IN-SITU MEASUREMENTS IN THE SOUTHERN MARGIN OF THE ORDOS BLOCK
-
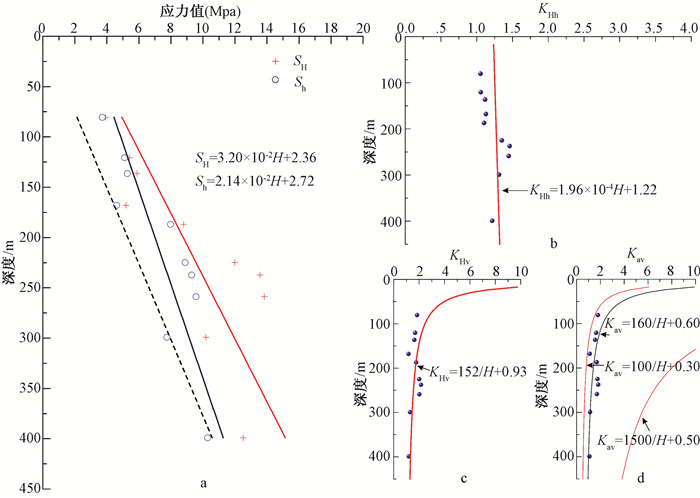
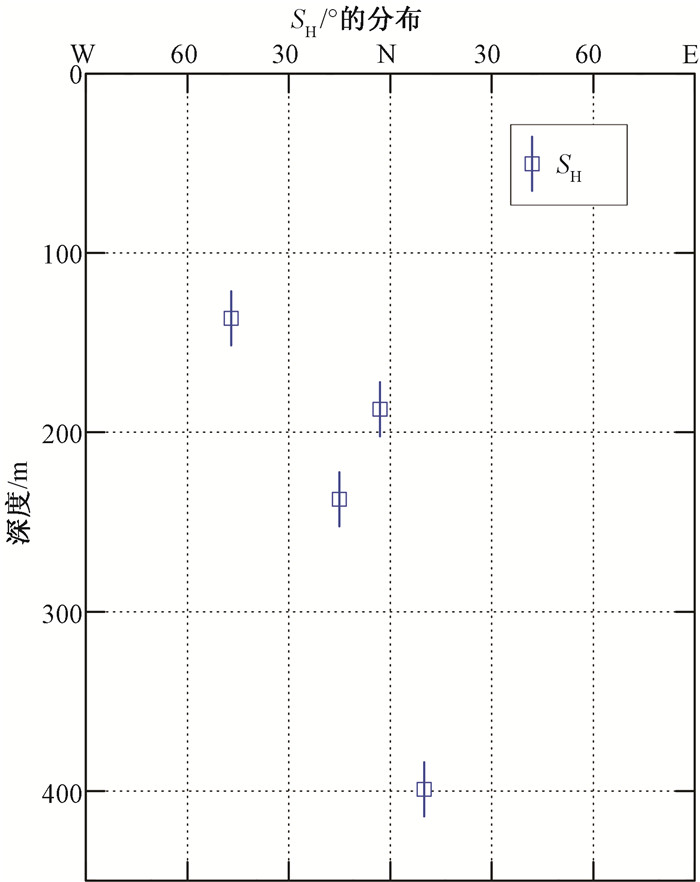
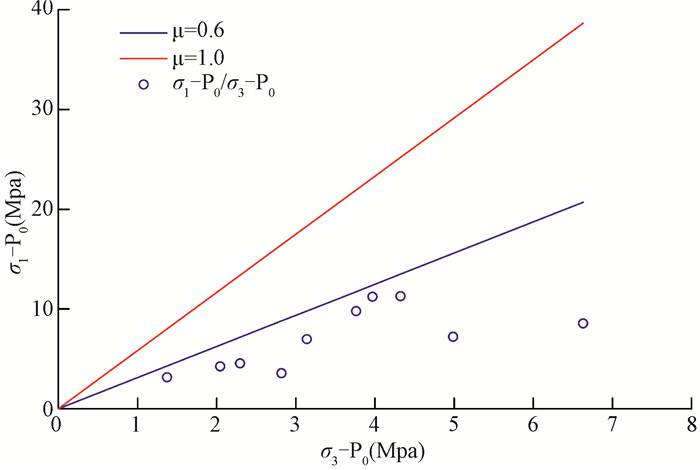
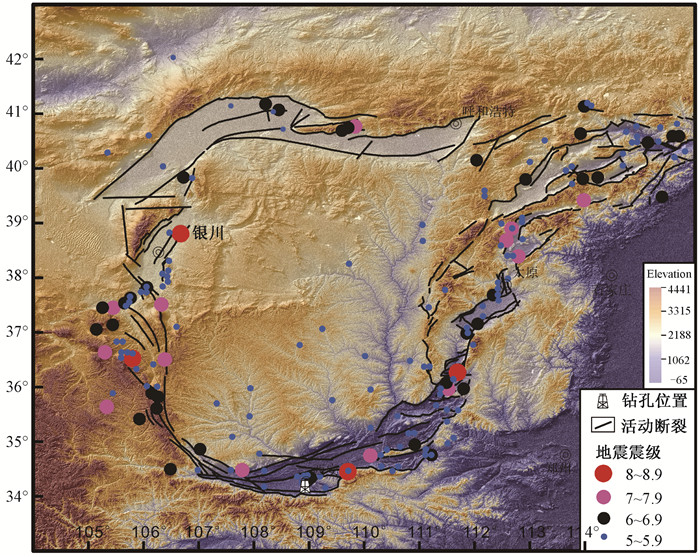
摘要: 利用水压致裂法得到的地应力测试数据对鄂尔多斯地块南缘地壳浅部地应力分布规律及断层活动性进行研究。结果表明:(1)两个水平主应力随深度线性增长,应力梯度分别为0.032和0.021,在测量深度域内水平和垂直应力的关系为SH > Sh > SV,该应力状态有利于断层发生逆断层活动,与1556年华山大地震的发震正断层的性质不同;(2)研究区的最大水平主应力方向为北南-北北西向,与区域速度矢量场方向一致,与其他资料解译的区域构造应力方向有一些差异,主要是受鄂尔多斯地块周缘断层活动的影响;(3)利用Mohr-Coulomb准则及Byerlee定律,摩擦系数取0.6~1.0,对研究区的地应力状态进行分析,发现鄂尔多斯地块南缘的测点未达到或超过地壳破裂极限状态,不存在断层失稳或地震等其他形式的地壳活动,处于较稳定地壳应力状态;(4)实测数据为该区补充了新的地应力测量资料,研究结果为该区工程设计及建设、构造应力场数值模拟提供了边界条件,对于该区地质灾害评价、地壳稳定性以及大陆动力学的研究具有重要意义。Abstract: The crustal stress distribution pattern and fault activity of the shallow crust in the southern margin of the Ordos block are studied by using the stress test data obtained from hydraulic fracturing method. The results reveal that the maximum and minimum horizontal principal stress show a good linear relationship with depth. The gradient is 0.032 and 0.021, respectively. Stress structure of SH > Sh > SV is favorable for the activity of the reverse fault and that is different from the normal fault occurred in the 1556 Huashan earthquake. The direction of the maximum horizontal principal stress is NS-NNW, which is consistent with the direction of velocity vector field. It is different from regional tectonic stress direction interpreted by other data, which may be affected by the fault activity around the Ordos block. The crustal activity in the study area is discussed by using the Mohr-Coulomb criterion and Byerlee's law under the premise that the friction coefficient is 0.6~1.0. We found that the measured points in the southern margin of Ordos block have not reached or exceeded the limit of the earth's crust rupture and there are no fault instability or earthquake and other forms of the activities, which is in a relatively stable state of crustal stress. New in-situ stress measurement data have been added to the area. The research results provide the boundary conditions for the engineering design and construction, numerical simulation of tectonic stress field in the area, which is of great significance for the study of geological hazard assessment, crustal stability and continental dynamics.
-
表 1 鄂尔多斯地块南缘地应力测量结果
Table 1. Results of in-situ stress measurement by hydraulic fracturing in southern margin of the Ordos block
测段序号 测段深度/m 孔隙压力Po/MPa 主应力值/MPa 应力特征参数 印痕裂缝方向/° SH Sh SV SH/ SV SH/ Sh (SH+Sh)/2SV (σ1-Po)/(σ3-Po) 1 80.50 0.76 3.91 3.71 2.13 1.84 1.05 1.79 0.44 2 120.60 1.16 5.40 5.11 3.20 1.69 1.06 1.64 0.48 3 136.40 1.31 5.88 5.27 3.61 1.63 1.12 1.54 0.50 N313°W 4 167.92 1.63 5.19 4.60 4.45 1.17 1.13 1.10 0.79 5 187.00 1.82 8.79 7.97 4.96 1.77 1.10 1.69 0.45 N357°W 6 224.80 2.20 11.99 8.88 5.96 2.01 1.35 1.75 0.38 7 237.26 2.32 13.56 9.29 6.29 2.16 1.46 1.82 0.35 N345°W 8 258.75 2.54 13.83 9.56 6.86 2.02 1.45 1.70 0.38 9 299.24 2.94 10.17 7.75 7.93 1.28 1.31 1.13 0.69 10 399.00 3.94 12.51 10.29 10.57 1.18 1.22 1.08 0.77 N10°E 注:SV为铅直应力(SV=ρgH, ρ取2650 kg/m3, H为上覆岩体的厚度), SH为最大水平主应力, Sh为最小水平主应力, σ1为最大主应力值, σ3为最小主应力值 -
[1] 郭祥云, 蒋长胜, 王晓山, 等.鄂尔多斯块体周缘中小地震震源机制及应力场特征[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 2017, 37(7):675~685. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dkxbydz201707003GUO Xiangyun, JIANG Changsheng, WANG Xiaoshan, et al. Characteristics of small to moderate focal mechanism solutions stress field of the Circum-Ordos Block[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2017, 37(7):675~685. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dkxbydz201707003 [2] 张培震, 邓起东, 张国民, 等.中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块[J].中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(增刊):12~20. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd2003z1002ZHANG Peizhen, DENG Qidong, ZHANG Guomin, et al. Active tectonic blocks and strong earthquakes in the continent of China[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2003, 46(S2):13~24. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd2003z1002 [3] 邓起东, 尤惠川.鄂尔多斯周缘断陷盆地带的构造活动特征及其形成机制[A].国家地震局地质研究所.现代地壳运动研究(1)——大陆裂谷与深部过程[M].北京:地震出版社, 1985. [4] 国家地震局《鄂尔多斯周缘活动断裂系》课题组.鄂尔多斯周缘活动断裂系[M].北京:地震出版社, 1988.Erdos Activity Periphery Fault System Research Group, State Seismological Bureau. Active fault system around Ordos Block[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 1988. (in Chinese) [5] 徐锡伟, 程国良, 马杏垣, 等.华北及其邻区块体转动模式和动力来源[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 1994, 19(2):129~138. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqkx199402000&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQXU Xiwei, CHENG Guoliang, MA Xingyuan, et al. Rotation model and dynamics of blocks in North China and its adjacent areas[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1994, 19(2):129~138. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqkx199402000&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [6] 张培震, 邓起东, 张竹琪, 等.中国大陆的活动断裂-地震灾害及其动力过程[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2013, 43(10):1607~1620. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/81d94fc776c66137ee0619f7.htmlZHANG Peizhen, DENG Qidong, ZHANG Zhuqi, et al. Active faults, earthquake hazards and associated geodynamic processes in continental China[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2013, 43(10):1607~1620. (in Chinese) http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/81d94fc776c66137ee0619f7.html [7] 国家地震局地质研究所, 宁夏回族自治区地震局.海原活动断裂带[M].北京:地震出版社, 1990.Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, The Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Seismological Bureau. Haiyuan active fault system[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 1990. (in Chinese) [8] Scholz C H. Earthquakes and friction laws[J]. Nature, 1998, 391(6662):36~42. doi: 10.1038/34095 [9] 周鼎武, 李文厚, 张云翔, 等.区域地质综合研究的方法与实践[M].北京:科学出版社, 2002.ZHOU Dingwu, LI Wenhou, ZHANG Yunxiang, et al. The method and practice of regional geological comprehensive study[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2002. (in Chinese) [10] 高立新, 韩晓明, 戴勇, 等.鄂尔多斯地块的运动特性与现今地震活动性[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 2017, 37(4):349~354. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dkxb201704005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQGAO Lixin, HAN Xiaoming, DAI Yong, et al. Movement characteristics and the present seismic behavior of the Ordos Block[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2017, 37(4):349~354. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dkxb201704005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [11] 高彬, 周仕勇, 蒋长胜.基于地震活动性资料估计鄂尔多斯块体周缘构造断层面倾角[J].地球物理学报, 2016, 59(7):2444~2452. doi: 10.6038/cjg20160711GAO Bin, ZHOU Shiyong, JIANG Changsheng. Estimate of dip angles of faults around Ordos Block based on earthquakes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(7):2444~2452. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/cjg20160711 [12] 邓起东, 程绍平, 闵伟, 等.鄂尔多斯块体新生代构造活动和动力学的讨论[J].地质力学学报, 1999, 5(3):13~21. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19990333&flag=1DENG Qidong, CHENG Shaoping, MIN Wei, et al. Discussion on Cenozoic tectonics and dynamics of Ordos Block[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 1999, 5(3):13~21. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19990333&flag=1 [13] 张培震, 张会平, 郑文俊, 等.东亚大陆新生代构造演化[J].地震地质, 2014, 36(3):574~585. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201403004.htmZHANG Peizhen, ZHANG Huiping, ZHENG Wenjun, et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of continental Eastern Asia[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2014, 36(3):574~585. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201403004.htm [14] 张岳桥, 施炜, 廖昌珍, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地周边断裂运动学分析与晚中生代构造应力体制转换[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(5):639~647. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb200605002ZHANG Yueqiao, SHI Wei, LIAO Changzhen, et al. Fault kinematic analysis and change in Late Mesozoic tectonic stress regimes in the peripheral zones of the Ordos Basin, North China[J]. Acta Geologica Sincia, 2006, 80(5):639~647. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb200605002 [15] 徐锡伟, 邓起东, 韩竹君.霍山山前断裂晚第四纪活动和古地震研究[A].马宗晋.山西临汾地震研究与系统减灾[M].北京:地震出版社, 1993.XU Xiwei, DENG Qidong, HAN Zhujun. The Late Quaternary activity of the piedmont fault of Mt. Huoshan and paleoearthquake study[A]. MA Zongjin. Earthquake Research and Systematical Disaster Reduction in Linfen, Shanxi[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 1993. (in Chinese) [16] 尤惠川.河套断陷盆地带地质构造特征及其成因机制的讨论[A].国家地震局地质研究所.现代地壳运动研究[M].北京:地震出版社, 1985:88~97.YOU Huichuan. Discusson geological structure characteristics and formation mechanism of the Hetao Fault Basin Zone[A]. Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration. Modern Crustal Movement Research[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 1985:88~97. (in Chinese) [17] 陈小斌, 臧绍先, 刘永岗, 等.鄂尔多斯地块的现今水平运动状态及其与周缘地块的相互作用[J].中国科学院研究生院学报, 2005, 22(3):309~314. http://www.doc88.com/p-0753138071893.htmlCHEN Xiaobin, ZANG Shaoxian, LIU Yonggang, et al. Horizontal movement of Ordos Block and the interaction of Ordos Block and adjacent blocks[J]. Journal of the Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005, 22(3):309~314. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.doc88.com/p-0753138071893.html [18] 李延兴, 张静华, 郭良迁, 等.鄂尔多斯的逆时针旋转与动力学[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 2005, 25(3):50~56. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dkxbydz200503010LI Yanxing, ZHANG Jinghua, GUO Liangqian, et al. Counterclockwise rotation and geodynamics of Ordos Block[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2005, 25(3):50~56. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dkxbydz200503010 [19] 陈小斌, 臧绍先, 魏荣强.稳定的鄂尔多斯地块在整体运动吗?[J].地球物理学报, 2011, 54(7):1750~1757. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb201107008CHEN Xiaobin, ZANG Shaoxian, WEI Rongqiang. Is the stable Ordos Block migrating as an entire block?[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(7):1750~1757. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb201107008 [20] Haimson B C, Cornet F H. ISRM suggested methods for rock stress estimation-Part 3:hydraulic fracturing (HF) and/or hydraulic testing of pre-existing fractures (HTPF)[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2003, 40(7~8):1011~1020. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2003.08.002 [21] 牛琳琳, 陈群策, 丰成君, 等.新疆某高放废物预选处置库区地应力测量研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 36(4):917~927. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yslx201704016&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQNIU Linlin, CHEN Qunce, FENG Chengjun, et al. In-situ stress measurement of candidate area for high level radioactive waste repository in Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 36(4):917~927. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yslx201704016&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [22] Lee M Y, Haimson B C. Statistical evaluation of hydraulic fracturing stress measurement parameter[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1989, 26(6):447~456. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222943883_Statistical_evaluation_of_hydraulic_fracturing_stress_measurement_parameters [23] Hayashi K, Haimson B C. Characteristics of shut-in curves in hydraulic fracturing stress measurements and determination of in situ minimum compressive stress[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1991, 96(B11):18311~18321. doi: 10.1029/91JB01867 [24] Hast N. The state of stress in the upper part of the earth's crust[J]. Tectonophysics, 1969, 8(3):169~211. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(69)90097-3 [25] Haimson B C. Near-surface and deep hydrofracturing stress measurements in the Waterloo Quartzite[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1980, 17(2):81~88. https://www.onepetro.org/conference-paper/ARMA-78-0414 [26] Worotniki G, Denham D. The state of stress in the upper part of the earth's crust in Australia according to measurements in tunnels and mines and from seismic observations[A]. Investigation of Stress in Rock-Advances in Stress Measurement[C]. Sydney, Australia: International Society for Rock Mechanics Symposium, 1976, 71~82. [27] 王艳华, 崔效锋, 胡幸平, 等.基于原地应力测量数据的中国大陆地壳上部应力状态研究[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(9):3016~3027. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.09.020WANG Yanhua, CUI Xiaofeng, HU Xingping, et al. Study on the stress state in upper crust of China mainland based on in-situ stress measurements[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(9):3016~3027. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.09.020 [28] 杨树新, 姚瑞, 崔效锋, 等.中国大陆与各活动地块、南北地震带实测应力特征分析[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(12):4207~4217. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.032YANG Shuxin, YAO Rui, CUI Xiaofeng, et al. Analysis of the characteristics of measured stress in Chinese mainland and its active blocks and North-South seismic belt[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(12):4207~4217. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.032 [29] 景锋, 盛谦, 张勇惠, 等.中国大陆浅层地壳实测地应力分布规律研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(10):2057~2062. http://www.docin.com/p-981812365.htmlJING Feng, SHENG Qian, ZHANG Yonghui, et al. Research on distribution rule of shallow crustal geostress in China Mainland[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(10):2057~2062. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.docin.com/p-981812365.html [30] Anderson E M. The dynamics of faulting[J]. Transactions of the Edinburgh Geological Society, 1905, 8(3):387~402. doi: 10.1144/transed.8.3.387 [31] Stacey T R, Wesseloo J. The in situ stress regime in Southern Africa[A]. Proceedings of the 9th ISRM Congress[C]. Paris, France: International Society for Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 1999, 1189~1192. [32] Brown E T, Hoek E. Technical note trends in relationships between measured in-situ stresses and depth[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1978, 15(4):211~215. doi: 10.1016/0148-9062(78)91227-5 [33] 李英康, 高锐, 高建伟, 等.秦岭造山带的东西向地壳速度结构特征[J].地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(3):1056~1069. doi: 10.6038/pg20150309LI Yingkang, GAO Rui, GAO Jianwei, et al. Characteristics of crustal velocity structure along Qingling orogenic belt[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(3):1056~1069. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/pg20150309 [34] 牛之俊, 王敏, 孙汉荣, 等.中国大陆现今地壳运动速度场的最新观测结果[J].科学通报, 2005, 50(8):839~840. http://www.doc88.com/p-5833048583242.htmlNIU Zhijun, WANG Min, SUN Hanrong, et al. Contemporary velocity field of crustal movement of Chinese mainland from Global Positioning System measurements[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(9):939~941. http://www.doc88.com/p-5833048583242.html [35] 江在森, 马宗晋, 张希, 等. GPS初步结果揭示的中国大陆水平应变场与构造变形[J].地球物理学报, 2003, 46(3):352~358. http://www.doc88.com/p-9035334253632.htmlJIANG Zaisen, MA Zongjin, ZHANG Xi, et al. Horizontal strain field and tectonic deformation of China mainland revealed by preliminary GPS[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2003, 46(3):352~358. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.doc88.com/p-9035334253632.html [36] 徐纪人, 赵志新, 石川有三.中国大陆地壳应力场与构造运动区域特征研究[J].地球物理学报, 2008, 51(3):770~781. http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geophy/CN/abstract/abstract402.shtmlXU Jiren, ZHAO Zhixin, Ishikawa Y. Regional characteristics of crustal stress field and tectonic motions in and around Chinese mainland[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2008, 51(3):770~781. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geophy/CN/abstract/abstract402.shtml [37] 杜兴信, 邵辉成.由震源机制解反演中国大陆现代构造应力场[J].地震学报, 1999, 21(4):354~360. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.1999.04.003DU Xingxin, SHAO Huicheng. Modern tectonic stress field in the Chinese mainland inversed from focal mechanism solutions[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 1999, 21(4):354~360. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.1999.04.003 [38] 徐学义, 何世平, 王洪亮, 等.中国西北部地质概论-秦岭、祁连、天山地区[M].北京:科学出版社, 2008.XU Xueyi, HE Shiping, WANG Hongliang, et al. Geological theory in Northwest China-Qinling, Qilian and Tianshan regions[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2008. (in Chinese) [39] 谢富仁, 陈群策, 崔效锋, 等.中国大陆地壳应力环境基础数据库[J].地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(1):131~136. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.23.031XIE Furen, CHEN Qunce, CUI Xiaofeng, et al. Fundamental database of crustal stress environment in continental China[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007, 22(1):131~136. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.23.031 [40] 苏恺之, 李方全, 张伯崇, 等.长江三峡坝区地壳应力与孔隙水压力综合研究[M].北京:地震出版社, 1996, 151~165.SU Kaizhi, LI Fangquan, ZHANG Bochong, et al. Integrated research on the crustal stress and pore water pressure at the dam site of the Three Gorges[M]. Beijing:Earthquake Press, 1996, 151~165. (in Chinese) [41] Byerlee J. Friction of rocks[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1978, 116(4~5):615~626. doi: 10.1007/BF00876528 [42] Zoback M D, Healy J H. Friction, faulting and in-situ stress[J]. Annales Geophsicae, 1984, 2:689~698. http://www.scirp.org/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=74664 [43] Zoback M D, Apel R, Baumgärtner J, et al. Upper-crustal strength inferred from stress measurements to 6 km depth in the KTB borehole[J]. Nature, 1993, 365(6447):633~635. doi: 10.1038/365633a0 -





 下载:
下载: