APPLICATION OF LASER RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY IN THE STUDY OF ORGANIC INCLUSIONS: A CASE STUDY ON OIL AND GAS INCLUSIONS IN THE 8th MEMBER OF THE SHIHEZI FORMATION IN WESTERN SULIGE GASFIELD
-
摘要: 以苏里格气田西部盒8段储层砂岩油气包裹体为例,应用激光拉曼探针微区原位分析技术,对其赋存于石英颗粒表面愈合裂隙、次生加大边的2期含烃有机包裹体的成分及其相对摩尔百分含量进行测定:早期包裹体主要为含气态烃和含盐水气态烃的气液两相有机包裹体,晚期包裹体为含气态烃气液两相有机包裹体;其气相成分以CO2、CH4和N2等气体为主,溶解有CO、H2S、H2、C2H2、C2H4、C2H6、C4H6等气体;液相成分以H2O和CO2为主,此外还含有极少量的阴离子SO42-和CO32-离子(小于0.03 mol/L)。研究表明:早期有机包裹体含有大量CO2无机气体、H2O和少量低碳烷烃,说明早期有机质成熟度处于未成熟—低成熟阶段,虽有天然气生成,但运移规模有限,形成的有机包裹体极少,反映了天然气进入储层后置换地层水的过程;晚期有机包裹体与之相反,烃类和N2含量均较高,而CO2无机气体和H2O含量均较低,可见晚期有机包裹体代表了油气形成高峰和大规模进入储层成藏期间的流体特征,为有机质的热演化程度,油气生成、运移,划分油气成藏期次提供了科学依据。Abstract: Based on the application of laser raman microprobe analysis in situ technique, the nature of oil and gas inclusions in the 8th member of the Shihezi formation in western Sulige gas field was identified. The composition and relative molar fraction of phaseⅡhydrocarbon-bearing organic inclusions in the healing fracture of the quartz grain surface and in the secondary enlargement margin were determined. The results show that the early-stage inclusions mainly are gas-liquid two-phase organic inclusions containing gaseous hydrocarbon and brine gaseous hydrocarbon, and the late-stage inclusions are gas-liquid two-phase organic inclusions containing gaseous hydrocarbon; The gas phase is dominated by gases such as CO2, CH4 and N2, and the CO, H2S, H2, C2H2, C2H4, C2H6, C4H6, H2O and CO2are dissolved in it; the liquid phase mainly is consist of H2O and CO2, and also contains a very small amount of anion SO42- and CO32-(less than 0.03 mol/L). The research makes clear that the early-stage organic inclusions contain large amounts of CO2, H2O and a small amount of inorganic gas of low carbon alkane. It indicates that the early maturity of organic matter was in immature-low mature stage. Although natural gas is generated, the migration is limited in scale. The organic inclusions are few and far between. It reflects the replacement of formation water by natural gas entering reservoir. The late-stage organic inclusions are the opposite. The content of hydrocarbons and N2 are higher, but the content of CO2, inorganic gas and H2O are lower. It represents the characteristics of the peak of oil and gas formation and large-scale oil and gas accumulation. It provides a scientific basis for the thermal evolution of organic matter, the generation and migration of oil and gas, and the division of oil and gas accumulation stages.
-
表 1 苏里格西部探区盒8段油气包裹体样品地质特征
Table 1. Geological characteristics of oil and gas inclusion samples in the 8th member of the Shihezi formation of Western Sulige exploration area
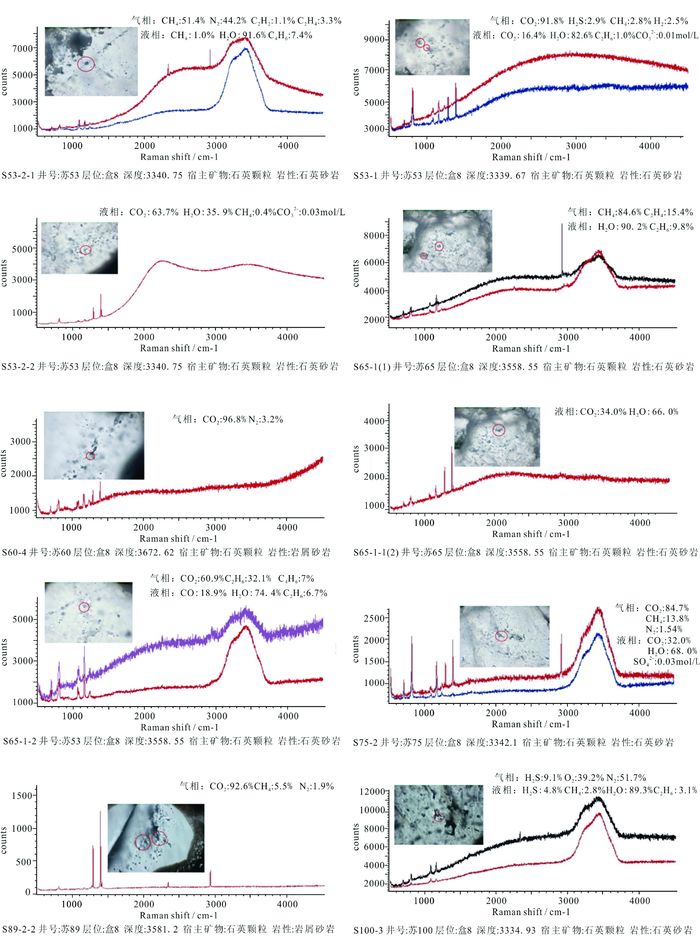
井号 样号 层位 深度/m 气/水层 岩性 苏53 S53-2-1 盒8 3340.75 — 石英砂岩 苏53 S53-1 盒8 3339.67 — 石英砂岩 苏53 S53-2-2 盒8 3340.75 — 石英砂岩 苏65 S65-1(1) 盒8 3558.55 — 石英砂岩 苏65 S65-1-1(2) 盒8 3558.55 — 石英砂岩 苏65 S65-1-2 盒8 3558.55 含气层 石英砂岩 苏75 S75-2 盒8 3342.1 — 石英砂岩 苏60 S60-4 盒8 3672.62 含气层 岩屑石英砂岩 苏89 S89-2-2 盒8 3581.2 含气层 岩屑石英砂岩 苏100 S100-3 盒8 3334.93 — 石英砂岩 表 2 苏里格气田西部探区盒8段流体包裹体气相激光拉曼分析结果
Table 2. Analysis results of laser raman spectroscopy of fluid inclusions in the 8th member of the Shihezi formation of Western Sulige exploration area
井号 样号 包裹体
期次层位 宿主
矿物包裹体
类型气相/%(摩尔数的相对百分含量) CO2 H2S CH4 N2 H2 O2 C2H2 C2H4 C2H6 C4H6 总和 苏53 S53-2-1 晚期 盒8 石英裂隙 气液两相包裹体 51.4 44.2 1.1 3.3 100.0 苏53 S53-1 早期 盒8 石英裂隙 气液两相包裹体 91.8 2.9 2.8 2.5 100.0 苏75 S75-2 早期 盒8 石英碎屑 气液两相包裹体 84.7 13.8 1.5 100.0 苏65 S65-1(1) 晚期 盒8 石英碎屑 气液两相包裹体 84.6 15.4 100.0 苏65 S65-1-2 早期 盒8 石英裂隙 气液两相包裹体 60.9 32.1 7.0 100.0 苏60 S60-4 早期 盒8 石英裂隙 纯气相包裹体 96.8 3.2 100.0 苏89 S89-2-2 早期 盒8 石英裂隙 纯气相包裹体 92.6 5.5 1.9 100.0 苏100 S100-3 晚期 盒8 石英裂隙 气液两相包裹体 9.1 51.7 39.2 100.0 表 3 苏里格气田西部探区盒8段流体包裹体液相激光拉曼分析结果
Table 3. Analysis results of laser raman spectroscopy of fluid inclusions in liquid phase
井号 样号 包裹体
期次层位 宿主
矿物包裹体
类型液相/%(摩尔数的相对百分含量) CO2 H2S CH4 CO H2O C2H6 C4H6 总和 SO42- CO32- 苏53 S53-2-1 晚期 盒8 石英裂隙 气液两相包裹体 1.0 91.6 7.4 100.0 苏53 S53-1 早期 盒8 石英裂隙 气液两相包裹体 16.4 82.6 1.0 100.0 0.01 苏75 S75-2 早期 盒8 石英碎屑 气液两相包裹体 32.0 68.0 100.0 0.03 苏65 S65-1(1) 晚期 盒8 石英碎屑 气液两相包裹体 90.2 9.8 100.0 苏65 S65-1-2 晚期 盒8 石英碎屑 气液两相包裹体 18.9 74.4 6.7 100.0 苏53 S53-2-2 早期 盒8 石英裂隙 纯液相包裹体 63.7 0.4 35.9 100.0 0.03 苏65 S65-1-1(2) 早期 盒8 石英裂隙 纯液相包裹体 34.0 66.0 100.0 苏100 S100-3 晚期 盒8 石英裂隙 气液两相包裹体 4.8 2.8 89.3 3.1 100.0 -
[1] 徐培苍, 李如碧, 王永强, 等.地学中的拉曼光谱[M].西安:陕西科学技术出版社, 1996, 102~103.XU Peicang, LI Rubi, WANG Yongqiang, et al. Raman spectroscopy in geosciences[M]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Science and Technology Press, 1996, 102~103. [2] 朱华东, 罗勤, 周理, 等.激光拉曼光谱及其在天然气分析中的应用展望[J].天然气工业, 2013, 33(11): 110~114. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2013.11.019ZHU Huadong, LUO Qin, ZHOU Li, et al. Application prospect of natural gas component analysis using Laser Raman spectroscopy[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2013, 33(11): 110~114. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2013.11.019 [3] Maiman T H. Stimulated optical radiation in ruby[J]. Nature, 1960, 187(4736): 493~494. doi: 10.1038/187493a0 [4] Abraham W Z. Charge coupled device: US, 3656011[P]. 1972-04-11. [5] Fleischmann M, Hendra P J, McQuillan A J. Raman spectra of pyridine adsorbed at a silver electrode[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 1974, 26(2): 163~166. doi: 10.1016/0009-2614(74)85388-1 [6] Strommen D P, Nakamoto K. Resonance Raman spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Chemical Education, 1977, 54(8): 474. doi: 10.1021/ed054p474 [7] Borman S A. Nonlinear Raman spectroscopy[J]. Aanlytical Chemistry, 1982, 54(9): 1024A~1026A. doi: 10.1021/ac00246a002 [8] 张美珍, 施伟军, 张志荣.显微激光拉曼光谱仪的地质应用[J].石油实验地质, 2003, 30(3): 307~310. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD200803019.htmZHANG Meizhen, SHI Weijun, ZHANG Zhirong. Laser Raman microscope and its application in geology[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2003, 30(3): 307~310. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD200803019.htm [9] 田国辉, 陈亚杰, 冯清茂.拉曼光谱的发展及应用[J].化学工程师, 2008, 22(1): 34~36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSSX201301003.htmTIAN Guohui, CHEN Yajie, FENG Qingmao. Development and application of Raman technology[J]. Chemical Engineer, 2008, 22(1): 34~36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSSX201301003.htm [10] 贡云云, 孙红华, 曾敏敏.激光拉曼光谱在油气包裹体中的应用[J].科技视界, 2014, (3): 163. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJSJ201403128.htmGONG Yunyun, SUN Honghua, ZENG Minmin. Application of laser Raman spectroscopy in oil and gas inclusions[J]. Science & Technology Vision, 2014, (3): 163. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJSJ201403128.htm [11] 潘立银, 倪培, 欧光习, 等.油气包裹体在油气地质研究中的应用—概念、分类、形成机制及研究意义[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2006, 25(1): 19~28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200601002.htmPAN Liyin, NI Pei, OU Guangxi, et al. Application of organic inclusion study in petroleum geology—Concept, classification, formation mechanism and significance[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2006, 25(1): 19~28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200601002.htm [12] Zhou W W, Jiang W R, Li R X, et al. Organic inclusion and its application on petroleum system in Zhu Depression, Peal River Mouth Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2004, 31(2): 128~134. doi: 10.1007%2Fs11771-013-1661-1.pdf [13] 黄伟林, 薛理辉, 彭东涛.利用U-1000型激光拉曼探针测定流体包裹体气体成分的研究[J].矿物学报, 1990, 10(1): 1~7, 97. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB199001000.htmHUANG Weilin, XUE Lihui, PENG Dongtao. Application of laser Raman microprobe (U-1000 RAMAN) to analyzing the gas compositions of fluid inclusions[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1990, 10(1): 1~7, 97. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB199001000.htm [14] 陈勇, Burke E A J.流体包裹体激光拉曼光谱分析原理、方法、存在的问题及未来研究方向[J].地质论评, 2009, 55(6): 851~861. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200906012.htmCHEN Yong, Burke E A J. Laser Raman microspectroscopy of fluid inclusions: theory, method, problems and future trends[J]. Geological Review, 2009, 55(6): 851~861. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200906012.htm [15] Rosasco G J, Roedder E, Simmons J H. Laser-excited Raman spectroscopy for nondestructive partial analysis of individual phases in fluid inclusions in minerals[J]. Science, 1975, 190(4214): 557~560. doi: 10.1126/science.190.4214.557 [16] Pasteris J D, Kuehn C A, Bodnar R J. Applications of the laser Raman microprobe RAMANOR U-1000 to hydrothermal ore deposits; Carlin as an example[J]. Economic Geology, 1986, 81(4): 915~930. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.81.4.915 [17] Mernagh T P, Wilde A R. The use of the laser Raman microprobe for the determination of salinity in fluid inclusions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53(4): 765~771. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(89)90022-7 [18] 葛云锦, 陈勇, 周瑶琪, 等.流体包裹体成分测定的低温相变和显微拉曼光谱分析技术研究进展[J].岩矿测试, 2008, 27(3): 207~210. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS200803016.htmGE Yunjin, CHEN Yong, ZHOU Yaoqi, et al. Advance in low temperature phase transition and Raman spectrum technique in composition determination of fluid inclusions[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2008, 27(3): 207~210. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS200803016.htm [19] 张鼐, 田作基, 冷莹莹, 等.烃和烃类包裹体的拉曼特征[J].中国科学D辑:地球科学, 2007, 37(7): 900~907. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200707004.htmZHANG Nai, TIAN Zuoji, LENG Yingying, et al. Raman characteristics of hydrocarbon and hydrocarbon inclusions[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2007, 50(8): 1171~1178. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200707004.htm [20] 何谋春, 吕新彪, 王群英.有机包裹体的拉曼光谱测定[J].石油实验地质, 2002, 24(2): 181~183, 186. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200202181HE Mouchun, LV Xinbiao, WANG Qunying. Measurement of laser Raman spectra in organic fluid inclusions[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2002, 24(2): 181~183, 186. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200202181 [21] 李荣西, 邸领军, 席胜利.鄂尔多斯盆地米脂气田天然气逸散:流体包裹体证据[J].中国科学D辑:地球科学, 2007, 37(S1): 103~109. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2007S1011.htmLI Rongxi, DI Lingjun, XI Shengli. Natural gas leakage of Mizhi gas reservoir in Ordos Basin, recorded by natural gas fluid inclusion[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2007, 50(S2): 124~132. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2007S1011.htm [22] 杨华, 付金华, 魏新善.鄂尔多斯盆地天然气成藏特征[J].天然气工业, 2005, 25(4): 5~8. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10710-1014071033.htmYANG Hua, FU Jinhua, WEI Xinshan. Characteristics of natural gas reservoir formation in E'Erduosi Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2005, 25(4): 5~8. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10710-1014071033.htm [23] 董会, 李宏, 王志海, 等.应用有机包裹体研究天然气成藏特征——以鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格气田西部山1段为例[J].西北地质, 2016, 49(2): 248~256. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201602025.htmDONG Hui, LI Hong, WANG Zhihai, et al. Application of organic fluid inclusion to study the characteristics of gas reservoir formation: example from the Sulige gas field in western Ordos Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2016, 49(2): 248~256. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201602025.htm [24] 刘新社, 周立发, 侯云东, 等.运用流体包裹体研究鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界天然气成藏[J].石油学报, 2007, 28(6): 38~42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200706007.htmLIU Xinshe, ZHOU Lifa, HOU Yundong, et al. Study of gas charging in the Upper Paleozoic of Ordos Basin using fluid inclusion[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(6): 38~42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200706007.htm [25] 邢振辉, 程林松, 周新桂, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地北部塔巴庙地区上古生界致密砂岩气藏天然裂缝形成机理浅析[J].地质力学学报, 2005, 11(1): 33~42. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20050107&flag=1XING Zhenhui, CHENG Linsong, ZHOU Xingui, et al. Mechanism of natural fracture formation in the Upper Paleozoic tight sand gas reservoirs in the Tabamiao area, North Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2005, 11(1): 33~42. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20050107&flag=1 [26] 张福礼.鄂尔多斯盆地早古生代复合的古构造体系与天然气[J].地质力学学报, 2002, 8(3): 193~200. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20020321&flag=1ZHANG Fuli. Compound ancient tectonic system and natural gas of early Paleozoic in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2002, 8(3): 193~200. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20020321&flag=1 [27] 殷秀兰, 周东升, 吕杰堂, 等.渤中坳陷流体包裹体特征及其对成藏研究的意义[J].地质力学学报, 2006, 12(1): 84~90. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060113&flag=1YIN Xiulan, ZHOU Dongsheng, LV Jietang, et al. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and their significance for research on oil accumulation in the central Bohai depression[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2006, 12(1): 84~90. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060113&flag=1 [28] 毛毳, 陈勇, 周瑶琪, 等.储层烃类包裹体类型识别与PVT模拟方法[J].岩矿测试, 2010, 29(6): 751~756. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201006027.htmMAO Cui, CHEN Yong, ZHOU Yaoqi, et al. Identification of hydrocarbon inclusion types and PVT simulation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2010, 29(6): 751~756. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201006027.htm [29] 施伟军, 蒋宏, 席斌斌, 等.油气包裹体成分及特征分析方法研究[J].石油实验地质, 2009, 31(6): 643~648. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200906643SHI Weijun, JIANG Hong, XI Binbin, et al. Studies of analysis approaches of oil-and-gas inclusion composition and characteristics[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2009, 31(6): 643~648. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200906643 [30] 张敏, 张建峰, 李林强, 等.激光拉曼探针在流体包裹体研究中的应用[J].世界核地质科学, 2007, 24(4): 238~244. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYD200704014.htmZHANG Min, ZHANG Jianfeng, LI Linqiang, et al. The application of laser Raman microprobe to the study of fluid inclusion[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2007, 24(4): 238~244. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYD200704014.htm -





 下载:
下载: