on the fault plane is about 188.4 to 218.3 MPa. The rock is in the plastic deformation stage with a simple fracture mode, generally good fault sealing, gas-bearing properties and test results, the brittleness index about 41.6% to 49.0% and the burst factor about 0.197 to 0.355.The present maximum principal stress of shale formation in the Longmaxi Formation of the Well DY1 is about 52.0 MPa, and the superimposed normal stress of the fault plane is about 75.8 to 83.1 MPa. The rock in the Longmaxi Formation of the Well DY1 is in the elastic deformation stage with a more complex fracture mode, generally bad fault sealing, gas-bearing properties and test results, the Rickman brittleness index about 48.5% to 55.0% and the rock fracture coefficient about 0.355 to 0.671. The fault sealing near shale formation of the Longmaxi Formation in the well DY3 and the well DY4 are generally normal.
-
Key words:
- fault sealing /
- Longmaxi Formation /
- shale /
- present ground stress /
- rock mechanics /
- Dingshan area
-
表 1 丁山周缘地区5个震源机制解与现今地应力方向(数据来源于中国地震台网中心)
Table 1. The five focal mechanism solutions and present stress directions in the surrounding Dingshan area
发震时间 震中位置 震级 断层性质 P轴 震源球示意图 现今最大水平
主应力方向经度 纬度 倾角 方位角 2006/07/22 104°18′36″ 28°0′36″ 4.9 左行逆冲走滑 5° 296° 
北西西—南东东(116°) 2006/08/25 105°0′0″ 28°0′0″ 5.0 左行逆冲走滑 4° 295° 
北西西—南东东(115°) 2012/09/07 104°11′24″ 27°28′12″ 5.3 左行逆冲走滑 7° 104° 
北西西—南东东(104°) 2013/04/24 104°49′48″ 28°27′36″ 4.7 左行逆冲走滑 21° 263° 
北东东—南西西(83°) 2015/02/06 105°0′0″ 28°19′48″ 4.8 逆冲 6° 295° 
北西西—南东东(115°) 表 2 DY1-4井龙马溪组水力压裂及应力估算值
Table 2. Hydraulic fracturing and stress estimation of Longmaxi formation in Well DY1-4
井位 井深/m 岩性 破泵压力/
MPa停泵压力/
MPa抗张强度/
MPa最大主
应力方向主应力值/MPa σv σH σh DY1井 2050.00 黑色页岩 63.6 50.1 5.0 水平 48.7 52.0 43.6 DY2井 4398.00 黑色页岩 117.0 74.2 9.6 垂直 145.0 121.6 109.0 DY3井 2200.00 黑色页岩 78.0 55.1 8.5 水平 61.0 70.0 58.0 DY4井 3726.39 黑色页岩 103.2 73.8 10.2 水平 93.0 112.0 90.0 注:σv为上覆地层压力,由密度测井计算而来;σH为最大水平主应力;σh为最小水平主应力。 表 3 丁山地区DY1-4井龙马溪组附近断层产状和断层面应力计算结果
Table 3. The attitude of fault and calculation results of fracture plane stress near Longmaxi formation of Well DY1-4 in Dingshan area
井位 断层 走向/(°) 倾角α/(°) σH/MPa σH方向/(°) σh/MPa β/° σv/MPa P/MPa DY1 F16 32.6 40~50 52.0 70~90 43.6 37.4~57.4 48.7 79.9~82.9 F18 18.2 60~70 51.8~71.8 75.8~83.1 DY2 F14 2.8 40~50 121.6 50~60 109 47.2~57.2 145.0 214.7~218.3 F40 23.3 40~50 26.7~36.7 208.8~215.8 F59 119.2 20~30 59.2~69.2 188.4~205.7 F64 114.2 40~50 54.2~64.2 211.9~217.6 DY3 F15 6.1 30~40 70.0 80~90 58.0 73.9~83.9 61.0 90.7~100.3 F21 39.1 40~50 40.9~50.9 104.4~108.8 F23 5.5 40~50 74.5~84.5 95.1~102.8 F26 93.8 40~50 3.8~13.8 86.9~95.1 DY4 F6 38.7 40~50 112.0 90~100 90 51.3~61.3 93.0 162.2~169.8 F48 20.1 40~50 69.9~79.9 152.3~164.0 F66 19.3 40~50 70.7~80.7 151.7~163.5 F3 35.4 50~70 54.6~64.6 163.2~169.7 F2 111.8 40~50 21.8~31.8 151.7~163.6 表 4 DY1-4井目的层页岩岩心弹性参数与脆性指数
Table 4. Elastic parameters and brittleness index of shale core in Well DY1-4
井位 应力测试段井深/m 抗压强度/MPa 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 脆性指数/% DY1 2025.50~2045.04 139.8~205.5(186.9) 25275~34292(32323) 0.195~0.254(0.228) 48.5%~55.0%(52.3%) DY2 4353.05~4364.73 224.0~286.7(253.9) 39326~52041(43299) 0.269~0.320(0.287) 41.6%~49.0%(46.3%) DY3 2207.68~2274.54 156.9~227.8(194.4) 29719~38202(34676) 0.214~0.264(0.234) 46.3%~54.1%(50.8%) DY4 3625.60~3728.33 216.2~258.7(235.5) 34515~41603(36130) 0.246~0.275(0.254) 43.1%~49.7%(47.8%) 注:括号内为平均值 表 5 地应力模拟结果与可靠度分析
Table 5. The simulation results of ground stress and reliability analysis
井位 最大水平地应力
压裂值/MPa最大水平地应力
模拟值/MPa应力误差范围/
%岩石破裂系数 可靠度 构造部位 DY1 52.0 61.2~65.3 17.7~25.6 0.355~0.671 良好 浅埋平缓区 DY2 121.6 104.5~111.3 8.5~14.1 0.197~0.355 较好 深埋平缓区 DY3 70.0 77.2~83.1 10.3~18.7 0.355~0.592 良好 中部低缓斜坡区 DY4 112.0 97.8~105.1 6.2~12.7 0.276~0.395 较好 东部高角度斜坡区 表 6 龙马溪组井位附近断层封闭性综合初步评价
Table 6. Comprehensive evaluation of fault sealing near well location in Longmaxi formation
井位 断层 埋深/m 断面叠合正压力/MPa 抗压强度/MPa 破裂模式 力学脆性 破裂系数 封闭性 DY1 F16 2025.50~2050.00 79.9~82.9 139.8~205.5
(186.9)劈裂型
