DISCUSSION ON GEOLOGICAL HAZARDS AND MAJOR ENGINEERING GEOLOGICAL PROBLEMS IN THE MIDDLE PART OF THE NORTH-SOUTH ACTIVE TECTONIC ZONE, CHINA
-
摘要: 甘肃天水等城镇和成兰交通廊道位于青藏高原东缘南北活动构造带中段,是中国东西部地质、地貌边界带,断裂活动性强,地震活动频繁。本文在区内地质资料收集分析和野外地质调查的基础上,从活动断裂、浅表层地质灾害、深埋隧道重大工程地质问题等角度,分析了甘肃天水等城镇和成兰交通廊道规划建设过程中可能遇到的工程地质问题,认为:研究区内对成兰铁路和甘肃天水等城镇具有重大影响的活动断裂带主要有15条,并对区域构造应力场具有重要影响,具有强震诱发背景;研究区内地质灾害极为发育,主要包括崩塌、滑坡和泥石流,地质灾害的发育分布受强降雨、地震和活动断裂影响大,并发育一系列古地震滑坡,部分崩塌和滑坡方量大,具有高位、高速远程等特征,已严重制约着城镇、铁路、公路等地面工程建设,危害严重;研究区内深埋长大隧道多且工程地质问题复杂,已经遇到并严重受高地应力、软岩大变形、涌水突泥和高地温等重大工程地质问题的影响,同时还存在活动断裂断错效应对深埋隧道和桥梁等重要工程设施的长期影响。针对上述工程地质问题,深入探讨了其发育分布规律,并提出了调查研究途径和解决办法,对区内重要城镇、重大工程规划建设具有一定的借鉴意义。Abstract: The area of Tianshui cities group, Gansu, and the Chengdu-Lanzhou traffic corridors are located in the middle of the north-south active seismic belt, eastern Tibetan Plateau. The study area is a geological and geomorphic boundary zone between the eastern and western China, with strong tectonic activities and frequent earthquakes. Based on the analysis of geological data and field geological survey, focusing on active faults, shallow geological hazards and engineering geological problems of deep-buried tunnels, the engineering geological problems which would be encountered during the construction of the Tianshui cities group and the Chengdu-Lanzhou traffic corridors were summarized in this article. The results show that, there are 15 active faults with great significance to the seismic and regional tectonic stress field. The geological hazards are well developed in this area, including collapses, landslides and debris flows, and they are seriously affected by heavy rainfalls, earthquakes and active faults. Also, there are a series of ancient earthquakes-induced landslides. Some of the collapses and landslides are in large size group and with high position, long-runout and other characteristics, with serious harm, and they could seriously affected the construction of cities, towns, railways, highways and other surface construction. There are some long and deep-buried tunnels in the study area and with serious engineering geological problems, such as high geo-stress, large deformation of soft rock, gushing water and high ground temperature, and other major engineering geological problems, and there are potential existence of fault breaking along the active faults to the deep-buried tunnels, important bridges and other engineering facilities. At last, The methods to solve the above-mentioned engineering geological problems and some solutions are suggested.
-
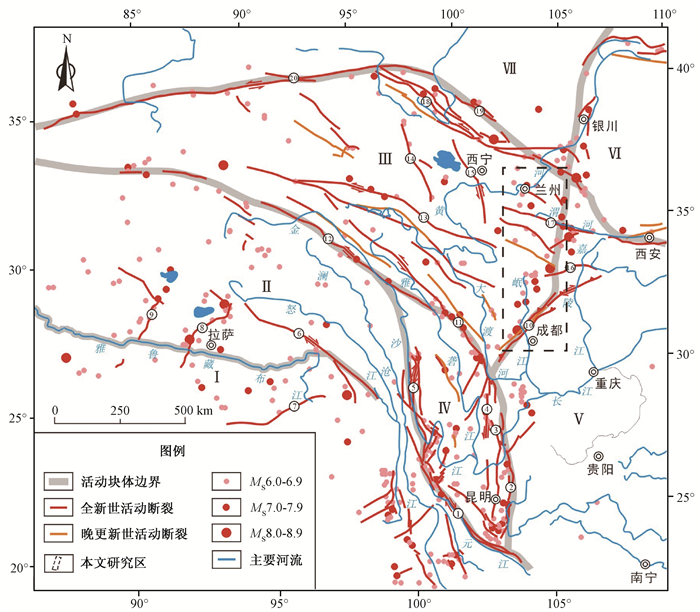
图 1 研究区构造位置图
Ⅰ-喜马拉雅区;Ⅱ-西藏块体;Ⅲ-甘青块体;Ⅳ-川滇块体;Ⅴ-华南地块;Ⅵ-鄂尔多斯地块;Ⅶ-塔里木块体;1-红河断裂;2-小江断裂;3-则木河断裂;4-安宁河断裂;5-金沙江断裂;6-嘉黎断裂带;7-喜马拉雅南麓主山断裂带;8-亚东-谷露断裂;9-甲岗定结断裂带;10-龙门山断裂带;11-鲜水河断裂;12-玉树断裂;13-东昆仑断裂带;14-鄂拉山断裂;15-日月山断裂;16-文县断裂;17-西秦岭北缘断裂;18-海原断裂带;19-龙首山断裂;20-阿尔金断裂带
Figure 1. Tectonic structure and location map of the study area
表 1 甘肃天水等城镇和成兰交通廊道沿线及邻区重要活动断裂特征与活动性一览表
Table 1. Characteristics and activity of important active faults in the study area and adjacent areas
编号 断裂名称及断裂分段特征 活动性质 活动时代 活动速率(VH-水平活动速率,Vv-垂直活动速率,mm/a) 与铁路或重点城镇的关系 1 龙门山前山断裂 江油-灌县断裂 逆冲兼右旋走滑 Q3~Q4 VH=5.0±,Vv≤0.5 与成兰铁路大角度相交 江油-广元断裂 右旋走滑/逆冲 Q1~Q2 VH=1.54 与兰渝铁路大角度相交 2 龙门山中央断裂 北川-映秀断裂 逆冲兼右旋走滑 Q3~Q4 VH=2.0~3.0,Vv=1.0± 与成兰铁路近于直交 茶坝-林庵寺断裂 南段走滑,北段逆冲 南段Q4,北段Q1-2 VH=1.0-5.0,Vv≤1.0 3 龙门山后山断裂 耿达-陇东断裂 逆冲兼右旋走滑 Q3~Q4 茂县-汶川断裂 右旋走滑/逆冲 Q4 VH=1.4±,Vv=0.5-0.9 与成兰铁路近于直交 平武-青川断裂 逆冲兼右旋走滑 Q3 VH=1.0±,Vv=0.5-0.7 4 岷江断裂 左旋走滑,走滑 Q4 VH≤0.2,Vv=0.37~0.53 与成兰铁路平行展布,与成兰铁路多次斜交 5 虎牙断裂 逆冲兼左旋走滑 Q4 VH=1.4~2.55,Vv=0.3~0.5 6 雪山梁子断裂 右旋走滑 Q3 与成兰铁路近于直交 7 龙日坝断裂 右旋兼逆断 Q4 VH=1~2,Vv=0.7 8 哈南-稻畦子断裂 左旋走滑兼逆冲 Q4 9 塔藏断裂 左旋走滑 Q4 VH=3.2~3.6,Vv=0.5~0.7 与成兰铁路大角度相交 10 迭部-白龙江断裂 左旋走滑兼逆冲 Q3~Q4 VH=5.0±,Vv=0.2~0.3 与成兰铁路近于直交 11 光盖山-迭山断裂 左旋走滑兼逆断 Q4 VH=0.51±0.13,Vv=0.49~1.15 与成兰铁路近于直交 12 临潭-宕昌断裂 左旋走滑兼逆冲 Q3~Q4 VH=2.0~2.5 与成兰铁路近于直交 13 礼县-罗家堡断裂 左旋兼正断 Q4 VH=0.64~1.25,Vv=0.24~0.47 穿越礼县县城 14 西秦岭北缘断裂 天水-凤凰山断裂 左旋兼正断 Q3~Q4 VH=2.1~2.8,Vv=0.4~0.7 穿越天水市区 甘谷-武山断裂 左旋走滑 Q4 VH=2.8 穿越甘谷县 漳县断裂 左旋走滑 Q4 VH=2.5 影响漳县和武山县 黄香沟断裂 左旋走滑兼正断 Q4 VH=2.3±0.2,Vv=0.28±0.08 与成兰铁路近于直交 15 马衔山断裂 左旋走滑 Q4 VH=2.5~3.0, 与成兰铁路大角度相交 -
[1] 王思敬.地球内外动力耦合作用与重大地质灾害的成因初探[J].工程地质学报, 2002, 10(2):115~117. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb200202001WANG Sijing. Coupling of earth's endogenic and exogenic geological processes and origins on serious geological disasters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2002, 10(2):115~117. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb200202001 [2] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(3):433~454. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb200703001HUANG Runqiu. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in china since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(3):433~454. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb200703001 [3] 黄润秋, 李为乐. "5.12"汶川大地震触发地质灾害的发育分布规律研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(12):2585~2592. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.028HUANG Runqiu, LI Weile. Research on development and distribution rules of geohazards induced by Wenchuan earthquake on 12th May, 2008[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(12):2585~2592. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.028 [4] 殷跃平.汶川八级地震地质灾害研究[J].工程地质学报, 2008, 16(4):433~444. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb200804001YIN Yueping. Researches on the geo-hazards triggered by Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2008, 16(4):433~444. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb200804001 [5] 张永双, 石菊松, 孙萍, 等.汶川地震内外动力耦合及灾害实例[J].地质力学学报, 2009, 15(2):131~141. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090203&flag=1ZHANG Yongshuang, SHI Jusong, SUN Ping, et al. Coupling between endogenic and exogenic geological processes in the Wenchuan earthquake and example analysis of geo-hazards[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 15(2):131~141. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090203&flag=1 [6] 石文慧.当代铁路隧道发展趋势及地质灾害防治[J].铁道工程学报, 1996, (2):55~62. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/291452SHI Wenhui. Development trend of contemporary railway tunnel and its geological hazard control[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 1996, (2):55~62. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/291452 [7] 陆玉珑.南昆铁路的工程地质与实践[J].工程地质学报, 1997, 5(2):97~103. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/291018LU Yulong. Engineering geology and practice on Nankun railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 1997, 5(2):97~103. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/291018 [8] 蒋忠信.南昆铁路地质灾害与防治[J].铁道工程学报, 2001, (1):83~88. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tdgcxb200101023JIANG Zhongxin. Geological hazards and control in Nanning-Kunming railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2001, (1):83~88. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tdgcxb200101023 [9] 胡小兵. 隧道逃生用波纹钢管力学性能分析及应用研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2016: 1~10.HU Xiaobing. Mechanical analysis and application of escape corrugated steel pipe in tunnel[D]. Chongqing:Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2016:1~10. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 杜宇本, 袁传保, 王彦东, 等.成兰铁路主要地质灾害与地质选线[J].铁道工程学报, 2012, (8):11~15. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tdgcxb201208003DU Yuben, YUAN Chuanbao, WANG Yandong, et al. Major geological hazard and geological alignment of Chengdu-Lanzhou Railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2012, (8):11~15. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tdgcxb201208003 [11] 李勇, 周荣军, Densmore A L, 等.青藏高原东缘龙门山晚新生代走滑-逆冲作用的地貌标志[J].第四纪研究, 2006, 26(1):40~51. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj200601006LI Yong, ZHOU Rongjun, Desmore A L, et al. Geomorphic evidence for the Late Cenozoic strike-slipping and thrusting in Longmen mountain at the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(1):40~51. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj200601006 [12] Kirby E, Reiners P W, Krol M A, et al. Late Cenozoic evolution of the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau:inferences from 40Ar/39Ar and (U-Th)/He thermochronology[J]. Tectonics, 2002, 21(1):1001. doi: 10.1029/2000TC001246/pdf [13] Zhang P Z, Shen Z, Wang M, et al. Continuous deformation of the Tibetan Plateau from global positioning system data[J]. Geology, 2004, 32(9):809~812. doi: 10.1130/G20554.1 [14] Burchfiel B C, Royden L H, Van Der Hilst R D, et al. A geological and geophysical context for the Wenchuan earthquake of 12 May 2008. Sichuan, People's Republic of China[J]. GSA Today, 2008, 18(7):4~11. doi: 10.1130/GSATG18A.1 [15] 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 叶建青, 等.汶川Ms 8.0地震地表破裂带及其发震构造[J].地震地质, 2008, 30(3):597~629. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzdz200803003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQXU Xiwei, WEN Xueze, YE Jianqing, et al. The Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake surface ruptures and its seismogenic structure[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2008, 30(3):597~629. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzdz200803003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [16] 周荣军, 黄润秋, 雷建成, 等.四川汶川8.0级地震地表破裂与震害特点[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(11):2173~2183. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.11.002ZHOU Rongjun, HUANG Runqiu, LEI Jiancheng, et al. Surface rupture and hazard characteristics of Wenchuan earthquake with magnitude 8.0 in Sichuan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(11):2173~2183. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.11.002 [17] 康来迅.西秦岭北缘断裂带晚更新世晚期以来断裂运动的基本特征及运动机理[J].中国地震, 1990, 6(3):53~61. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zgzd199003006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQKANG Laixun. A study on movement characteristics and mechanism of the fault zone along the north edge of west Qinling mountains since Late Epipleistocene Epoch[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 1990, 6(3):53~61. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zgzd199003006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [18] 陈长云, 贺建明.西秦岭北缘断裂分段运动变形特征分析[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 2016, 36(9):784~788. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dkxb201609007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQCHEN Changyun, HE Jianming. Analysis of the motion and deformation characteristics of subordinary segments of the west Qinling fault[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2016, 36(9):784~788. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dkxb201609007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [19] 吴玮江.天水市滑坡泥石流灾害[J].水文地质工程地质, 2003, 30(5):75~78. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swdzgcdz200305017WU Weijiang. Landslide and debris flow hazards in city of Tianshui[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2003, 30(5):75~78. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swdzgcdz200305017 [20] 黄晓, 杨为民, 张春山, 等.舟曲泄流坡滑坡变形特征及其形成机理[J].地质力学学报, 2013, 19(2):178~187. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130207&flag=1HUANG Xiao, YANG Weimin, ZHANG Chunshan, et al. Deformation characteristics and formation mechanism of Xieliupo landslide in Zhouqu[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2013, 19(2):178~187. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130207&flag=1 [21] 薛振勇, 侯书云.人类活动诱发的地质灾害——天水锻压机床厂滑坡[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 1991, 2(4):52~60. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zgdh199104006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQXUE Zhenyong, HOU Shuyun. The geological hazard induced by human activity:The landslide in Tianshui forging & pressing machine tool factory[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1991, 2(4):52~60. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zgdh199104006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [22] 田尤, 杨为民, 刘廷, 等.天水锻压机床厂滑坡变形破坏机制及形成演化[J].地质力学学报, 2015, 21(2):298~308. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150220&flag=1TIAN You, YANG Weimin, LIU Ting, et al. Deformation mechanism and evolutionary process of the Tianshui forging machine plant landslide in Gansu[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2015, 21(2):298~308. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150220&flag=1 [23] 张永双, 苏生瑞, 吴树仁, 等.强震区断裂活动与大型滑坡关系研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2011, 30( http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yslx2011s2020&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQS2):3503~3513. ZHANG Yongshuang, SU Shengrui, WU Shuren, et al. Research on relationship between fault movement and large-scale landslide in intensive earthquake region[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(S2):3503~3513. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yslx2011s2020&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [24] 王涛.南北活动构造带地震滑坡危险性评估服务山区城镇规划减灾[J].中国地质调查成果快讯, 2016, 2(15/16):1~4. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yslx2011s2020&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQWANG Tao. Multi-scale potential seismic landslide hazard assessment supports urban planning and disaster mitigation in mountainous area along SN-trending active tectonic belt[J]. News Letters of China Geological Survey, 2016, 2(15/16):1~4. (in Chinese) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yslx2011s2020&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [25] Sun P, Shao T Q, Shi J S, et al. Giant landslides triggered by the 1718 Tongwei earthquake in Pan'an, Gansu Province, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2015, 89(1):309~310. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12417 [26] 田颖颖. 2013年甘肃省岷县地震滑坡空间分布规律及几何特征分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016: 1~60.TIAN Yingying. Spatial distribution and geometrical characteristic of landslides related to the 2013 Minxian earthquake of Gansu Province[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2016:1~60. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] 许冲, 徐锡伟, 郑文俊, 等. 2013年甘肃岷县漳县6.6级地震触发滑坡及其构造分析[J].地震地质, 2013, 35(3):616~626. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdz201303015XU Chong, XU Xiwei, ZHENG Wenjun, et al. Landslides triggered by the 2013 Minxian-Zhangxian, Gansu Province Ms 6.6 earthquake and its tectonic analyses[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2013, 35(3):616~626. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdz201303015 [28] 王兰生, 杨立铮, 李天斌, 等.四川岷江叠溪较场地震滑坡及环境保护[J].地质灾害与环境保护, 2000, 11(3):195~199. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzzhyhjbh200003001WANG Lansheng, YANG Lizheng, LI Tianbin, et al. Evolution mechanism of Jiaochang earthquake landslide on Ming River and its controlling[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2000, 11(3):195~199. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzzhyhjbh200003001 [29] 曹廷. 西南某铁路高烈度地震山区地质选线研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2012.CAO Ting. Geological route selection of railway along high seismic moutain region in southwest China[D]. Chengdu:Southwest Jiaotong, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30] 杨甲奇.成兰铁路槽木沟泥石流的形成机制研究[J].公路交通科技, 2015, (8):267~269. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gljj201508096&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQYANG Jiaqi. Study on the forming mechanism of Caomugou debris flow alone Chengdu-Lanzhou railway[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2015, (8):267~269. (in Chinese) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gljj201508096&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [31] 张永双, 胡道功, 吴中海, 等.滇藏铁路沿线地壳稳定性及重大工程地质问题[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009.ZHANG Yongshuang, HU Daogong, WU Zhonghai, et al. Research on the crustal stabilty and key engineering geological problems along the Yunnan-Tibet railway[M]. Beijing:Geosciences Press, 2009. (in Chinese) [32] 张鹏.活动断裂调查与地应力测量技术服务兰渝铁路长隧道优化设计[J].中国地质调查成果快讯, 2015, (39/40):47~49. http://www.academia.edu/3882403/Technical_Report_on_Brick_masonry_StructuresZHANG Peng. Active faults investigation and in-situ geo-stress measuring serve optimum designing of long tunnel in Lanzhou-Chongqing Railway[J]. News Letters of China Geological Survey, 2016, (39/40):47~49. (in Chinese) http://www.academia.edu/3882403/Technical_Report_on_Brick_masonry_Structures [33] 何玉林. 青藏高原东缘主干断裂活动性及其构造变形模式研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2013.HE Yulin. Study on the main fault activities and tectonic deformation tectonics in the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34] 袁传保, 宋章.成兰铁路地应力分布特征及工程评价[J].建筑技术开发, 2014, 41(7):16~22. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jzjskf201407005YUAN Chuanbao, SONG Zhang. Distribution characteristics and project appraisal of crustal stress for Chengdu-Lanzhou railway[J]. Building Technique Development, 2014, 41(7):16~22. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jzjskf201407005 [35] 宋章, 蒋良文, 杜宇本, 等.成兰铁路软岩隧道大变形特征及成因机制探析[J].工程地质学报, 2016, 24( http://www.gcdz.org/CN/abstract/abstract12062.shtmlS):11~16. SONG Zhang, JIANG Liangwen, DU Yuben, et al. Analysis on characteristic and formation mechanism of larger deformation for the tunnel of Chengdu-Lanzhou railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(S):11~16. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.gcdz.org/CN/abstract/abstract12062.shtml [36] 周宝春.成兰铁路柿子园隧道4号横洞挤压性围岩大变形施工技术[J].路基工程, 2016, (3):232~236. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ljgc201603048ZHOU Baochun. Construction technology for squeezed surrounding rock deformation of No.4 transverse gallery of Shiziyuan tunnel of Chengdu-Lanzhou Railway[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2016, (3):232~236. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ljgc201603048 -





 下载:
下载: