PHYSICAL MODEL EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON DEFORMATION AND FAILURE OF OVERLYING ROCK SLOPE UNDER THE CONDITION OF STEEP COAL SEAM MINING
-
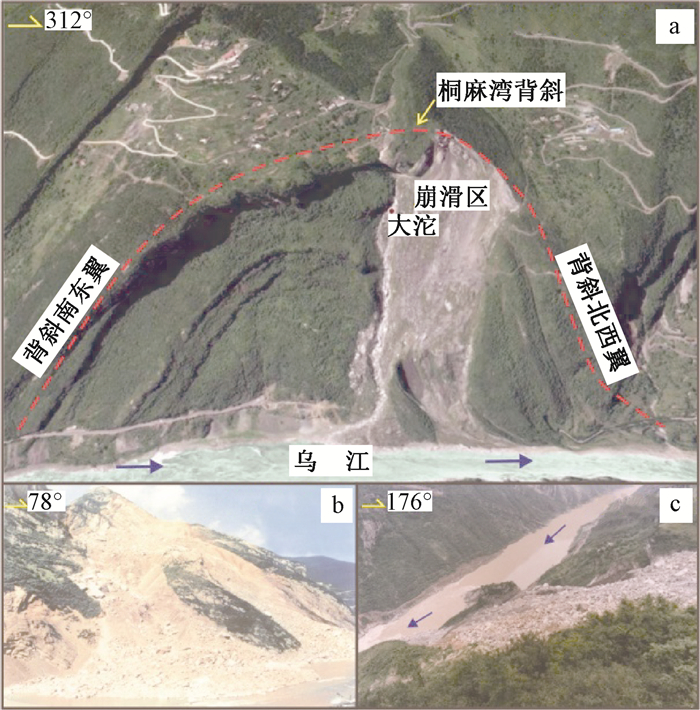
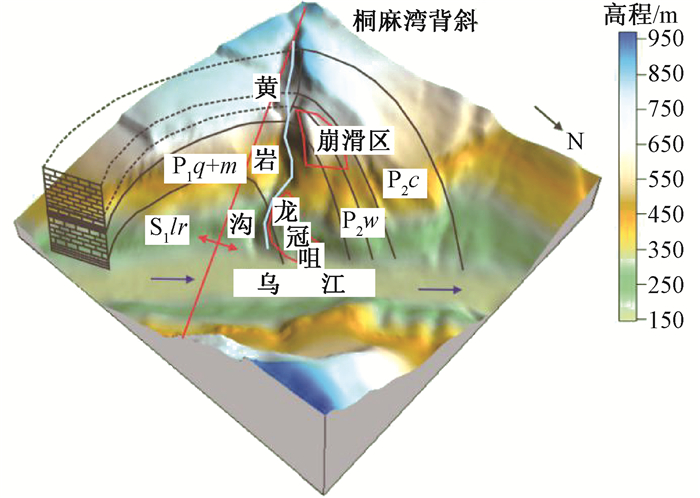
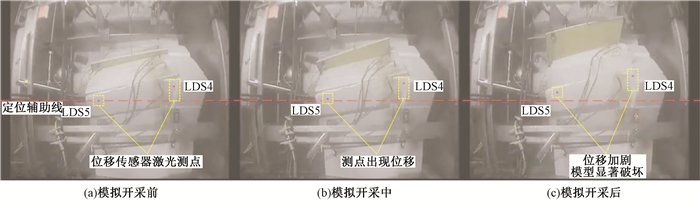
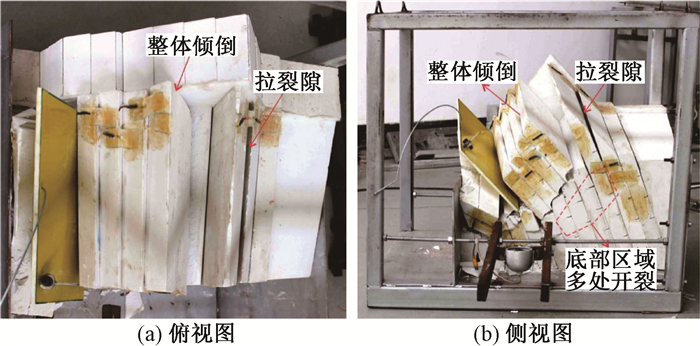
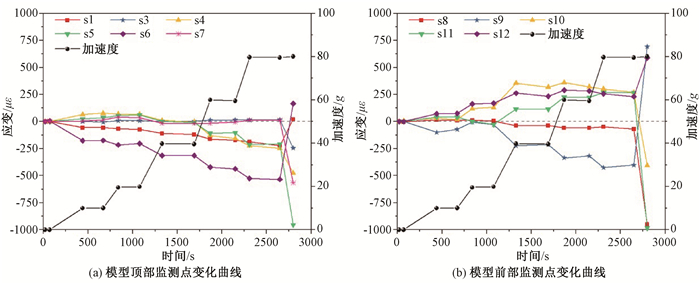
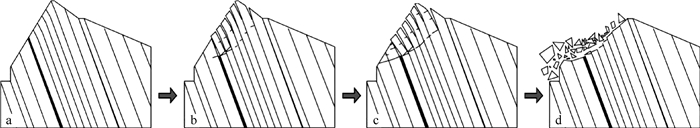
摘要: 大型岩质滑坡是中国西南岩溶矿区的主要地质灾害类型,其破坏和成灾过程具有复合性。以我国重庆武隆鸡冠岭滑坡为例,通过离心物理模型试验研究了地下开采条件下陡倾灰岩斜坡的变形失稳机制。试验时随着煤层模型板被拔出,上覆岩层在拟重力作用下开始出现位移与层间错动,当煤层模型被拔出150 mm时,模型山体发生显著破坏。试验结果表明:陡倾灰岩斜坡在长期重力作用下,会出现弯曲倾倒的变形,随着地下煤层逐渐采空,上覆陡倾层状岩体失去支撑,岩层层面分离并产生拉张裂缝,岩体变形加剧发生倾倒破坏,并对煤层下部的稳定岩体形成挤压,下伏稳定岩体发生剪切破坏,最终导致鸡冠岭以倾倒-滑移的复合模式整体失稳。这一研究对中国西南山区大型岩质滑坡的早期识别与失稳机制分析具有指导意义。Abstract: Major rockslide is the main type of geological hazards in the mining mountainous areas of southwestern China. The failure modes and behaviors of this kind of rockslides are complex. Taking the Jiguanling landslide as an example, centrifuge modelling was taken to analyze the failure mechanism of a steep-dip carbonate slope which was induced by goaf in this study. With the model plate of coal seam was pulling out, the overlying strata began to move and dislocate under centrifugal acceleration. The model rock slope failed completely when the model plate was pulled out about 150mm.The experimental results show that the deformation tendency of bending and toppling appeared in steep-dip and layered limestone slopes by gravity. With the underground mining of coal seams, overlying steep-dip and layered rock slope lost its support, then strata got separated and tension fissures were generated. These rock strata were toppled due to severe deformation. The underlying stable rock mass was squeezed by the toppled overlying strata, and shear failure occurred. In the end, the Jiguangling rock slope was failed with the composite mode of toppling-sliding. This study could be a guide of early identification and failure mechanism analysis for major rockslides in mountainous area of southwestern China.
-
Key words:
- steep-dip and layered slope /
- underground goaf /
- failure /
- centrifuge model /
- toppling-sliding
-
东昆仑山脉位于青海省南部,展布于中国中央造山带西段南侧,面积10×104 km2以上,由于自然条件恶劣,地质研究程度很低,区域矿产研究和开发工作才刚起步。面对国家经济发展逐步向西转移的战略决策实施,对该区的资源远景研究显得十分迫切[1]。大干沟一带由于恶劣的自然地理条件,资源潜力调查一直遭遇瓶颈。笔者经过近4年的野外地质调查,在大干沟一带取得了一系列新发现和找矿成果。
1. 区域成矿地质背景
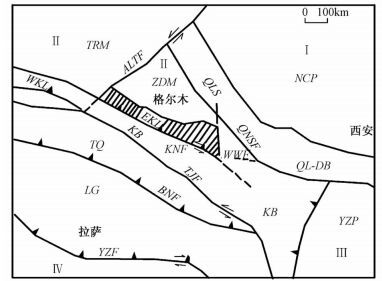
东昆仑地区处于中朝、塔里木—柴达木、扬子和印度板块的拼合部位,特殊的大地构造位置决定了其构造演化的复杂性和独特性。元古宙以来,东昆仑经历了多期次的裂解和拼合,自北向南发育有昆北、昆中、昆南和北巴颜喀拉4条深大断裂带,将东昆仑及邻区划分为昆北火山—侵入岩带、昆中花岗—变质杂岩带、昆南陆源活动带、阿尼玛卿火山-侵入岩带和北巴颜喀拉造山带,奠定了东昆仑地区的构造格架,控制着各成矿带的成矿作用和矿产分布(见图 1)[2~7]。
 图 1 东昆仑区域大地构造位置(据许志琴等,1996,改编)NCP—华北地台;YZP—扬子地台;TRM—塔里木陆块;ZDM—柴达木陆块;TQ—唐古拉—羌塘地体;LG—拉萨地体;QLS—祁连构造带;QL-DB—秦岭—大别构造带;EKL—东昆仑构造带;WKL—西昆仑构造带;KB—可可西里—巴颜喀拉构造带;ALTF—阿尔金断裂;QNSF—青海南山断裂;WWF—哇洪山—温泉断裂;KNF—昆南断裂;TJF—沱沱河—金沙江断裂;BNF—班公湖—澜沧江断裂;YZF—雅鲁藏布江断裂;Ⅰ—中朝板块;Ⅱ—塔里木—柴达木板块;Ⅲ—华南板块;Ⅳ—印度板块Figure 1. Tectonic map of East Kunlun Mountain area
图 1 东昆仑区域大地构造位置(据许志琴等,1996,改编)NCP—华北地台;YZP—扬子地台;TRM—塔里木陆块;ZDM—柴达木陆块;TQ—唐古拉—羌塘地体;LG—拉萨地体;QLS—祁连构造带;QL-DB—秦岭—大别构造带;EKL—东昆仑构造带;WKL—西昆仑构造带;KB—可可西里—巴颜喀拉构造带;ALTF—阿尔金断裂;QNSF—青海南山断裂;WWF—哇洪山—温泉断裂;KNF—昆南断裂;TJF—沱沱河—金沙江断裂;BNF—班公湖—澜沧江断裂;YZF—雅鲁藏布江断裂;Ⅰ—中朝板块;Ⅱ—塔里木—柴达木板块;Ⅲ—华南板块;Ⅳ—印度板块Figure 1. Tectonic map of East Kunlun Mountain area东昆仑是一个具有复杂演化历史的多旋回复合造山带,主要经历了前寒武纪古陆形成、早古生代洋陆转化、晚古生代—早中生代洋陆转化以及中—新生代叠复造山等4个构造旋回。
其中,早古生代与晚古生代—早中生代构造旋回与本区内铜、金、锑等多金属矿产的形成关系最为密切[8~11]。
2. 区域成矿特征及矿床类型
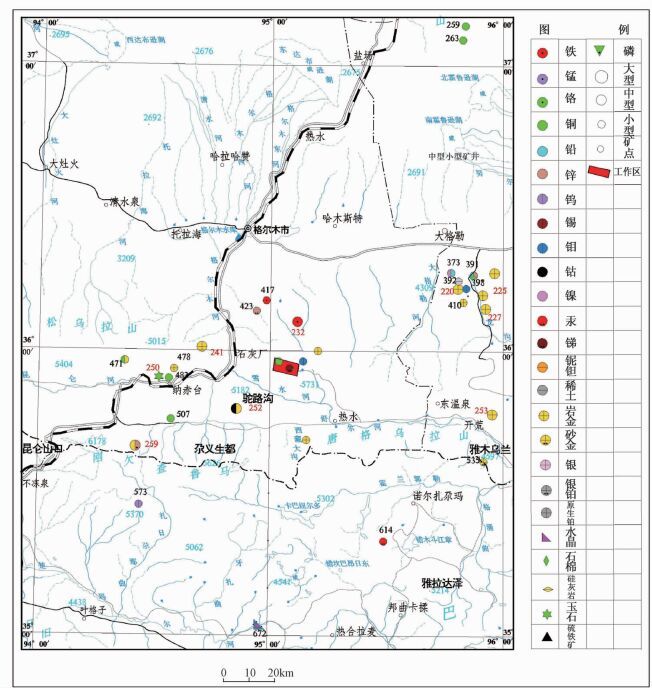
根据成矿区带划分,该区属于秦—祁—昆成矿域(Ⅰ1),东昆仑成矿省(Ⅱ1),雪山峰—布尔汉布达华力西—印支期钴、金、铜、玉石(稀有、稀土)成矿带(Ⅲ13)[12]。目前在该带内已发现有开荒北金矿床、小干沟金矿床、督冷沟铜(钴)矿床、驼路沟钴(金)矿床以及东大滩金锑矿点、雪峰沟金矿点、纳赤台铜金矿点等(见图 2)。
东昆仑北邻柴达木盆地,南接特提斯构造域,是显生宙以来全球典型的陆缘活动—造山带,具有得天独厚的成矿地质环境,是成矿和聚矿十分有利的区带,同时也是金和多金属理想的衍生场所。加里东成矿期,发育有与海相中基性—酸性火山岩有关的铜、铅、锌、钴矿床成矿系列,矿床类型为火山喷气沉积型,以驼路沟钴(金)矿床、督冷沟铜(钴)矿床为代表。华力西—印支期是本区比较重要的成矿时期,矿化比较普遍,以铜、金多金属为主,但规模不大,多属矿点、矿化点。成矿与同造山期中酸性侵入岩关系密切,矿床类型为接触交代型、
热液型及石英脉—构造蚀变岩型(金矿)。此类矿床构成了与花岗岩类有关的金、铜、铅、锌、铁、稀土成矿系列,较重要的矿床(点)有开荒北金矿床、小干沟金矿床、纳赤台铜金矿点等[13]。
徐文艺等[3]和张德全等[4]按成矿的动力学环境将东昆仑地区矿床类型划分为两类,一类是与拉张环境海底喷流沉积作用有关的,如火山岩容矿的块状硫化物型(VHMS)矿床和沉积岩容矿的喷气型(SEDEX);另一类是与挤压造山环境有关的,如斑岩型铜矿床,夕卡岩型铁—金—多金属矿,热液脉型、层控改造型金矿等。
3. 矿体地质特征
目前在大干沟一带已发现铜多金属矿化带一条、金锑含矿构造蚀变带一条。矿化特征基本一致,均赋存于中三叠统闹仓坚沟组北西西向脆韧性剪切带内及两侧的灰白—烟灰色方解石石英脉内,且具有南侧金锑矿化、北侧铜多金属矿化的分带特征。
3.1 铜多金属矿(化)带
矿(化)带内主要岩石为岩屑砂岩和石英脉,石英脉具褐铁矿化、碳酸盐化。该矿化带长度约5 km,宽度5~20 m,其走向为北西西向,与地层走向基本一致;倾向北,倾角40°—50°。该矿(化)带北侧有小规模花岗斑岩体出露,二者间距800~1500 m,区内矿化与该岩体的形成关系密切。
带内已圈定铜多金属矿(化)体9条,单矿(化)体控制长度2~30 m,厚度0.5~2.0 m。矿(化)体主要以含铜石英脉形式产出,含铜石英脉走向为北西西向或东西向,顺层或以锐角与矿(化)带斜交,呈串珠状展布。单工程铜多金属品位变化较大,一般Cu品位0.15×10-2~2.25×10-2,局部见有特高品位达14.71×10-2;Au品位0.23×10-6~0.79×10-6;Ag品位8.33×10-6~32.2×10-6,局部特高品位达933×10-6。
根据成矿作用将含铜、金石英脉按成矿阶段划分为两期。
① 第Ⅰ成矿期:成分简单,含矿性较差。矿物组合为辉铜矿+石英+方解石+蓝铜矿,辉铜矿呈块状、不规则脉状,以浸染状形式充填于方解石或石英脉中(见图 3)。含矿石英脉颜色呈灰白色或乳白色,半油脂光泽,单脉宽1~50 cm不等,呈脉状、网脉状或透镜状产出,围岩未见有明显矿化现象。石英脉中矿化较不均匀,品位变化较大,方解石呈菱面状铜矿化富集。
② 第Ⅱ成矿期:此阶段含矿性较好,如黄铁矿、黄铜矿、方铅矿、辉铜矿、辉银矿等,因为这一阶段的石英脉含有多种金属硫化物(见图 4)。矿物组合为辉铜矿+辉银矿+黄铜矿+黄铁矿+方铅矿+石英+方解石,辉铜矿呈细脉状、树枝状,以浸染形式充填于石英脉内或方解石边部。含矿石英脉颜色呈烟灰—青灰色,油脂光泽;长度一般在10~30 m,单脉宽10~50 cm不等,呈豆荚状、脉状、网脉状或透镜状斜穿层理产出。铜矿化在石英脉中分布极不均匀,品位变化较大。
3.2 金锑含矿构造蚀变带
金锑含矿构造蚀变带赋存于中三叠统闹仓坚沟组第二岩性段脆韧性剪切带内,金锑矿(化)与北西西向脆韧性剪切带关系极为密切。含矿构造蚀变带控制长度约3.5 km,出露宽度3~16 m。走向近北西西向,倾向北,倾角45°—55°。通过槽探工程控制,在带内初步圈定金矿体1条、锑矿体1条。
3.2.1 锑矿体
根据容矿岩石类型和成矿作用将锑矿划分为两种类型,即产于石英方解石脉中辉锑矿和产于薄层灰岩裂隙内脉状辉锑矿。
产于石英方解石脉中辉锑矿(见图 5)含矿石英方解石脉一般长6~25 m,宽度多为10~60 cm,以多条细脉组成的脉群形式产出,Sb品位为15.40×10-2~39.96×10-2,Au品位为0.15×10-6~0.23×10-6。该矿石矿物组合简单,金属矿物主要为辉锑矿,脉石矿物有石英、方解石等。围岩蚀变主要为碳酸盐化、绢云母化、硅化等,其中与锑矿化最为紧密的是碳酸盐化、硅化。
产于薄层灰岩裂隙内脉状辉锑矿(见图 6)矿体形态简单,呈脉状、透镜状产于薄层灰岩裂隙内,具局部膨胀、收缩及尖灭再现的特点,出露长度30~200 m,宽度30~50 cm,少数可达80 cm。Sb品位为39.96×10-2~41.68×10-2,Au品位为0.35×10-6~0.39×10-6。矿石矿物主要为辉锑矿、锑华、锑赭石、孔雀石、蓝铜矿,脉石矿物有石英、方解石,围岩蚀变为硅化、碳酸盐化、黄铁矿化、绢云母化等,其中与锑矿化最为紧密的为硅化、碳酸盐化。围岩蚀变具明显的分带性,由矿体向两侧依次为:矿体→断层→强蚀变带→弱蚀变带→片理化带,矿体向外侧蚀变带含矿性依次减弱。
3.2.2 金矿(化)体
地表长度180~200 m,出露宽度1.09~1.42 m。矿化岩石为薄层灰岩夹泥钙质板岩、构造片岩(见图 7)。矿化以黄铁矿及风化矿物(褐铁矿)为主,Au品位为0.52×10-6~2.48×10-6。金矿(化)体围岩蚀变主要为黄铁矿化、硅化、褐铁矿化、绢云母化,其中黄铁矿化、绢云母化与金矿化关系最为紧密,矿体向外侧蚀变强度依次减弱。
4. 找矿标志
4.1 铜多金属矿找矿标志
4.1.1 岩浆岩标志
大干沟中部靠近矿化带一侧有小规模花岗斑岩出露,近东西向呈串珠状展布,岩体与铜多金属矿化的关系主要表现在3个方面:① 岩体的展布方向与含矿石英脉的展布方向基本一致,说明含矿石英脉的形成与岩体侵入地层内形成的张裂隙有关;② 岩体附近石英脉、碳酸盐脉呈网脉状发育,单脉宽0.5~20.0 cm不等,而远离岩体石英脉发育程度降低;③ 岩体内部发育的石英脉与含矿石英脉特征基本一致。
4.1.2 岩性标志
含矿围岩主要是紫红色细粒—中粒长石岩屑砂岩,而在灰绿色砂岩内虽有热液活动但未见有矿化现象。
4.1.3 热液标志
依据热液与围岩的穿插关系及热液受控的构造方向,将热液活动期次划分为Ⅳ期。Ⅰ期石英脉为纯白色,无明显矿化,与围岩顺层,产状一致,呈北西西向展布;Ⅱ期石英脉呈乳白色—烟灰色,隐晶结构,油脂光泽,含矿性较好并可见有碳酸盐化、褐铁矿化等蚀变信息,与围岩穿层,呈北西西向展布;Ⅲ期石英脉呈纯白色—烟灰色,半油脂光泽,含矿性稍差,可见有碳酸盐化、褐铁矿化等蚀变信息,与围岩穿层,北东向展布;Ⅳ期石英脉呈乳白色,半油脂光泽,未见有矿化显示,但见有褐铁矿化。
4.1.4 围岩蚀变标志
围岩蚀变主要为硅化,其次为碳酸盐化、褐铁矿化等,特别是方解石以菱面状的形态出现时,标志着热液矿化期由石英阶段向方解石阶段的转化,铜矿化也明显富集。
4.2 金锑矿找矿标志
4.2.1 地球化学标志
1:50000水系沉积物Au-As-Sb综合异常浓集中心以及Au、Sb单元素异常高值点是本区寻找金锑矿的重要地球化学标志。
4.2.2 构造标志
北西西向脆韧性剪切带作为导矿构造是含矿热液上升的通道,剪切带内一系列皱褶构造的出现特别是褶皱的转折端或背斜核部是含矿热液的有利储存场所,而在其他褶皱不发育地段未见有明显矿化富集。
4.2.3 岩性标志
含矿围岩主要为薄层灰岩夹泥钙质板岩,分析由于薄层灰岩脆性大且化学性质活泼,在构造应力作用下易发生破碎形成许多裂隙,成为矿液运移的通道和矿质沉淀的场所,矿液与围岩以交代方式形成具工业意义的矿体,而在其他化学性质不活泼的岩性内矿化信息较弱。
4.2.4 热液标志
注意寻找低温热液方解石石英组合,脉体地表风化面见有硫黄、褐铁矿化等特征。
5. 讨论与结论
东昆仑地区自元古宙以来,加里东、华力西、印支与燕山期等均有成矿作用发生,且具有多期次、多矿种和多类型的特点,在空间展布上具有一定的规律性,表现为不同级别的构造控矿作用不同,而昆北、昆中、昆南和北巴颜喀拉4条区域性深大断裂的存在,是造成东昆仑现今构造格局、分带及沉积建造差异的主要原因,并对区域地质发展演化和成矿带的空间展布具控制作用。
本区构造对矿体的控制较明显,脆韧性剪切带与铜、金、锑成矿作用的空间关系主要表现在两方面:一是作为导矿构造控制矿体的分布,即矿体或矿化富集带直接定位于脆韧性剪切带内;二是作为含矿构造矿体分布于脆韧性剪切带的低序次的派生构造带中。
-
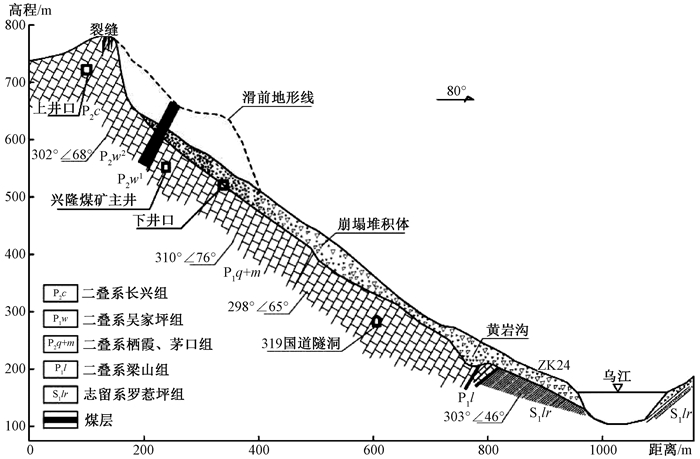
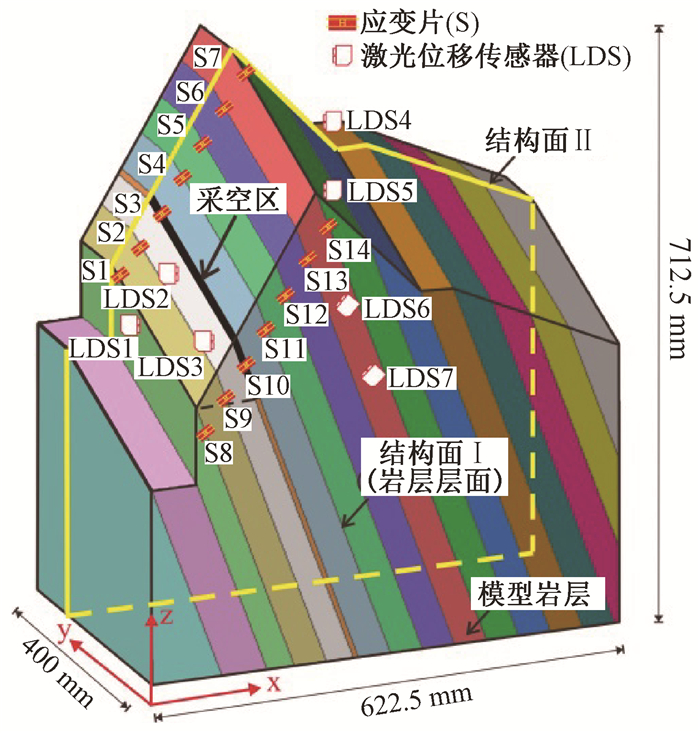
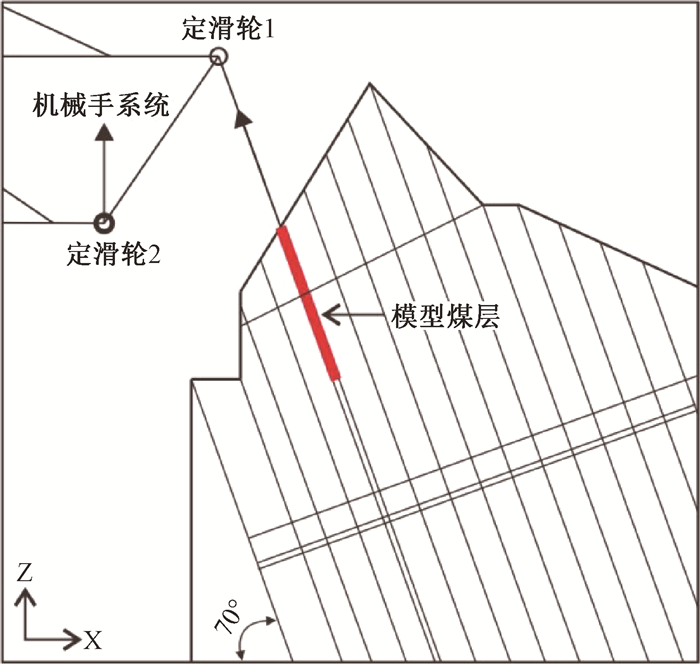
表 1 鸡冠岭滑坡离心模型试验主要物理量比尺关系
Table 1. Scale relation of physical model experiment on the Jiguangling rockslide
物理量 原型与模型比例关系 原型与模型比例数值 长度 1:1/CL 800 加速度 1:n 1:80 容重 1:n/q 1:1248 位移 1:1/CL 800 弹性模量 1:n/qCL 15.6 粘聚力c 1:n/qCL 15.6 内摩擦角φ 1:1 1:1 泊松比υ 1:1 1:1 抗拉强度 1:n/qCL 15.6 注:表中CL为离心试验几何相似比;n为试验离心加速度;q为离心试验容重相似比 -
[1] Yin Y P. Recent catastrophic landslides and mitigation in China[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2011, 3(1):10~18. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1235.2011.00010 [2] Yin Y P, Sun P, Zhang M, et al. Mechanism on apparent dip sliding of oblique inclined bedding rockslide at Jiweishan, Chongqing, China[J]. Landslides, 2011, 8(1):49~65. doi: 10.1007/s10346-010-0237-5 [3] Yin Y P, Sun P, Zhu J L, et al. Research on catastrophic rock avalanche at Guanling, Guizhou, China[J]. Landslides, 2011, 8(4):517~525. doi: 10.1007/s10346-011-0266-8 [4] Li W X, Mei S H, Zai S H, et al. Fuzzy models for analysis of rock mass displacements due to underground mining in mountainous areas[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2006, 43(4):503~511. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2005.09.008 [5] Marschalko M, Fuka M, Třeslín L. Influence of mining activity on selected landslide in the Ostrava-karviná coalfield[J]. Acta Montanistica Slovaca, 2008, 13(1):58~65. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/26503965_Influence_of_Mining_Activity_on_Selected_Landslide_in_the_Ostrava-Karvina_Coalfield [6] Marschalko M, Hofrichterova L, Lahuta H. Utilization of geophysical method of multielectrode resistivity measurements on a slope deformation in the mining district[C]//8th International Scientific Conference on Modern Management of Mine Producing, Geology and Environmental Protection. Sofia, 2008, 315~324. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284988200_Utilization_of_geophysical_method_of_multielectrode_resistivity_measurements_on_a_slope_deformatin_in_the_mining_district [7] Altun A O, Yilmaz I, Yildirim M. A short review on the surficial impacts of underground mining[J]. Scientific Research and Essays, 2010, 5(21):3206~3212. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6fcbfbd78c79d9540abe039ad71d9058&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [8] Tang F Q. Research on mechanism of mountain landslide due to underground mining[J]. Journal of Coal Science and Engineering (China), 2009, 15(4):351~354. doi: 10.1007/s12404-009-0403-3 [9] 宋彦辉, 聂德新, 陈龙.采动斜坡变形破坏模式分析及预测[J].灾害学, 2003, 18(2):32~37. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zhx200302007SONG Yanhui, NIE Dexin, CHEN Long. Analysis on deformation and failure model of excavating slope and prediction[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2003, 18(2):32~37. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zhx200302007 [10] 梅松华, 盛谦, 李文秀.地表及岩体移动研究进展[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(S1):4535~4539. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/735cb415f18583d04964596a.htmlMEI Songhua, SHENG Qian, LI Wenxiu. Research advances in surface and rock-mass movement[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(S1):4535~4539. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/735cb415f18583d04964596a.html [11] 范士凯.采空区上边坡稳定问题[J].资源环境与工程, 2006, 20(S1):617~627. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hbdk2006z1005FAN Shikai. A discussion on the slope stability on the goaf[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2006, 20(S1):617~627. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hbdk2006z1005 [12] Brady B H G, Brown E T. Rock mechanics:for underground mining[M]. 3rd ed. India:Springer, 2006, 484~517. [13] Zhang D S, Fan G W, Wang X F. Characteristics and stability of slope movement response to underground mining of shallow coal seams away from gullies[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2012, 22(1):47~50. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2011.06.005 [14] Marschalko M, Yilmaz I, Bednárik M, et al. Influence of underground mining activities on the slope deformation genesis:doubrava vrchovec, doubrava ujala and staric case studies from Czech republic[J]. Engineering Geology, 2012, 147~148:37~51. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.07.014 [15] Lana M S. Numerical modeling of failure mechanisms in phyllite mine slopes in Brazil[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2014, 24(6):777~782. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2014.10.007 [16] 孙玉科, 姚宝魁.盐池河磷矿山体崩坍破坏机制的研究[J].水文地质工程地质, 1983, (1):1~7. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGYJ198606003017.htmSUN Yuke, YAO Baokui. Mechainism research on the collapse of Yanchi river mining area[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 1983, (1):1~7. (in Chinese) http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGYJ198606003017.htm [17] Hoek E. Progressive caving induced by mining an inclined ore body[J]. Transactions of the Institution of Mining and Metallurgy, Section A:Mining Technology, 1974, 83(815):33~39. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284300864_Progressive_caving_induced_by_mining_an_inclined_ore_body [18] 赵建军, 肖建国, 向喜琼, 等.缓倾煤层采空区滑坡形成机制数值模拟研究[J].煤炭学报, 2014, 39(3):424~429. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=mtxb201403005ZHAO Jianjun, XIAO Jianguo, XIANG Xiqiong, et al. Failure mechanism numerical simulation of mining landslide with gentle bedding coal strata[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(3):424~429. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=mtxb201403005 [19] Brown E T, Ferguson G A. Progressive hanging wall caving at Gath's mine, Rhodesia[J]. Transactions of the Institution of Mining and Metallurgy, 1979, 88:A92~105. [20] Alejano L R, Ferrero A M, Ramírez-Oyanguren P, et al. Comparison of limit-equilibrium, numerical and physical models of wall slope stability[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2011, 48(1):16~26. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.06.013 [21] Majdi A, Amini M. Analysis of geo-structural defects in flexural toppling failure[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2011, 48(2):175~186. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.11.007 [22] Agliardi F, Crosta G B, Meloni F, et al. Structurally-controlled instability, damage and slope failure in a porphyry rock mass[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 605:34~47. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2013.05.033 [23] 李滨, 王国章, 冯振, 等.地下采空诱发陡倾层状岩质斜坡失稳机制研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(6):1148~1161. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-1012371283.htmLI Bin, WANG Guozhang, FENG Zhen, et al. Failure mechanism of steeply inclined rock slopes induced by underground mining[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(6):1148~1161. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-1012371283.htm [24] 李滨, 王国章, 冯振, 等.陡倾层状岩质斜坡极限平衡稳定分析[J].岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(5):839~846. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201505009LI Bin, WANG Guozhang, FENG Zhen, et al. Limit equilibrium and stability analysis of steep stratified rock slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(5):839~846. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201505009 [25] 陈自生, 张晓刚. 1994~04~30四川省武隆县鸡冠岭滑坡→崩塌→碎屑流→堵江灾害链[J].山地研究, 1994, 12(4):225~229. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201403011.htmCHEN Zisheng, ZHANG Xiaogang. A hazard-chain of landslide→collapse→debris flow→river stoppage in Wulong county, Sichuan province on April 30, 1994[J]. Mountain Research, 1994, 12(4):225~229. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201403011.htm [26] 殷跃平, 康宏达, 何思为, 等.乌江鸡冠岭危岩体整治爆破工程方案[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 1994, 5(S1):324~331. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH4S1.052.htmYIN Yueping, KANG Hongda, HE Siwei, et al. Explosive engineering of Jiguanling dangerous rockmass prevention of the Wu River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1994, 5(S1):324~331. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH4S1.052.htm [27] 刘传正, 黄学斌, 黎力.乌江鸡冠岭山崩堵江地质灾害及其防治对策[J].水文地质工程地质, 1995, (4):6~11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG504.002.htmLIU Chuanzheng, HUANG Xuebin, LI Li. Landslide dam in Wu River and its control counter measure in Jiguanling M t[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 1995, (4):6~11. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG504.002.htm 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 刘松岩,张达,杨明建,张鑫明,未国栋,聂胜强,王轩,冯彦平,栗文杰,陈贵兰. 熊耳山矿集区蒿坪沟Ag–Au多金属矿床绿泥石特征及其找矿意义. 地质力学学报. 2024(01): 129-146 .  本站查看
本站查看2. 郭小刚,路万全,周宏,王秦,杨镇熙,郭东宝,苟瑞. 甘蒙北山四道梁南钼矿土壤地球化学异常特征及找矿潜力分析. 地质与勘探. 2023(04): 774-790 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:


 百度学术
百度学术