双剪型48.5%~55.0%
(52.3%)0.355~0.671 较差 F18 75.8~83.1 DY2 F14 4353.05~4398.00 214.7~218.3 224.0~286.7
(253.9)单剪型 41.6%~49.0%
(46.3%)0.197~0.355 较好 F40 208.8~215.8 F59 188.4~205.7 F64 211.9~217.6 DY3 F15 2200.00~2274.54 90.7~100.3 156.9~227.8
(194.4)劈裂型
双剪型46.3%~54.1%
(50.8%)0.355~0.592 较差 F21 104.4~108.8 F23 95.1~102.8 F26 86.9~95.1 DY4 F6 3626.35~3728.33 162.2~169.8 216.2~258.7
(235.5)双剪性
单剪型43.1%~49.7%
(47.8%)0.276~0.395 一般 F48 152.3~164.0 F66 151.7~163.5 F3 163.2~169.7 F2 151.7~163.6 注:括号内为平均值 -
[1] 邱贻博, 查明, 曲江秀.高邮凹陷陈堡及陈堡东地区断层封闭性研究[J].石油勘探与开发, 2007, 34(2):197~201. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-NMKX201112001120.htmQIU Yibo, ZHA Ming, QU Jiangxiu. Fault sealing performance in Chenbao and eastern Chenbao areas, Gaoyou Sag[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2007, 34(2):197~201. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-NMKX201112001120.htm [2] 王新新, 戴俊生, 李旭航, 等.多种方法评价断层封闭性——以金湖凹陷石港断裂带为例[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 2013, 33(3):69~75. https://t.docin.com/p-97679417.htmlWANG Xinxin, DAI Junsheng, LI Xuhang, et al. Assessment of fault sealing ability:An example from the Shigang fault zone in the Jinhu depression, northern Jiangsu[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2013, 33(3):69~75. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://t.docin.com/p-97679417.html [3] 闻竹, 付晓飞, 吕延防.断层封闭性评价及断圈含油气预测[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(4):1209~1218. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.04.018WEN Zhu, FU Xiaofei, LÜ Yanfang. Evaluation of fault seal and hydrocarbon potential prediction of fault traps[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2016, 47(4):1209~1218. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.04.018 [4] 陈永峤, 周新桂, 于兴河, 等.断层封闭性要素与封闭效应[J].石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(6):38~40. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98500A/201303/48341544.htmlCHEN Yongqiao, ZHOU Xingui, YU Xinghe, et al. Sealing factors of faults and their sealing effects[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(6):38~40. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98500A/201303/48341544.html [5] 吕延防, 黄劲松, 付广, 等.砂泥岩薄互层段中断层封闭性的定量研究[J].石油学报, 2009, 30(6):824~829. doi: 10.7623/syxb200906006LÜ Yanfang, HUANG Jinsong, FU Guang, et al. Quantitative study on fault sealing ability in sandstone and mudstone thin interbed[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(6):824~829. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7623/syxb200906006 [6] 季宗镇, 戴俊生, 汪必峰.地应力与构造裂缝参数间的定量关系[J].石油学报, 2010, 31(1):68~72. doi: 10.7623/syxb201001011JI Zongzhen, DAI Junsheng, WANG Bifeng. Quantitative relationship between crustal stress and parameters of tectonic fracture[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(1):68~72. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7623/syxb201001011 [7] 王珂, 戴俊生.地应力与断层封闭性之间的定量关系[J].石油学报, 2012, 33(1):74~81. doi: 10.7623/syxb201201009WANG Ke, DAI Junsheng. A quantitative relationship between the crustal stress and fault sealing ability[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(1):74~81. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7623/syxb201201009 [8] 周新桂, 孙宝珊, 谭成轩, 等.现今地应力与断层封闭效应[J].石油勘探与开发, 2000, 27(5):127~131. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/90664X/200005/4834102.htmlZHOU Xingui, SUN Baoshan, TAN Chengxuan, et al. State of current geo-stress and effect of fault sealing[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2000, 27(5):127~131. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/qk/90664X/200005/4834102.html [9] 谭成轩, 张明利.地应力与油气运移[J].中国西部油气地质, 2005, 1(1):70~76. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98573X/200803/27486558.htmlTAN Chengxuan, ZHANG Mingli. Crustal stress and petroleum migration[J]. West China Petroleum Geosciences, 2005, (1):70~76. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98573X/200803/27486558.html [10] 王连捷, 孙宝珊, 王薇, 等.地应力对油气运移的驱动作用[J].地质力学学报, 2011, 17(2):132~143. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20110203&journal_id=dzlxxbWANG Lianjie, SUN Baoshan, WANG Wui, et al. Driving effect of the crustal stress on petroleum migration[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2011, 17(2):132~143. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20110203&journal_id=dzlxxb [11] 郭鹏, 李春林, 哈文雷, 等.构造应力场与油气运聚规律探讨——以鄂尔多斯盆地苏10区块为例[J].特种油气藏, 2011, 18(5):64~66. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98573X/201105/39771518.htmlGUO Peng, LI Chunlin, HA Wenlei, et al. Discussion of tectonic stress field and hydrocarbon migration and accumulation in the Su 10 block, Ordos Basin[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2011, 18(5):64~66. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98573X/201105/39771518.html [12] 高伟中, 孙鹏, 田超, 等.东海盆地西湖凹陷地应力场与油气运移关系探讨[J].油气藏评价与开发, 2015, 5(1):1~6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KTDQ201501001.htmGAO Weizhong, SUN Peng, TIAN Chao, et al. Relation between crustal stress field and hydrocarbon migration in West Lake sag, East China Sea basin[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2015, 5(1):1~6. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KTDQ201501001.htm [13] 付广, 杨勉.利用断裂填充物中泥质含量研究断层封闭性的改进方法[J].江汉石油学院学报, 2002, 24(1):1~4. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94420X/2002001/6341742.htmlFU Guang, YANG Mian. Improved method for studying fault closure by using shal e content in fault filling materials[J]. Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute, 2002, 24(1):1~4. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94420X/2002001/6341742.html [14] 孟令东, 付晓飞, 王雅春, 等.徐家围子断陷火山岩断层带内部结构与封闭性[J].石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(2):150~157. doi: 10.11698/PED.2014.02.03MENG Lingdong, FU Xiaofei, WANG Yachun, et al. Internal structure and sealing properties of the volcanic fault zones in Xujiaweizi Fault Depression, Songliao Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(2):150~157. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11698/PED.2014.02.03 [15] 童亨茂.断层开启与封闭的定量分析[J].石油与天然气地质, 1998, 19(3):215~220. doi: 10.11743/ogg19980308TONG Hengmao. Quantitative analysis of fault opening and sealing[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1998, 19(3):215~220. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11743/ogg19980308 [16] 梅廉夫, 刘昭茜, 汤济广, 等.湘鄂西-川东中生代陆内递进扩展变形:来自裂变径迹和平衡剖面的证据[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2010, 35(2):161~174.MEI Lianfu, LIU Zhaoqian, TANG Jiguang, et al. Mesozoic intra-continental progressive deformation in western Hunan-Hubei-Eastern Sichuan Provinces of China:Evidence from apatite fission track and balanced cross-section[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010, 35(2):161~174. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 孙玮, 刘树根, 王国芝, 等.川东南丁山构造震旦系-下古生界油气成藏条件及成藏过程[J].地质科技情报, 2010, 29(1):49~55. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201001008SUN Wei, LIU Shugen, WANG Guozhi, et al. Petroleum formed condition and process research for sinian to Low Paleozoic at Dingshan structure in Southeast of Sichuan Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2010, 29(1):49~55. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201001008 [18] 黄仁春, 魏祥峰, 王强.四川盆地东南缘丁山地区页岩气成藏富集的关键控制因素[J].海相油气地质, 2017, 22(2):25~30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SKYK201401003.htmHUANG Renchun, WEI Xiangfeng, WANG Qiang. Key factors of shale gas accumulation in Dingshan area of southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2017, 22(2):25~30. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SKYK201401003.htm [19] 王东. 川东南桑木场-酒店垭构造形成演化与多期流体充注[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2009.WANG Dong. The evolution and multi-phase fluids injection of Sangmuchang-Jiudianya structure, southeast of Sichuan Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] 宋光永, 刘树根, 黄文明, 等.川东南丁山-林滩场构造灯影组热液白云岩特征[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 36(6):706~715. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=32705903SONG Guangyong, LIU Shugen, HUANG Wenming, et al. Characteristics of hydrothermal dolomite of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation in the Dingshan-Lintanchang structural zone, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2009, 36(6):706~715. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=32705903 [21] 杨淑雯. 川南地区古生界构造特征及其对页岩气保存条件的影响[D]. 荆州: 长江大学, 2015.YANG Shuwen. Tectonic characteristics of Paleozoic in southern Sichuan region and its effects on shale gas preservation[D]. Jingzhou: Yangtze University, 2015(in Chinese with English abstract) [22] 魏祥峰, 赵正宝, 王庆波, 等.川东南綦江丁山地区上奥陶统五峰组-下志留统龙马溪组页岩气地质条件综合评价[J].地质论评, 2017, 63(1):153~164. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10616-1013288912.htmWEI Xiangfeng, ZHAO Zhengbao, WANG Qingbo, et al. comprehensive evaluation on geological conditions of the shale gas in upper Ordovician Wufeng formation-Lower Silurian Longmaxi formation in Dingshan Area, Qijiang, southeastern Sichuan[J]. Geological Review, 2017, 63(1):153~164. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10616-1013288912.htm [23] 董大忠, 程克明, 王玉满, 等.中国上扬子区下古生界页岩气形成条件及特征[J].石油与天然气地质, 2010, 31(3):288~299, 308. doi: 10.11743/ogg20100304DONG Dazhong, CHENG Keming, WANG Yuman, et al. Forming conditions and characteristics of shale gas in the Lower Paleozoic of the Upper Yangtze region, China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2010, 31(3):288~299, 308. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11743/ogg20100304 [24] 邹才能, 董大忠, 王社教, 等.中国页岩气形成机理、地质特征及资源潜力[J].石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(6):641~653. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SKYK201301003.htmZOU Caineng, DONG Dazhong, WANG Shejiao, et al. Geological characteristics, formation mechanism and resource potential of shale gas in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(6):641~653. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SKYK201301003.htm [25] 郭彤楼, 刘若冰.复杂构造区高演化程度海相页岩气勘探突破的启示——以四川盆地东部盆缘JY1井为例[J].天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(4):643~651. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/word/a4d1fde103d8ce2f0166233e-1.docGUO Tonglou, LIU Ruobing. Implications from marine shale gas exploration breakthrough in complicated structural area at high thermal stage:Taking Longmaxi formation in well JY1 as an example[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(4):643~651. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/word/a4d1fde103d8ce2f0166233e-1.doc [26] 张小龙, 李艳芳, 吕海刚, 等.四川盆地志留系龙马溪组有机质特征与沉积环境的关系[J].煤炭学报, 2013, 38(5):851~856. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/MTXB201305025.htmZHANG Xiaolong, LI Yanfang, LÜ Haigang, et al. Relationship between organic matter characteristics and depositional environment in the Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2013, 38(5):851~856. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/MTXB201305025.htm [27] 范存辉, 李虎, 钟城, 等.川东南丁山构造龙马溪组页岩构造裂缝期次及演化模式[J].石油学报, 2018, 39(4):379~390. doi: 10.7623/syxb201804002FAN Cunhui, LI Hu, ZHONG Cheng, et al. Tectonic fracture stages and evolution model of Longmaxi Formation shale, Dingshan structure, Southeast Sichuan[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(4):379~390. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7623/syxb201804002 [28] Zeng W T, Zhang J C, Ding W L, et al. Fracture development in Paleozoic shale of Chongqing area (South China). Part one:Fracture characteristics and comparative analysis of main controlling factors[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 75:251~266. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.07.014 [29] 胡东风, 张汉荣, 倪楷, 等.四川盆地东南缘海相页岩气保存条件及其主控因素[J].天然气工业, 2014, 34(6):17~23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201406003.htmHU Dongfeng, ZHANG Hanrong, NI Kai, et al. Main controlling factors for gas preservation conditions of marine shales in southeastern margins of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(6):17~23. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201406003.htm [30] 牟传龙, 周恳恳, 梁薇, 等.中上扬子地区早古生代烃源岩沉积环境与油气勘探[J].地质学报, 2011, 85(4):526~532. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201104008MU Chuanlong, ZHOU Kenken, LIANG Wei, et al. Early Paleozoic sedimentary environment of hydrocarbon source rocks in the middle-upper Yangtze region and petroleum and gas Exploration[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(4):526~532. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201104008 [31] 郭旭升.南方海相页岩气"二元富集"规律——四川盆地及周缘龙马溪组页岩气勘探实践认识[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(7):1209~1218. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KTSY201504001.htmGUO Xusheng. Rules of two-factor enrichiment for marine shale gas in southern China——understanding from the Longmaxi formation shale gas in Sichuan Basin and its surrounding area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(7):1209~1218. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KTSY201504001.htm [32] 金之钧, 胡宗全, 高波, 等.川东南地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气富集与高产控制因素[J].地学前缘, 2016, 23(1):1~10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201601002.htmJIN Zhijun, HU Zongquan, GAO Bo, et al. Controlling factors on the enrichment and high productivity of shale gas in the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations, southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(1):1~10. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201601002.htm [33] 郭旭升, 郭彤楼, 魏志红, 等.中国南方页岩气勘探评价的几点思考[J].中国工程科学, 2012, 14(6):101~105, 112. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZXE201407001.htmGUO Xusheng, GUO Tonglou, WEI Zhihong, et al. Thoughts on shale gas exploration in southern China[J]. Engineering Science, 2012, 14(6):101~105, 112. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZXE201407001.htm [34] 魏志红.四川盆地及其周缘五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气的晚期逸散[J].石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(4):659~665. doi: 10.11743/ogg20150416WEI Zhihong. Late fugitive emission of shale gas from Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin and its periphery[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(4):659~665. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11743/ogg20150416 [35] 张晨晨, 王玉满, 董大忠, 等.四川盆地五峰组-龙马溪组页岩脆性评价与"甜点层"预测[J].天然气工业, 2016, 36(9):51~60. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.09.006ZHANG Chenchen, WANG Yuman, DONG Dazhong, et al. Evaluation of the Wufeng-Longmaxi shale brittleness and prediction of "sweet spot layers" in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(9):51~60. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.09.006 [36] 杨振恒, 魏志红, 何文斌, 等.川东南地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩现场解吸气特征及其意义[J].天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(1):156~163. http://www.doc88.com/p-4973871975617.htmlYANG Zhenheng, WEI Zhihong, HE Wenbin, et al. Characteristics and significance of onsite gas desorption from Wufeng-Longmaxi shales in southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(1):156~163. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.doc88.com/p-4973871975617.html [37] 王浩, 王才志, 刘英明, 等.利用测井资料合成井壁破坏图像分析地应力新方法[J].测井技术, 2016, 40(4):488~492, 516. doi: 10.16489/j.issn.1004-1338.2016.04.020.htmlWANG Hao, WANG Caizhi, LIU Yingming, et al. NEW method for formation stress analysis based on wellbore failure image created by log data[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2016, 40(4):488~492, 516. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16489/j.issn.1004-1338.2016.04.020.html [38] Kingdon A, Fellgett M W, Williams J D O. Use of borehole imaging to improve understanding of the in-situ stress orientation of Central and Northern England and its implications for unconventional hydrocarbon resources[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 73:1~20. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.02.012 [39] Rajabi M, Tingay M, Heidbach O. The present-day state of tectonic stress in the Darling Basin, Australia:Implications for exploration and production[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 77:776~790. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.07.021 [40] Pedrera A, Ruiz-Constán A, Galindo-Zaldívar J, et al. Is there an active subduction beneath the Gibraltar orogenic arc? Constraints from Pliocene to present-day stress field[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 2011, 52(2):83~96. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2010.12.003 [41] Zarifi Z, Nilfouroushan F, Raeesi M. Crustal stress map of Iran:Insight from seismic and geodetic computations[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 2014, 171(7):1219~1236. doi: 10.1007/s00024-013-0711-9 [42] Bada G, Horváth F, Dövényi P, et al. Present-day stress field and tectonic inversion in the Pannonian basin[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2007, 58(1~4):165~180. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.01.007 [43] Ju W, Sun W F, Ma X J. Tectonic stress pattern in the Chinese Mainland from the inversion of focal mechanism data[J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 2017, 126(3):41. doi: 10.1007/s12040-017-0814-2 [44] 唐颖, 唐玄, 王广源, 等.页岩气开发水力压裂技术综述[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(2~3):393~399. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2011Z1027.htmTANG Ying, TANG Xuan, WANG Guangyuan, et al. Summary of hydraulic fracturing technology in shale gas development[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2011, 30(2~3):393~399. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2011Z1027.htm [45] Kim H, Xie L M, Min K B, et al. Integrated in situ stress estimation by hydraulic fracturing, borehole observations and numerical analysis at the exp-1 borehole in Pohang, Korea[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2017, 50(12):3141~3155. doi: 10.1007/s00603-017-1284-1 [46] 丁文龙, 李超, 李春燕, 等.页岩裂缝发育主控因素及其对含气性的影响[J].地学前缘, 2012, 19(2):212~220. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY201202031.htmDING Wenlong, LI Chao, LI Chunyan, et al. Dominant factor of fracture development in shale and its relationship to gas accumulation[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(2):212~220. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY201202031.htm [47] 杨宝刚, 潘仁芳, 赵丹, 等.四川盆地长宁示范区龙马溪组页岩岩石力学特性及脆性评价[J].地质科技情报, 2015, 34(4):183~188. http://www.doc88.com/p-2724480335167.htmlYANG Baogang, PAN Renfang, ZHAO Dan, et al. Mechanical properties and brittleness evaluation of Longmaxi shale rock of Changning demonstration area in Sichuan Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(4):183~188. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.doc88.com/p-2724480335167.html [48] 梁利喜, 庄大琳, 刘向君, 等.龙马溪组页岩的力学特性及破坏模式研究[J].地下空间与工程学报, 2017, 13(1):108~116. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/BASE201701016.htmLIANG Lixi, ZHUANG Dalin, LIU Xiangjun, et al. Study on mechanical properties and failure modes of Longmaxi Shale[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2017, 13(1):108~116. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/BASE201701016.htm [49] Rickman R, Mullen M J, Petre J E, et al. A practical use of shale petrophysics for stimulation design optimization: All shale plays are not clones of the Barnett Shale[A]. SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition[C]. Colorado, USA: SPE, 2008, 1~11. [50] 聂海宽, 包书景, 高波, 等.四川盆地及其周缘下古生界页岩气保存条件研究[J].地学前缘, 2012, 19(3):280~294. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DXQY201203030.htmNIE Haikuan, BAO Shujing, GAO Bo, et al. A study of shale gas preservation conditions for the Lower Paleozoic in Sichuan Basin and its periphery[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(3):280~294. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DXQY201203030.htm -





 下载:
下载: