THE EFFECT OF SALT-GYPSUM DEHYDRATION ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF SALT DIAPIR: A CASE STUDY OF DONGYING SAG
-
摘要: 基于国内外已经取得的盐构造研究成果, 根据东营凹陷盐构造的发育特征, 指出流体在盐构造发育过程的重要作用。东营凹陷沙四段含有大量膏盐和含膏地层, 根据岩心、测井和地震等资料分析了东营凹陷盐构造特征。由于膏盐脱水作用会导致地层内部产生异常高压, 而异常高压可以作为动力迫使流体向上流动继而在上覆地层产生水压力裂缝, 流体上涌过程中可以带动盐类物质向上运动, 因此认为膏盐脱水对盐构造形成发育有重要作用。基于膏盐脱水和超压流体作用, 建立了东营凹陷沙四段盐底辟构造发展史模型, 分析了东营凹陷盐构造在流体作用下形成发育过程, 结果表明膏盐脱水在盐构造发育初期和中期具有重要作用。Abstract: There is a series of achievements about salt tectonics both at home and abroad. This paper points out that fluid in the tectonics development of the important role of salt, which is based on previous studies and the developmental characteristics of salt tectonics in Dongying sag. It contains a lot of salt-gypsum and salt-gypsum formations. This paper analyzes the characteristic of the salt tectonics according to the core, logging and seismic data. Abnormal high pressure created by salt-gypsum dehydration in stratum, high pressure can be used as a dynamic force fluid flow upward and this contributes to hydraulic fracturing in the overlying strata and can drive the salts material in the process of fluid upwelling upward movement. This paper proposes that salt-gypsum dehydration has an important influence on the formation of the salt tectonics. Based on the effect of salt-gypsum dehydration and overpressure fluid, the history of model of member 4 of Shahejie Formation salt diapir in Dongying sag is established according to seismic cross-section and logging data. Salt tectonics is analyzed during the migration of fluids in the process of development, salt-gypsum dehydration effect in early and mid-salt tectonic development important role.
-
Key words:
- Dongying sag /
- salt diapir /
- salt-gypsum dehydration
-
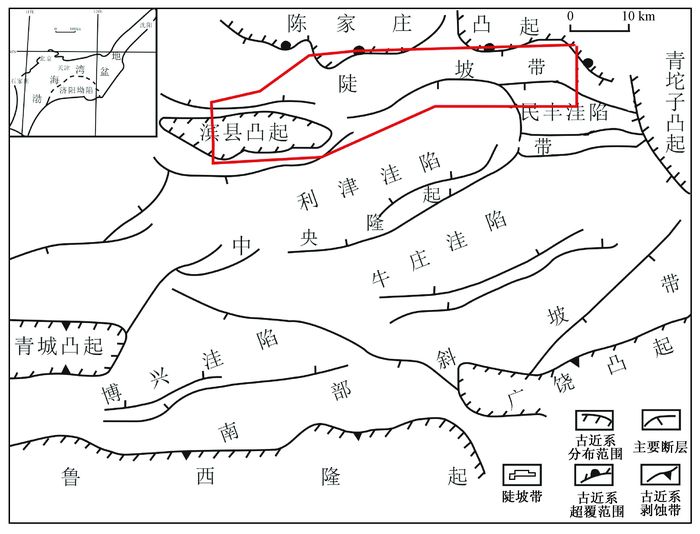
图 1 东营凹陷构造分区图(据文献[19],有修改)
Figure 1. Structural scheme of Dongying sag
表 1 膏盐层厚度数据表
Table 1. The data sheet of thickness for gypsum-salt strata
井号 石膏岩 泥膏岩 石膏质
泥岩含膏
泥岩盐膏岩 膏盐岩 含膏
盐岩岩盐 泥盐岩 盐质
泥岩含盐
泥岩含盐含
膏泥岩泥质
盐膏岩石膏质
白云岩东风1 140.50 - - - - - - 167.50 - - - - - - 东风2 189.00 - - - - - - 16.50 - - - - - - 东风3 6.50 20.50 - 4.00 - 11.50 - 44.50 12.50 - - - - - 东风5 4.55 5.11 - 338.84 - 21.65 - 47.61 41.13 19.97 - - - 0.05 东风8 - 266.50 - 18.50 - 44.00 - 57.00 14.00 34.00 - 33.00 - - 新东风10 3.00 137.00 34.50 95.50 - 32.00 14.00 43.00 2.50 1.00 - 1.00 - - 丰8 21.00 13.00 115.00 171.50 - 82.00 - 1.00 - 18.00 - - - 丰深1 65.00 3.00 35.90 72.30 - - 61.00 - 12.50 - 18.00 - - 丰深2 15.50 230.50 112.50 147.00 162 36.00 - 375.57 - 110.19 73.54 24.70 - - 丰深3 44.50 - - 34.00 - 21.50 - 187.50 - 18.00 - 15.00 - - 丰深4 5.50 36.50 34.50 45.70 - 42.00 - 37.00 - 9.00 - - - - 丰深5 3.00 11.00 44.50 48.70 79 22.50 - 83.00 - 41.00 9.50 14.50 8.50 - 郝科1 18.00 26.50 25.20 257.80 - 47.00 39.00 185.50 - 7.00 17.50 7.50 - - -
[1] Trusheim F. Mechanism of salt migration in northern Germany [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1960, 44(9): 1519~1540. http://archives.datapages.com/data/bulletns/1957-60/data/pg/0044/0009/1500/1519.htm?q=%2BtextStrip%3Atectonics+textStrip%3Asouthern+textStrip%3Aoklahoma [2] Rowan M G, Jackson M P A, Trudgill B D. Salt-related fault families and fault welds in the northern Gulf of Mexico [J]. AAPG bulletin, 1999, 83(9): 1454~1484. http://archives.datapages.com/data/bulletns/1999/09sep/1454/1454.htm?q=%2BtextStrip%3Aaapg+textStrip%3Aexploraiton+textStrip%3Awell+textStrip%3Aclassification [3] Buchanan P G, Bishop D J, Hood D N. Development of salt-related structures in the Central North Sea: Results from section balancing [J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1996, 100(1): 111~128. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1996.100.01.09 [4] Talbot C J, Alavi M. The past of a future syntaxis across the Zagros [J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1996, 100(1): 89~109. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1996.100.01.08 [5] Letouzey J, Colletta B, Vially R. Evolution of salt-related structures in compressional settings[C]//AAPG. Salt tectonics: A global perspective. Tulsa: AAPG, 1995: 41~60. [6] Vendeville B C, Jackson M P A. The rise of diapirs during thin-skinned extension [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1992, 9(4): 331~354. doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(92)90047-I [7] Vendeville B C, Jackson M P A. The fall of diapirs during thin-skinned extension [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1992, 9(4): 354~371. doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(92)90048-J [8] 汤良杰, 金之钧, 贾承造, 等.塔里木盆地多期盐构造与油气聚集[J].中国科学:D辑, 2004, 34(A01):89~97. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2004S1009.htmTANG Liang-jie, JIN Zhi-jun, JIA Cheng-zao, et al. A lot of salt tectonics and hydrocarbon accumulation in Tarim basin [J]. Science in China: Series D, 2004, 34(A01): 89~97. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2004S1009.htm [9] 贾承造, 赵文智, 魏国齐, 等.盐构造与油气勘探[J].石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(2):17~19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200302003.htmJIA Cheng-zao, ZHAO Wen-zhi, WEI Guo-qi, et al. Salt structures and exploration of oil and gas [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(2): 17~19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200302003.htm [10] 邬光辉, 蔡振中, 赵宽志, 等.塔里木盆地库车坳陷盐构造成因机制探讨[J].新疆地质, 2006, 24(2):182~186. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI200602018.htmWU Guang-hui, CAI Zhen-zhong, ZHAO Kuan-zhi, et al. The mechanics of salt tectonics in Kuche depression, Tarim Basin [J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2006, 24(2): 182~186. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI200602018.htm [11] 刘晓峰, 解习农, 张成, 等.东营凹陷盐-泥构造的样式和成因机制分析[J].地学前缘, 2006, 12(4):403~409. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200504012.htmLIU Xiao-feng, XIE Xi-nong, ZHANG Cheng, et al. Study on structural styles and genetic mechanism of salt-mud tectonics in Dongying depression[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(4): 403~409. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200504012.htm [12] Neal J T, Magorian T R, Thoms R L, et al. Anomalous zones in Gulf Coast salt domes with special reference to Big Hill, TX, and Weeks Island, LA[R]. Albuquerque: Sandia National Labs, 1993. [13] Frumkin A. Uplift rate relative to base-levels of a salt diapir (Dead Sea basin, Israel) as indicated by cave levels [J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1996, 100(1): 41~47. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1996.100.01.04 [14] Davison I, Bosence D, Alsop G I, et al. Deformation and sedimentation around active Miocene salt diapirs on the Tihama Plain, northwest Yemen [J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1996, 100(1): 23~39. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1996.100.01.03 [15] 袁静, 覃克.东营凹陷沙四段深水成因蒸发岩特征及其与油气藏的关系[J].石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2001, 25(1):9~11, 15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200101003.htmYUAN Jing, QIN Ke. Characteristics of evaporate generated in deep water of Sha-4 Member in Dongying sag [J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2001, 25(1): 9~11, 15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200101003.htm [16] 于建国, 李三忠, 王金铎, 等.东营凹陷盐底辟作用与中央隆起带断裂构造成因[J].地质科学, 2005, 40(1):55~68. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200501006.htmYU Jian-guo, LI San-zhong, WANG Jin-duo, et al. Salt diapirism and faulting of the gentral uplift belt in the Dongying sag, Bohai Bay Basin, north China [J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2005, 40(1): 55~68. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200501006.htm [17] 汤良杰, 贾承造, 皮学军, 等.库车前陆褶皱带盐相关构造样式[J].中国科学:D辑, 2003, 33(1):39~46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200301004.htmTANG Liang-jie, JIA Cheng-zao, PI Xue-jun, et al. Salt-related structural style in the Kuche foreland fold belt[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2003, 33(1): 39~46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200301004.htm [18] 叶兴树, 王伟锋, 陈世悦, 等.东营凹陷断裂活动特征及其对沉积的控制作用[J].西安石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2006, 21(5):29~33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200605005.htmYE Xing-shu, WANG Wei-feng, CHEN Shi-yue, et al. Characteristics of the fault activities in Dongying depression and their controlling effects on sediment[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University: Natural Science Edition, 2006, 21(5): 29~33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200605005.htm [19] 王艳忠. 东营凹陷北带古近系次生孔隙发育带成因机制及演化模式[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10425-2010280255.htmWANG Yan-zhong. Genetic mechanism and evolution model of secondary pore development zone of Paleogene in the north zone in Dongying Depression[D]. Qingdao: China Petroleum University, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10425-2010280255.htm [20] 刘晖, 操应长, 姜在兴, 等.渤海湾盆地东营凹陷沙河街组四段膏盐层及地层压力分布特征[J].石油与天然气地质, 2009, (3):287~293. doi: 10.11743/ogg20090306LIU Hui, CAO Ying-chang, JIANG Zai-xing, et al. Distribution characteristics of evaporates and formation pressure of the fourth Member of the Shahejie Formation in the Dongying sag, the Bohai Bay Basin [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2009, (3): 287~293. doi: 10.11743/ogg20090306 [21] 徐磊, 操应长, 王艳忠, 等.东营凹陷古近系膏盐岩成因模式及其与油气藏的关系[J].中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 32(3):30~35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200803008.htmXU Lei, CAO Ying-chang, WANG Yan-zhong, et al. Genetic model of salt-gypsum rock of Paleogene in Dongying depression and its relationship with hydrocarbon reservoir[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2008, 32(3): 30~35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200803008.htm [22] 费琪, 王燮培.初论中国东部含油气盆地的底辟构造[J].石油与天然气地质, 1982, 3(2):113~123. doi: 10.11743/ogg19820202Fei QI, WANG Xie-pei. A preliminary study on diapiric structure in oil and gas-bearing basins in eastern China [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1982, 3(2): 113~123. doi: 10.11743/ogg19820202 [23] Rayleigh L. Investigation of the character of the equilibrium of an incompressible heavy fluid of variable density[C]//Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society, 1983: 170~177. [24] Urai J L, Spiers C J, Zwart H J, et al. Weakening of rock salt by water during long-term creep [J]. Nature, 1986, 324(6097): 554~557. doi: 10.1038/324554a0 [25] Waltham D. Why does salt start to move? [J]. Tectonophysics, 1997, 282(1): 117~128. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1997Tectp.282..117W [26] 陈勇, 周振柱, 高永进, 等.济阳坳陷东营凹陷盐岩中的烃类包裹体及其地质意义[J].地质论评, 2014, 60(2):464~472. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201402021.htmCHEN Yong, ZHOU Zhen-zhu, GAO Yong-jin, et al. Hydrocarbon inclusions in salt rock of Dongying sag, Jiyang depression, and their geological implications [J]. Geologecal Review, 2014, 60(2): 464~472. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201402021.htm [27] Schléder Z, Urai J L, Nollet S, et al. Solution-precipitation creep and fluid flow in halite: A case study of Zechstein (Z1) rocksalt from Neuhof salt mine (Germany) [J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2008, 97(5): 1045~1056. doi: 10.1007/s00531-007-0275-y [28] Schoenherr J, Urai J L, Kukla P A, et al. Limits to the sealing capacity of rock salt: A case study of the infra-Cambrian Ara Salt from the South Oman salt basin [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(11): 1541~1557. doi: 10.1306/06200706122 [29] Davison I. Faulting and fluid flow through salt [J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2009, 166(2): 205~216. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492008-064 [30] Jowett E C, Cathles Ⅲ L M, Davis B W. Predicting depths of gypsum dehydration in evaporitic sedimentary basins [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1993, 77(3): 402~413. http://archives.datapages.com/data/bulletns/1992-93/data/pg/0077/0003/0400/0402.htm?q=%2BtextStrip%3Alow+textStrip%3Aporosity+textStrip%3Aoverpressured+textStrip%3Athin+textStrip%3Afluvial+textStrip%3Aoil+textStrip%3Asandstone+textStrip%3Areservoir+%2ByearSort%3A%5B1980+TO+2012%5D [31] Connolly J A D, Holness M B, Rubie D C, et al. Reaction-induced microcracking: An experimental investigation of a mechanism for enhancing anatectic melt extraction [J]. Geology, 1997, 25(7): 591~594. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0591:RIMAEI>2.3.CO;2 [32] Fertl B, Sahay W H. Origin and evaluation of formation pressures [M]. Allied Publishers, 1988. [33] Demercian S, Szatmari P, Cobbold P R. Style and pattern of salt diapirs due to thin-skinned gravitational gliding, Campos and Santos basins, offshore Brazil [J]. Tectonophysics, 1993, 228(3): 393~433. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1993Tectp.228..393D [34] Vendeville B C. A new interpretation of Trusheim's classic model of salt-diapir growth [J]. Trans-Gulf Cost Assoc Geol Soc, 2002, 52: 943~952. http://archives.datapages.com/data/gcags/data/052/052001/0943.htm?q=%2BtextStrip%3Amediterranean+textStrip%3Amiocene+textStrip%3Acarbonates+-isMeetingAbstract%3Amtgabsyes -





 下载:
下载: