EXTRACTION OF LITHOLOGIC INFORMATION FROM THE EAST KULUN OROGENIC BELT USING ASTER REMOTE SENSING IMAGE
-
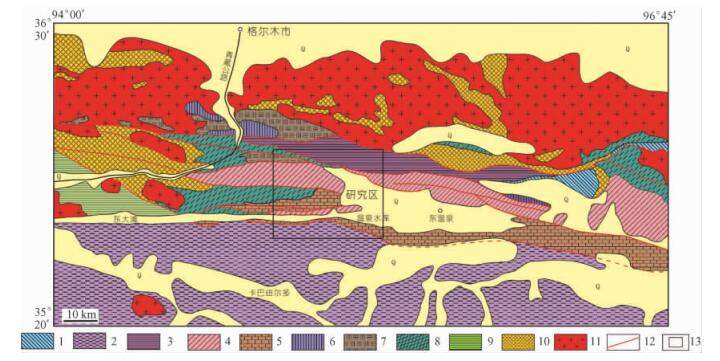
摘要: 应用ASTER数据,通过主成分分析和矿物指数等岩性信息提取方法,对东昆仑造山带温泉水库地区进行了岩性信息的遥感识别与提取。研究结果表明,主成分图像和矿物指数图能很好地反映岩石物质组成信息。元古宇结晶灰岩、二叠系灰岩、中三叠统闹仓坚沟组砂岩以及上三叠统八宝山组碎屑岩等分布面积较大的岩石地层单位在ASTER图像上可以识别出来。ASTER图像对基岩裸露区岩性信息进行提取是行之有效的方法,特别是碳酸盐岩及具有不同SiO2含量的沉积岩和火山岩; 但对厚度较小的岩性识别及岩石蚀变还需要进一步研究。
-
关键词:
- 高级星载热发射和反射辐射计(ASTER) /
- 岩性提取 /
- 主成分分析 /
- 矿物指数 /
- 东昆仑造山带
Abstract: By using ASTER data and such methods for extraction of lithologic information as major composition image and the mineral index, a discrimination for and extraction of lithologic information has been made in the Wenquan Reservoir area of the East Kunlun orogenic belt. The results show that the major composition image and the mineral index can well reveal the composition of rocks. Clearly shown on ASTER images are lithostratigraphic units covering a relatively large area, including Proterozoic crystalline limestone, the limestone in Permian Malzheng Formation, the sandstone in Middle Triassic Naocangjiangou Formation and the clastic rocks in Upper Triassic Babaoshan Formation. ASTER images would prove to be an effective method for extraction of lithologic information in bedrock exposed areas, especially for carbonate rocks as well as sedimentary and volcanic rocks with varying SiO2 contents. But for the rock units of small thickness or altered rocks, the methods need to be improved.-
Key words:
- ASTER /
- lithologic extraction /
- major composition analysis /
- mineral index /
- East Kunlun orogenic belt
-
表 1 ASTER系统的基本物理参数[8]
Table 1. Basic physical parameters of the ASTER system

-
[1] 傅碧宏.遥感岩石学的研究及进展[J].地球科学进展, 1996, 11 (3) : 252 ~ 258.FU Bi-hong. Study and recent advances of remote sensine petrology[J]. Advance in Earth Science, 1996, 11 (3) : 252 ~ 258. [2] 甘甫平, 王润生, 马蔼乃, 等.光谱遥感岩矿识别基础与技术研究进展[J].遥感技术与应用, 2002, 17 (3) : 140 ~ 147. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2002.3.140GAN Fu-ping, WANG Run-sheng, MA Ai-nai, et al. The development and tendency of both basis and techniques of discrimination for minerals and rocks using spectral remote sensing data[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2002, 17 (3) : 140 ~ 147. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2002.3.140 [3] 张玉君, 杨建民, 陈薇. ETM+ (TM)蚀变遥感异常提取方法研究与应用———地质依据和波谱前提[J].国土资源遥感, 2002, (4) : 30 ~ 36. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2002.04.07ZHANG Yu-jun, YANG Jian-min, CHEN Wei. A study of the method for extraction of alteration anomalies from the ETM + (TM) data and its application: Geologic basis and spectral precondition[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2002, (4) : 30 ~ 36. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2002.04.07 [4] 张玉君, 曾朝铭, 陈薇. ETM + (TM)蚀变遥感异常提取方法研究与应用———方法选择和技术流程[J].国土资源遥感, 2003, (2) : 44 ~ 49. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2003.02.11ZHANG Yu-jun, ZENG Zhao-ming, CHEN Wei. A study of the method for extraction of alteration anomalies from the ETM + (TM) data and its application: Method selection and technological flow chart[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2003, (2) : 44 ~ 49. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2003.02.11 [5] Ce'cile Gomez, Christophe Delacourt, Pascal Allemand, et al. Using ASTER remote sensing data set for geological mapping, in Namibia[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 2005, 30 (1-3) : 97 ~ 108. doi: 10.1016/j.pce.2004.08.042 [6] Vaughan R G, Hook S J, Calvin W M, et al. Surface mineral mapping at Steamboat Springs, Nevada, USA, with multiwavelength thermal infrared images[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2005, 99 (1- 2) : 140 ~ 158. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2005.04.030 [7] 二宫芳树, 傅碧宏.帕米尔东北缘ASTER多光谱热红外遥感数据的岩性信息提取[J].新疆地质, 2002, 21 (1) : 22 ~ 30. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_xjdz200301004Yoshiki Ninomiya, FU Bi-hong. Extracting lithologic information from ASTER multispectral thermal infrared data in the northeastern Pamirs[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2002, 21 (1) : 22 ~ 30. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_xjdz200301004 [8] 耿新霞, 杨建民, 张玉君, 等. ASTER在浅覆盖区蚀变遥感异常信息提取中应用———以新疆西准噶尔包古图斑岩铜矿岩体为例[J].地质论评, 2008, 54 (2) : 184 ~ 191.GENG Xin-xia, YANG Jian-min, ZHANG Yu-jun, et. al. The application of ASTER remote sensing data for extraction of alteration anomalies information in shallow overburden area: A case study of the Baoguto porphyry copper deposit intrusion in western Junggar, Xinjiang[J]. Geological Review, 2008, 54 (2) : 184 ~ 191. [9] 倪晋宇, 胡道功, 周春景.东昆仑造山带纳赤台群形成的大地构造环境探讨[J].地质力学学报, 2010, 16 (1) : 11 ~ 20. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100102&journal_id=dzlxxbNI Jin-yu, HU Dao-gong, ZHOU Chun-jing. Discussion on tectonic environment of Naij Tal Group, East Kunlun orogenic belt[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 16 (1) : 11 ~ 20. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100102&journal_id=dzlxxb [10] 周春景, 胡道功, Barosh P J, 等.东昆仑三道湾流纹英安斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质力学学报, 2010, 16 (1) : 28 ~ 35. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100104&journal_id=dzlxxbZHOU Chun-jing, HU Dao-gong, Barosh P J, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating of the rhyolite-dcite porphyry in the Sandaowan of east Kunlun MTS and its geological significance[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 16 (1) : 28 ~ 35. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100104&journal_id=dzlxxb [11] 陆露, 胡道功, 张永清, 等.昆中断裂带同构造花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义[J].地质力学学报, 2010, 16 (1) : 36 ~ 43. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100105&journal_id=dzlxxbLU Lu, HU Dao-gong, ZHANG Yong-qing, et al. Ziron U-Pb age for syntectoin granitic porphyry and its teceonic significance in the middle Kunlun fallt belt[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 16 (1) : 36 ~ 43. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100105&journal_id=dzlxxb [12] 吴芳, 张绪教, 张永清, 等.东昆仑闹仓坚沟组流纹质凝灰岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质力学学报, 2010, 16 (1) : 44 ~ 50. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100106&journal_id=dzlxxbWU Fang, ZHANG Xu-jiao, ZHANG Yong-qing, et al. Zircon U-Pb ages for rhyolite tuff of the Naocangjiangou Formation in the east Kulun orogenic belt and their implication[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 16 (1) : 44 ~ 50. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100106&journal_id=dzlxxb [13] 张紫程, 张绪教, 高万里, 等.东昆仑左行韧性剪切带形成时代的锆石U-Pb年龄证据[J].地质力学学报, 2010, 16 (1) : 51 ~ 58. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100107&journal_id=dzlxxbZHANG Zi-cheng, ZhANG Xu-jiao, GAO Wan-li, et. al. Evidence of zircon U-Pb ages for the formation time of the East Kunlun Left-Lateral Ductile Shear Belt[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 16 (1) : 51 ~ 58. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100107&journal_id=dzlxxb [14] 张耀玲, 张绪教, 胡道功, 等.东昆仑造山带纳赤台群流纹岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄[J].地质力学学报, 2010, 16 (1) : 21 ~ 27, 50. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100103&journal_id=dzlxxbZHANG Yao-ling, ZHANG Xu-jiao, HU Dao-gong, et al. SHRIMP-based zircon U-Pb ages for rhyolite of the Naij Tal Group in the east Kulun orogenic belt[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 16 (1) : 21 ~ 27, 50. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100103&journal_id=dzlxxb [15] 薛腊梅, 赵希涛, 张耀玲, 等.遥感技术在东昆仑新生代地质填图中的应用[J].地质力学学报, 2010, 16 (1) : 70 ~ 77. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100109&journal_id=dzlxxbXUE La-mei, ZHAO Xi-tao, ZHANG Yao-ling, et al. Application of remote sensing technique in the east Kunlun Cenozoic geological mapping[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 16 (1) : 70 ~ 77. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100109&journal_id=dzlxxb [16] 吴珍汉, 吴中海, 胡道功, 等.青藏高原新生代构造演化与隆升过程[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009.WU Zhen-han, WU Zhong-hai, HU Dao-gong, et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution and uplift process of the Tibetan plateau [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2009. [17] 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 等.造山的高原———青藏高原地体的拼合、碰撞造山及隆盛机制[M].北京:地质出版社, 2007. 1 ~ 458.XU Zhi-qin, YANG Jing-shui, LI Hai-bing, et al. An orogenic plateau: Terrain tectonics, collisional orogenesis, and rising mechanisms of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007. 1 ~ 458. [18] 郭亚东, 史舟.先进星载热发射和反射辐射仪(ASTER)的特点及应用[J].遥感技术与应用, 2003, 18 (5) : 346 ~ 352. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2003.5.346GUO Ya-dong, SHI Zhou. Characteristics and applications of ASTER[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2003, 18 (5) : 346 ~ 352. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2003.5.346 [19] Aleks Kalinowski, Simon Oliver. ASTER mineral index processing manual[M]. Remote Sensing Applications Geoscience Austrilia, 2004, 10. [20] John R Jensen. 遥感数字影像处理导论(第3版)[M]. 陈晓玲, 龚威, 李平湘, 等(译). 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2007. 281 ~ 287.John R Jensen. Introductory digital image processing: A remote sensing perspective (3rd Edition)[M ]. CHEN Xiaoling, GONG Wei, LI Ping-xiang, et al. (Trans. ). Beijing: China Machine Press, 2007. 281 ~ 287. [21] 李建国, 毛德宝.基于ETM +与ASTER数据的矿化蚀变信息提取方法研究———以满都拉地区为例[J].地质调查与研究, 2007, 30 (3) : 234 ~ 240. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qhwjyjjz200703011LI Jian-guo, MAO De-bao. The methods for extracting alteration anomalies based on the ETM + and ASTER data: A case study of the Mandula area[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2007, 30 (3) : 234 ~ 240. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qhwjyjjz200703011 -





 下载:
下载: