PALAEOMAGNETIC STUDY OF THE LATE CENOZOIC STRATA IN THE CENTRAL TARIM BASIN:IMPLICATION ON THE EVOLUTION OF TAKELIMAKAN DESERT
-
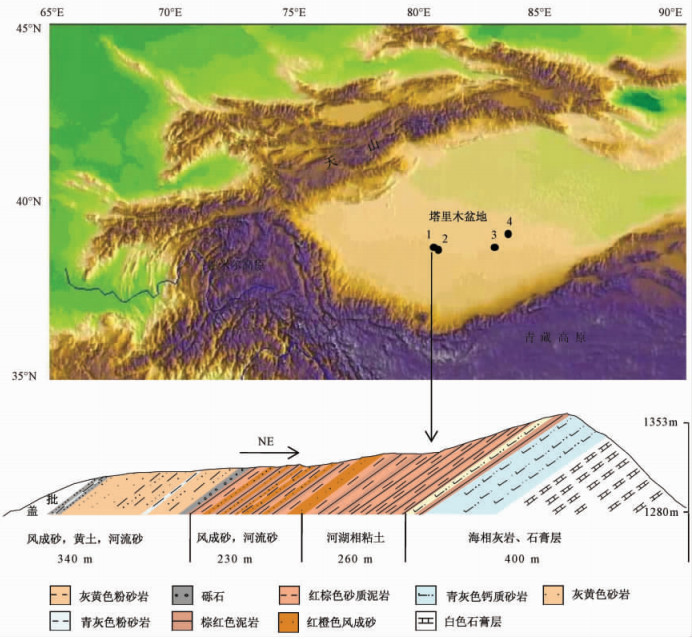
摘要: 选择了塔里木盆地腹地的红白山剖面, 对出露连续的晚新生代地层进行了高分辨率的磁性地层研究和古环境分析。结果表明:4.2Ma~3.4Ma, 塔里木盆地腹地的自然环境为干旱沉积平原, 气候条件相对湿热; 3.4Ma, 首次出现流动沙丘, 塔克拉玛干沙漠开始形成; 2.8Ma开始, 干旱化程度显著加强, 最终形成当今极度干旱的大型沙漠环境。在塔里木盆地的干旱化过程中, 副特提斯海的消亡、青藏高原的隆升和北极冰盖的演化均起到关键作用。Abstract: High resolution magnetostratigraphy study and paleoenvironment analysis were developed to the parallel section in the central of Tarim basin. The results indicate that dry land environment with relative warm and humid climate pattern dominant in the area between 4.2~3.4Ma. The oldest in-situ eolian dun sands formed in 3.4Ma, which in turn indicate the age of Taklimakan desert. The dry climate significant intensified by 2.8Ma, consequently forming the extremely dry environment like those of present. We argue that the retreat of Para-Tethys, uplift of Tibet Plateau and evolution of Northern Hemisphere glaciations are all played key roles in the desertification of interior Asian.
-
Key words:
- Tarim Basin /
- Taklimakan Desert /
- Magnetostratigraphy
-
图 2 红白山剖面地层柱状图与典型岩性照片(柱状图图例参照图 1)
Figure 2. Column of the Hongbaishan Section and photos of typical lithology
图 4 红白山剖面色度、磁化率指标及其反映的古环境演化序列(柱状图图例参照图 1)
Figure 4. Color index and magnetic susceptibility of Hongbaishan Section and inferred paleoenvironment evolution
-
[1] Molnar P and Tapponnier P. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia:Effects of a continental collision[J]. Science, 1975, 189:419 ~426. doi: 10.1126/science.189.4201.419 [2] Searle M P, Windley B F, Coward M P, et al. The closing of Tethys and the tectonics of the Himalaya[J]. Geological Society of American Bulletin, 1987, 98:678~701. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1987)98<678:TCOTAT>2.0.CO;2 [3] Ramstein G, Fluteau F, Besse J, et al. Effect of orogeny, plate motion and land-sea distribution on eurasian climate change over the past 30 million years[J]. Nature, 1997, 386:788~795. doi: 10.1038/386788a0 [4] Zhang Z S, Wang H J, Guo Z T, et al. What triggers the transition of palaeoenvironmental patterns in China, the Tibetan Plateau uplift or the Paratethys Sea retreat[J]. Palaeogeography, 2007, 245:317~331. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.08.003 [5] Manabe S and Broccoli A J. Mountains and arid climates of middle latitudes[J]. Science, 1990, 247:192~195. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4939.192 [6] Kutzbach J E, Prell W L, Ruddiman W F. Sensitivity of Eurasian climate to surface uplift of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geology, 1993, 101:177~190. doi: 10.1086/648215 [7] Ruddiman W F and Kutzbach J E. Forcing of later Cenozoic Northern Hemisphere climate by plateau uplift in Southern Asia and the American west[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1989, 94:18409~18427. doi: 10.1029/JD094iD15p18409 [8] 周志毅, 陈丕基, 等. 塔里木生物地层和地质演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1990.ZHOU Zhiyi, Chen Peiji, Eds. Biostratigraphy and geological evolution of Tarim[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1990. [9] 唐天福, 薛耀松, 俞从流.新疆塔里木盆地西部晚白垩世至早第三纪海相地层沉积特征及沉积环境[M].北京:科学出版社, 1992.TANG, Tianfu, XUE Yaosong, YU Congliu. Characteristics and sedimentary environments of the late cretaceous to early tertiary marine strata in the western Tarim Basin, China[M]. Sceince Press, Beijing, 1992. [10] 郝诒纯, 曾学鲁.从有孔虫的特征探讨中新生代西塔里木古海湾的演变[J].微体古生物学报, 1984, 1 (1):1~ 18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000003218967HAO Yichun, ZENG Xuelu. On the Evolution of the West Tarim Gulf From Mesozoic to Cenozoic In Terms of Characteristics of Foraminiferal Fauna[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 1984.1, 1~18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000003218967 [11] 雍天寿, 单金榜.白垩纪及早第三纪塔里木海湾的形成与发展[J].沉积学报, 1986, 4 (3):67~75. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000029812YONG Tianshou, SHAN Jinbang. The Development and formation if the Tarim Gulf in Cretaceous-Paleogene Ages[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1986.4, 67~75. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000029812 [12] Guo, Z T, Ruddiman W F, Hao Q Z, et al. Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China[J]. Nature, 2002, 416:159~162. doi: 10.1038/416159a [13] 郑洪波, 陈惠中, 曹军骥.塔里木盆地南缘上新世至早更新世风成黄土的古环境意义[J].科学通报, 2002, 47 (3):226~230. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2002.03.015Zheng Hongbo, Chen Huizhong, Cao Junji. Palaeoenvironmental implication of Pliocene-Early Pleistocene aeolian loess in Tarim basin. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 47 (3):226~230. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2002.03.015 [14] 郑洪波.从新疆叶城剖面砂岩和砾岩组分看西昆仑山的剥蚀历史[J].地质力学学报, 2002, 8 (4):297~305. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2002.04.002ZHENG Hongbo. Unroofing history of the west Kunlun viewed from the petrography of sandstone and conglomerate from Yecheng section, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Geomechan-ics, 2002, 8 (4):297~305. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2002.04.002 [15] Sun J M and Liu T S. The Age of Taklimakan Desert[J]. Science, 2006, 312:1621. doi: 10.1126/science.1124616 [16] Sun J M, Zhang Z, Zhang L. New evidence on the age of the Taklimakan Desert[J]. Geology, 2009, 37:159~162. doi: 10.1130/G25338A.1 [17] 孙东怀, 陈发虎, 易治宇, 等, 晚新生代塔里木盆地中西部地区磁性地层与环境演化[J].兰大学报, 2009, 45 (4):1~6. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lzdxxb200904001SUN Donghuai, CHEN Fahu, YI Zhiyu et al, Late cenozoic magnetostratigraphy and palaeoclimate records of the central and western Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural sciences), 2009, 45 (4):1~6. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lzdxxb200904001 [18] 施炜, 马寅生, 吴满路, 等.青藏高原东北缘共和盆地第四纪磁性地层学研究[J].地质力学学报, 2006, 12 (3):317~323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2006.03.005SHI Wei, MA Yinsheng, WU Manlu, et al. Quaternary Magnetostratigraphy Of The Gonghe Basin On The Northeastern Of The Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal Of Geomechan-Ics, 2006, 12 (3):317~323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2006.03.005 [19] 乔彦松, 刘冬雁, 李朝柱, 等.川西甘孜地区黄土的磁性地层学研究[J].地质力学学报, 2007, 13 (4):289~ 296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2007.04.001QIAO Yansong, LIU Dongyan, LI Chaozhu, et al. Magnetostratigraphy Of A Loess-Soil Sequence In The Garze Area Western Sichuan[J]. Journal Of Geomechan~Ics, 2007, 13 (4):289~296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2007.04.001 [20] 雍天寿, 单金榜, 王诗佾.玛扎塔克山区的几个地质问题——兼谈塔克拉玛干大沙漠形成的地质时代[J].新疆石油地质, 1983, 04:1~9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000004786286Yong Tianshou, Shan Jinbang, Wang Shiyi. Several geologic problems in Mazatag Mountain region:Talk about the formation time of Taklimakan Desert. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 1983, (4):1~9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000004786286 [21] Dupont-Nivet G, Guo Z, Butler R F, et al. Discordant paleomagnetic direction in Miocene rocks from the central Tarim. Basin:evidence for local deformation and inclination shallowing[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 199 (3):473~482. doi: 10.1016-S0012-821X(02)00566-6/ [22] Cande S C and Kent D V. Revised calibration of the geomagnetic polarity timescale for the late Cretaceous and Cenozoic [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1995, 100:6093~6095. doi: 10.1029/94JB03098 [23] 张鸿义, 门国发.塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地第四纪地层划分与环境变迁[J].新疆地质, 2002, 20 (3):256~261. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2002.03.017ZHANG Hongyi, MEN Guofa. Stratigraphic subdivision and climatic change of the quaternary of the center Taklimakan desert[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2002, 20 (3):256~261. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2002.03.017 [24] 徐建明, 杨振京, 郑宏瑞, 等.塔里木盆地第四纪磁性地层学研究[J].地层学杂志, 2003, 27 (4):276~281. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2003.04.002XU Jianming, YANG Zhenjing, ZHENG Hongrui et al. Quaternary magnetic stratigraphy of the Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2003, 27, 276~289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2003.04.002 [25] Rossel V, Minasny B, Roudier P, et al. Colour space models for soil science[J]. Geoderma, 2006, 133:320~337. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.07.017 [26] Thompson J A and Bell J. Color index for identifying hydric conditions for seasonally saturated mollisols in Minnesota[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1996, 60:1979~1988. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1996.03615995006000060051x [27] Deng T. Chinese Neogene mammal biochronology[J]. Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2006, 44:143~163. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gjzdwxb200602003 [28] 王跃, 董光荣, 王贵勇, 等.麻扎塔格山隆起的时代、形式、幅度及意义[J].中国沙漠, 1995, 15 (1):42~ 48. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500624408WANG Yue, DONG Guang Rong, WANG Guiyong et al. A discussion on the period, form and amplitude of Mazartag Mountain uplift and its effect[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 1995, 15, 42~48. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500624408 [29] Li J J, Wen S X, Zhang Q. Investigation on the uplift times, amplitude and styles of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science in China (Series B), 1979, 6:608~616. [30] Li J J., The environmental effects of the uplift of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1991, 10: 479~483. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(91)90041-R [31] Zheng H B, Powell C, An Z S, et al. Pliocene uplift of the northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geology, 2000, 28:715~ 718. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<715:PUOTNT>2.0.CO;2 [32] Yin A, Rumelhart P E, Butler R F, et al. Tectonic history of the Altyn Tagh fault system in northern Tibet inferred from Cenozoic sedimentation[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2002, 114:1257~1295. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2002)114<1257:THOTAT>2.0.CO;2 [33] Zheng H, Powell C M, Rea D K, et al. Late Miocene and mid-Pliocene enhancement of the East Asian monsoon as viewed from land and sea[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2004, 41:147~155. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2004.01.003 [34] Fang X, Yan M D, Van der Voo R, et al. Late Cenozoic deformation and uplift of the NE Tibetan Plateau:evidence from high-resolution magnetostratigraphy of the Guide Basin, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America, 2005, 117:1208~1225. doi: 10.1130/B25727.1 [35] Li J J, Fang X M, Ma H Z, et al. Geomorphological and environmental evolution in the upper reaches of the Yellow River during the late Cenozoic[J]. Science in China (Series D), 1996, 39:380~390. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3749db02c85f65571b1873782c43e1eb&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [36] Li J J, Fang X M, Van R, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of river terraces:rapid and intermittent incision by the Yellow River of the northeastern margin of the Tibet Plateau during the Quaternary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1997, 102:10121~10132. doi: 10.1029/97JB00275 [37] Li J J and Fang X M. Uplift of the Tibetan Plateau and environmental changes[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 44: 2117~2124. doi: 10.1007/BF03182692 [38] An Z S, Kutzbach J E, Prell W L, et al. Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan plateau since Late Miocene times[J]. Nature, 2001, 411:62~66. doi: 10.1038/35075035 -





 下载:
下载: