AGE OF THE VERMICULATED RED SOIL IN JIUJIANG AREA,CENTRAL CHINA
-
摘要: 长江中下游地区广泛发育网纹红土。本文对九江长虹大道剖面进行了初步研究。该剖面地层自下而上可分为河流相冲积砂砾石、以发育水平状网纹为特征的铁质网纹红土、以垂向网纹为特征的网纹红土、红色粘土和风成下蜀黄土,分别厚3.3、4.5、5.9、3.6和4.1m。磁性地层研究结果,布容正向极性带/松山反向极性带的界限出现于网纹红土层中部,距顶深部12.9m处;贾拉米洛正向极性亚带出现在铁质网纹红土层中,距顶深度15.1-16.1m处。根据CandeandKent古地磁极性年表的模式年龄和热释光年龄,计算出沉积速率,进而计算出各层的界限年龄。结果表明,铁质网纹红土沉积于1232-869kaBP;网纹红土大约沉积于869-392kaBP;红色粘土沉积于392-101kaBP。九江长虹大道剖面代表了该地区从河流沉积、铁质网纹红土、网纹红土、红色粘土到风成黄土沉积的演变过程,并显示出准0.4 Ma的周期变化。这与黄土高原、青藏高原构造层和地球公转轨道偏心率变化所反映的准0.4 Ma构造气候旋回基本一致。Abstract: There is a wide distribution of the vermiculated red soil in the middle and lower reaches of the Changjiang River.A preliminary study of the Changhongdadao profile in Jiujiang City was carried out in this paper.In the profile,the strata can be divided from the bottom upwards into fluvial sandy gravel,horizontally vermiculated ferruginous red soil,vertically vermiculated red soil,red clay and eolian Xiashu loess,3.3m,4.5m,5.9m,3.6m and 4.1m thick respectively.The boundary between the Brunhes normal zone and the Matsuyama reversed zone is know from magnetostratigraphic study to occur in the middle part of the vermiculated red soil bed at a depth of 12.9m and the Jaramillo normal subzone in the ferruginous vermiculated red soil bed at a depth of 15.1m to 16.1m.The average sedimentation rate is calculated by Cande and Kent's palaeomagnetic age model and by thermoluminescent dating and hence the age of bed boundaries.The results show that the ferruginous vermiculated red soil was deposited during 1.232-0.869MaBP,the vermiculated red soil during 0.869-0.392 MaBP and the red soil during 0.392-0.101MaBP.
The sedimentary sequence in the Changhongdadao profile indicates a periodic climate change of about 0.4Ma.It is consistent with the tectonoclimatic cycles as revealed by the tectonic layers in the Loess Plateau and the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and the change of the earth's orbital eccentricity.-
Key words:
- vermiculated red soil /
- geologic age /
- periodic climate change /
- Jiujiang
-
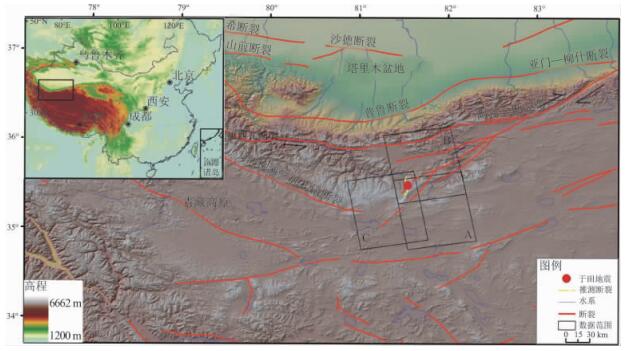
2008年3月21日发生在新疆于田(东经81°32',北纬35°28',深度23 km) [1]的7.3级地震是继2001年11月昆仑山口西8.1级地震后中国内陆发生的最大一次7级以上地震,打破中国大陆7级以上地震平静多年的现象。地震是构造活动的集中反映,会伴随着较大的地表形变及断裂的明显活动,能够放大构造的正常活动方式,同震变形场是这种放大作用在地表的直观反映,对于认识发震断裂运动性质,研究邻近构造活动性具有重要意义。同震形变监测和发震构造活动性的研究方法主要有现场测量、构造形迹分析、震源机制解和数值模拟等。然而在青藏高原西北缘恶劣的自然环境中,常规方法无法对于田地震开展及时有效的同震形变测量,凸显出差分干涉雷达(InSAR,Differential Interferometry Synthetic Aperture Radar)的优势[2~4]。本文介绍了InSAR观测原理,并重点分析了通过干涉雷达对于田地震同震形变场的观测结果,据此分析发震机制及邻近构造带的活动性。
1. 研究区构造背景
于田7.3级地震宏观震中位于青藏高原西北缘的阿什库勒地区(见图 1)。青藏高原北缘的2条大断裂自第四纪以来的运动方式与滑移速率对认识青藏高原西北部变形作用和机制,以及对地震的预测具有重要意义。研究区断裂活动的复杂性源于印度板块冲击欧亚板块,青藏高原开始对大陆岩石圈碰撞挤压,在塔里木盆地古老岩石的阻挡下,使青藏高原地壳缩短和高原隆升。由于青藏高原西部的块体向北推进,阿尔金断裂及其南盘山体隆起强烈,山前、山间拗陷剧烈,断错地貌明显,震区及附近的构造变形活动异常剧烈,尤以垂直运动最为显著,运动幅度达5000~7000 m[5]。地壳活动块体间的相互作用,使得该地区的新构造活动状态更为复杂,垂直、水平运动和内部变形均很明显,导致了高原边缘地区的构造以挤压、拉张为主,兼有走滑运动[6]。大的区域构造应力方向为南北向,所以形成的几个大的断裂带都是东西向的,如:阿尔金断裂带、康西瓦断裂带、大红柳滩—郭扎错断裂、普鲁断裂等。同时于田地震就发生在康西瓦断裂和阿尔金断裂的交汇处,所以通过震源机制解和其他的一些方法都认为于田地震所处的断裂走向应该是东西向,是阿尔金深断裂左旋扭错,致使断裂带西南端的破裂构造继续活动的结果。
2. 差分干涉雷达的监测原理
干涉雷达作为一项新的地球物理技术,是以合成孔径雷达复数图像的相位信息获取地表变形信息的技术,测量精度可以达到厘米级甚至更高。InSAR技术的应用为地震地质研究开拓了一条新的途径。InSAR技术可以使我们直接获取大范围的、连续空间覆盖的断层位移和运动速率等定量化的基础数据,为深入了解断裂活动方式、区域地壳稳定性、地震重复间隔、潜在震源区等问题做数据支撑。InSAR技术不受大空间尺度和复杂自然因素影响,可以获得极为经济的垂直形变信息,结合GPS的高精度水平形变信息,在时间轴上进行矢量叠加,可以得到区域地表的三维动态位移场、速度场和应变场,对于监测震前的微量形变、震时的同震位错和震后的变形回弹等地形形变研究有着极其重要的意义,可为地震预测提供丰富可靠的定量信息。
地形变InSAR监测至少需要根据同一区域两次重复的雷达数据获取,雷达传感器的回波信号携带了地物后向散射体的相位和强度信息,计算同一区域不同时间获取的两景单视复数(SLC,Single Look Complex)雷达影像(φm及φs)的相位差生成干涉图Δφ,该干涉图中既包含了两次成像期间地表相对运动的相位信息(φdef),也含有成像区域的地形信息(φtopo)、观测向斜距信息(φflat)、传感器轨道误差(φorbit)、大气效应(φatmos)和其他去相干因素的相位(φnoise)值,公式表示为:

(1) 差分干涉的基本任务就是从干涉图中提取有用的φdef信息。式(1)中的地形相位φtopo可以采用数字高程模型或多轨观测方法去除,观测向斜距φflat属于系统观测常量,通过卫星姿态参数校正,其他相位信息引起的测量误差在厘米级,是阻碍InSAR测量精度提高的主要因素,目前尚未有完善的解决手段。处理后的地形变干涉相位信息(φdef)与沿传感器视线向(LOS,Line of Sight)地表变形ΔR的关系为:

(2) 式中λ为雷达波波长,cm。
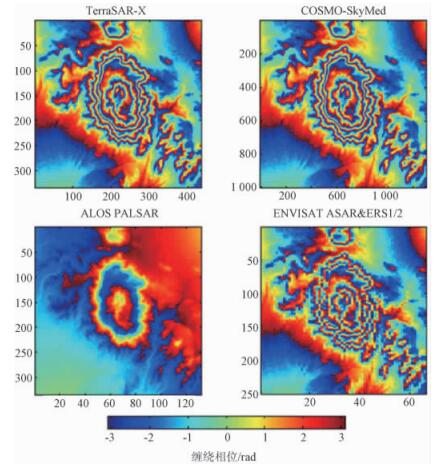
可见对于相同的地表变形ΔR,雷达波长与干涉条纹的密度成反比,对于同一变形,波长分别为X波段(3.0 cm,TerraSAR-X & COSMO-SkyMed)、C波段(5.6 cm,EnviSAT ASAR & ERS1/2)和L波段(23.5 cm,ALOS卫星的PALSAR传感器)的干涉条纹如图 2所示。干涉图像中每个干涉条纹代表波长一半的变形量,即X波段图像上的一个条纹为1.5 cm变形,C波段为2.8 cm变形,L波段为11.8 cm变形[3~4],也就是波长越短相对测量精度越高。但短波雷达数据受环境影响显著,不易形成干涉,因此在应用中应结合自然环境和研究精度需求确定采用的波段。
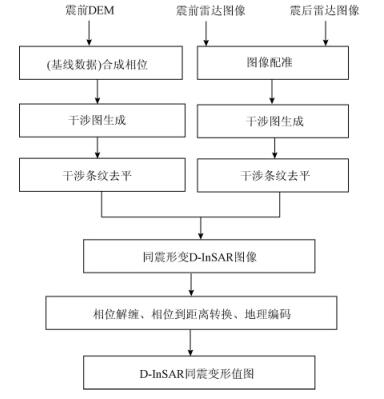
3. D-InSAR处理同震形变的步骤
本文中采用“3.21”于田地震前后的PALSAR雷达数据,结合数字高程模型(DEM)数据,对阿什库勒盆地及其邻近构造带进行“二通道+ DEM”的干涉监测(见图 3)。于田地震影响区主要为高原山区与现代冰川,雷达回波中噪声较大,ALOS卫星的PALSAR雷达数据拥有较长的L波段(23.6 cm),在2次成像中雷达后向散射保持很好的相关性,可以获得较高质量的全区干涉图(每个条纹周期代表 11.8 cm的变形)。
InSAR监测地震同震形变场,必须要有震前和震后观测的雷达数据。按ALOS卫星的观测策略,震前一年内库存了至少1次该地区的PALSAR观测数据。在“3.21”震后日本宇航局(JAXA)启动应急补充观测,构成了完整的阿什库勒地区地震前后的干涉像对,本文中应用了震前震后的3对雷达数据。数据的轨道号、获取时间、垂直基线长度等信息见表 1。
表 1 雷达数据信息Table 1. Information of radar data
4. InSAR监测的初步成果与分析
据日本航空航天局(JAXA)的全球观测策略,目前在于田地区PALSAR雷达数据大部分为升轨时拍摄,垂向入射角均为34.3°,视线向为北东81.84°,相应的雷达视线向变形量(dLOS)与垂直(dup)、北(dn)、东(de)变形量关系为[3] :

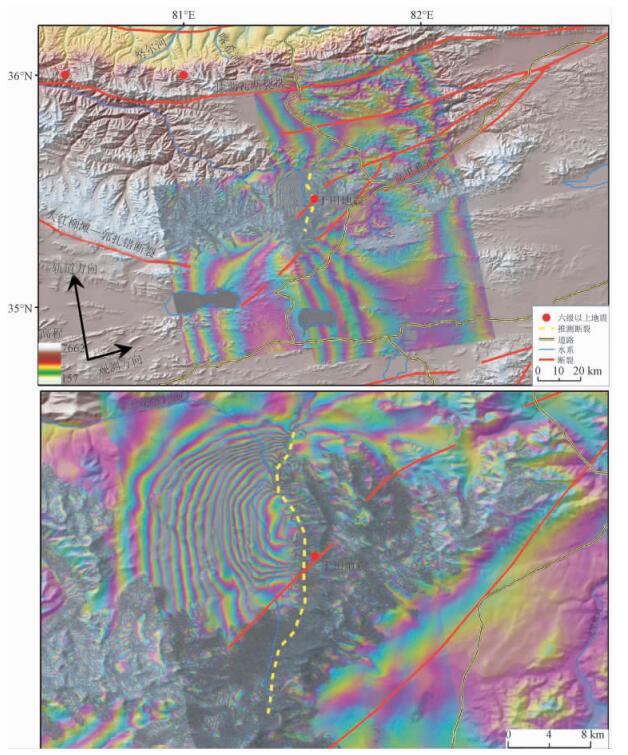
(3) 可以看出,垂直形变与东西向形变的敏感度相差不大,但两者对视线向的贡献为相反方向。如果野外调查获得了地表水平和垂直位错量,通过公式(3),再结合断层的走向和雷达成像几何关系,可以计算出实际的视线向位错量,从而实现野外观测与D-InSAR的互相检验和比较。图 4将PALSAR干涉雷达形变图像附在地形图上,是缠绕在一个相位周期(-π~π弧度)内的D-InSAR观测结果,相当于视线向变形的等值线,PALSAR数据波长为23.6 cm,每个条纹代表 11.8 cm的视线向形变。这其中还包括InSAR的地形误差、轨道误差、大气延迟误差和电离层干扰误差等,但相对于本次地震形变量居于次要地位。
通过图 4可见发震断裂走向总体为南北向,此地震破裂主要以正断层破裂方式为主,兼有左旋走滑运动的倾滑破裂特征:西向为上盘发生沉降,东向为下盘发生隆起。同时,根据图 4可以粗略地算出该发震断裂的长度为25.6 km,明显的地震形变影响范围为2500 km2,西侧上盘的视线向形变为200.6 cm (11.8 cm/条纹× 17条纹),按入射角可分解为上盘下沉量166.5 cm,上盘水平位移量112.3 cm。虽然位移量较大,但此次于田地震所发生的位置人员稀少,所造成的损失也比较小,没有人员伤亡。通过InSAR干涉测量方法,能准确地确定断裂走向和地震形变影响范围,为分析青藏高原西北缘的构造变形和动力学机制提供准确、客观的依据。
Shan等(2009) [7]用EnviSAT卫星的C波段(5.6 cm)雷达数据对于田地震也进行了干涉观测(见图 5)。通过比较可见C波段干涉图中,发震断裂的总体走向也是南北向,其东盘的干涉条纹比较清晰,而西盘的条纹模糊,这与本文中所做出的干涉条纹情况刚好相反。在研究地表变形的时候,可以综合图 4、图 5这2个干涉图进行分析。
 图 5 C波段(5.6 cm)于田地震的干涉图[7]Figure 5. InSAR map of Yutian earthquake be made by C-band wave (5.6 cm)
图 5 C波段(5.6 cm)于田地震的干涉图[7]Figure 5. InSAR map of Yutian earthquake be made by C-band wave (5.6 cm)干涉图产生差异的原因: ①由于卫星的类型不同,本文使用的是日本ALOS卫星的PALSAR L波雷达数据,而干涉图 5用的是欧空局EnviSAT卫星的ASAR-C波雷达数据; ②卫星的拍摄角度不同,本文采用的ALOS卫星PALSAR数据是升轨数据,雷达视线向为近东向(见图 4); EnviSAT卫星的ASAR是降轨观测,视线近西向(见图 5); ③数据拍摄的时间不同,这对形成干涉的效果也会产生一定的影响。
结合目前地震前后各方面的观测结果,可以从InSAR变形场中解译出重要的构造信息:由于青藏高原西南部的块体向北推进,阿尔金断裂及其南盘山体隆起强烈,山前、山间拗陷剧烈,断错地貌明显; 同时地壳活动块体间的相互作用,使得这个地区的新构造活动状态更为复杂,垂直、水平运动和内部变形均很明显。于田地震所处的断裂走向不是东西向,而是和大的作用力方向一致的南北向,这并不矛盾。在大的南北向作用力作用下,大断裂的走向基本上都是东西向的,特别是板块碰撞边界线更是如此; 但于田地震发生处与板块碰撞边界线还有一些距离,在东西向阿尔金断裂和康西瓦断裂的共同作用下,阿尔金断裂和康西瓦断裂的中间地带是有可能形成南北向破裂的,同时与发震断裂近平行发育的玉龙喀什河的走向也佐证了这条断裂的走向。通过震源机制解分析这次地震就是由于阿尔金断裂的左旋扭错,致使阿尔金断裂西南端发生破裂,只是破裂的方向是与阿尔金断裂垂直的南北向。这条南北向断裂也正反映了该地区构造活动的复杂性,说明断裂之前也存在很强的相互影响,本次于田7.4级地震之后的一个多月就发生了5月12日的四川汶川8级地震。
5. 结论
通过ALOS卫星的PLSAR雷达数据InSAR形变观测,本文获得了于田地震的同震地表形变图像,对于理解该地震的发震机理及该区域的构造变形具有重要意义。
2008年3月21日于田Ms 7.3级地震的宏观震中位于康西瓦断裂东南端的南北2分支(大红柳滩断裂和墓士山南麓断裂)和阿尔金断裂西南端帚状的3个分支交汇的三角地带。于田地震引发了阿尔金断裂的一个近南北向分支断裂的同震地表破裂,破裂长度为25.6 km。根据干涉雷达变形图像推测于田地震震源机制解为正断层,断层倾向西,上盘的最大运动幅度在200 cm以上。于田地震所在的两大断裂交汇处的构造应力场以近南北向挤压为主。
虽然距离得出精确的断层破裂模型还有较长的路要走,但是从原始的干涉形变图像上已经可以得出一些重要的地质和地球物理信息,这些信息对于深入研究地震构造都具有重要意义。下一步需要研究宽幅InSAR同震形变的观测,获取青藏高原北缘更大范围内对本次地震的变形反应,以期待全面分析同震和震后应力应变场演化等更为重要的科学问题。
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 254
- HTML全文浏览量: 69
- PDF下载量: 16
- 被引次数: 0





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载: