FORMATION CONDITIONS AND SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF GEO-HAZARDS IN SOUTHERN URBAN AGGLOMERATION OF CHENGDU-CHONGQING ECONOMIC ZONE
-
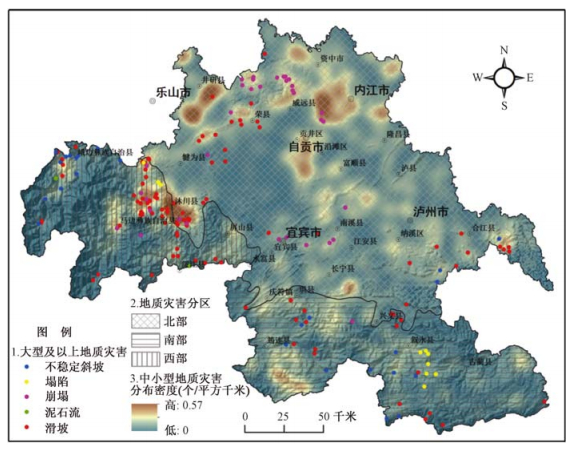
摘要: 通过资料分析与实地调查相结合,对成渝经济区南部城市群孕灾条件和地质灾害空间分布特征进行了区域对比分析。研究结果表明,城市群由南而北、自西向东在地形地貌、地质构造、地层岩性等孕灾地质背景及降雨、地震活动、人类工程活动等诱发因素方面均有明显不同,进而导致地质灾害空间分布及发育特征的差异。西部中高山峡谷区地层岩性及地质构造极为复杂,地形起伏大,活动断裂发育且地震活动较为频繁,地质灾害具有规模大、泥石流相对发育、沿构造线和河流线状分布的特点;南部低中山及岩溶发育区地形起伏较大,地质构造及岩性较复杂,碳酸盐岩极为发育,采矿活动强烈,以地面塌陷相对发育为主要特点;北部红层丘陵区地质构造及岩性简单,地形起伏小,人类工程活动强烈,地质灾害类型单一、数量多、规模小,分布上具有面上松散分布、局部相对集中的特点。Abstract: Based on the data analysis and field investigation, the spatial distribution characteristics of geological hazards in the south urban agglomeration of Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone are compared and analyzed. Study result shows that both of the formation conditions (topography, geological structure, lithology) and triggering condition (rainfall, seismic activity, human engineering activities) vary significantly from south to north, from west to East, leading to great difference of spatial distribution and characteristics of geological hazards. In the west part, the formation factors such as lithology and geological structure are very complex, the topography undulates greatly, and the seismic activity is frequent. As a result, the geological hazards take on the characteristics of larger magnitude, more debris flows, and linear distribution along the river and tectonic. In the south part, due to the wide distribution of carbonate rocks and intense mining activity, ground collapse becomes the main type of geological hazard. As far as the north part is concerned, the geological and lithology are simple and the terrain is flat, but the human engineering activities are the most intense of the urban agglomeration of south Sichuan Province, simpler type, larger quantity, smaller scale, wide distribution compose the main features of the geological hazards in this part.
-
图 8 芙蓉山崩塌碎屑流素描图(据李云贵等[12],2004)
Figure 8. Sketch of Furongshan rock-fall and debris flow
表 1 南部城市群地质灾害类型与规模统计表
Table 1. Type and magnitude of geological hazards
规模 滑坡 崩塌 泥石流 不稳定斜坡 地面塌陷 合计 特大型 6 0 0 0 0 6 大型 99 35 2 26 10 172 中型 395 153 2 99 12 661 小型 1738 992 32 296 114 3172 合计 2238 1180 36 421 136 4011 表 2 西部中高山峡谷区地质灾害发育特征
Table 2. Characteristics of geo-hazards in western middle and high mountain canyon area
规模 滑坡 崩塌 不稳定斜坡 地面塌陷 泥石流 小计(处)/密度(处/100 km2) 特大型 6 0 0 0 0 6/0.08 大型 41 6 12 3 2 64/0.84 中型 130 17 16 6 2 171/2.25 小型 254 43 12 3 23 335/4.41 小计(处)/密度(处/100 km2) 431/5.67 66/0.87 40/0.53 12/0.16 27/0.36 576/7.58 表 3 南部低中山及岩溶发育区地质灾害发育特征
Table 3. Characteristics of geo-hazards in southern karst development area
规模 滑坡 崩塌 不稳定斜坡 地面塌陷 泥石流 小计(处)/密度(处/100 km2) 特大型 0 大型 18 1 10 7 0 36/0.34 中型 41 10 37 5 0 93/0.88 小型 355 130 43 84 8 620/5.87 小计(处)/密度(处/100 km2) 414/3.92 141/1.34 90/0.85 96/0.91 8/0.08 749/7.09 表 4 北部红层丘陵区地质灾害发育特征
Table 4. Characteristics of geohazards in northern red layer and hilly areas
规模 滑坡 崩塌 不稳定斜坡 地面塌陷 泥石流 小计(处)/密度(处/100 km2) 特大型 大型 40 28 4 72/0.28 中型 224 126 46 1 397/1.56 小型 1129 819 241 27 1 2217/8.69 小计(处)/密度(处/100 km2) 1393/5.46 973/3.82 291/1.14 28/0.11 1/0.004 2686/10.53 -
[1] 严福章, 袁兆祥, 盛大凯.500kV二滩-自贡输电线路地质灾害及防治之启示[J].电力建设, 2010, 31(5):26~29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLJS201005008.htmYAN Fu-zhang, YUAN Zhao-xiang, SHENG Da-kai. Geo-hazard and prevention for Ertan-Zigong 500kV transmission lines[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2010, 31(5):26~29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLJS201005008.htm [2] 许向宁, 黄润秋.金沙江水电工程区(宜宾-白鹤滩段)岸坡变形破坏特征及其与赋存环境的相关性[J].地球科学进展, 2004, 19(增刊):211~216. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ2004S1041.htmXU Xiang-ning, HUANG Runqiu. The features of deformation and failure on bank slopes and the pertinence on its environmental effect in hydroeijectric development zone[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2004, 19(Supp.):211~216. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ2004S1041.htm [3] 康小兵, 潘国耀.泸盐路宜宾至南溪段地质灾害危险性评估[J].水土保持研究, 2008, 15(1):216~222. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY200801062.htmKANG Xiao-bing, PAN Guo-yao. Risk evaluation of geological disaster for Luyan Road from Yibin to Nanxi[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2008, 15(1):216~222. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY200801062.htm [4] 彭鑫.泸州某工程边坡稳定性分析及防治措施[J].成都大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 32(4):416~418. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDDD201304025.htmPENG Xin. Stability analysis and prevention measures of engineering slope in Luzhou[J]. Journal of Chengdu University:Natural Science Edition, 2013, 32(4):416~418. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDDD201304025.htm [5] 徐争强, 杨秋梅, 张成江, 等.论四川自贡市的城市地质环境[J].四川地质学报, 2008, 28(4):313~315. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB200804014.htmXU Zheng-qiang, YANG Qiu-mei, ZHANG Cheng-jiang, et al. On urban geological environment in Zigong City[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2008, 28(4):313~315. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB200804014.htm [6] 周皎, 张成, 江王茜, 等.四川内江市地质灾害危险性分区评价[J].地质学报, 2009, 29(1):62~65. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB200901018.htmZHOU Jiao, ZHANG Cheng, JIANG Wang-qian, et al. Assessment of division of danger of geological hazards in the Neijiang region, Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 29(1):62~65. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB200901018.htm [7] 朱洪林, 唐小平, 马和平, 等.四川内江-宜宾高速公路两滑坡的成因分析与治理[J].地质灾害与环境保护, 2000, 11(3):242~244. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZHB200003010.htmZHU Hong-lin, TANG Xiao-ping, MA He-ping, et al. The genesis analysis and controlling of two landslides of Neijiang-Yibin express way[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2000, 11(3):242~244. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZHB200003010.htm [8] 樊建利, 李天斌.四川省内江市东兴区地质灾害发育特征及控制因素分析[J].中国地质灾害及防治学报, 2007, 18(4):24~28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200704010.htmFAN Jian-li, LI Tian-bin. The developing features and controlling factors of geological hazards in Dongxing District of Neijiang City, Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2007, 18(4):24~28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200704010.htm [9] 张世民, 聂高众, 刘旭东, 等.荥经-马边-盐津逆冲构造带运动组合及地震分段特征[J].地震地质, 2005, 27(2):221~233. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200502004.htmZHANG Shi-min, NIE Gao-zhong, LIU Xu-dong, et al. Kinematical and structural patterns of Yingjing-Mabian-Yanjin thrust fault zone, southeast of Tibetan Plateau, and its segmentation from earthquakes[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2005, 27(2):221~233. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200502004.htm [10] 彭云金, 吕加蓉.荥经-马边-盐津断裂带新活动特征分析[J].四川地震, 2004, (3):34~36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHZ200403006.htmPENG Yun-jin, LÜ Jia-rong. Consideration about the neo-active feature of Yingjing-Mabian-Yanjin fault zone[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan, 2004, (3):34~36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHZ200403006.htm [11] 巴仁基, 王丽, 郑万模, 等.大渡河流域地质灾害特征与分布规律[J].成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2011, 38(5):529~537. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201105010.htmBA Ren-ji, WANG Li, ZHENG Wan-mo, et al. Characteristics and distribution of the geology disasters of the Dadu River in Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology:Science & Technology Edition, 2011, 38(5):529~537. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201105010.htm [12] 李云贵, 钟沛林, 杨昶, 等.四川省矿山地质环境综合调查与评估成果报告[R].成都:四川省地质环境监测总站, 2004:40~42.LI Yun-gui, ZHONG Pei-lin, YANG Chang, et al. Comprehensive investigation and evaluation of mine geological environment in Sichuan Province[R]. Chengdu:Geo-environmental Monitoring Station of Sichuan Province, 2004:40~42. [13] 杨宗才, 张俊云, 周德培.红层泥岩边坡快速风化特性研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(2):275~283. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200602009.htmYANG Zong-cai, ZHANG Jun-yun, ZHOU De-pei. Study on fast weathering characteristics of red bed mudstone slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(2):275~283. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200602009.htm [14] 李保雄, 苗天德.红层软岩滑坡运移机制[J].兰州大学学报:自然科学版, 2004, 40(3):95~98. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK200403020.htmLI Bao-xiong, MIA0 Tian-de. The sliding mechanism of red-mudstone layer landslide[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University:Natural Sciences, 2004, 40(3):95~98. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK200403020.htm -





 下载:
下载: