THE APPLICATION OF GROUND PENETRATING RADAR TECHNOLOGY IN GEOLOGICAL MAPPING OF SHALLOW COVERED ACTIVE TECTONICS REGION:A CASE STUDY OF 1:50000 MAPPING OF NEOTECTONIC ZONE AND ACTIVE TECTONIC ZONE IN QING TONGXIA AREA, NINGXIA
-
摘要: 地质雷达探测以其分辨率高、定位准确、快速经济、灵活方便、剖面直观、实时图像显示等优点,成为地质调查中广泛使用的一种探测方法。本次宁夏青铜峡地区1:5万新构造与活动构造区填图中运用地质雷达探测技术对第四系和隐伏断层进行了探测。结果表明,40 MHz地质雷达可以有效地探测地表以下30 m内的第四系结构,可清晰地识别出3套第四纪地层。这一地层结构划分被第四系浅钻证实,其为第四系全新统灵武组,自下而上由泥岩、砂砾石层和含砾的砂或泥等3套地层组成。对测区主干断裂——柳木高断裂南段的地质雷达探测表明,断裂带表现为近地表发散向下汇聚的正花状结构,这与探槽揭露的特征一致,表明地质雷达探测可以准确标定隐伏断层平面位置与垂向精细结构。本次宁夏地质填图证实,地质雷达技术是浅覆盖活动构造区进行隐伏断裂调查和第四纪地层层序划分的可行、高效、便捷的技术方法之一。Abstract: Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) detectionisa widely-used detection method in geological survey owing to its advantages of high-resolution, accurate positioning, high speed, flexibility, convience, profile visualization, real-time image display and so on. GPR detection technology is applied to detect Quaternary system and blind faults in the mapping of 1:50000 shallow covered active tectonics zone of Qingtongxia, Ningxia. Detection results show that 40MHz GPR can effectively detect the quaternary system structure within 30 m below the surface, and 3 sets of Quaternary strata can be clearly defined. Drilling results confirm that Holocene Lingwu formation (Ql) from bottom to top is comprised of mudstone, gravel layer, and sand or mud with gravel. The radar image reveals that the south of the Liumugao fault of main fault has structural features of upward divergence and downward convergence with flower structure, which is consistent with the results of trench investigation.It shows that GPR can accurately demarcate the plane position and vertical detail structure of blind faults. This work indicates that GPR technology is feasible, effective and convenient for blind fault investigation and sequence division of the upper part of the Quaternary in shallow covered active tectonic zone.
-
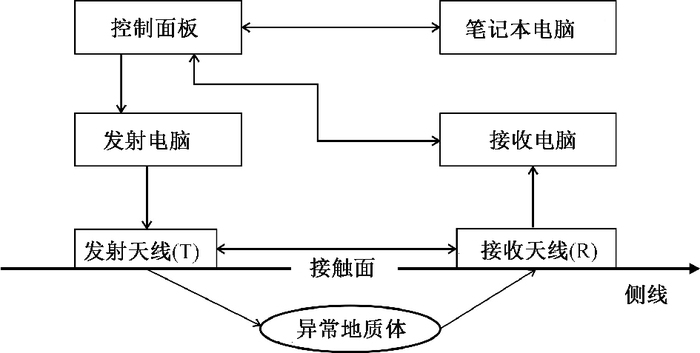
图 1 地质雷达系统结构[4]
Figure 1. Siructure of ground-penetrating radar
图 2 检测结果与实际对照图[4]
Figure 2. Test results VS. physical truth
图 3 反射探测原理图[4]
Figure 3. The diagram of reflection detection principle
表 1 不同频率天线的探测深度和分辨率[6]
Table 1. Different frequency antenna detecting depth VS. resolution
中心频率/MHz 探测深度/m 分辨率/cm 10 60 200 25 50 100 40 40 50 100 25 25 200~250 12 12.5 350~500 7 5 800 2.5 3 1000 1.5 2.5 1200~1600 1 1.5 2000~2500 0.5 0.8 表 2 宁夏地质填图使用的主要仪器设备
Table 2. The main instruments and equipments in geological mapping, Ningxia
序号 名称 型号 设备编号 1 地质雷达 RIS-K2型 06034 2 40MHz天线 TR 40 K2 AS 01366_A_00 3 手持式GPS -
[1] El-Said M A H. Geophysical prospection of underground water in the desert by means of electromagnetic interference fringes[J]. Proceedings of the IRE, 1956, 44(1):24~30. doi: 10.1109/JRPROC.1956.274846 [2] 王承强, 胡少伟, 周惠.地质雷达在环境工程中的应用和发展[J].地球与环境, 2005, 33(1):79~83. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ20050100C.htmWANG Cheng-qiang, HU Shao-wei, ZHOU Hui.Application and development of geologic radar in environmental engineering[J]. Earth and Environment, 2005, 33(1):79~83. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ20050100C.htm [3] 杜树春.地质雷达及其在环境地质中的应用[J].物探与化探, 1996, 20(5):384~392. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH605.011.htmDU Shu-chun. Geologic radar and its application in environmental geology[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 1996, 20(5):384~392. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH605.011.htm [4] 蒋焜.地质雷达及其在地质探测中的应用[J].工程质量, 2016, 34(2):18~20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCZL201602006.htmJIANG Kun.Geology radar and its application in geological exploration[J]. Construction Quality, 2016, 34(2):18~20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCZL201602006.htm [5] 宋晓明. PDA在路基施工检测数据处理中的应用研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2009.SONG Xiao-ming.Researches on PDA application in data processing of subgrade construction[D]. Chongqing:Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2009. [6] 何仲太.低频地质雷达在活断层探测的应用[J].地壳构造与地壳应力文集, 2013, 25:116~124. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEIS201300011.htmHE Zhong-tai. Low frequency application of Ground-penetrating radar to active fault detection[J]. Bulletin of the Institute of Crustal Dynamics, 2013, 25:116~124. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEIS201300011.htm [7] 白旸, 王乃昂, 何瑞霞, 等.巴丹吉林沙漠湖相沉积的探地雷达图像及光释光年代学证据[J].中国沙漠, 2011, 31(4):842~847.BAI Yang, WANG Nai-ang, HE Rui-xia, et al. Ground Penetrating Radar images and optically stimulated luminescence dating for lacustrine deposition of the Badain Jarandesert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2011, 31(4):842~847. [8] 赵文婷, 胡道功.东昆仑地质填图中北斗卫星定位系统应用研究[J].地质力学学报, 2012, 18(3):254~263. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120306&flag=1ZHAO Wen-ting, HU Dao-gong.The application of Beidou satellite positioning system in geological mapping in East Kunlun[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2012, 18(3):254~263. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120306&flag=1 [9] 晏华平.地下管线探测中地质雷达的应用[J].价值工程, 2016, 35(7):200~202. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZGC201607085.htmYAN Hua-ping.Application of the geological radar in detecting underground pipeline[J]. Value Engineering, 2016, 35(7):200~202. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZGC201607085.htm [10] Bristow C S, Jol H M. An introduction to ground penetrating radar (GPR) in sediments[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2003, 211(1):1~7. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2003.211 [11] 张彪.地下管线探测中地质雷达的运用[J].中华建设, 2014, (6):100~101. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJA201406044.htmZHANG Biao.The application of ground-penetrating radar in underground pipeline detection[J]. China Construction, 2014, (6):100~101. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJA201406044.htm [12] 薛建, 贾建秀, 黄航, 等.应用探地雷达探测活动断层[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2008, 38(2):347~350.XUE Jian, JIA Jian-xiu, HUANG Hang, et al. Application of GPR in active fault detection[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2008, 38(2):347~350. [13] 吴晔, 林彤.地质雷达在隧道超前地质预报中的应用[J].山西建筑, 2014, 40(21):178~181. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE2015S1034.htmWU Ye, LIN Tong. Application of ground penetrating radar to geological forecast for tunnel construction[J]. Shanxi Architecture, 2014, 40(21):178~181. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE2015S1034.htm [14] 田洪义.地质雷达(GPR)超前地质预报系统初步判释解译模型建立[J].四川建材, 2016, 42(1):254~255, 260. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCJZ201601125.htmTIAN Hong-yi.The establishment and theoretical research of GPR geological prediction preliminary interpretation model[J]. Sichuan Building Materials, 2016, 42(1):254~255, 260. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCJZ201601125.htm [15] Malik J N, Sahoo A K, Shah A A, et al. Ground-penetrating radar investigation along Pinjore Garden Fault:implication toward identification of shallow subsurface deformation along active fault, NW Himalaya[J]. Current Science, 2007, 93(10):1422~1427. [16] 薛腊梅, 赵希涛, 张耀玲, 等.遥感技术在东昆仑新生代地质填图中的应用[J].地质力学学报, 2010, 16(1):70~77. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100109&flag=1XUE La-mei, ZHAO Xi-tao, ZHANG Yao-ling, et al. Application of remote sensing technique in the mapping of Cenozoic geology of the east Kunlun mountains[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 16(1):70~77. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100109&flag=1 [17] 肖宏跃, 雷宛, 杨威.地质雷达特征图像与典型地质现象的对应关系[J].煤田地质与勘探, 2008, 36(4):57~61. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT200804016.htmXIAO Hong-yue, LEI Wan, YANG Wei.Correspondence between geological characteristics of radar images and typical geological phenomenon[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2008, 36(4):57~61. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT200804016.htm [18] 郭彬彬, 赵卫华, 王红才, 等.千灵山岩质边坡地质雷达探测及稳定性分析[J].地质力学学报, 2013, 19(1):104~112. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130111&flag=1GUO Bin-bin, ZHAO Wei-hua, WANG Hong-cai, et al. Geological radar survey and stability analysis of rock slope in Qianlingmountain[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2013, 19(1):104~112. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130111&flag=1 [19] 施炜, 刘源, 刘洋, 等.青藏高原东北缘海原断裂带新生代构造演化[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(4):1~17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304003.htmSHI Wei, LIU Yuan, LIU Yang, et al. Cenozoic evolution of the Haiyuan fault zone in the northeast margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4):1~17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304003.htm [20] 陈虹, 胡健民, 公王斌, 等.青藏高原东北缘牛首山-罗山断裂带新生代构造变形与演化[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(4):18~35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304004.htmCHEN Hong, HU Jian-min, GONG Wang-bin, et al. Cenozoic deformation and evolution of the Niushou Shan Luo Shan fault zone in the northeast margin of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4):18~35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304004.htm [21] 公王斌, 施炜, 陈虹, 等.牛首山-罗山断裂带北段柳木高断裂第四纪活动特征[J].地质力学学报, 2016, 22(4):1004~1014. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160418&flag=1GONG Wang-bin, SHI Wei, CHEN Hong, et al. Quaternary active characteristics of the Liumugao fault in the northern segment of the Niushoushan-Luoshanfault[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 22(4):1004~1014. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160418&flag=1 -





 下载:
下载: