RESEARCH ON DETECTION AND ACTIVITY OF THE HENGGANG BRICKYARD FAULT IN RUICHANG CITY, JIANGXI PROVINCE
-
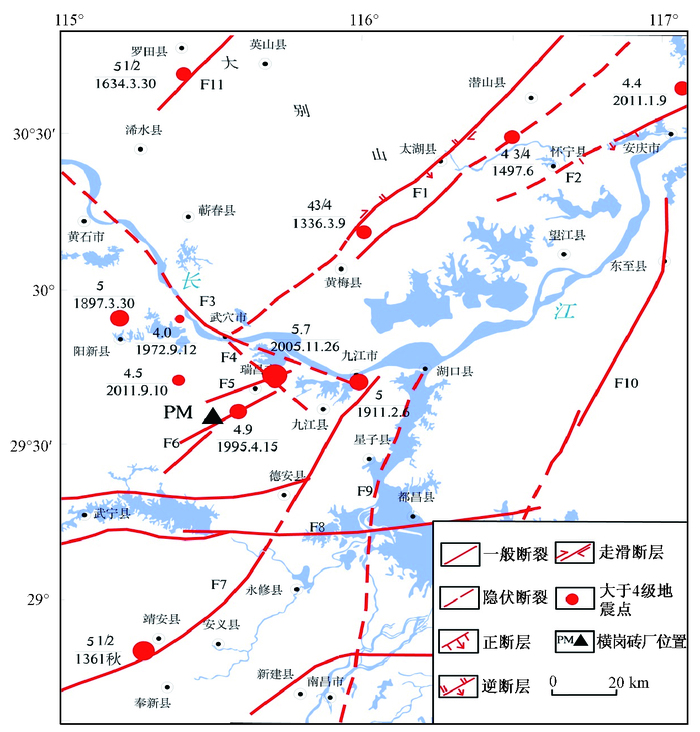
摘要: 经化探、物探和槽探工程,对出露于江西瑞昌横岗砖厂取土开挖场地内的地裂缝的成因、特征及意义进行了分析。该区地裂缝总体走向均为北东向,呈“簇”状密集分布,总体延伸长度超过300 m,且地裂缝内均有灰白色、浅灰色矿物充填。解析认为该区分布一条北东走向陡倾正断裂,断裂倾向南东,倾角60°-75°。局部探槽开挖揭露该断裂其中一断裂面错动第四纪坡洪积物,断裂产状为155°∠71°,走向65°,上盘下降,错距达到3 m(未揭露到底)。断层壁平直,断裂面擦痕清晰,可见5条长1~2 m的铲刮沟槽,槽深5~20 mm,显示该断层呈左旋倾滑性质。取上断点地层沉积物ESR测年,测年范围为距今0.27~0.42 Ma,研究表明该断裂在中更新世中期显著活动过,为一条中更新世活动断裂。综合分析认为该区地裂缝发育受横岗砖厂断裂控制,地裂缝的形成是横岗砖厂断裂活动在第四系地表的响应。Abstract: In the fault activity survey, we found much more fissures in the Henggang Brickyard in Ruichang City, Jiangxi province. The overall trend of the fissures is NE, the fissures distribute densely in a "cluster" shape, with length more than three hundreds. And filled by gray-white and light gray minerals Through the analysis, this paper considers that there is a north-east trend steep normal fault, with south-east strike and dip angle 60°~75°. Local trench excavation exposes that one of the fault planes diastrophism the Quaternary slope alluvial material, the fault occurrence is 155°∠71°, fault strike NE 65°, upside down, stagger distance up to 3 m (not reveal bottom). The fault is straight, we can clearly visible scratches on the fault plane, and five 1~2 m long scraping grooves with 5~20 m deep. These display the fault is left-lateral dip-slip. Through ESR to date the strata sediment from upper breakpoint, the age range is 0.27~0.42 Ma. Research showes that this fault is significantly active in Middle Pleistocene, it is a Middle Pleistocene active fault. It is analysed that the development of ground fissures in this area are controlled by the Henggang Brickyard fracture, the forming of fissures responded to the activity of Henggang Brickyard fracture in Quaternary.
-
Key words:
- fissure /
- active fault /
- ESR dating /
- high density resistivity method
-
-
[1] 曾文敬, 赵爱平, 汤兰荣.九江-瑞昌5.7级地震余震震源机制解[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 2009, 29(4):42~47. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB200904011.htmZENG Wen-jing, ZHAO Ai-ping, TANG Lan-rong. Focal mechanism solutions of aftershocks of Jiujiang-Ruichang earthquake[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2009, 29(4):42~47. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB200904011.htm [2] 吕坚, 曾文敬, 谢祖军.2011年9月10日瑞昌-阳新4.6级地震的震源破裂特征与区域强震危险性[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(11):3625~3633. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.11.011LÜ Jian, ZENG Wen-jing, XIE Zu-jun. Rupture characteristics of the Ms4.6 Ruichang-Yangxin earthquake of Sep.10, 2011 and the strong earthquake risk in the region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(11):3625~3633. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.11.011 [3] 邓起东.中国活动构造研究的进展与展望[J].地质评论, 2002, 48(2):168~177. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200202008.htmDENG Qi-dong. Advances and overview on researches of active tectonics in China[J]. Geological Review, 2002, 48(2):168~177. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200202008.htm [4] 王秋良, 王恒希, 陈园园, 等.土氡测量在城市断层探测中的应用[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 2010, 30(1):38~42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB201001009.htmWANG Qiu-liang, WANG Heng-xi, CHEN Yuan-yuan, et al. Application of soil radon measurement in urban fault surveying[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2010, 30(1):38~42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB201001009.htm [5] 程邈, 傅焰林, 李振宇.高密度电法在查明潜伏断裂中的应用[J].工程地球物理学报, 2011, 8(4):417~420. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDQ201104008.htmCHENG Miao, FU Yan-lin, LI Zhen-yu. Application of high density resistivity method to hidden fault investigation[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2011, 8(4):417~420. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDQ201104008.htm -





 下载:
下载: