MAIN TYPES AND HYDROCARBON EXPLORATION DIRECTION OF THE PALEO-UPLIFTS IN THE QAIDAM BASIN
-
摘要: 柴达木盆地古隆起分布广泛,具有巨大的勘探潜力。为指明柴达木盆地古隆起的勘探方向,通过地震资料解释及近年来已发现古隆起油气藏实例解剖,对盆地主要古隆起的构造样式、沉积特征、演化期次、运动学特征及成藏规律等进行总结。将盆地古隆起划分为稳定型、活动型、残余型与消亡型等4种主要类型。同时,盆地的古隆起分布具有一定的规律性,古隆起主要发育于盆地深大断裂两侧,盆地不同性质的边界条件决定了古隆起的发育类型。古隆起在油气运聚、储层类型、圈闭类型、输导条件及保存条件等方面具备优越的成藏条件。以此确定了柴达木盆地古隆起两个有利勘探方向,一是已发现油气田的挖潜;二是成藏条件较好的盆缘山前构造带。Abstract: The paleo-uplifts in the Qaidam Basin are widely distributed and have great exploration potential. In order to indicate the exploration direction of the Qaidam Basin, the structural styles, sedimentary characteristics, evolution stages, kinematic characteristics and reservoir-forming laws of the main paleo-uplifts are summarized in this article through the interpretation of seismic data and the example analysis of discovered hydrocarbon reservoirs in paleo-uplifts in recent years. The paleo-uplifts in the basin are divided into 4 main types:stable type, active type, residual type and extinction type. At the same time, the distribution of paleo-uplifts in the basin has a certain regular pattern:the paleo-uplifts mainly developed on both sides of the deep faults, and the boundary conditions of different properties of basin determined the type of the paleo-uplift. The paleo-uplifts have superior reservoir forming conditions in the migration and accumulation of hydrocarbon, reservoir types, trap types, transportation conditions and preservation conditions etc. Therefore, two favorable exploration directions of the paleo-uplifts in the Qaidam Basin are confirmed:one is tapping the potential of the discovered hydrocarbon fields; the other one is the piedmont tectonic belt with relatively good reservoir conditions on the basin margin.
-
Key words:
- paleo-uplift /
- hydrocarbon exploration direction /
- distribution laws /
- the Qaidam Basin
-
东昆仑山脉位于青海省南部,展布于中国中央造山带西段南侧,面积10×104 km2以上,由于自然条件恶劣,地质研究程度很低,区域矿产研究和开发工作才刚起步。面对国家经济发展逐步向西转移的战略决策实施,对该区的资源远景研究显得十分迫切[1]。大干沟一带由于恶劣的自然地理条件,资源潜力调查一直遭遇瓶颈。笔者经过近4年的野外地质调查,在大干沟一带取得了一系列新发现和找矿成果。
1. 区域成矿地质背景
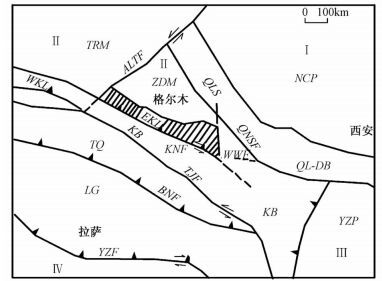
东昆仑地区处于中朝、塔里木—柴达木、扬子和印度板块的拼合部位,特殊的大地构造位置决定了其构造演化的复杂性和独特性。元古宙以来,东昆仑经历了多期次的裂解和拼合,自北向南发育有昆北、昆中、昆南和北巴颜喀拉4条深大断裂带,将东昆仑及邻区划分为昆北火山—侵入岩带、昆中花岗—变质杂岩带、昆南陆源活动带、阿尼玛卿火山-侵入岩带和北巴颜喀拉造山带,奠定了东昆仑地区的构造格架,控制着各成矿带的成矿作用和矿产分布(见图 1)[2~7]。
 图 1 东昆仑区域大地构造位置(据许志琴等,1996,改编)NCP—华北地台;YZP—扬子地台;TRM—塔里木陆块;ZDM—柴达木陆块;TQ—唐古拉—羌塘地体;LG—拉萨地体;QLS—祁连构造带;QL-DB—秦岭—大别构造带;EKL—东昆仑构造带;WKL—西昆仑构造带;KB—可可西里—巴颜喀拉构造带;ALTF—阿尔金断裂;QNSF—青海南山断裂;WWF—哇洪山—温泉断裂;KNF—昆南断裂;TJF—沱沱河—金沙江断裂;BNF—班公湖—澜沧江断裂;YZF—雅鲁藏布江断裂;Ⅰ—中朝板块;Ⅱ—塔里木—柴达木板块;Ⅲ—华南板块;Ⅳ—印度板块Figure 1. Tectonic map of East Kunlun Mountain area
图 1 东昆仑区域大地构造位置(据许志琴等,1996,改编)NCP—华北地台;YZP—扬子地台;TRM—塔里木陆块;ZDM—柴达木陆块;TQ—唐古拉—羌塘地体;LG—拉萨地体;QLS—祁连构造带;QL-DB—秦岭—大别构造带;EKL—东昆仑构造带;WKL—西昆仑构造带;KB—可可西里—巴颜喀拉构造带;ALTF—阿尔金断裂;QNSF—青海南山断裂;WWF—哇洪山—温泉断裂;KNF—昆南断裂;TJF—沱沱河—金沙江断裂;BNF—班公湖—澜沧江断裂;YZF—雅鲁藏布江断裂;Ⅰ—中朝板块;Ⅱ—塔里木—柴达木板块;Ⅲ—华南板块;Ⅳ—印度板块Figure 1. Tectonic map of East Kunlun Mountain area东昆仑是一个具有复杂演化历史的多旋回复合造山带,主要经历了前寒武纪古陆形成、早古生代洋陆转化、晚古生代—早中生代洋陆转化以及中—新生代叠复造山等4个构造旋回。
其中,早古生代与晚古生代—早中生代构造旋回与本区内铜、金、锑等多金属矿产的形成关系最为密切[8~11]。
2. 区域成矿特征及矿床类型
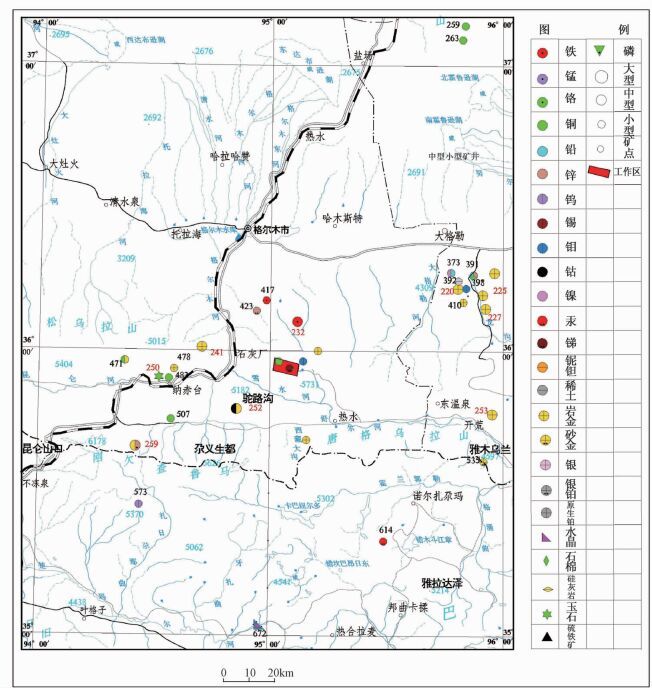
根据成矿区带划分,该区属于秦—祁—昆成矿域(Ⅰ1),东昆仑成矿省(Ⅱ1),雪山峰—布尔汉布达华力西—印支期钴、金、铜、玉石(稀有、稀土)成矿带(Ⅲ13)[12]。目前在该带内已发现有开荒北金矿床、小干沟金矿床、督冷沟铜(钴)矿床、驼路沟钴(金)矿床以及东大滩金锑矿点、雪峰沟金矿点、纳赤台铜金矿点等(见图 2)。
东昆仑北邻柴达木盆地,南接特提斯构造域,是显生宙以来全球典型的陆缘活动—造山带,具有得天独厚的成矿地质环境,是成矿和聚矿十分有利的区带,同时也是金和多金属理想的衍生场所。加里东成矿期,发育有与海相中基性—酸性火山岩有关的铜、铅、锌、钴矿床成矿系列,矿床类型为火山喷气沉积型,以驼路沟钴(金)矿床、督冷沟铜(钴)矿床为代表。华力西—印支期是本区比较重要的成矿时期,矿化比较普遍,以铜、金多金属为主,但规模不大,多属矿点、矿化点。成矿与同造山期中酸性侵入岩关系密切,矿床类型为接触交代型、
热液型及石英脉—构造蚀变岩型(金矿)。此类矿床构成了与花岗岩类有关的金、铜、铅、锌、铁、稀土成矿系列,较重要的矿床(点)有开荒北金矿床、小干沟金矿床、纳赤台铜金矿点等[13]。
徐文艺等[3]和张德全等[4]按成矿的动力学环境将东昆仑地区矿床类型划分为两类,一类是与拉张环境海底喷流沉积作用有关的,如火山岩容矿的块状硫化物型(VHMS)矿床和沉积岩容矿的喷气型(SEDEX);另一类是与挤压造山环境有关的,如斑岩型铜矿床,夕卡岩型铁—金—多金属矿,热液脉型、层控改造型金矿等。
3. 矿体地质特征
目前在大干沟一带已发现铜多金属矿化带一条、金锑含矿构造蚀变带一条。矿化特征基本一致,均赋存于中三叠统闹仓坚沟组北西西向脆韧性剪切带内及两侧的灰白—烟灰色方解石石英脉内,且具有南侧金锑矿化、北侧铜多金属矿化的分带特征。
3.1 铜多金属矿(化)带
矿(化)带内主要岩石为岩屑砂岩和石英脉,石英脉具褐铁矿化、碳酸盐化。该矿化带长度约5 km,宽度5~20 m,其走向为北西西向,与地层走向基本一致;倾向北,倾角40°—50°。该矿(化)带北侧有小规模花岗斑岩体出露,二者间距800~1500 m,区内矿化与该岩体的形成关系密切。
带内已圈定铜多金属矿(化)体9条,单矿(化)体控制长度2~30 m,厚度0.5~2.0 m。矿(化)体主要以含铜石英脉形式产出,含铜石英脉走向为北西西向或东西向,顺层或以锐角与矿(化)带斜交,呈串珠状展布。单工程铜多金属品位变化较大,一般Cu品位0.15×10-2~2.25×10-2,局部见有特高品位达14.71×10-2;Au品位0.23×10-6~0.79×10-6;Ag品位8.33×10-6~32.2×10-6,局部特高品位达933×10-6。
根据成矿作用将含铜、金石英脉按成矿阶段划分为两期。
① 第Ⅰ成矿期:成分简单,含矿性较差。矿物组合为辉铜矿+石英+方解石+蓝铜矿,辉铜矿呈块状、不规则脉状,以浸染状形式充填于方解石或石英脉中(见图 3)。含矿石英脉颜色呈灰白色或乳白色,半油脂光泽,单脉宽1~50 cm不等,呈脉状、网脉状或透镜状产出,围岩未见有明显矿化现象。石英脉中矿化较不均匀,品位变化较大,方解石呈菱面状铜矿化富集。
② 第Ⅱ成矿期:此阶段含矿性较好,如黄铁矿、黄铜矿、方铅矿、辉铜矿、辉银矿等,因为这一阶段的石英脉含有多种金属硫化物(见图 4)。矿物组合为辉铜矿+辉银矿+黄铜矿+黄铁矿+方铅矿+石英+方解石,辉铜矿呈细脉状、树枝状,以浸染形式充填于石英脉内或方解石边部。含矿石英脉颜色呈烟灰—青灰色,油脂光泽;长度一般在10~30 m,单脉宽10~50 cm不等,呈豆荚状、脉状、网脉状或透镜状斜穿层理产出。铜矿化在石英脉中分布极不均匀,品位变化较大。
3.2 金锑含矿构造蚀变带
金锑含矿构造蚀变带赋存于中三叠统闹仓坚沟组第二岩性段脆韧性剪切带内,金锑矿(化)与北西西向脆韧性剪切带关系极为密切。含矿构造蚀变带控制长度约3.5 km,出露宽度3~16 m。走向近北西西向,倾向北,倾角45°—55°。通过槽探工程控制,在带内初步圈定金矿体1条、锑矿体1条。
3.2.1 锑矿体
根据容矿岩石类型和成矿作用将锑矿划分为两种类型,即产于石英方解石脉中辉锑矿和产于薄层灰岩裂隙内脉状辉锑矿。
产于石英方解石脉中辉锑矿(见图 5)含矿石英方解石脉一般长6~25 m,宽度多为10~60 cm,以多条细脉组成的脉群形式产出,Sb品位为15.40×10-2~39.96×10-2,Au品位为0.15×10-6~0.23×10-6。该矿石矿物组合简单,金属矿物主要为辉锑矿,脉石矿物有石英、方解石等。围岩蚀变主要为碳酸盐化、绢云母化、硅化等,其中与锑矿化最为紧密的是碳酸盐化、硅化。
产于薄层灰岩裂隙内脉状辉锑矿(见图 6)矿体形态简单,呈脉状、透镜状产于薄层灰岩裂隙内,具局部膨胀、收缩及尖灭再现的特点,出露长度30~200 m,宽度30~50 cm,少数可达80 cm。Sb品位为39.96×10-2~41.68×10-2,Au品位为0.35×10-6~0.39×10-6。矿石矿物主要为辉锑矿、锑华、锑赭石、孔雀石、蓝铜矿,脉石矿物有石英、方解石,围岩蚀变为硅化、碳酸盐化、黄铁矿化、绢云母化等,其中与锑矿化最为紧密的为硅化、碳酸盐化。围岩蚀变具明显的分带性,由矿体向两侧依次为:矿体→断层→强蚀变带→弱蚀变带→片理化带,矿体向外侧蚀变带含矿性依次减弱。
3.2.2 金矿(化)体
地表长度180~200 m,出露宽度1.09~1.42 m。矿化岩石为薄层灰岩夹泥钙质板岩、构造片岩(见图 7)。矿化以黄铁矿及风化矿物(褐铁矿)为主,Au品位为0.52×10-6~2.48×10-6。金矿(化)体围岩蚀变主要为黄铁矿化、硅化、褐铁矿化、绢云母化,其中黄铁矿化、绢云母化与金矿化关系最为紧密,矿体向外侧蚀变强度依次减弱。
4. 找矿标志
4.1 铜多金属矿找矿标志
4.1.1 岩浆岩标志
大干沟中部靠近矿化带一侧有小规模花岗斑岩出露,近东西向呈串珠状展布,岩体与铜多金属矿化的关系主要表现在3个方面:① 岩体的展布方向与含矿石英脉的展布方向基本一致,说明含矿石英脉的形成与岩体侵入地层内形成的张裂隙有关;② 岩体附近石英脉、碳酸盐脉呈网脉状发育,单脉宽0.5~20.0 cm不等,而远离岩体石英脉发育程度降低;③ 岩体内部发育的石英脉与含矿石英脉特征基本一致。
4.1.2 岩性标志
含矿围岩主要是紫红色细粒—中粒长石岩屑砂岩,而在灰绿色砂岩内虽有热液活动但未见有矿化现象。
4.1.3 热液标志
依据热液与围岩的穿插关系及热液受控的构造方向,将热液活动期次划分为Ⅳ期。Ⅰ期石英脉为纯白色,无明显矿化,与围岩顺层,产状一致,呈北西西向展布;Ⅱ期石英脉呈乳白色—烟灰色,隐晶结构,油脂光泽,含矿性较好并可见有碳酸盐化、褐铁矿化等蚀变信息,与围岩穿层,呈北西西向展布;Ⅲ期石英脉呈纯白色—烟灰色,半油脂光泽,含矿性稍差,可见有碳酸盐化、褐铁矿化等蚀变信息,与围岩穿层,北东向展布;Ⅳ期石英脉呈乳白色,半油脂光泽,未见有矿化显示,但见有褐铁矿化。
4.1.4 围岩蚀变标志
围岩蚀变主要为硅化,其次为碳酸盐化、褐铁矿化等,特别是方解石以菱面状的形态出现时,标志着热液矿化期由石英阶段向方解石阶段的转化,铜矿化也明显富集。
4.2 金锑矿找矿标志
4.2.1 地球化学标志
1:50000水系沉积物Au-As-Sb综合异常浓集中心以及Au、Sb单元素异常高值点是本区寻找金锑矿的重要地球化学标志。
4.2.2 构造标志
北西西向脆韧性剪切带作为导矿构造是含矿热液上升的通道,剪切带内一系列皱褶构造的出现特别是褶皱的转折端或背斜核部是含矿热液的有利储存场所,而在其他褶皱不发育地段未见有明显矿化富集。
4.2.3 岩性标志
含矿围岩主要为薄层灰岩夹泥钙质板岩,分析由于薄层灰岩脆性大且化学性质活泼,在构造应力作用下易发生破碎形成许多裂隙,成为矿液运移的通道和矿质沉淀的场所,矿液与围岩以交代方式形成具工业意义的矿体,而在其他化学性质不活泼的岩性内矿化信息较弱。
4.2.4 热液标志
注意寻找低温热液方解石石英组合,脉体地表风化面见有硫黄、褐铁矿化等特征。
5. 讨论与结论
东昆仑地区自元古宙以来,加里东、华力西、印支与燕山期等均有成矿作用发生,且具有多期次、多矿种和多类型的特点,在空间展布上具有一定的规律性,表现为不同级别的构造控矿作用不同,而昆北、昆中、昆南和北巴颜喀拉4条区域性深大断裂的存在,是造成东昆仑现今构造格局、分带及沉积建造差异的主要原因,并对区域地质发展演化和成矿带的空间展布具控制作用。
本区构造对矿体的控制较明显,脆韧性剪切带与铜、金、锑成矿作用的空间关系主要表现在两方面:一是作为导矿构造控制矿体的分布,即矿体或矿化富集带直接定位于脆韧性剪切带内;二是作为含矿构造矿体分布于脆韧性剪切带的低序次的派生构造带中。
-
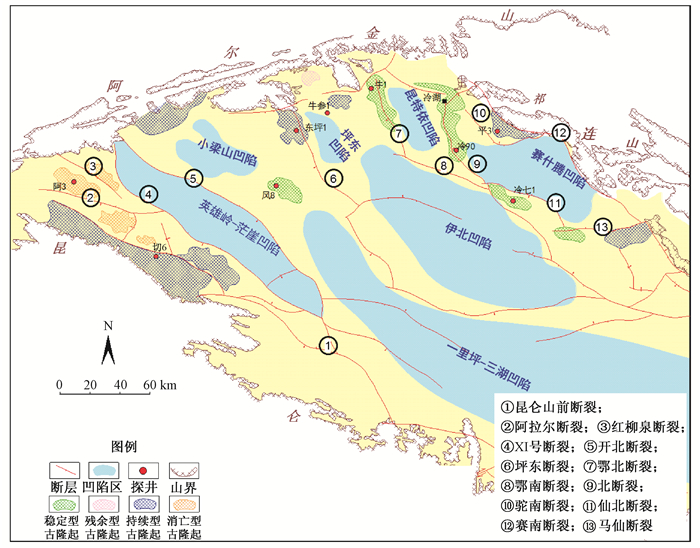
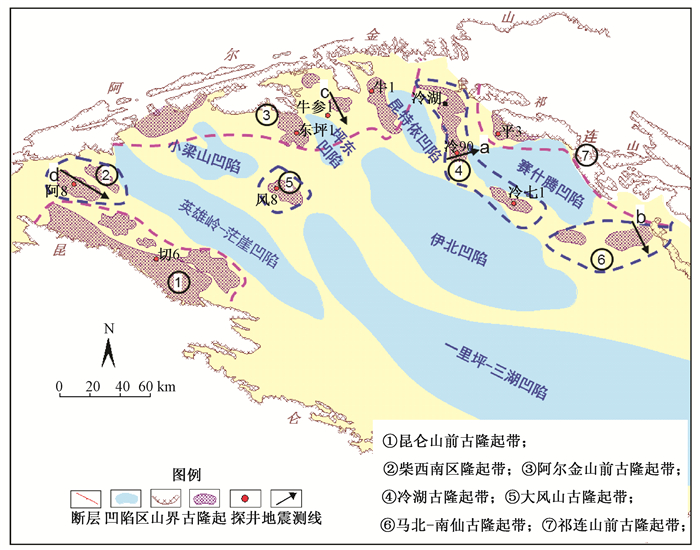
图 2 柴达木盆地不同类型古隆起地震剖面(测线位置见图 1地震测线)
E1+2—路乐河组;E31—下干柴沟组下段;E32—下干柴沟组上段;N1—上干柴沟组;N21—下油砂山组;N22—上油砂山组;N22—狮子沟组;Mz—中生界;NB1、L90、L92—探井名称a—稳定型古隆起,冷湖五号古隆起地震剖面;b—持续型古隆起,平台隆起构带造地震剖面;c—残余型古隆起,牛北2号构造地震剖面;d—消亡型古隆起,红柳泉斜坡地震剖面图 2
Figure 2. The seismic sections of different types of paleo-uplifts in the Qaidam Basin (The location of the measured line is shown in figure 1)
表 1 柴达木盆地不同类型古隆起成藏特征表
Table 1. Reservoir forming characteristics of different types of paleo-uplifts in the Qaidam Basin
古隆起类型 储集条件 盖层条件 圈闭类型 保存条件 成藏模式 稳定型古隆起 基岩风化壳储层较发育,上覆地层砂体发育 优越 基岩以构造圈闭为主,上覆地层发育断块圈闭、岩性圈闭等 浅层一般发育滑脱断层,保存条件一般 下生上储为主 持续型古隆起 基岩风化壳储层极为发育,上覆地层砂体极为发育 优越 基岩以构造圈闭为主,上覆地层发育构造圈闭、地层圈闭、岩性圈闭等 具有良好的保存条件 旁生侧储为主 残余型古隆起 风化壳储层不发育,基岩内幕储层较发育 差 构造圈闭为主 差 旁生侧储为主 消亡型古隆起 基岩风化壳储层较为发育 优越 基岩以构造圈闭为主,上覆地层发育岩性圈闭等 具有良好的保存条件 下生上储、旁生侧储 -
[1] 何登发, 李德生, 童晓光, 等.多期叠加盆地古隆起控油规律[J].石油学报, 2008, 29(4):475~488. doi: 10.7623/syxb200804001HE Dengfa, LI Desheng, TONG Xiaoguang, et al. Accumulation and distribution of oil and gas controlled by paleo-uplift in poly-history superimposed basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2008, 29(4):475~488. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7623/syxb200804001 [2] Allen P A, Allen J R. Basin analysis:principles and application to petroleum play assessment[M]. 3rd ed. Chichester:Wiley-Blackwell, 2013, 345~348. [3] 何登发, 周新源, 杨海军, 等.塔里木盆地克拉通内古隆起的成因机制与构造类型[J].地学前缘, 2008, 15(2):207~221. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98600X/200802/26712067.htmlHE Dengfa, ZHOU Xinyuan, YANG Haijun, et al. Formation mechanism and tectonic types of intracratonic paleo-uplifts in the Tarim basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(2):207~221. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98600X/200802/26712067.html [4] 何登发, 翟光明, 况军, 等.准噶尔盆地古隆起的分布与基本特征[J].地质科学, 2005, 40(2):248~261, 304. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200502009.htmHE Demgfa, ZHAI Guangming, KUANG Jun, et al. Distribution and tectonic features of paleo-uplifts in the Junggar Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2005, 40(2):248~261, 304. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200502009.htm [5] 何登发, 李德生.塔里木盆地构造演化与油气聚集[M].北京:地质出版社, 1996, 1~52.HE Dengfa, LI Desheng. Tectonic evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation in Tarim Basin[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1996, 1~52. (in Chinese) [6] 能源, 邬光辉, 黄少英, 等.再论塔里木盆地古隆起的形成期与主控因素[J].天然气工业, 2016, 36(4):27~34. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.04.004NENG Yuan, WU Guanghui, HUANG Shaoying, et al. Formation stage and controlling factors of the paleo-uplifts in the Tarim Basin:a further discussion[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(4):27~34. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.04.004 [7] 魏国齐, 杨威, 杜金虎, 等.四川盆地高石梯-磨溪古隆起构造特征及对特大型气田形成的控制作用[J].石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(3):257~265. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SKYK201503002.htmWEI Guoqi, YANG Wei, DU Jinhu, et al. Tectonic features of Gaoshiti-Moxi paleo-uplift and its controls on the formation of a giant gas field, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(3):257~265. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SKYK201503002.htm [8] 付锁堂.柴达木盆地天然气勘探领域[J].中国石油勘探, 2014, 19(4):1~10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201404001.htmFU Suotang. Natural gas exploration in Qaidam Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2014, 19(4):1~10. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201404001.htm [9] 隋凤贵, 林会喜, 赵乐强, 等.准噶尔盆地周缘隆起带油气成藏模式[J].新疆石油地质, 2015, 36(1):1~7. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93464X/201501/663902626.htmlSUI Fenggui, LIN Huixi, ZHAO Leqing, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation patterns in peripheral uplift belts of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2015, 36(1):1~7. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93464X/201501/663902626.html [10] 张林炎, 范昆, 黄臣军, 等.冀中坳陷深层油气成藏潜力与勘探方向[J].地质力学学报, 2011, 17(2):144~157. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20110204&journal_id=dzlxxbZHANG Linyan, FAN Kun, HUANG Chenjun, et al. Potential of the deep oil-gas reservoir-forming and exploitation direction in Jizhong depression[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2011, 17(2):144~157. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20110204&journal_id=dzlxxb [11] 庞雄奇, 罗晓容, 姜振学, 等.中国西部复杂叠合盆地油气成藏研究进展与问题[J].地球科学进展, 2007, 22(9):879~887. http://www.adearth.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1087.shtmlPANG Xiongqi, LUO Xiaorong, JIANG Zhenxue, et al. Advancements and problems on hydrocarbon accumulation research of complicated superimposed basins in Western China[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2007, 22(9):879~887. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.adearth.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1087.shtml [12] 卫平生, 郭彦如, 张景廉, 等.古隆起与大气田的关系——中国西部克拉通盆地与中亚卡拉库姆盆地天然气地质比较研究之一[J].天然气地球科学, 1998, 9(5):1~9. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.1998.05.1WEI Pingsheng, GUO Yanru, ZHANG Jinglian, et al. Relations between palaeo-uplifts and gian t gas fields:A comparative study on natural gas geology of the craton basin in West China and the Karakum Basin in Central Asia[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 1998, 9(5):1~9. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.1998.05.1 [13] 冉启贵, 陈发景, 张光亚.中国克拉通古隆起的形成、演化及与油气的关系[J].现代地质, 1997, 11(4):478~487. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201208013.htmRAN Qigui, CHEN Fajing, ZHANG Guangya. Formation and tectonic evolution of Cratonic palaeouplifts and its relation to hydrocarbon migration and accumulation in China[J]. Journal of Graduate School, China University of Geoscience, 1997, 11(4):478~487. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201208013.htm [14] 何碧竹, 焦存礼, 许志琴, 等.塔里木盆地显生宙古隆起的分布及迁移[J].地学前缘, 2015, 22(3):277~289. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200502009.htmHE Bizhu, JIAO Cunli, XU Zhiqin, et al. Distribution and migration of the Phanerozoic palaeo-uplifts in the Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(3):277~289. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200502009.htm [15] 何登发, 谢晓安.中国克拉通盆地中央古隆起与油气勘探[J].勘探家, 1997, 2(2):11~19. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90278X/1997002/2500563.htmlHE Dengfa, XIE Xiaoan. Petroleum exploration in central paleo uplifts of cratonic basins in China[J]. Petroleum Explorationist, 1997, 2(2):11~19. (in Chinese) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90278X/1997002/2500563.html [16] 孙龙德, 周新源, 王国林.塔里木盆地石油地质研究新进展和油气勘探主攻方向[J].地质科学, 2005, 40(2):167~178. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201205006.htmSUN Longde, ZHOU Xinyuan, WANG Guolin. Contributions of petroleum geology an d main directions of oil-gas exploration in the Tarim Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2005, 40(2):167~178. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201205006.htm [17] 杨跃明, 文龙, 罗冰, 等.四川盆地乐山-龙女寺古隆起震旦系天然气成藏特征[J].石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(2):179~188. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201602004.htmYANG Yueming, WEN Long, LUO Bing, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation of Sinian natural gas reservoirs, Leshan-Longnvsi paleohigh, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration & Development, 2016, 43(2):179~188. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201602004.htm [18] 汤显明, 惠斌耀.鄂尔多斯盆地中央古隆起与天然气聚集[J].石油与天然气地质, 1993, 14(1):64~71. doi: 10.11743/ogg19930109TANG Xianming, HUI Binyao. The central uplift of Ordos Basin and its gas accumulation[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1993, 14(1):64~71. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11743/ogg19930109 [19] 况军.准噶尔盆地古隆起与油气勘探方向[J].新疆石油地质, 2005, 26(5):502~509. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjsydz200505008KUANG Jun. Palaeohighs and targets for petroleum exploration in Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2005, 26(5):502~509. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjsydz200505008 [20] 付锁堂, 汪立群, 徐子远, 等.柴北缘深层气藏形成的地质条件及有利勘探区带[J].天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(6):841~846. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx200906002FU Suotang, WANG Liqun, XU Ziyuan, et al. Geological conditions of deep gas pools and their favorable prospects[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(6):841~846. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx200906002 [21] 付锁堂, 马达德, 汪立群, 等.柴达木盆地昆北冲断带古隆起油藏特征及油气成藏条件[J].石油学报, 2013, 34(4):675~682. doi: 10.7623/syxb201304007FU Suotang, MA Dade, WANG Liqun, et al. Characteristics and accumulation conditions of paleo-uplift reservoirs in Kunbei thrust belt, Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(4):675~682. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7623/syxb201304007 [22] 曹正林, 孙秀建, 汪立群, 等.柴达木盆地阿尔金山前东坪-牛东斜坡带天然气成藏条件[J].天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(6):1125~1131. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201306005.htmCAO Zhenglin, SUN Xiujian, WANG Liqun, et al. The gas accumulation conditions of Dongping-Niudong slope area in front of Aerjin Mountain of Qaidam Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(6):1125~1131. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201306005.htm [23] 袁苏杭, 付金华, 肖安成, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶纪中央古隆起水平迁移规律——来自于同沉积记录的证据[J].浙江大学学报(理学版), 2014, 41(1):100~107. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zjdxxb201401022YUAN Suhang, FU Jinhua, XIAO Ancheng, et al. Discussion of the horizontal migration of the Oradovician central Paleouplift in Ordos basin:evidence form the synsedimentary record[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition), 2014, 41(1):100~107. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zjdxxb201401022 [24] 邬光辉, 李启明, 肖中尧, 等.塔里木盆地古隆起演化特征及油气勘探[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 33(1):124~130. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/DGYK200901017.htmWU Guanghui, LI Qiming, XIAO Zhongyao, et al. The evolution characteristics of palaeo-uplifts in Tarim Basin and its exploration directions for oil and gas[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2009, 33(1):124~130. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/DGYK200901017.htm [25] 付锁堂, 张道伟, 薛建勤, 等.柴达木盆地致密油形成的地质条件及勘探潜力分析[J].沉积学报, 2013, 31(4):672~682. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/CJXB201304015.htmFU Suotang, ZHANG Daowei, XUE Jianqin, et al. Exploration potential and geological conditions of tight oil in the Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(4):672~682. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/CJXB201304015.htm [26] Wang Y D, Zheng J J, Zhang W L, et al. Cenozoic uplift of the Tibetan Plateau:evidence from the tectonic-sedimentary evolution of the western Qaidam Basin[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2012, 3(2):175~187. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=dd419e72b660ec26cb6661042d84ebf4&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [27] 毛黎光, 肖安成, 王亮, 等.柴达木盆地西北缘始新世晚期古隆起与阿尔金断裂的形成[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(8):2876~2882. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/download_pdf.aspx?file_no=20130823&year_id=2013&quarter_id=8&falg=1MAO Liguang, XIAO Ancheng, WANG Liang, et al. Uplift of NW margin of Qaidam Basin in the late Eocene:implications for the initiation of Altyn fault[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(8):2876~2882. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/download_pdf.aspx?file_no=20130823&year_id=2013&quarter_id=8&falg=1 [28] 刘永江, Neubauer F, 葛肖虹, 等.阿尔金断裂带年代学和阿尔金山隆升[J].地质科学, 2007, 42(1):134~146. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yongjiang_Liu/publication/288531072_Geochronology_of_the_Altun_Fault_Zone_and_rising_of_the_Altun_Mountains/links/577efe0708ae69ab8820f34a.pdf?origin=publication_listLIU Yongjiang, Neubauer F, GE Xiaohong, et al. Geochronology of the Altun fault zone and rising of the Altun mountains[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2007, 42(1):134~146. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yongjiang_Liu/publication/288531072_Geochronology_of_the_Altun_Fault_Zone_and_rising_of_the_Altun_Mountains/links/577efe0708ae69ab8820f34a.pdf?origin=publication_list -





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载: