DIFFERENCE IN FAULT DEVELOPMENT AND ITS CONTROLLING ON OIL AND GAS ACCUMULATION IN MAICHEN SAG, BEIBUWAN BASIN
-
摘要: 利用地震、钻井等资料对迈陈凹陷东部断裂系统的发育演化及成因机制进行了分析, 同时探讨了断裂对油气成藏的影响。研究结果表明, 迈陈凹陷不同区域断裂的组合和活动特征存在明显差异, 发育6种构造样式:多米诺式、阶梯式、复式“Y”形(塌陷构造)、铲式扇、牵引式、叠加式; 4种断裂活动类型:持续活动型、早期活动型、中期活动型、晚期活动型。迈陈凹陷断裂系统是在先存构造条件下, 两期不同方向的裂陷作用(E1ch—E2l时期为北西—南东方向伸展, E3w时期为南北向伸展)叠加形成, 不同区域构造样式和断裂活动的差异主要是由先存构造分布和活动的差异性造成。断裂系统一方面控制了迈陈凹陷主力烃源岩的沉积厚度与分布范围, 另一方面对油气运移有控制作用, 进而控制了油气成藏模式, 造成了迈陈凹陷油气的差异分布特征。Abstract: Using the seismic and drilling data, the development, evolution and origin of the fault system in the east of Maichen Sag were analyzed, and the influence of fault on oil and gas accumulation were discussed in this paper. The results show that the fault combinations and activity characteristics have obvious differences in different regions of Maichen Sag; There are six types of tectonic styles developed, including domino structure, stepped fault, complicated "Y" shaped structure (collapse structure), listric-fan structure, drag structure, and superposed fault; And there are four types of fault activities, including continuous activity, early-activity, midterm-activity and late-activity. The fault system in Maichen Sag are developed in the superposition of multi-periodic rifting with different extension directions (NW-SE extension during E1ch-E2l, NS extension during E3w) under the pre-existing tectonic conditions. The differences of structural styles and fault activities are caused by different distribution and activity of pre-existing structures. The fault system control not only the thickness and distribution of source rock but also the oil and gas migration which impact the oil-gas accumulation model and lead to different oil and gas distribution in Maichen Sag.
-
Key words:
- Maichen Sag /
- fault system /
- structural style /
- oil and gas migration /
- oil and gas accumulation
-
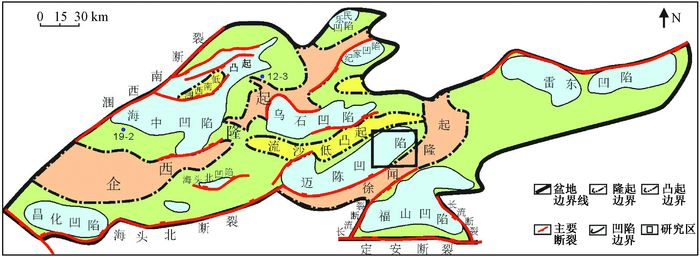
图 1 北部湾盆地区域构造单元分布图[8]
Figure 1. The distribution of tectonic units in Beibuwan Basin
-
[1] 童亨茂, 孟令箭, 蔡东升, 等.裂陷盆地断层的形成和演化——目标砂箱模拟实验与认识[J].地质学报, 2009, 83(6):759~774. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200906003.htmTONG Heng-mao, MENG Ling-jian, CAI Dong-sheng, et al. Fault formation and evolution in rift basins: Sandbox modeling and cognition[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 83(6): 759~774. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200906003.htm [2] Bosworth W. Geometry of propagating continental rifts[J]. Nature, 1985, 316: 625~627. doi: 10.1038/316625a0 [3] Ebinger C J. Geometric and kinematic development of border faults and accommodation zones, Kivu-Rusizi rift, Africa[J]. Tectonics, 1989, 8: 117~133. doi: 10.1029/TC008i001p00117 [4] Rosendahl B R, Reynolds D, Lorber P, et al. Structural expressions of rifting: Lessons from Lake Tanganyika, Africa[C]//Frostick L E, Renaut R W, Reid I, et al. Sedimentation in the East African Rifts. Spec. Publ. Geol. Sot. Lond, 1986, 25: 29~43. [5] Morley, C K. Variable extension in Lake Tanganyika[J]. Tectonics, 1988, 7: 785~801. doi: 10.1029/TC007i004p00785 [6] Moustafa A R, Fouda H G. Gebel Sufr El Dara accommodation zone: Southwestern part of the Suez rift[J]. Earth Science Series, 1988, 2: 227~239. [7] 陈长征, 陈伟, 吴峰, 等.北部湾盆地迈陈凹陷东部构造物理模拟研究[J].石油实验地质, 2014, 36(7):516~522. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201404021.htmCHEN Chang-zheng, CHEN Wei, WU Feng, et al. Structural physical simulation research of eastern Maichen sag, Beibuwan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2014, 36(7): 516~522. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201404021.htm [8] 李春荣, 张功成, 梁建设, 等.北部湾盆地断裂构造特征及其对油气的控制作用[J].石油学报, 2012, 33(2):195~203. doi: 10.7623/syxb201202003LI Chun-rong, ZHANG Gong-cheng, LIANG Jian-she, et al. Characteristics of fault structure and its control on hydrocarbons in the Beibuwan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(2): 195~203. doi: 10.7623/syxb201202003 [9] 王鹏, 赵志刚, 柳永杰, 等.迈陈凹陷构造特征与油气勘探方向分析[J].海洋石油, 2011, 31(2):13~19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY201102005.htmWANG Peng, ZHAO Zhi-gang, LIU Yong-jie, et al. Structural characteristics and petroleum exploration direction analysis in Maichen sag[J]. Offshore Oil, 2011, 31(2): 13~19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY201102005.htm [10] 袁冰.南海北部湾盆地迈陈凹陷构造演化与变形机制[J].科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(18):199~203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.18.038YUAN Bing. Structural evolution and deformation mechanism of Maichen sag in Beibu Gulf Basin, South China Sea[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(18): 199~203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.18.038 [11] Tong H, Cai D, Wu Y, et al. Activity criterion of pre-existing fabrics in non-homogeneous deformation domain[J]. Science in China: Earth Science, 2010, 53(1): 1~11. doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-3080-6 [12] Tong H, Yin A. Reactivation tendency analysis: A theory for predicting the temporal evolution of preexisting weakness under uniform stress state[J]. Tectonophysics, 2011, 503: 195~200. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2011.02.012 [13] 徐建永, 张功成, 梁建设, 等.北部湾盆地古近纪幕式断陷活动规律及其与油气的关系[J].中国海上油气, 2011, 23(6):362~368. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201106001.htmXU Jian-yong, ZHANG Gong-cheng, LIANG Jian-she, et al. Paleogene activities of episodic rifting and their relationships with hydrocarbon in Beibuwan Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2011, 23(6): 362~368. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201106001.htm [14] 钱浩, 陈伟, 卢黎霞, 等.迈陈凹陷东部构造特征对沉积、生烃的影响[J].复杂油气藏, 2014, 7(1):9~12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ201401003.htmQIAN Hao, CHEN Wei, LU Li-xia, et al. Effect of tectonic characteristics of eastern part in Maichen sag on deposition and hydrocarbon generation[J]. Complex Hydrocarbon Reservoirs, 2014, 7(1): 9~12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ201401003.htm [15] 童亨茂, 聂金英, 孟令箭, 等.基底先存构造对裂陷盆地断层形成和演化的控制作用规律[J].地学前缘, 2009, 16(4):97~104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200904012.htmTONG Heng-mao, NIE Jin-ying, MENG Ling-jian, et al. The law of basement pre-existing fabric controlling fault formation and evolution in rift basin[J]. Earth Science Frontier, 2009, 16(3): 97~104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200904012.htm [16] Tong H, Koyi H, Huang S, et al. The effect of multiple pre-existing weaknesses on formation and evolution of faults in extended sandbox models[J]. Tectonophysics, 2014, 626: 197~212. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.04.046 [17] Tong H, Wang J, Zhao H, et al. Mohr space and its application to the activation prediction of pre-existing weakness[J]. Science in China: Earth Sciences, 2014, 57 (7): 1595~1604. doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4860-1 [18] 宋国奇, 刘克奇.断层两盘裂缝发育特征及其石油地质意义[J].油气地质与采收率, 2009, 16(4):1~3. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200904004.htmSONG Guo-qi, LIU Ke-qi. Fracture characteristics around faults and their significance in petroleum accumulation[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2009, 16(4): 1~3. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200904004.htm [19] 吴智平, 陈伟, 薛雁, 等.断裂带的结构特征及其对油气的输导和封堵性[J].地质学报, 2010, 84(4):570~577. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201004012.htmWU Zhi-ping, CHEN Wei, XUE Yan, et al. Structural characteristics of faulting zone and its ability in transporting and sealing oil and gas[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(4): 570~577. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201004012.htm -





 下载:
下载: