ANALYSIS ON THE DEVELOPMENT CHARACTERISTICS AND ENGINEERING GEOMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE SONGPAN LOESS, WESTERN SICHUAN PROVINCE, CHINA
-
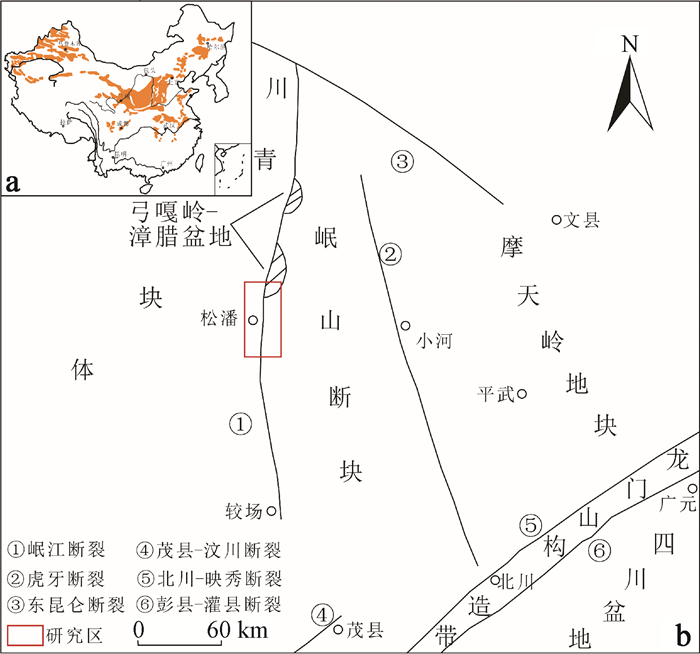
摘要: 以松潘幅和漳腊幅1:5万工程地质调查为基础,通过野外地质调查、地质测年、地理空间分析、室内试验和大型原位直剪试验等工作手段,对松潘黄土的发育分布特征和工程地质力学特性进行研究分析,认为松潘黄土具有以下特性:(1)松潘黄土为风成黄土,局部地形的变化通过控制近地面气流的运动从而影响松潘黄土的堆积,使得松潘黄土的分布与研究区地形、地貌的变化联系密切;(2)松潘黄土粉砂含量大于80%,大多含有碎石,碎石物质成分主要以砂板岩、炭质板岩和石英为主;(3)研究区内的松潘黄土主要分布于2712~3437 m的高程范围内,在山体南坡的分布远多于北坡,在地形开阔的断陷盆地内,黄土发育厚度大且呈广泛连续式分布,在高深的峡谷区,黄土的发育厚度变化大且呈零星的片状分布;(4)松潘黄土结构性明显,其力学性质受物质成分、含水率和天然结构面的影响,具有中等—强的湿陷性,黄土的结构性、水敏性、湿陷性等性质是该套地层内地质灾害发育的主要因素,松潘黄土的不良工程地质特性严重影响着研究区内未来重大工程的规划建设。Abstract: Based on the 1:50000 geological survey of Songpan map and Zhangla map, through the field geological survey, geological dating, geography space analysis, laboratory test and in-situ large scale direct shear test, the development and distribution characteristics and engineering geomechanical properties of the Songpan loess are studied in this article. The Songpan loess has the following features:(1) The Songpan loess is an eolian deposit and the changes of local terrain affect the accumulation of the Songpan loess by controlling the movement of the air near the ground. So the distribution of the Songpan loess is closely related to the topography and geomorphology of the study area.(2) The Songpan loess contains more than 80% silt and mostly with gravels, and the material composition of gravels mainly are sandy slate, carbonaceous slate and quartz.(3) The Songpan loess in the study area is mainly distributed within the scope of elevation between 2712~2712 m, mostly in the south slope of the mountain, within the broad fault basin. It has a large and extensive continuous distribution, while in the deep canyon area with a patchy distribution. (4) The Songpan loess has a distinct structure, and its mechanical properties are influenced by material composition, moisture content and natural structure plane, with an intermediate to high collapsibility. The loess characteristics of structure, water sensitivity and collapsibility are the main factors in the development of geological disasters in the strata and the construction of the future major projects in the research area will be influenced by the undesirable engineering geological characteristics and geological disasters of the Songpan loess.
-
Key words:
- Qinghai-Tibet Plateau /
- in-situ direct shear /
- engineering geology /
- Songpan /
- loess
-
表 1 松潘黄土的基本物理特性
Table 1. Basic physical properties of the Songpan loess
样品野外编号 取样地点 样品特征 含水率/% 密度/(g/cm3) 干密度(g/cm3) 饱和度/% 孔隙比 孔隙度/% 液限/% 塑限(%) 塑性指数(%) 液性指数 CL16ZJ03 大寨村 黄土 20.12 1.69 1.56 31 0.732 42.3 28.8 19.7 9.1 0.077 CL16ZJ01 大窑沟 黄土 20.4 1.77 1.42 59.1 0.92 47.9 35.4 22.9 12.5 -0.200 CL16ZJ02 红花屯滑坡 黄土 17.17 1.90 1.66 54 0.650 38.5 27.4 17.9 9.5 -0.287 SCL16G4015 石河桥村滑坡 粉质粘土 22.6 1.88 1.57 73.9 0.736 42.4 36.9 23.6 13.3 -0.271 SCL16G204 石坝子村 粉土 18.1 2.11 1.79 95.6 0.511 33.8 30.4 20.1 9.3 -0.215 SCL16G07 安宏乡格机寨 粉土 16.9 1.84 1.53 83.4 0.547 35.4 27.6 19.4 8.2 -0.305 表 2 松潘黄土粒度组成特征
Table 2. Characteristics of grain-size composition of the Songpan loess
试样编号 采样地点 粒径分布(%) 不均匀系数Cu 曲率系数Cc 定名 > 0.075 0.075~0.005 mm < 0.005 mm CL16ZJ03 大寨村公路旁 1.3 85.7 13 9.8 1.6 粉土 CL16ZJ02 红花屯滑坡 1 81 18 9.7 1.65 粉土 SCL16G2046 石坝子公路旁 4.5 82 13.5 13.2 0.022 粉土 表 3 松潘黄土湿陷性测试分析结果
Table 3. Test results of collapsibility of the Songpan loess in the study area
样品编号 取样地点 黄土湿陷系数(荷重200 kPa) 湿陷等级 CL16ZJ02 安宏乡红花屯村 0.068 中等湿陷 CL16ZJ03 大寨乡大寨村 0.140 强烈湿陷 表 4 松潘黄土原位大型直剪试验结果
Table 4. Result of large-scale in-situ direct shear test of the Songpan loess
试验编号 试验地点 试样描述 高程/m 含水率/% 密度/(g/cm3) 法向压力/kPa 抗剪强度参数 c/kPa φ/° CL16ZJ0101 大窑沟 黄土(含硝酸盐,天然含水率) 2979 20.4 1.774 50;100;150 64.68 16.21 CL16ZJ0102 大窑沟 黄土(含硝酸盐,加水) 2979 22.52 1.905 50;100;150;200 49.12 21.51 CL16ZJ0301 大寨村 黄土(加水) 3192 22.02 1.865 50;100;150;200 60.41 16.69 CL16ZJ0302 大寨村 黄土(天然含水率) 3192 20.12 1.853 50;100;150;200 83.5 14.95 -
[1] 刘东生, 文启忠, 郑洪汉, 等.黄土的物质成分和结构与水土保持的关系[J].水土保持通报, 1981, (1):16~19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-STTB198101003.htmLIU Dongsheng, WEN Qizhong, ZHENG Honghan, et al. The relationship between the material composition and structure of loess and soil and water conservation[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 1981, (1):16~19. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-STTB198101003.htm [2] 刘东生.黄土与环境[M].北京:科学出版社, 1985.LIU Dongsheng. Loess and Environment[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1985. (in Chinese) [3] 刘东生, 张宗祜.中国的黄土[J].地质学报, 1962, 41(1):1~14. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1008998LIU Dongsheng, ZHANG Zonghu. The loess in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1962, 41(1):1~14. (in Chinese) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1008998 [4] 柏松. 岷江上游干旱河谷黄土剖面的土壤发生特征及其古环境意义[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2005. http://www.doc88.com/p-7748820007858.htmlBAI Song. Research on pedogenetic properties and paleo-environment implication of loess in dry valley of the Minjiang river[D]. Chengdu:Sichuan University, 2005. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.doc88.com/p-7748820007858.html [5] 陈敬戈. 松潘牟尼沟黄土滑坡风险评估与防范研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y3040567CHEN Jingge. Risk assessment and prevention research of the loess landslide at Songpan Mounigou[D]. Chendu:Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y3040567 [6] 张永双, 张士运, 曲永新, 等.黄土高原北部坍窑灾害的形成机理分析[J].地球学报, 2004, 25(5):565~569. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200405013ZHANG Yongshuang, ZHANG Shiyun, QU Yongxin, et al. The mechanism of cave dwelling collapse in northern Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Geosicientia Sinica, 2004, 25(5):565~569. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200405013 [7] 彭建兵, 林鸿州, 王启耀, 等.黄土地质灾害研究中的关键问题与创新思路[J].工程地质学报, 2014, 22(4):684~691. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201404018PENG Jianbing, LIN Hongzhou, WANG Qiyao, et al. The critical issues and creative concepts in mitigation research of loess geological hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(4):684~691. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201404018 [8] 彭建兵, 吴迪, 段钊, 等典型人类工程活动诱发黄土滑坡灾害特征与致灾机理[J].西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(5):971~980. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xnjtdxxb201605021PENG Jianbing, WU Di, DUAN Zhao, et al. Disaster characteristics and destructive mechanism of typical loess landslide cases triggered by human engineering activities[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5):971~980. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xnjtdxxb201605021 [9] 孙瑛琳, 孙革军, 郭晓庚.四川松潘县小姓乡白柱头滑坡稳定分析与评价[J].东北水利水电, 2012, 30(4):15~16. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dbslsd201204007SUN Yinglin, SUN Gejun, GUO Xiaogeng. Analysis and evaluation of the landslide stability of Xiaoxing town, Songpan county, Sichuan province[J]. Water Resources & Hydropower of Northeast, 2012, 30(4):15~16. (in Chinese) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dbslsd201204007 [10] Fang X M. The origin and provenance of Malan loess along eastern margin of Qinhai-Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau and its adjacent area[J]. Science in China (Series B), 1995, 38(7):876~887. [11] Guo Z T, Ruddiman W F, Hao Q Z, et al. Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China[J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6877):159~163. doi: 10.1038/416159a [12] 方小敏, 李吉均, 陈富斌, 等.甘孜黄土与青藏高原冰冻圈演化[J].冰川冻土, 1996, 18(3):193~200 http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y2216139FANG Xiaomin, LI Jijun, CHEN Fubin, et al. Garz loess and the evolution of the cryosphere on the Tibetan plateau[J]. Journal of Glaciolgy and Geocryology, 1996, 1996, 18(3):193~200(in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y2216139 [13] 蒋复初, 吴锡浩, 肖华国, 等.川西高原甘孜黄土地层学[J].地球学报, 1997, 18(4):413~420. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj200602013JIANG Fuchu, WU Xihao, Xiao Huaguo, et al. The Ganzi loess stratigraphy in the west Sichuan Plateau[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 1997, 18(4):413~420. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj200602013 [14] 李铮华, 叶浩, 陈云, 等.黄土高原末次间冰期气候的不稳定性特征[J].地质力学学报, 1998, 4(4):48~49. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19980445&flag=1LI Zhenghua, YE Hao, CHEN Yun, et al. The palaeoclmatic evolution of the yellow river source area since 130ka B P[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 1998, 4(4):46~49. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19980445&flag=1 [15] 王运生, 李永昭, 向芳.川西高原甘孜黄土的成因[J].地质力学学报, 2003, 9(1):91~96. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20030112&flag=1WANG Yunsheng, LI Yongzhao, XIANG Fang. The Ganzi loess origin in the west Sichuan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2003, 9(1):91~96. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20030112&flag=1 [16] 乔彦松, 赵志中, 王燕, 等.川西甘孜黄土-古土壤序列的地球化学演化特征及其古气候意义[J].科学通报, 2010, 55(3):255~260. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=33081062QIAO Yansong, ZHAO Zhizhong, WANG Yan, et al. Variations of geochemical compositions and the paleoclimatic significance of a loess-soil sequence from Ganzê county of western Sichuan Province, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(24):4697~4703 http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=33081062 [17] 王书兵, 蒋复初, 田国强.理县黄土地层与环境记录[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(3):115~119. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200603016WANG Shubing, JIANG Fuchu, TIAN Guoqiang. Loess stratigraphy and environment records in Lixian county, Sichuan province[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(3):115~119. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200603016 [18] 彭东, 曹俊, 杨俊义, 等.四川九寨沟地区黄土的初步研究[J].中国区域地质, 2001, 20(4):359~365, 451. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200104005PENG Dong, CAO Jun, YANG Junyi, et al. Study of loess in the Jiuzhaigou area, Sichuan[J]. Regional Geology of China, 2001, 20(4):359~365, 451. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200104005 [19] 文星跃, 唐亚, 黄成敏, 等.青藏高原东缘风成黄土的多源性-以九寨沟黄土为例[J].山地学报, 2014, 32(5):603~614. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90138X/201405/662202675.htmlWEN Xingyue, TANG Ya, HUANG Chengmin, et al. Multi-material source of loess deposits from the Jiuzhaigou national nature, reserve on the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2014, 32(5):603~614. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90138X/201405/662202675.html [20] 刘维亮, 李国新, 谷曼.川西高原可尔因地区黄土成因研究[J].地质与资源, 2007, 16(4):300~302. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gjsdz200704012LIU Weiliang, LI Guoxin, GU Man. Study on the origin of the loess in Keryin area, West Sichuang Plateau[J]. Geology and Resources, 2007, 16(4):300~302. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gjsdz200704012 [21] 欧先交, 曾兰华, 周尚哲, 等.四川西部黄土沉积与环境演变研究综述[J].地球环境学报, 2012, 3(1):692~704. http://wuxizazhi.cnki.net/Search/DQHJ201201002.htmlOU Xianjiao, ZENG Lanhua, ZHOU Shangzhe, et al. A review on research of loess and environment change in west Sichuan Plateau of the eastern Qinghai-Tibentan Plateau[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2012, 3(1):692~704. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://wuxizazhi.cnki.net/Search/DQHJ201201002.html [22] 方小敏.青藏高原东部边缘及邻区马兰黄土成因与来源的初步研究[J].中国科学(B辑), 1994, 24(5):539~546. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JBXK199405013.htmFANG Xiaomin. The origin and provenance of Malan loess along the eastern margin of Qinghai-Xizang(Tibetan) Plateau and its adjacent area[J]. Science in China (Series B), 1993, 38(7):876~887. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JBXK199405013.htm [23] 王建民, 潘保田.青藏高原东部黄土沉积的基本特征及其环境[J].中国沙漠, 1997, 17(4):395~402. http://zgsm.westgis.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract4045.shtmlWANG Jianmin, PAN Baotian. Loess deposit in eastern part of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau:Its characteristics and environment[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 1997, 17(4):395~402. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://zgsm.westgis.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract4045.shtml [24] 钱洪, 马声浩, 龚宇.关于岷江断裂若干问题的讨论[J].中国地震, 1995, 11(2):140~146. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/scdz199903002QIAN Hong, MA Shenghao, GONG Yu. Discussions on the Minjiang Fault[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 1995, 11(2):140~146. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/scdz199903002 [25] 李吉均, 方小敏.青藏高原隆起与环境变化研究[J].科学通报, 1998, 43(15):1569~1574. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/237299LI Jijun, FANG Xiaomin. Uplift of the Tibetan Plateau and environmental changes[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 44(23):2117~2124. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/237299 [26] 施雅风, 李吉均.晚新生代青藏高原的隆升与东亚环境变化[J].地理学报, 1999, 54(1):10~21. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlxb199901002SHI Yafeng, LI Jijun. Uplift of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau and East Asia environmental change during Late Cenozoic[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1999, 54(1):10~21. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlxb199901002 [27] 刘晓东.青藏高原隆升对亚洲季风形成和全球气候与环境变化的影响[J].高原气象, 1999, 18(3):321~332. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gyqx199903008LIU Xiaodong. Influences of Qinghai-Xizang(Tibetan) Plateau uplift on the atmospheric circulation global climate and environment changes[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 1999, 18(3):321~332. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gyqx199903008 [28] Bronger A, Heinkele T. Mineralogical and clay mineralogical aspects of loess research[J]. Quaternary International, 1990, 7/8:37~51. doi: 10.1016/1040-6182(90)90037-5 [29] 刘维明, 杨胜利, 方小敏.川西高原黄土记录的末次冰期气候变化[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2013, 43(3):974~982. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hndzykc201103009LIU Weiming, YANG Shengli, FANG Xiaomin. Loess recorded climatic change during the last glaciation on the eastern Tibetan Plateau, Western Sichuan[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2013, 43(3):974~982. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hndzykc201103009 [30] 刘东生, 安芷生, 袁宝印.中国的黄土与风尘堆积[J].第四纪研究, 1985, 6(1):113~125. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb200605001LIU Dongsheng, AN Zhisheng, YUAN Baoyin. Eolian process and dust mantle(loess) in China[J]. Quaternary Science 1985, 6(1):113~125. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb200605001 [31] 司建涛, 刘顺.青藏高原东缘岷江断裂构造特征、变形序列和演化历史[J].四川地质学报, 2008, 28(1):1~5. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/scdzxb200801001SI Jiantao, LIU Shun. Geological features, deformation sequence and evolution of the Minjiang fault on the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2008, 28(1):1~5. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/scdzxb200801001 [32] 赵小麟, 邓起东, 陈社发.岷山隆起的构造地貌学研究[J].地震地质, 1994, 16(4):429~439. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200304026ZHAO Xiaolin, DENG Qidong, CHEN Shefa. Tectonic geomorphology of the Minshan uplift in theWestern Sichuan, Southwestern China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1994, 16(4):429~439. (in Chinese) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200304026 [33] 杨德江.狭管效应与气象灾害[J].科技创新导报, 2010, (21):142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-098X.2010.21.116YANG Dejiang. Narrow pipe effect and metrological disasters[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2010, (21):142. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-098X.2010.21.116 [34] 赵景波, 岳应利, 陈云.黄土湿陷性及其成因[J].地质力学学报, 1997, 3(4):62~67. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19970448&flag=1ZHAO Jingbo, YUE Yingli, CHEN Yun. Collapsibility of loess and its origin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 1997, 3(4):62~67. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19970448&flag=1 [35] 张永双, 曲永新.陕北晋西砂黄土的胶结物与胶结作用研究[J].工程地质学报, 2005, 13(1):18~28. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb200501003ZHANG Yongshuang, QU Yongxin. Cements of sand loess and their cementation in north Shaanxi and west Shanxi[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2005, 13(1):18~28. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb200501003 [36] 郭长宝, 张瑞端, 张永双, 等. 带有自动数据采集系统的岩土体原位直剪试验装置及方法: ZL201310538634. 8[P]. 2015~11-06.GUO Changbao, ZHANG Ruiduan, ZHANG Yongshuang, et al. The in-situ direct shear test device and method of the geotechnical body with automatic data acquisition system:ZL201310538634.8[P]. 2015~11-06. (in Chinese) [37] 吴瑞安, 张永双, 王献礼, 等.汶川地震区崩滑堆积体强度现场直剪试验研究[J].地质力学学报, 2017, 23(1):105~114. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170106&flag=1WU Rui'an, ZHANG Yongshuang, WANG Xianli, et al. In-situ direct shearing test on landslide accumulation body intensity of Wenchuan earthquake region[J]. Journal of Geomechanics 2017, 23(1):105~114. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170106&flag=1 [38] 曹玲, 罗先启.三峡库区千将坪滑坡滑带土干-湿循环条件下强度特性试验研究[J].岩土力学, 2007, 28(S1):93~97. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/6471866CAO Ling, LUO Xianqi. Experimental study of dry-wet circulation of Qianjiangping Landslide's unsaturated soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(S1):93~97. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/6471866 [39] 肖丁, 张沛然, 杨帆, 等.黄土抗剪强度试验研究[J].四川建筑, 2015, 35(1):102~103. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/scjzkxyj201504009XIAO Ding, ZHANG Peiran, YANG Fan, et al. Experimental study on shear strength of Loess[J]. Sichuan Architecture, 2015, 35(1):102~103. (in Chinese) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/scjzkxyj201504009 -





 下载:
下载: