CHARACTERISTICS AND DEFORMATION MECHANISM OF SHUIWAN SEISMIC LOESS LANDSLIDE IN MAIJI, TIANSHUI
-
摘要: 以天水市税湾地震黄土滑坡为例, 依据野外调查和室内测试结果, 总结天水地区历史地震黄土滑坡特点, 剖析地震黄土滑坡发生的力学机制, 初步提出历史地震黄土滑坡的识别标志。税湾滑坡及柳沟右岸滑坡群属典型的地震黄土滑坡, 具有规模大、滑动面切割深、滑坡坡度小、成群成带分布和高位下滑等特点, 可作为识别历史地震黄土滑坡的重要标志。税湾滑坡及柳沟右岸滑坡群坡体具有明显的黄土/泥岩二元斜坡结构, 极易沿黄土/泥岩接触面滑动。当坡体受到地震力作用时, 地震产生的循环动荷载一方面降低滑坡岩土体的抗剪强度, 另一方面改变滑坡体的力学状态, 坡体应力平衡遭到破坏, 地震力增加坡体下滑力、减小坡体抗滑力, 导致坡体失稳发生滑坡。目前, 税湾滑坡处于欠稳定状态, 遇地震或强降雨有可能再次失稳下滑, 因而有必要进一步开展地震黄土滑坡的成灾模式研究, 为潜在强震区防灾减灾提供科学依据。Abstract: Many historical earthquakes happened in Tianshui and its adjacent region, which resulted in seismic loess landslides developing extremely. According to field survey and indoor synthetic analysis, Shuiwan landslide and landslide groups of Liugou belong to typical seismic loess landslides, which are usually performance for large-scale, the sliding surface cutting deeply, thickness greatly, small slope, distributed along zones, appeared in groups and decline in high position and other characteristics. The characteristics above can be used as important symbols of field identification of seismic loess landslides. The slopes involved in Shuiwan landslide and the right bank Liugou landslides are characterized by loess/mudstone slope double layers structure. Under the condition of internal power, it is easy to slip along the loess/mudstone contact surfaces. Under the dynamic circulative loading, shear strength of the landslide rock mass is decreased on one hand. On the other hand it also changes the mechanical status of landslide, and the balance of the slope body is destroyed, which induce landslide happened. So, Shuiwan landslide is still in understable state. In case of an earthquake or heavy rainfall, it is likely to reoccur again. There is a necessary for further research of the disaster model of seismic loess landslide. It will provide a scientific basis for prevention and mitigation disaster of potential meizoseismal area.
-
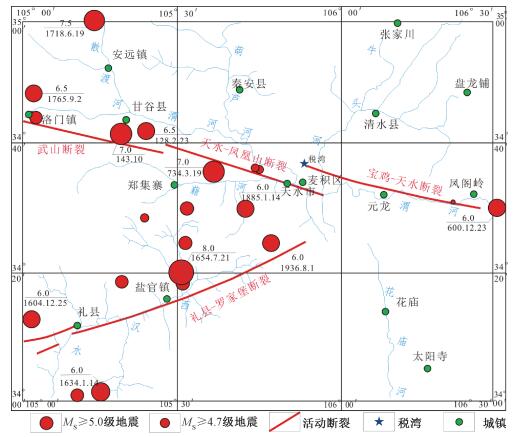
图 1 天水地区主要活动断裂及地震分布图(据文献[14]修编)
Figure 1. The main active faults and earthquakes distribution in Tianshui area
表 1 柳沟冲沟两岸滑坡特征统计
Table 1. Characteristics statistics of landslides in both sides of Liugou
滑坡位置 滑坡编号 长×宽(m) 厚度/m 规模/(104 m3) 切割深度/m 距梁顶水平距离/m 坡度/(°) 滑坡成因类型 柳沟右岸 1 500×600 40~50 750 20~30 0 13 地震 2 200×100 10~15 12 6~10 0 10 地震 3 600×350 80 800 40~50 0 12.5 地震 4 550×450 80~100 990 50~60 0 13 地震 5 500×400 80~100 800 70~80 0 15 地震 柳沟左岸 6 250×400 20 150 0~5 300 15 降雨 7 800×500 30 700 20~30 150 12 地震 8 100×100 20 10 0 120 40 降雨 9 200×200 40 100 0 80 35 降雨 10 150×100 10~20 15 0 80 32 降雨 11 180×150 15 16 0 50 28 降雨 12 200×150 10~15 30 0 30 35 降雨 13 230×190 30~40 80 0 50 40 降雨 表 2 滑床岩土体部分物理力学性质表
Table 2. Physical and mechanical properties of rock and soil mass of slider bed
岩土体类型 密度/(g·cm-3) 含水率/% 渗透系数/(10-6 cm·s-1) 粘聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) Q3黄土 1.88~1.92 18.0~19.0 5~20 30.2~49.4 23.7~29.2 古土壤 2.01~2.06 18.1~22.0 0.4~1.2 48.0~85.6 25.0~32.9 风化带土 1.98~2.02 20.6~24.2 40~60 34.2~54.0 22.2~28.5 泥岩 2.03~2.12 15.9~24.1 0.01~0.10 117.0~193.0 21.8~32.0 -
[1] 殷跃平.汶川八级地震滑坡特征分析[J].工程地质学报, 2009, 17(1):29~38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200901005.htmYIN Yue-ping. Features of landslides triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(1): 29~38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200901005.htm [2] 陈永明, 石玉成.中国西北黄土地区地震滑坡基本特征[J].地震研究, 2006, 29(3):276~280, 318. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYJ200603012.htmCHEN Yong-ming, SHI Yu-cheng. Basic characteristics of seismic landslides in loess area of northwest china [J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 2006, 29(3): 276~280, 318. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYJ200603012.htm [3] 李树德, 任秀生, 岳升阳, 等.地震滑坡研究[J].水土保持研究, 2001, (2):24~25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJDB201416023.htmLI Shu-de, REN Xiu-sheng, YUE Sheng-yang, et al. Study of earthquake-landslide [J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2001, (2): 24~25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJDB201416023.htm [4] 邓龙胜, 范文.宁夏海原8.5级地震诱发黄土滑坡的变形破坏特征及发育机理[J].灾害学, 2013, 28(3):30~37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU201303008.htmDENG Long-sheng, FAN Wen. Deformation breakage characteristics and development mechanism of loess landslide triggered by Haiyuan M8.5 earthquake in Ningxia [J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2013, 28(3): 30~37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU201303008.htm [5] 邹谨敞, 邵顺妹, 蒋荣发.古浪地震滑坡的分布规律和构造意义[J].中国地震, 1994, 10(2):168~174. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD402.008.htmZOU Jin-chang, SHAO Shun-mei, JIANG Rong-fa. Distribution and tectonic implications on the Gulang seismie landslide[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 1994, 10(2): 168~174. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD402.008.htm [6] 张振中, 郑恒利, 王兰民.黄土随机振动强度参数在地震滑坡分析中的应用[J].西北地震学报, 1991, 13(3):45~49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ199103007.htmZHANG Zhen-zhong, ZHENG Heng-li, WANG Lan-min. Application of loess strength parameters under random vibration in analysis of seismic landslides[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 1991, 13(3): 45~49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ199103007.htm [7] Sasaki Y, Towhata I. Mechanism of permants displacement of ground caused by seismic liquefaction[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1992, 32(3): 79~96. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.32.3_79 [8] Pilgrim N K. Earthquake-related deformation beneath gently inclined ground[J]. Geotechnique, 1998, 48(2): 187~199. doi: 10.1680/geot.1998.48.2.187 [9] Sassa K. The mechanism of debris flows[C] //11th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. San Francisco, 1985: 1173~1176. [10] 王家鼎, 白铭学, 肖树芳.强震作用下低角度黄土斜坡滑移的复合机理研究[J].岩土工程学报, 2001, 23(4):445~449. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC200104014.htmWANG Jia-ding, BAI Xue-ming, XIAO Shu-fang. A study on compound mechanism of earthquake-related sliding displacements on gently inclined loess slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2001, 23(4): 445~449. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC200104014.htm [11] 张茂省, 李同录.黄土滑坡诱发因素及其形成机理研究[J].工程地质学报, 2011, 19(4):530~540. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201104015.htmZHANG Mao-sheng, LI Tong-lu. Triggering factors and forming mechanism of loess land-slides[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(4): 530~540. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201104015.htm [12] 孙萍, 殷跃平, 吴树仁, 等.高速远程地震黄土滑坡发生机制试验研究[J].工程地质学报, 2009, 17(4):449~454. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200904005.htmSUN Ping, YIN Yue-ping, WU Shu-ren, et al. An experimental study on the initiation mechanism of rapid and long run-out loess landslide caused by1920 Haiyuan earthquake [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(4): 449~454. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200904005.htm [13] 白启圣, 王之佩.甘肃天水地区1654年罗家堡7 1/2级地震构造背景的初步分析[J].西北地震学报, 1984, 6(1):65~71. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ198401010.htmBAI Qi-sheng, WANG Zhi-pei. Elementary analysis of geotectonic background for1654 Luojiapu earthquake in the Tianshui area, Gansu Province[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 1984, 6(1): 65~71. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ198401010.htm [14] 成玉祥, 张骏, 杜东菊.天水地区断裂活动性与地质灾害的相关性研究[J].工程地质学报, 2007, 15(1):33~37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200701004.htmCHENG Yu-xiang, ZHANG Jun, DU Dong-ju. On the relationship between fault activity and geological hazard in tianshui area, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2007, 15(1): 33~37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200701004.htm [15] 李传友. 青藏高原东北部几条主要断裂带的定量研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所, 2005. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-85402-2006175968.htmLI Chuan-you. Quantitative studies on major active fault zones in Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[D]. Beijing: Geology Institute of China Earthquake Administration, 2005. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-85402-2006175968.htm [16] 成玉祥, 张骏, 杜东菊.天水地区新构造运动特征研究[J].工程地质学报, 2007, 15(4):549~554. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200704021.htmCHENG Yu-xiang, ZHANG Jun, DU Dong-ju. Study on Neotectonic movement features in Tianshui area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2007, 15(4): 549~554. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200704021.htm [17] 赖晓玲, 李松林, 宋占龙, 等.南北构造带天水、武都强震区地壳和上地幔顶部结构[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2009, 34(4):651~657. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200904012.htmLAI Xiao-ling, LI Song-lin, SONG Zhan-long, et al. Structure of crust and upper mantle in Tianshui Wudu strong earthquake region of north-south tectonic belt[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2009, 34(4): 651~657. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200904012.htm [18] 雷中生, 袁道阳, 葛伟鹏, 等.734年天水7级地震考证与发震构造分析[J].地震地质, 2007, 29(1):51~62. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200701004.htmLEI Zhong-sheng, YUAN Dao-yang, GE Wei-peng, et al. Textual research on the Tianshui M7 earthquake in 734 AD and analysis of its causative structure[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2007, 29(1): 51~62. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200701004.htm [19] 杨晓平, 冯希杰, 黄雄南, 等.礼县—罗家堡断裂晚第四纪活动特征:兼论1654年礼县8级地震孕震机制[J].地球物理学报, 2015, 58(2):504~519. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150214YANG Xiao-ping, FENG Xi-jie, HUANG Xiong-nan, et al.The late Quaternary activity characteristics of the Lixian-Luojiapu fault: A discussion on the seismogenic mechanism of the Lixian M8 earthquake in 1654 [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(2): 504~519. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150214 [20] 徐张建, 林在贯, 张茂省.中国黄土与黄土滑坡[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(7):1297~1312. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200707001.htmXU Zhang-jian, LIN Zai-guan, ZHANG Mao-sheng. Loess in China and loess landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(7): 1297~1312. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200707001.htm [21] 李为乐, 黄润秋, 裴向军, 等.基于Google Earth的1920年海原8.5级大地震地质灾害研究[J].灾害学, 2015, 30(2):26~31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU201502006.htmLI Wei-le, HUANG Run-qiu, PEI Xiang-jun, et al. Study on geological disasters caused by Haiyuan M8.5 earthquake in 1920 based on Google Earth[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2015, 30(2): 26~31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU201502006.htm [22] 黄润秋.汶川8.0级地震触发崩滑灾害机制及其地质力学模式[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(6):1239~1249. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200906023.htmHUANG Run-qiu. Mechanism and geomechanical modes of landslide hazards triggered by Wenchuan 8.0 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(6): 1239~1249. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200906023.htm [23] 吴玮江, 王念秦.甘肃滑坡灾害[M].兰州:兰州大学出版社, 2006.WU Wei-jiang, WANG Nian-qin. Gansu landslide disaster[M]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University Press, 2006. [24] 许强, 李为乐.汶川地震诱发大型滑坡分布规律研究[J].工程地质学报, 2010, 18(6):818~826. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201006002.htmXU Qiang, LI Wei-le. Distribution of large-scale landslides induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(6): 818~826. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201006002.htm [25] 许强, 李为乐.汶川地震诱发滑坡方向效应研究[J].四川大学学报:工程科学版, 2010, (S1):7~14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLH2010S1003.htmXU Qiang, LI Wei-le. Study on the direction effects of landslides triggered by Wenchuan earthquake [J]. Journal of Sichuan University: Engineering Science Edition, 2010, (S1): 7~14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLH2010S1003.htm -





 下载:
下载: