Yanshanian gold metallogenic system and metallogenic model of the Guilaizhuang gold ore field, western Shandong
-
摘要: 鲁西归来庄金矿田是中国东部最重要的富碲型金矿田之一,也是鲁西地区迄今唯一的特大型金矿田。矿田中各金矿床受铜石潜火山穹隆控制,产出于不同深度、不同地质构造部位、不同的地质体中,矿化类型多样,但它们的形成环境、成矿地质背景、成矿作用特征总体一致:①归来庄金矿田是一个主要由前寒武纪基底岩石和早古生代碳酸盐岩盖层组成、中生代构造–岩浆作用较为发育的内生中低温热液金矿集区;②燕甘断裂是郯庐断裂带派生构造,控制着区内地层、岩浆岩、次级构造及金矿床/点的展布;燕甘断裂的次级断裂、潜火山穹隆的放射状、环状构造是矿液运移和沉淀聚集的良好场所;③金矿化以隐爆角砾岩型、镁质碳酸盐岩微细浸染型、斑岩型、矽卡岩叠加型及破碎带蚀变岩型为主,矿石普遍发育浸染状、细脉浸染状、网脉状、团块状和块状构造,反映其形成于岩浆期后热液环境;④具有碲与金超常富集共存的显著特征,金属矿物除常见的自然金、银金矿外,另有含碲矿物碲铜金矿、碲金银矿、碲银矿、碲金矿等;⑤早侏罗世中偏碱性岩浆侵位初步启动了该区的金成矿过程,为早白垩世的中碱性岩浆活动提供了母岩和成矿物质来源,早白垩世可能是鲁西归来庄金矿田的主要成矿时期;⑥成矿流体具有低温、低盐度特征,同位素特征具有多来源性,以岩浆水和大气降水为主,并有少量变质水的参与;⑦在成矿热液中可能是Au与Te、S结合生成可搬运的配合物进行运移;成矿热液中有较高的碲逸度,在中低温条件下碲易置换硫而进入硫化物晶格,在高碲逸度的条件下碲则易与Au、Ag、Pb等元素形成碲化物而参与成矿。这种区域上成矿特征表现出的一致性,表明鲁西归来庄地区中生代大规模金成矿作用受控于统一的地质事件,可划归为一个统一的潜火山中—低温热液金成矿系统。Abstract: The Guilaizhuang gold ore field is one of the essential tellurium-rich goldfields in eastern China and the only super-large goldfield in western Shandong so far. These gold deposits controlled by the Tongshi subvolcanic dome occur in different depths, geological structures, and geological bodies. Though their mineralization types are diverse, their host wall rocks, formation environment, geological background, and metallogenic characteristics are generally consistent: (1) The Guilaizhuang gold ore field, mainly composed of Precambrian basement rocks and early Paleozoic carbonate cap rocks, is an endogenous medium−low hydrothermal gold concentration area of relatively developed Mesozoic tectonic magmatism. (2) Yangan fault, a derivative structure of the Tanlu Fault Zone, controls the distribution of strata, magmatic rocks, secondary structures, and gold deposits (points) in this area. The sub-faults of the Yangan fault and the radial and circular structures of subvolcanic domes are good places for ore fluid migration and sedimentation. (3) The mineralization types are mainly cryptoexplosive breccia, magnesian carbonate micro-disseminated, porphyry, skarn superposition, and altered fracture zone. The ores generally develop into disseminated, veinlet disseminated, stockwork, crumb, and block structures, reflecting that they were formed in the post-magmatic hydrothermal environment. (4) It shows a distinguished character of coexistence of tellurium and gold super concentration. In addition to common native gold and electrum, there are also tellurium-containing minerals such as bessmertnovite, petzite, hessite, calaverite, etc. (5) The early Jurassic intermediate alkaline magma initially started the gold mineralization process in this area and provided parent rock and material source for the early Cretaceous alkaline magmatic activities. The main mineralization period of the Guilaizhuang gold ore field in western Shandong may be in the early Cretaceous. (6) The ore-forming fluid has the characteristics of low temperature and low salinity. The isotopic characteristics are multi-sourced. They are dominated by magmatic water and atmospheric precipitation, with a small amount of metamorphic water. (7) Au likely combines with Te and S to form transportable complexes for migration in the ore-forming hydrothermal fluid. There is a high tellurium fugacity in the ore-forming hydrothermal fluid. Under medium- and low- temperature conditions, tellurium can easily replace sulfur and enter the sulfide lattice. Under high tellurium fugacity conditions, tellurium is prone to form telluride with elements such as gold, silver and lead to mineralization. The consistency of the regional metallogenic characteristics indicates that the Mesozoic large-scale gold mineralization in the Guilaizhuang area of western Shandong is controlled by a unified geological event and can be classified into a unified subvolcanic medium-low hydrothermal gold metallogenic system.
-
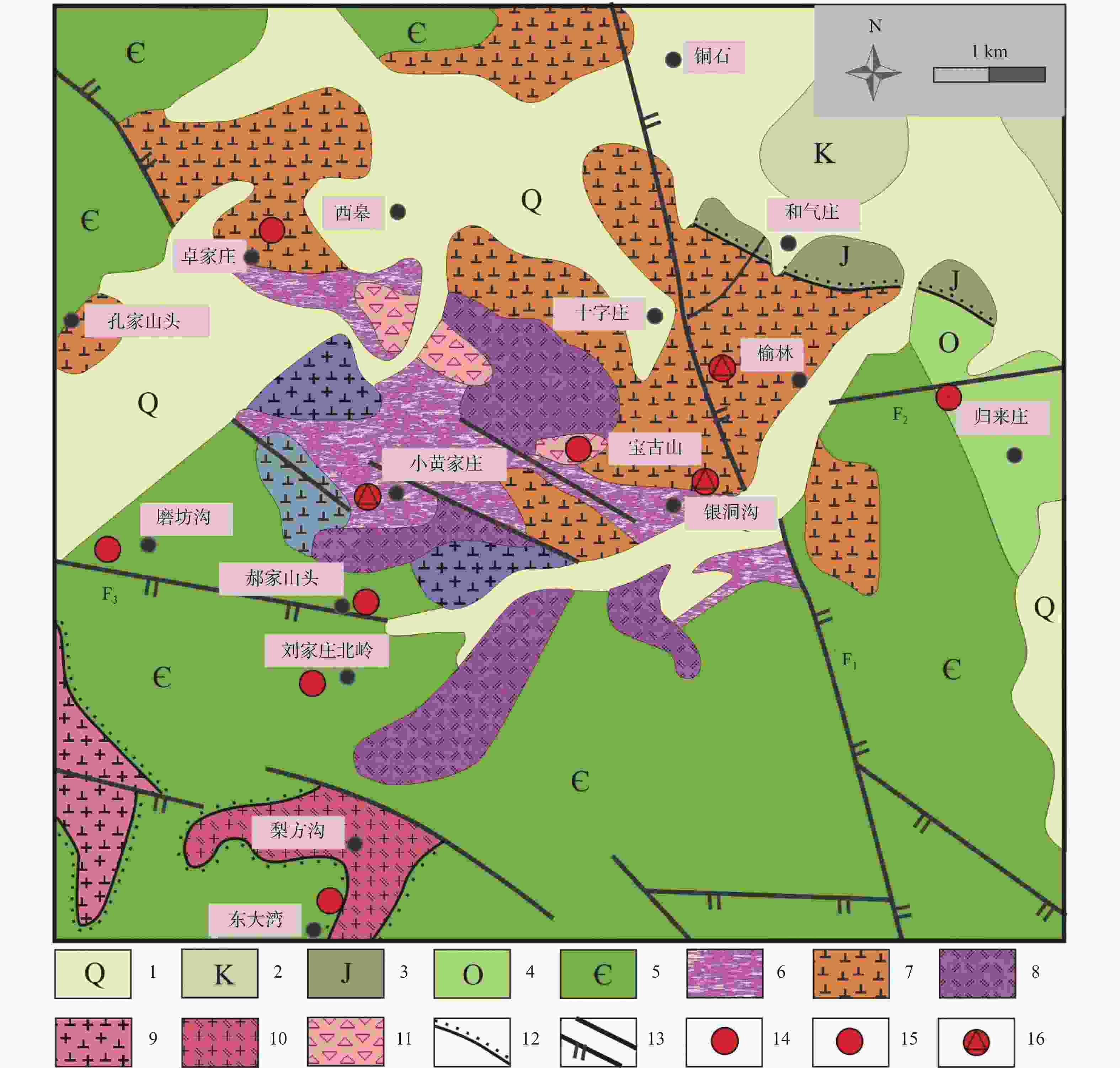
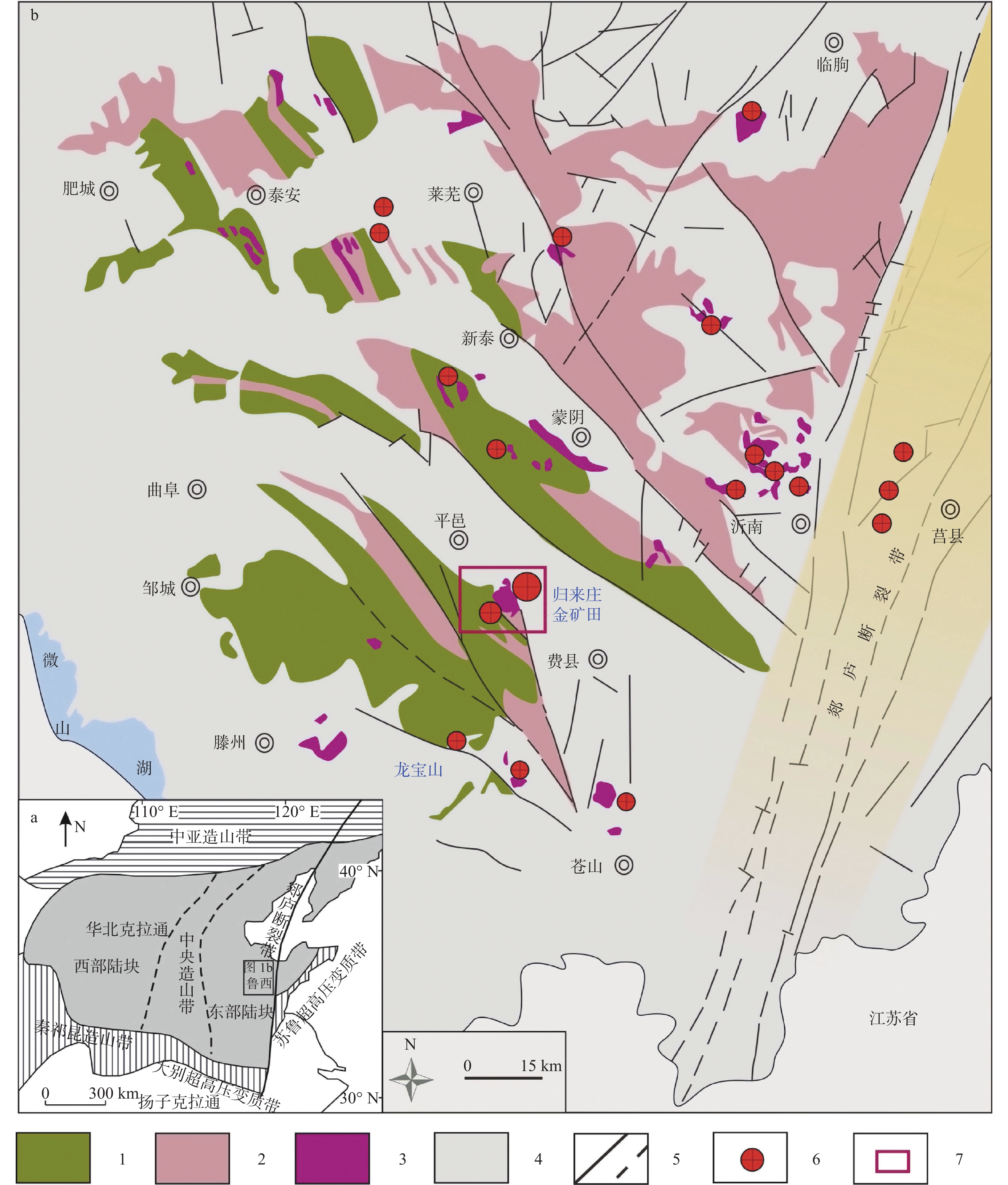
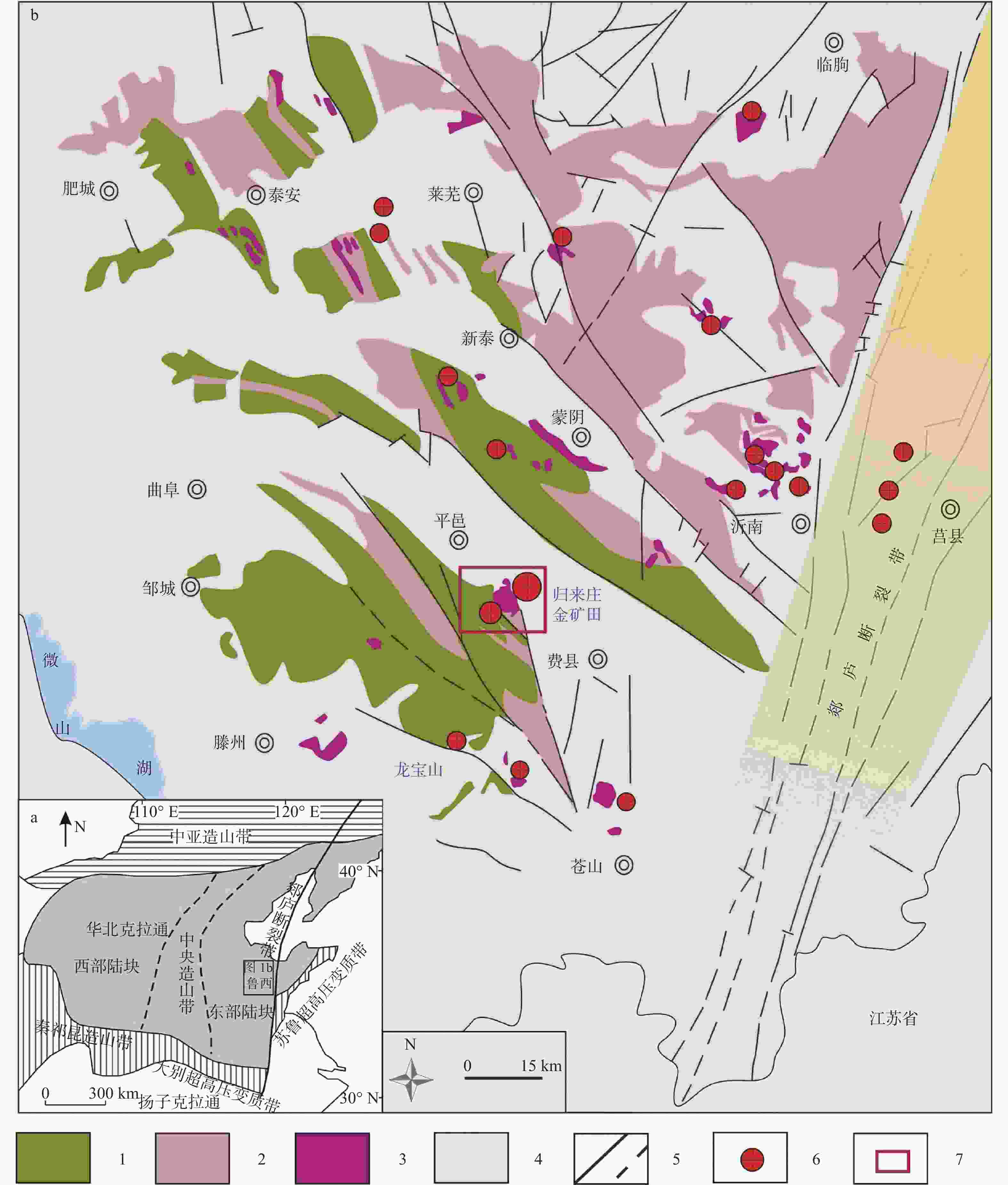
图 1 鲁西地区金矿地质简图(于学峰等,2016)
1—太古宙侵入岩类;2—元古宙侵入岩类;3—中生代侵入岩类;4—地层;5—已知和推断断层;6—金矿床(矿点);7—归来庄金矿田
Figure 1. Sketch geological map of the gold deposits in western Shandong( Yu et al., 2016)
1–Archean intrusions; 2–Proterozoic intrusions; 3–Mesozoic intrusions; 4–Stratum; 5–Faults and inferred faults; 6–Gold deposits ( occurrence ); 7–Guilaizhuang gold ore field
图 2 归来庄金矿田地质简图(于学峰等,2019)
1—第四系;2—白垩系;3—侏罗系;4—奥陶系;5—寒武系;6—新太古代泰山岩群山草峪组;7—燕山早期二长闪长玢岩;8—燕山早期二长斑岩;9—新太古代花岗闪长岩;10—新太古代二长花岗岩;11—隐爆角砾岩;12—角度不整合地质界线;13—断裂及编号;14—隐爆角砾岩型(归来庄式)金矿床;15—镁质碳酸盐岩微细浸染型(磨坊沟式)金矿床;16—其他热液型金矿床(点);F1—燕甘断裂;F2—归来庄断裂;F3—营子洼断裂
Figure 2. Sketch geological map of the Guilaizhuang gold ore field(Yu et al., 2019)
1–Quaternary; 2–Cretaceous; 3–Jurassic; 4–Ordovician; 5–Cambrian; 6–Shancaoyu formation of the Taishan group in the Neoarchean; 7–Early Yanshanian monzodiorite porphyrite; 8–Early Yanshanian monzonite porphyry; 9–Neoarchean granodiorite; 10–Neoarchean monzonitic granite; 11–Cryptoexplosive breccia; 12–Angular unconformity geological boundary; 13–Fault and its serial number; 14–Cryptoexplosive breccia type (Guilaizhuang type) gold deposit; 15–Micro-disseminated magnesium carbonate (Mofanggou type) gold deposit; 16–Other hydrothermal gold deposits (ore spots); F1–Yan–Gan fault; F2–Guilaizhuang fault; F3–Yingziwa fault
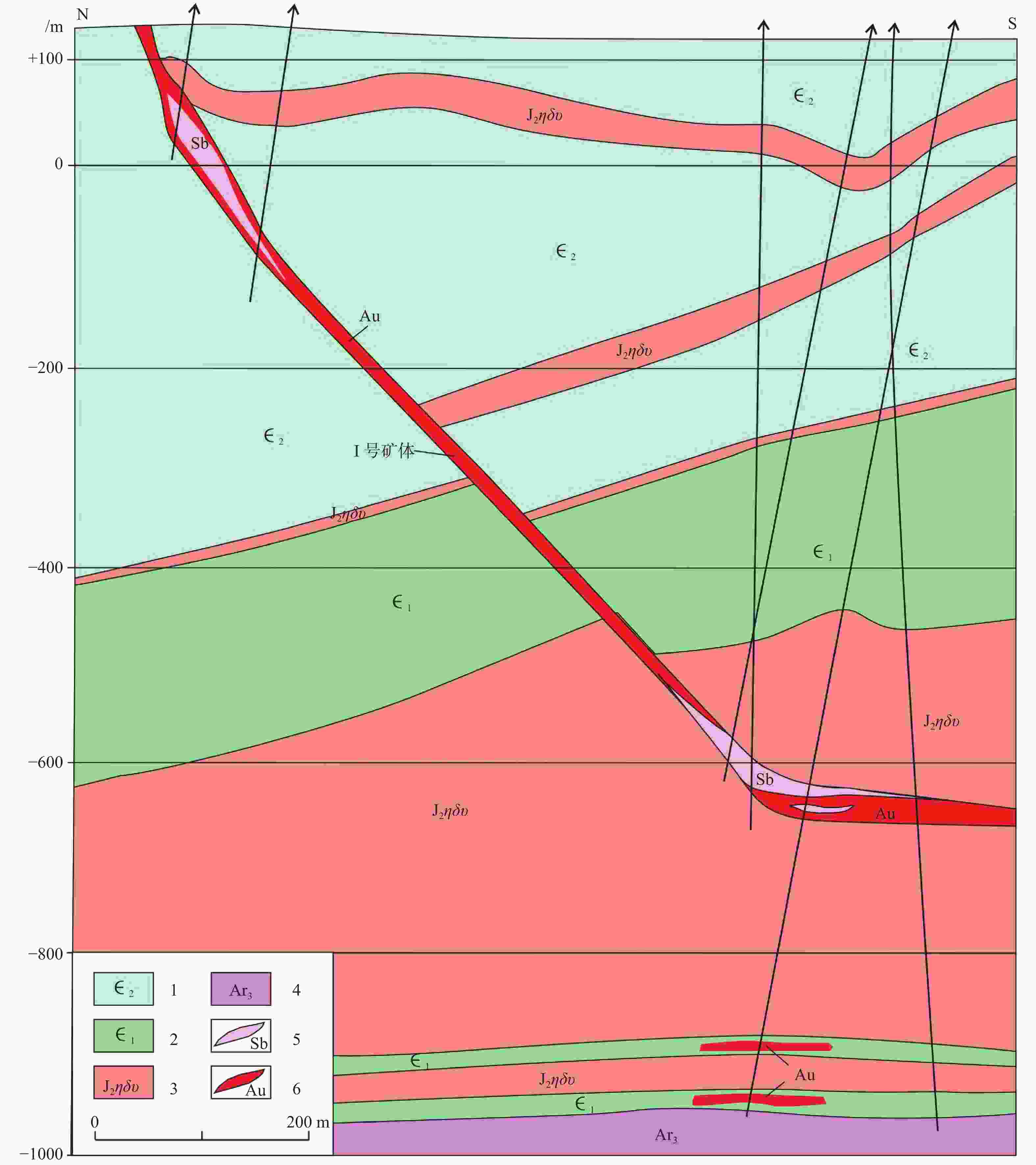
图 3 归来庄金矿深部32 勘探线剖面图(于学峰等,2016)
1—寒武—奥陶纪三山子组+炒米店组+崮山组;2—寒武纪张夏组+馒头组+朱砂洞组;3—侏罗纪二长闪长玢岩;4—前寒武纪变质基底;5—蚀变角砾岩;6—金矿体
Figure 3. Section map of the No.32 prospecting line in the Guilaizhuang gold deposit(Yu et al., 2016)
1–Cambrian–Ordovician Sanshanzi group, Chaomidian group and Gushan group; 2–Cambrian Zhangxia group, Mantou group and Zhushadong group; 3–Jurassic monzonitic diorite porphyrite; 4–Precambrian metamorphic basement; 5–Broken alteration breccia; 6–Gold ore bodies
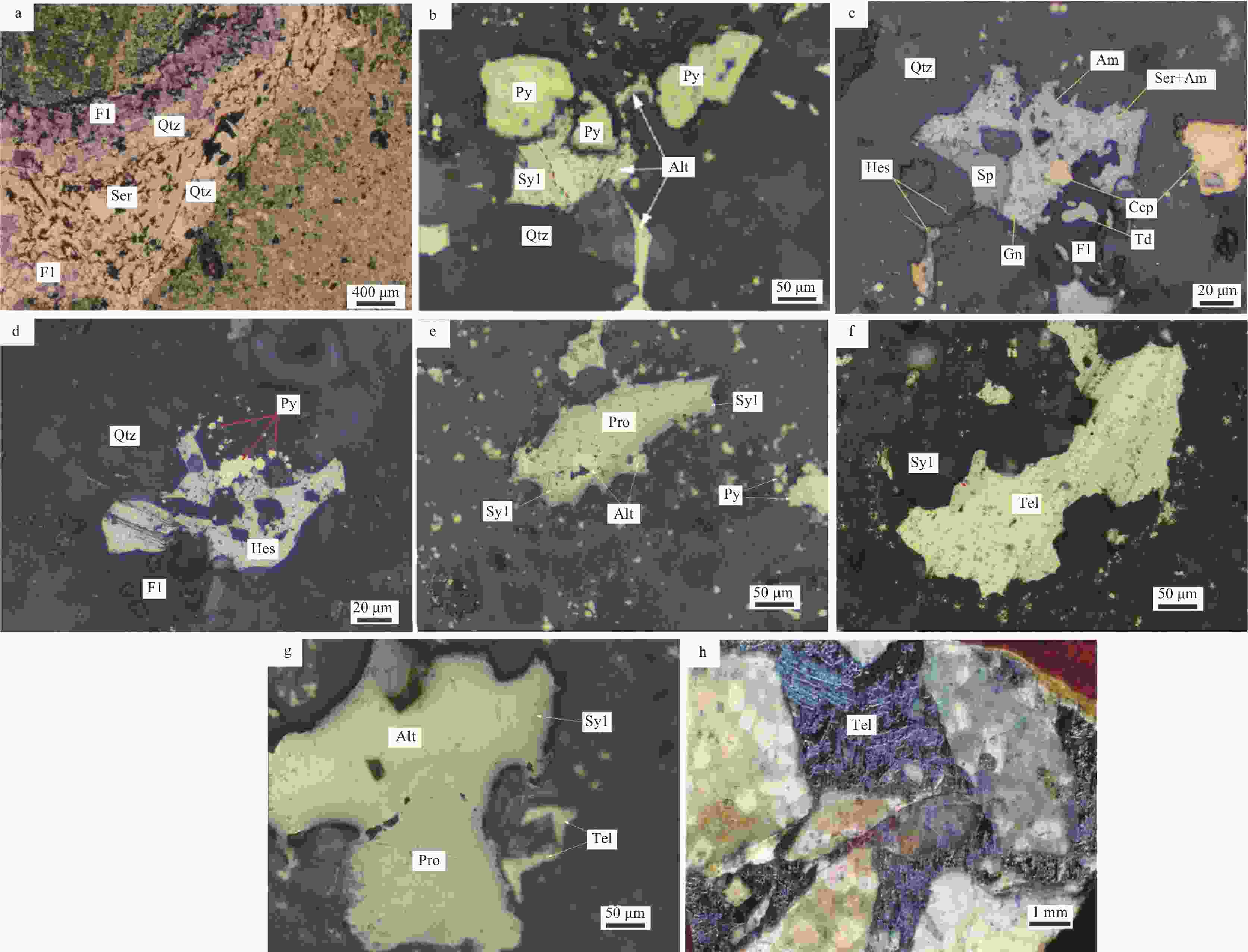
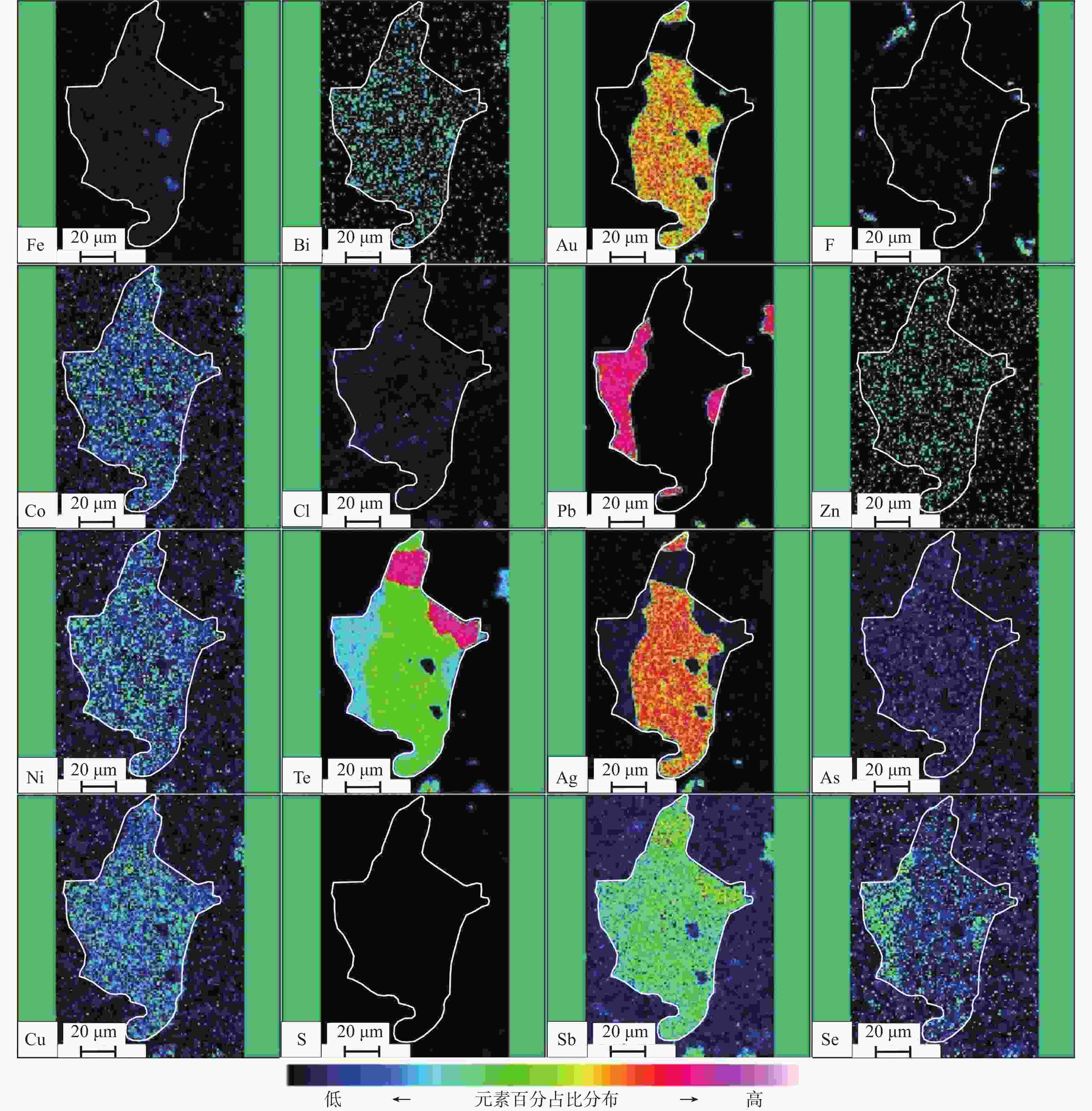
图 4 卓家庄金矿富碲型金矿石矿相学特征(于学峰等,2019)
Alt—碲铅矿;Syl—针碲金银矿;Py—黄铁矿;Qtz—石英;Fl—萤石;Ser—绢云母;Hes—碲银矿;Am—辉银矿;Gn—方铅矿;Sp—闪锌矿;Ccp—黄铜矿;Pro—碲铁矿;Tel—自然碲a—石英–萤石–多金属硫化物–金–碲化物脉体沿早期石英–黄铁矿化的岩石裂隙充填,又被成矿后期的绢云母脉体充填穿插(单偏光);b—碲铅矿和针碲金银矿连生分布于黄铁矿周围,晚于黄铁矿形成(反射光);c—碲银矿与辉银矿呈不规则状交生体状,并见许多乳滴状碲银矿分布于石英粒间(反射光);d—碲银矿和黄铁矿分布于石英萤石粒间(反射光);e—碲铅矿和针碲金银矿分布于碲铁矿边部(反射光);f—自然碲及针碲金银矿连生分布于石英、萤石等非金属矿物中(反射光);g—碲铁矿和自然碲及针碲金银矿连生分布于非金属矿物石英、萤石中(反射光);h—自然碲分布于胶结物中(反射光)
Figure 4. Mineralogical characteristics of the Te-rich gold ores in the Zhuojiazhuang gold deposit(Yu et al., 2019)
(a) Zhuojiazhuang gold ores: Quartz, fluorspar-polymetallic sulfide-gold telluride vein bodies are filled along the early quartz-pyritization rock fractures, and then interspersed with the later sericite vein bodies; (b) Zhuojiazhuang gold ores: Altaite and sylvanite are distributed around pyrite and formed later than pyrite; (c) Guilaizhuang gold ores: Hessite and argentite are irregularly distributed together with galena, sphalerite and chalcopyrite. Tellurite deposits are metasomatized along the chalcopyrite edges. Many tellurite crystals are distributed between quartz grains; (d) Guilaizhuang gold ores: Hessite and pyrite are distributed among quartz fluorite minerals. The residual bulk pyrite is distributed between tellurite and quartz fluorite grains; (e) Zhuojiazhuang gold ores: Altaite and sylvanite are distributed at the edge of cuzticite. The micrograined pyrite is distributed in quartz, fluorite and so on; (f) Zhuojiazhuang gold ores: Native tellurium and sylvanite coexist in minerals such as quartz and fluorite; (g) Zhuojiazhuang gold ores: Cuzticite, native tellurium and sylvanite are symbiotically distributed in quartz and fluorite; (h) Zhuojiazhuang gold ores: Native tellurium is distributed in the cements Alt–Altaite; Syl–Sylvanite; Py–Pyrite; Qtz–Quartz; Fl–Fluorite; Ser–Sericite; Hes–Hessite; Am–Argentite; Gn–Galena; Sp–Sphalerite; Ccp–Chalcopyrite; Pro–Cuzticite; Tel–Native tellurium
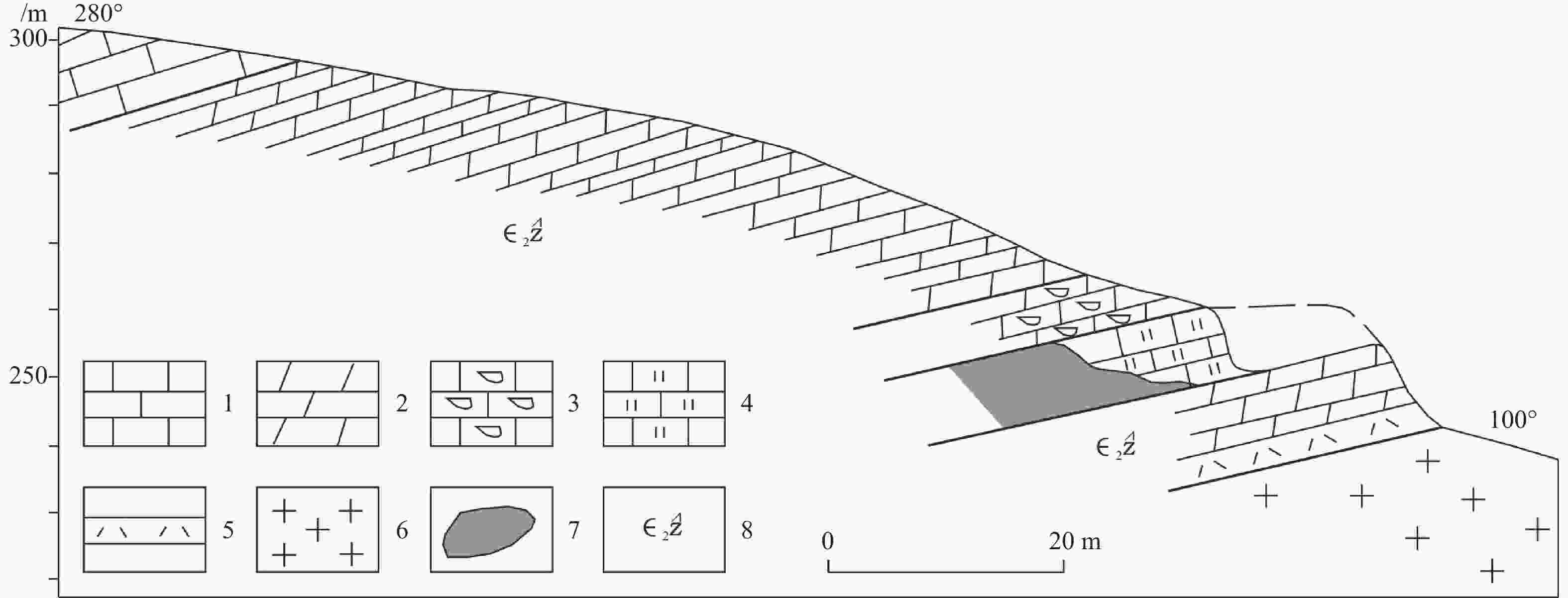
图 5 平邑磨坊沟金矿地质剖面图(于学峰等,2009)
1—石灰岩;2—白云质灰岩;3—含燧石结核灰岩;4—萤石化白云质灰岩;5—中生代燕山期二长斑岩;6—新太古代二长花岗岩;7—金矿体;8—早寒武世朱砂洞组
Figure 5. Geological profile of the Mofanggou gold deposit in Pingyi county (Yu et al., 2009)
1–Limestone; 2–Dolomitic limestone; 3–Flint-bearing nodule limestone; 4–Fluoritized dolomitic limestone; 5–Mesozoic Yanshanian monzonitic porphyry; 6–Neoarchean admellite; 7–Gold ore body; 8–Early Cambrian Zhushadong formation
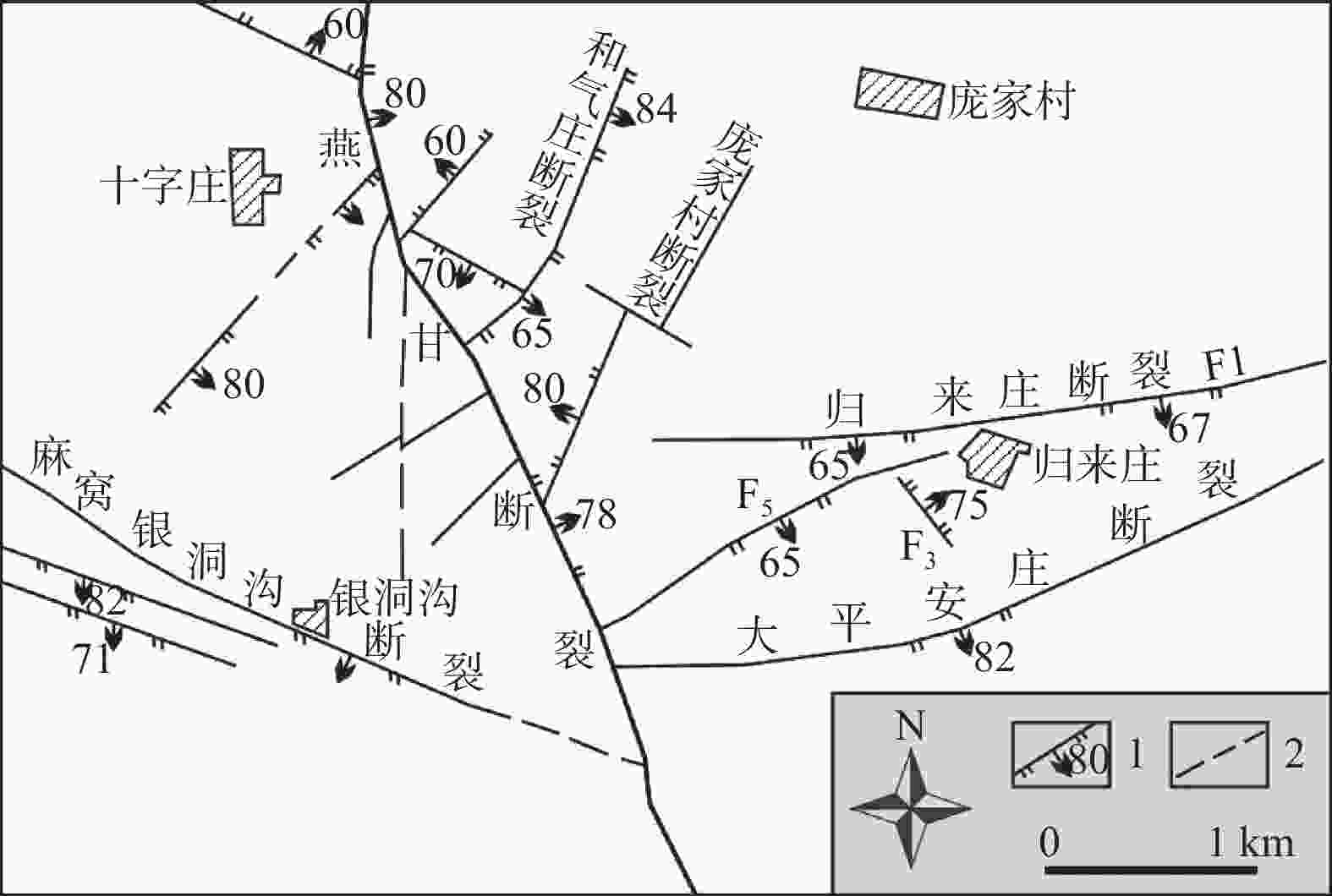
图 6 燕甘断裂及其派生断裂构造展布图(据林景仟等,1997)
1—实测断层及倾角/(°);2—推测断层
Figure 6. Structural distribution map of the Yan–gan fault and its sub-faults(Lin et al., 1997)
1–Faults and dip angle(°); 2–Inferred faults
图 8 Au–Ag–Te三角图解(底图据Cabri, 1965;Afifi et al., 1988)
投点采用矿物元素的质量百分数
Figure 8. Triangular diagram of Au–Ag–Te(Base diagram after Cabri, 1965; Afifi et al., 1988)
Mass percentage of mineral elements is used in the diagram
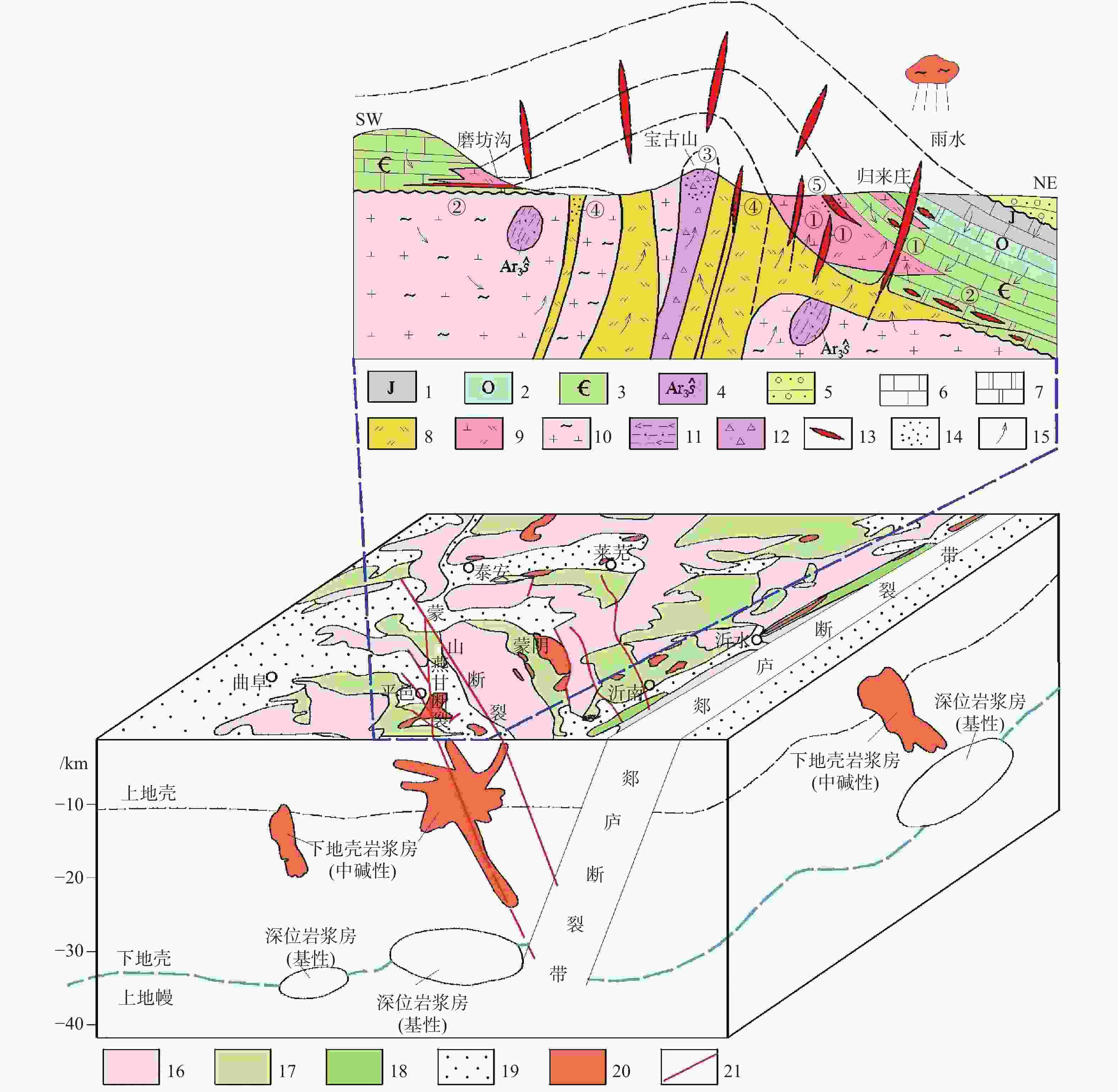
图 9 归来庄金矿田成矿模式图
①—隐爆侵入角砾岩型金矿床 (归来庄式);②—镁质碳酸盐岩微细浸染型金矿床 (磨坊沟式);③—隐爆崩塌角砾岩型金矿化(宝古山式);④—斑岩型金矿化 (银洞沟式);⑤—矽卡岩叠加型金矿化 (十字庄式)1—侏罗系;2—奥陶系;3—寒武系;4—新太古代泰山岩群山草峪组;5—古近纪砂砾岩;6—石灰岩;7—白云岩;8—二长斑岩;9—二长闪长玢岩;10—片麻状花岗闪长岩;11—黑云角闪变粒岩;12—隐爆角砾岩;13—金矿体;14—金矿化体;15—热液运移方向;16—前寒武纪基底;17—古生代地层;18—中生代地层;19—新生代地层;20—中生代岩浆岩;21—断层
Figure 9. Metallogenic model of the Guilaizhuang gold ore field
1–Jurassic; 2–Ordovician; 3–Cambrian; 4–Shancaoyu formationin of the Neoarchean Taishan group; 5–Paleogene conglomerate; 6–Limestone; 7–Dolomite; 8–Monzonitic porphyry; 9–Monzonitic dioritic porphyry; 10–Gneissoid granodiorite;11–Biotite hornblende granulites; 12–Cryptoexplosive breccia; 13–Gold ore body; 14–Gold ore mineralization; 15–Hydrothermal migration direction; 16–Precambrian basement; 17–Palaeozoic strata; 18–Mesozoic strata; 19–Cenozoic strata; 20–Mesozoic magmatic rocks; 21–faults; ①–Cryptoexplosive intrusive breccia type gold deposit (Guilaizhuang type); ②–Magnesium carbonate micro-disseminated gold deposit (Mofanggou type); ③–Cryptoexplosive breccia type gold mineralization (Baogushan type); ④–Porphyry type gold mineralization (Yindonggou type); ⑤–Skarn-stacking type gold mineralization (Shizizhuang type)
表 1 归来庄金矿田成矿系列划分表
Table 1. Division of the minerogenetic series of the Guilaizhuang gold ore field
成矿系列 成矿亚系列 矿床式 成因
类型成因亚
类型代表矿
床(点)主要
矿种产出环境及矿化特征 鲁西中生代侵入岩Au、Cu、Fe成矿系列 归来庄燕山早期中偏碱性潜火山杂岩Au、Cu、Fe成矿亚系列 归来庄式 隐爆角砾岩型 脉状型 归来庄 Au、Ag、Te 大型金矿,产于杂岩体东边缘脉状隐爆角砾岩带中,围岩为碳酸盐岩;矿体呈脉状,长550 m、斜深650 m以上,平均厚度为6.21 m;金品位平均为8.10×10−6 筒状型 卓家庄 中型金矿,产于杂岩体边部筒状隐爆角砾岩中;金平均品位156.77×10−6,最高达2000×10−6以上 磨坊沟式 镁质碳酸盐岩微细浸染型 磨坊沟 Au、Ag 中型金矿,产于杂岩体西南边缘,寒武系底部碳酸盐岩中;矿体呈似层状,长300 m以上,厚2.05~2.82 m,金品位一般为4.5×10−6~11.6×10−6 斑岩型 脉状型 银洞沟 Au、Ag 小型金矿,产于杂岩体中部的二长斑岩岩墙中;矿化体呈脉状,长350 m以上,厚1.5~3 m,金品位一般为2× 10−6~5×10−6,蚀变为硅化、黄铁矿化 似层状型 黄家庄 产在杂岩体中部的二长斑岩岩床中,金矿化不均匀、规模较小 含铁矽卡岩上叠加型 十字庄 Fe、Cu、Au 小型铁矿,伴生铜、金;在二长闪长玢岩与石灰岩的接触带生成的含铁夕卡岩带上,有后期金矿化叠加,金矿化不均匀 破碎带蚀变岩型 董李 Au 金矿点,位于杂岩体南边部,在断裂破碎带内的蚀变角砾岩、碎裂岩中形成金矿化体,金矿化不均匀、规模较小 表 2 归来庄金矿田主要碲化物和自然金电子探针波谱定量分析结果
Table 2. Results of the EMPA spectroscopic quantitative analysis of main telluride and native gold in the Guilaizhuang gold ore field
矿物种类 含量/% 总计/% Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Hg Bi Te Au Ag Sb Se 自然碲 0.06 — 0.02 0.02 0.02 — 0.11 98.77 — — 0.68 0.07 99.75 自然碲 — — 0.02 — 0.01 0.13 0.07 99.14 0.05 — 0.65 — 100.08 自然碲 — — — — — — 0.11 98.84 — — 0.65 0.03 99.65 自然碲 — — 0.03 — 0.02 — 0.05 99.01 0.01 — 0.67 0.07 99.87 斜方碲金矿 0.01 — — 0.16 — — 0.29 59.01 30.32 8.20 0.40 0.08 98.45 斜方碲金矿 0.01 — — 0.16 — — 0.34 59.11 30.31 8.40 0.39 0.04 98.76 斜方碲金矿 — — — 0.19 0.01 — 0.29 59.16 30.60 8.18 0.40 0.03 98.88 斜方碲金矿 0.01 — — 0.18 — — 0.38 58.48 30.06 8.62 0.41 — 98.15 斜方碲金矿 0.01 0.04 — 0.08 1.65 — 0.31 59.31 29.18 9.25 0.36 — 100.23 针碲金银矿 — 0.02 0.08 0.01 0.02 — 0.22 61.92 25.81 12.13 — — 100.22 针碲金银矿 — — — 0.01 — — 0.24 61.63 27.00 11.30 — — 100.20 碲银矿 — — — — 0.02 — 0.02 39.04 0.04 60.02 — — 99.15 碲银矿 0.59 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.02 0.56 — 39.15 0.03 59.78 — — 100.26 碲银矿 0.94 0.04 0.06 0.05 — 1.25 — 41.11 — 57.14 — — 100.60 碲银矿 0.04 0.01 — 0.02 0.01 0.50 — 38.40 — 60.31 — — 99.37 碲银矿 — — — — 0.02 0.51 0.04 38.30 — 60.66 — — 99.55 碲金银矿 0.03 — 0.03 — 0.04 — 0.25 33.16 25.78 41.79 — — 101.07 碲金银矿 — — 0.01 — 0.05 — 0.22 33.34 26.18 41.64 — — 101.45 碲金银矿 0.03 — 0.01 0.01 0.03 0.09 0.18 33.02 25.09 41.84 — — 100.31 自然金 — 0.11 — 0.05 0.05 0.36 0.68 0.07 89.80 10.52 — — 101.67 自然金 0.03 0.02 — 0.03 0.08 0.11 0.85 0.07 90.09 10.55 — — 101.83 自然金 0.02 0.02 0.05 0.04 — — 0.76 0.01 86.69 13.15 — — 100.74 自然金 — 0.02 0.04 — 0.04 — 0.85 0.03 87.44 12.60 — — 101.02 -
AFIFI A M, KELLY W C, ESSENE E J, 1988. Phase relations among tellurides, sulfides, and oxides: I. Thermochemical data and calculated equilibria[J]. Economic Geology, 83(2): 377-394. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.83.2.377 AN M J, FENG M, ZHAO Y, 2009. Destruction of lithosphere within the North China Craton inferred from surface wave tomography[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 10(8): Q08016. BOWELL R J, 1992. Supergene gold mineralogy at Ashanti, Ghana: implications for the supergene behaviour of gold[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 56(385): 545-560. doi: 10.1180/minmag.1992.056.385.10 BOYLE R W, 1979. The geochemistry of gold and its deposits[R]. Ottawa: Geological Survey of Canada: 1-580. CABRI L J, 1965. Phase relations in the Au-Ag-Te systems and their mineralogical significance[J]. Economic Geology, 60(8): 1569-1606. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.60.8.1569 CHEN Y Q, ZHAO P D, 1998. Zonation in primary halos and geochemical prospecting pattern for the Guilaizhuang gold deposit, Eastern China[J]. Nonrenewable Resources, 7(1): 37-44. doi: 10.1007/BF02782507 CIOBANU C L, COOK N J, SPRY P G, 2006. Preface – special issue: telluride and selenide minerals in gold deposits – how and why?[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 87(3): 163-169. DENG J, WANG Q F, SANTOSH M, et al. , 2020. Remobilization of metasomatized mantle lithosphere: a new model for the Jiaodong gold province, Eastern China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 55(2): 257-274. doi: 10.1007/s00126-019-00925-0 DENG J F, SU S G, ZHAO H L, et al. , 2003. Deep processes of Mesozoic Yanshanian lithosphere thinning in North China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(3): 41-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) FAURE G, 1986. Principles of isotope geology[M]. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons: 1-589. FORNADEL A P, SPRY P G, JACKSON S E, et al. , 2014. Methods for the determination of stable Te isotopes of minerals in the system Au-Ag-Te by MC-ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 29(4): 623-637. doi: 10.1039/C3JA50237F GAO S, LUO T C, ZHANG B R, et al. , 1998. Chemical composition of the continental crust as revealed by studies in East China[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 62(11): 1959-1975. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00121-5 GOSS S C, WILDE S A, WU F Y, et al. , 2010. The age, isotopic signature and significance of the youngest Mesozoic granitoids in the Jiaodong terrane, Shandong Province, North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 120(3-4): 309-326. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.019 GUO F, FAN W M, WANG Y J, et al. , 2003. Geochemistry of late Mesozoic mafic magmatism in west Shandong Province, Eastern China: characterizing the lost lithospheric mantle beneath the North China block[J]. Geochemical Journal, 37(1): 63-77. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.37.63 GUO P, SANTOSH M, LI S R, 2013. Geodynamics of gold metallogeny in the Shandong Province, NE China: an integrated geological, geophysical and geochemical perspective[J]. Gondwana Research, 24(3-4): 1172-1202. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.02.004 HENLEY R W, BERGER B R, 2011. Magmatic-vapor expansion and the formation of high-sulfidation gold deposits: chemical controls on alteration and mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 39(1-2): 63-74. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2010.11.003 HOEFS J, 1997. Stable isotope geochemistry[M]. Berlin: Springer: 1-281. HOU M L, JIANG Y H, JIANG S Y, et al. , 2007. Contrasting origins of late Mesozoic adakitic granitoids from the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: implications for crustal thickening to delamination[J]. Geological Magazine, 144(4): 619-631. doi: 10.1017/S0016756807003494 HU B Q, GAO H D, WANG Y, et al. , 2021. A preliminary study on the Mesozoic massive gold metallogenic mechanism of the deep-large fault coupling with critical water in the Jiaodong area, China [J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27 (4): 585-595. HU H B, MAO J W, LIU D Y, et al. , 2004. The SHRIMP age of zircon from Tongshi magmatic complex in western Shandong and its geological implications[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(2): 453-460. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU H B, 2005. The ore-forming fluid and mineralization of epithermal gold deposits in Pingyi, western Shandong[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract) HU H B, MAO J W, NIU S Y, et al. , 2006. Geology and geochemistry of telluride-bearing Au deposits in the Pingyi area, western Shandong, China[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 87(3-4): 209-240. doi: 10.1007/s00710-006-0126-8 HU Y P, YU X F, LI D P, et al. , 2016. Modes of occurrence of telluride in Zhuojiazhuang tellurium-bearing gold deposit within Guilaizhuang gold orefield, Shandong Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 35(3): 475-490. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIANG N, CHEN J Z, GUO J H, et al. , 2012. In situ zircon U-Pb, oxygen and hafnium isotopic compositions of Jurassic granites from the North China Craton: evidence for Triassic subduction of continental crust and subsequent metamorphism-related 18O depletion[J]. Lithos, 142-143: 84-94. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.02.018 JIN L Y, SHEN K, 1995. Ore composition and genesis of the Guilaizhuang gold deposit in Pingyi Shandong Province[J]. Geology of Shandong, 11(1): 30-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) KELLEY K D, ROMBERGER S B, BEATY D W, et al. , 1998. Geochemical and geochronological constraints on the genesis of Au-Te deposits at Cripple Creek, Colorado[J]. Economic Geology, 93(7): 981-1012. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.93.7.981 KELLEY K D, SPRY P G, 2016. Critical elements in alkaline igneous rock-related epithermal gold deposits[M]//VERPLANCK P L, HITZMAN M W. Reviews in Economic Geology: Rare Earth and Critical Elements in Ore Deposits. Littleton: Society of Economic Geologists: 195-216. KESLER S E, DEDITIUS A P, CHRYSSOULIS S, 2007. Geochemistry of Se and Te in Arsenian pyrite: new evidence for the role of Se and Te hydrothermal complexes in Carlin and epithermal-type deposits[J]. Geological Survey of Finland, Guide, 53: 57-59. LAN T G, FAN H R, SANTOSH M, et al. , 2012. Early Jurassic high-K calc-alkaline and shoshonitic rocks from the Tongshi intrusive complex, eastern North China Craton: implication for crust–mantle interaction and post-collisional magmatism[J]. Lithos, 140-141: 183-199. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.01.015 LI L, LI S R, SANTOSH M, et al. , 2018. Early Jurassic decratonic gold metallogenesis in the eastern North China Craton: constraints from S-Pb-C-D-O isotopic systematics and pyrite Rb-Sr geochronology of the Guilaizhuang Te-Au deposit[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 92: 558-568. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.12.009 LI S R, SANTOSH M, 2017. Geodynamics of heterogeneous gold mineralization in the North China Craton and its relationship to lithospheric destruction[J]. Gondwana Research, 50: 267-292. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2017.05.007 LI S Y, LI J, JIANG L, et al. , 2021. Zircon U-Pb dating of diorite porphyrite in the Guilaizhuang gold deposit, western Shandong[J]. Geology in China, 48(1): 334-336. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI T, 1992. The statistical characteristics of the abundance of chemical elements in the earth’s crust[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 28(10): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Z S, WU M, HOU M L, et al. , 2015. Discovery and genesis of Au2-xTe in Guilaizhuang gold deposit, Shandong[J]. Geological Review, 61(S1): 339-340. (in Chinese) LIN J Q, TAN D J, JIN Y, 1996. 40Ar/39Ar ages of Mesozoic igneous activities in western Shandong[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 15(3): 22-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIN J Q, TAN D J, YU X F, et al. , 1997. Genesis of Guilaizhaung gold deposit, western Shandong[M]. Ji’nan: Shandong Science and Technology Press. (in Chinese) LIU J J, ZHAI D G, DAI H Z, et al. , 2017. Nanoscale characterization of Au2Te grains from the Sandaowanzi gold deposit, Northeast China[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 55(2): 181-194. doi: 10.3749/canmin.1600077 MAO J W, WANG Y T, ZHANG Z H, et al. , 2003. Geodynamic settings of Mesozoic large-scale mineralization in North China and adjacent areas[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(8): 838-851. MAO J W, XIE G Q, ZHANG Z H, et al. , 2005. Mesozoic large-scale metallogenic pulses in North China and corresponding geodynamic settings[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(1): 169-188. (in Chinese with English abstract) NIU S Y, SUN A Q, CHEN C, et al. , 2020. Multistage evolution of mantle plume and the ore-forming and ore-controlling role of mantle branch structure: A study on mineralization of the Guojiadian mantle branch structure in northwestern Jiaodong[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26 ( 5 ) : 656 - 672. (in Chinese with English abstract) OHMOTO H, RYE R O, 1979. Isotopes of sulfur and carbon[M]//BARNES H L. Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons: 509-567. POKROVSKI G S, BORISOVA A Y, BYCHKOV A Y, 2013. Speciation and transport of metals and metalloids in geological vapors[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 76(1): 165-218. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2013.76.6 QIAN H D, CHEN W, HUANG J, et al. , 2000. Mineralogical paragenetic relationships of Au-Ag tellurides in some gold deposits of China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 6(2): 220-224. (in Chinese with English abstract) QIU J S, WANG D Z, REN Q J, 1994. The first example of tellurium-gold type epithermal deposit in China-the Guilaizhuang gold deposit[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 30(1): 7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) SAKAI H, 1968. Isotopic properties of sulfur compounds in hydrothermal processes[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2(1): 29-49. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.2.29 SHEN K, NI P, LIN J Q, 2001. Characteristics and evolution of ore fluids in Guilaizhuang gold deposit, southwest Shandong[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 36(1): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHEN Y C, ZENG Q D, LIU T B, et al. , 2000. Geological features and metallogenitic prognostication of Zhuojiazhuang gold deposit, Pingyi County, Shandong Province[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 36(4): 20-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) SONG M C, LI S Z, YI P H, et al. , 2014. Classification and metallogenic theory of the Jiaojia-style gold deposit in Jiaodong peninsula, China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 44(1): 87-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) SONG M C, LI S Z, SANTOSH M, et al. , 2015. Types, characteristics and metallogenesis of gold deposits in the Jiaodong peninsula, eastern North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 612-625. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.06.019 SONG M C, LI J, ZHOU J B, et al. , 2020. The discovery and tectonic setting of the Early Cretaceous high-Mg diorites in the Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(1): 279-296. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.01.22 SONG Y X, YU X F, LI D P, et al. , 2020. Petrogenesis of the Beijie pluton from the northwestern Jiaodong peninsula: constraints from zircon U-Pb age, petrogeochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(5): 1477-1500. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.05.10 SUO X J, LIU S H, LI S R, et al. , 2020. Geologic feature and metallogenic model of Guilaizhuang gold deposit, Shandong[J]. Global Geology, 39(3): 544-556. (in Chinese with English abstract) TAN D J, LIN J Q, XU W L, et al. , 1993. The 40Ar/39Ar age of Tongshi subvolcanic complex and the mineralization period of Guilaizhuang gold deposit[J]. Geology of Shandong, 9(2): 68-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) TANG Y J, ZHANG H F, YING J F, 2011. Sr-Nd-Li isotopic constraints on the origin of EM1 end-member[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 30(1): 11-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) TOMBROS S, ST. SEYMOUR K, WILLIAMS-JONES A E, et al. , 2007. The genesis of epithermal Au-Ag-Te mineralization, Panormos Bay, Tinos Island, Cyclades, Greece[J]. Economic Geology, 102(7): 1269-1294. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.102.7.1269 VOUDOURIS P C, MELFOS V, SPRY P G, et al. , 2011. Mineralogy and geochemical environment of formation of the Perama Hill high-sulfidation epithermal Au-Ag-Te-Se deposit, Petrota graben, NE Greece[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 103(1-4): 79-100. doi: 10.1007/s00710-011-0160-z XIE J D, QIAN H D, LI Y H, 2000. Geochemical characteristics of tellurium and minerogenic mechanism of the Guilaizhuang tellurium-type gold deposit, Shandong Province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 15(2): 133-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU A T, WANG H Y, MA X L, et al. , 2018. Discussion on the occurrence law of stratoid carbonate type gold deposit in Guilaizhuang gold deposit[J]. China Metal Bulletin(3): 248-249. (in Chinese) XU H, YU Y X, WU X K, et al. , 2012. Intergrowth texture in Au-Ag-Te minerals from Sandaowanzi gold deposit, Heilongjiang Province: implications for ore-forming environment[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57(21): 2778-2786. doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5170-7 XU W G, FAN H R, HU F F, et al. , 2014. Gold mineralization in the Guilaizhuang deposit, southwestern Shandong Province, China: insights from phase relations among sulfides, tellurides, selenides and oxides[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 56: 276-291. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.06.010 XU W G, FAN H R, HU F F, et al. , 2015. Geochronology of the Guilaizhuang gold deposit, Luxi Block, eastern North China Craton: constraints from zircon U–Pb and fluorite-calcite Sm–Nd dating[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 390-399. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.10.010 YANG D P, LIU P R, 2001. Characteristics of tellur-seleno minerals in Zhuojiazhuang gold deposit of Pingyi and their ore-prospecting significance[J]. Geology of Shandong, 17(3-4): 102-106. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG J H, WU F Y, WILDE S A, 2003. A review of the geodynamic setting of large-scale Late Mesozoic gold mineralization in the North China Craton: an association with lithospheric thinning[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 23(3-4): 125-152. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(03)00033-7 YANG K F, FAN H R, SANTOSH M, et al. , 2012. Reactivation of the Archean lower crust: implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry of Late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong terrane, the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 146-147: 112-127. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.04.035 YANG L Q, DENG J, WANG Z L, et al. , 2014. Mesozoic gold metallogenic system of the Jiaodong gold province, Eastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2447-2467. (in Chinese with English abstract) YU X F, 1996. A new type gold deposit in Shandong: Guilaizhaung[M]//Shandong Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Collected Works on Geology and Mineral Resources in Shandong Province. Ji’nan: Shandong Science and Technology Press: 129-140. (in Chinese) YU X F, 1996. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Guilaizhuang gold deposit[C]//30th International Geological Congress Proceedings, Volume 2 of 3. YU X F, 2001. Ore-froming series and model of Tongshi gold field in Pingyi, Shandong Province[J]. Geology of Shandong, 17(3-4): 59-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) YU X F, HAN Z Z, 2008. Geology of micro-disseminated magnesium carbonate rock type gold deposit in the Tongshi area, western Shandong[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 44(4): 39-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) YU X F, FANG B M, HAN Z Z, 2009. Study on ore-forming series and mineralization of the Guilaizhuang gold field in western Shandong[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(1): 55-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) YU X F, 2010. Study on gold mineralization ore-forming rules and prospecting direction of Guilaizhuang gold mine in Pingyi County in Shandong Province[D]. Qingdao: Shandong University of Science and Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract) YU X F, SONG M C, LI D P, et al. , 2016. Prospecting breakthroughs and prospect of gold deposits in Shandong Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(10): 2847-2862. (in Chinese with English abstract) YU X F, LI D P, LI Z S, et al. , 2019. Research on geochemical process of Te-Au elements in Guilaizhuang gold deposit of western Shandong[J]. Mineral Deposits, 38(2): 277-290. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAI D G, 2014. Geological and geochemical characteristics and ore genesis of the Sadaowanzi gold-telluride deposit in Heilongjiang Province, NE China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAI D G, LIU J J, 2014. Gold-telluride-sulfide association in the Sandaowanzi epithermal Au-Ag-Te deposit, NE China: implications for phase equilibrium and physicochemical conditions[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 108(6): 853-871. doi: 10.1007/s00710-014-0334-6 ZHANG G Q, 2017. Study on characteristics and metallogenic mechanism of deep deposits in Guilaizhuang gold deposit in Pingyi County of Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 33(9): 7-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG H F, NAKAMURA E, KOBAYASHI K, et al. , 2010. Recycled crustal melt injection into lithospheric mantle: implication from cumulative composite and pyroxenite xenoliths[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 99(6): 1167-1186. doi: 10.1007/s00531-009-0467-8 ZHANG H F, ZHU R X, SANTOSH M, et al. , 2013. Episodic widespread magma underplating beneath the North China Craton in the Phanerozoic: implications for craton destruction[J]. Gondwana Research, 23(1): 95-107. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.12.006 ZHANG T, ZHANG Y Q, 2007. Geochronological sequence of Mesozoic intrusive magmatism in Jiaodong Peninsula and its tectonic constraints[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 13(2): 323-336. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Y M, ZHANG G Q, CHEN K M, et al. , 2018. Prospecting potential in the depth and periphery of Guilaizhuang gold deposit in western Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 34(10): 33-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Z C, LI Z N, 1997. Physicochemical conditions for the formation of tellurides rich gold deposits as exemplified by the Shuiquangou gold orefield[J]. Mineral Deposits, 16(1): 41-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAO P D, CHEN Y Q, 1998. The main way of geo-anomaly location of ore body[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geosciences, 23(2): 111-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHENG Y F, CHEN J F, 2000. Stable isotope geochemistry[M]. Beijing: China Science Publishing House: 1-316. (in Chinese) ZHOU X H, YANG J H, ZHANG L C, 2003. Metallogenesis of superlarge gold deposits in Jiaodong region and deep processes of subcontinental lithosphere beneath North China Craton in Mesozoic[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(S1): 14-25. ZHU D P, ZHANG G A, 1998. The geological and stress field characteristics of the ore-controlling tectonics of Gui-Lai-Zhuang gold deposit, Pingyi County, Shandong Province[J]. Gold, 19(5): 13-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU J, 2014. Geochronology, metallogenic model and ore prospecting of the Guilaizhuang gold deposit, west of Shandong Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU R X, FAN H R, LI J W, et al. , 2015. Decratonic gold deposits[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 58(9): 1523-1537. doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5139-x 邓晋福, 苏尚国, 赵海玲, 等. 2003华北地区燕山期岩石圈减薄的深部过程[J]. 地学前缘, 2003(03): 41-50. 胡宝群, 高海东, 王运, 等, 2021. 胶东中生代巨量金矿堆积的深大断裂-临界水耦合成矿机制新探[J]. 地质力学学报. 27(04): 585-585. 胡华斌, 毛景文, 刘敦一, 等, 2004. 鲁西铜石岩体的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 11(2): 453-460. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.02.015 胡华斌, 2005. 鲁西平邑地区浅成低温热液金矿床成矿流体及成矿作用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京). 胡勇平, 于学峰, 李大鹏, 等, 2016. 山东省归来庄金矿田卓家庄含碲金矿床的碲化物赋存状态研究[J]. 矿床地质, 35(3): 475-490. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2016.03.003 金隆裕, 沈昆, 1995. 山东省平邑县归来庄金矿物质组分及矿床成因分析[J]. 山东地质, 11(1): 30-40. 李世勇, 李杰, 蒋雷, 等, 2021. 鲁西归来庄金矿床矿化闪长玢岩锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 中国地质, 48(1): 334-336. doi: 10.12029/gc20210124 黎彤, 1992. 地壳元素丰度的若干统计特征[J]. 地质与勘探, 28(10): 1-7. 李增胜, 吴敏, 侯明兰, 等, 2015. 山东归来庄金矿床Au2-xTe的发现及其成因探讨[J]. 地质论评, 61(S1): 339-340. 林景仟, 谭东娟, 金烨, 1996. 鲁西地区中生代火成活动的40Ar/39Ar年龄[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 15(3): 22-29. 林景仟, 谭东娟, 于学峰, 等, 1997. 鲁西归来庄金矿成因[M]. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社. 毛景文, 谢桂青, 张作衡, 等, 2005. 中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背景[J]. 岩石学报, 21(1): 169-188. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2005.01.017 牛树银, 孙爱群, 陈超, 等, 2020, 地幔热柱多级演化及其幔枝构造成矿控矿: 以胶西北郭家 店幔枝构造为例[J]. 地质力学学报. 26(05): 656-672. 钱汉东, 陈武, 黄瑾, 等, 2000. 我国某些金矿床中金银碲化物矿物的共生关系[J]. 高校地质学报, 6(2): 220-224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2000.02.018 邱检生, 王德滋, 任启江, 等, 1994. 我国首例碲金型浅成低温热液金矿床: 山东平邑归来庄金矿床[J]. 地质与勘探, 30(1): 7-12. 沈昆, 倪培, 林景仟, 2001. 鲁西南归来庄金矿成矿流体特征和演化[J]. 地质科学, 36(1): 1-13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2001.01.001 沈远超, 曾庆栋, 刘铁兵, 等, 2000. 山东平邑卓家庄金矿地质特征及成矿预测[J]. 地质与勘探, 36(4): 20-23. 宋明春, 李三忠, 伊丕厚, 等, 2014. 中国胶东焦家式金矿类型及其成矿理论[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 44(1): 87-104. 宋明春, 李杰, 周建波, 等, 2020. 胶东早白垩世高镁闪长岩类的发现及其构造背景[J]. 岩石学报, 36(1): 279-296. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.01.22 宋英昕, 于学峰, 李大鹏, 等, 2020. 胶东西北部北截岩体岩石成因: 锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石地球化学与Sr-Nd-Pb同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 36(5): 1477-1500. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.05.10 索晓晶, 刘顺好, 李胜荣, 等, 2020. 山东归来庄金矿床地质特征及成矿模型[J]. 世界地质, 39(3): 544-556. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2020.03.004 谭东娟, 林景仟, 许文良, 等, 1993. 铜石杂岩体40Ar/39Ar年龄, 兼论归来庄金矿成矿时代[J]. 山东地质, 9(2): 68-72. 汤艳杰, 张宏福, 英基丰, 2011. 地幔中EM1端员成因的锂同位素制约[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 30(1): 11-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2011.01.002 谢家东, 钱汉东, , 李永徽. 2000. 山东省平邑归来庄碲型金矿床碲元素地球化学特征及成矿机制探讨[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2000(02): 133-141. 徐安泰, 王洪洋, 马小丽, 等, 2018. 归来庄金矿床似层状碳酸盐岩型金矿体赋存规律探讨[J]. 中国金属通报(3): 248-249. 杨德平, 刘鹏瑞, 2001. 山东平邑卓家庄金矿中的碲硒矿物特征[J]. 山东地质, 17(3-4): 102-106. 杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 等, 2014. 胶东中生代金成矿系统[J]. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2447-2467. 于学峰, 1996. 山东金矿新类型: 归来庄金矿床[M]//山东地质矿产局. 山东地质矿产研究文集. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社: 129-140. 于学峰, 2001. 山东平邑铜石金矿田成矿系列及成矿模式[J]. 山东地质, 17(3-4): 59-64. 于学峰, 韩作振, 2008. 鲁西铜石地区镁质碳酸盐岩微细浸染型金矿成矿地质特征[J]. 地质与勘探, 44(4): 39-44. 于学峰, 方宝明, 韩作振, 2009. 鲁西归来庄金矿田成矿系列及成矿作用研究[J]. 地质学报, 83(1): 55-64. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.01.006 于学峰, 2010. 山东平邑归来庄矿田金矿成矿作用成矿规律与找矿方向研究[D]. 青岛: 山东科技大学. 于学峰, 宋明春, 李大鹏, 等, 2016. 山东金矿找矿突破进展与前景[J]. 地质学报, 90(10): 2847-2862. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.10.021 于学峰, 李大鹏, 李增胜, 等, 2019. 鲁西归来庄金矿田碲金元素地球化学过程研究[J]. 矿床地质, 38(2): 277-290. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2019.02.004 翟德高, 2014. 黑龙江省三道湾子碲化物型金矿床地质地球化学特征与成矿机制[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京). 张国权, 2017. 山东省平邑归来庄金矿深部矿床特征及成矿规律研究[J]. 山东国土资源, 33(9): 7-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2017.09.002 张田, 张岳桥, 2007. 胶东半岛中生代侵入岩浆活动序列及其构造制约[J]. 高校地质学报, 13(2): 323-336. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.02.015 张英梅, 张国权, 陈昆明, 等, 2018. 鲁西归来庄金矿床深部外围找矿前景[J]. 山东国土资源, 34(10): 33-42. 张招崇, 李兆鼐, 1997. 富碲化物型金矿形成的物理化学条件: 以水泉沟金矿田为例[J]. 矿床地质, 16(1): 41-52. 赵鹏大, 陈永清, 1998. 地质异常矿体定位的基本途径[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 23(2): 111-114. 郑永飞, 陈江峰, 2000. 稳定同位素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-316. 祝德平, 张广安, 1998. 平邑归来庄金矿床控矿构造地质及其应力场特征[J]. 黄金, 19(5): 13-15. 朱金, 2014. 山东省平邑县归来庄隐爆角砾岩型金矿成矿年代、成因模式与找矿研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京). 朱日祥, 范宏瑞, 李建威, 等, 2015. 克拉通破坏型金矿床[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 45(8): 1153-1168. -




 下载:
下载: