LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY ASSESSMENT BASED ON GIS IN BAILONGJIANG WATERSHED, GANSU PROVINCE
-
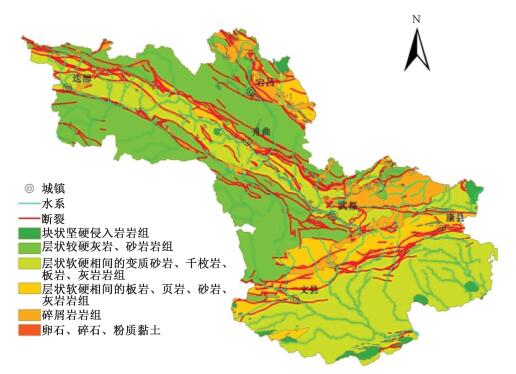
摘要: 在甘肃省白龙江流域地质灾害资料收集及现场调查的基础上, 统计分析了该区滑坡发育与地层岩性、坡度、坡向、高程、断裂、植被等因素之间的关系, 建立了白龙江流域滑坡易发性评价指标体系。采用基于GIS的层次分析法评价模型, 完成了滑坡易发性分区评价, 将研究区滑坡按易发程度划分为高易发区、中易发区、低易发区和极低易发区, 其中, 高易发区占研究区总面积的13.59%, 主要分布在断裂带、白龙江两侧以及软弱岩土体分布的区域; 中易发区占27.85%;主要分布在白龙江支流以及主要道路两侧的一定范围内; 低易发区占33.09%, 主要分布在海拔相对较高、植被覆盖度较高、基本上无断裂带通过的区域; 其余区域为极低易发区, 占25.46%。对比分析显示评价结果与实际滑坡发育情况吻合, 可以较好地反映区内滑坡灾害发育的总体特征。Abstract: Based on geohazard data collections and field investigations in Bailongjiang watershed, this paper analyzed the statistical relationship of lithology, slope gradient, slope aspect, elevation, drainages, faults, vegetation coverage and landslide occurrence. The evaluation index system of susceptibility assessment was established and the landslide susceptibility assessment in Bailongjiang watershed was accomplished by using AHP method. The landslide susceptibility map was classified into four classes: very low, low, moderate, and high. The high landslide susceptibility areas, 13.59% of the study area, were mainly distributed along the faults and Bailongjiang River, and in the regions characterized by presence of soft rocks. The moderate landslide susceptibility areas, covering 27.85% of the study area, were mostly along the main roads and tributaries of the Bailongjiang River. The low landslide susceptibility areas, accounting for 33.09%, had relatively high elevation and vegetation coverage, and there were no faults passing through. The rest were very low landslide susceptibility areas, making up 25.46% of the study area. The results from the evaluation coincided well with the previous landslide occurrence, which could reflect general characteristics of landslide hazard development.
-
Key words:
- landslide /
- susceptibility assessment /
- GIS /
- AHP /
- Bailongjiang watershed
-
表 1 评价因子量级划分
Table 1. Grade standard of evaluation factors
评价指标 指标分级 级数得分 地层岩性 块状坚硬侵入岩岩组 1 层状较硬灰岩、砂岩岩组 1 层状软硬相间变质砂岩等岩组 2 层状软硬相间的板岩等岩组 3 碎屑岩岩组 3 松散堆积物岩组 4 高程 <1000 m 4 1000~1500 m 3 1500~2000 m 2 2000~2500 m 2 2500~3000 m 1 >3000 m 1 坡向 北 2 东北 2 东 3 东南 3 南 4 西南 4 西 3 西北 3 平坦 1 坡度 0°—15° 2 15°—30° 4 30°—45° 3 >45° 1 断裂 <500 m 4 500~1000 m 3 1000~1500 m 2 1500~2000 m 2 >2000 m 1 水系 < 200 m 4 200~400 m 4 400~600 m 3 600~800 m 2 800~1000 m 2 >1000 m 1 植被 <10% 3 10%~30% 4 30%~45% 4 45%~60% 2 >60% 1 表 2 判断矩阵的标度及其含义
Table 2. Scale of judgment matrix and its meaning
标度 含义 1 表示两个因素相比,具有同样重要性 3 表示两个因素相比,前者比后者稍微重要 5 表示两个因素相比,前者比后者明显重要 7 表示两个因素相比,前者比后者强烈重要 9 表示两个因素相比,前者比后者极端重要 2、4、6、8 上述两相邻判断的中值 倒数 与上述情况相反 表 3 因子层次排序结果一览表
Table 3. The result of the AHP evaluation
基础因子 地层岩性 坡度 坡向 高程 断裂 水系 植被 权重 地层岩性 1 2 4 3 2 3 3 0.29 坡度 0.5 1 4 2 2 3 3 0.22 坡向 0.25 0.25 1 0.5 0.3333 0.5 0.5 0.05 高程 0.333 0.5 2 1 0.5 2 2 0.12 断裂 0.5 0.5 3 2 1 2 2 0.16 水系 0.3333 0.3333 2 0.5 0.5 1 1 0.08 植被 0.3333 0.3333 2 0.5 0.5 1 1 0.08 一致性检验 CI=0.025,CR=0.019<0.1 表 4 地质灾害易发性统计
Table 4. Statistics of landslide susceptibility
易发性分区 面积/km2 面积百分比/% 灾害数量/个 灾害点密度/(个·km-2) 高易发区 3217.92 13.59 729 0.71 中易发区 6597.53 27.85 239 0.23 低易发区 7838.47 33.09 52 0.05 极低易发区 6031.36 25.46 11 0.01 -
[1] BRABB E E. Innovative approaches to landslide hazard and risk mapping[C] //Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on landslides. Toronto, 1984: 307~323. [2] VAN Westen C J. Application of geographic information systems to landslide hazard zonation [D]. TU Delft: Delft University of Technology, 1993. [3] OHLMACHER G C, DAVIS J C. Using multiple logistic regression and GIS technology to predict landslide hazard in northeast Kansas, USA [J]. Engineering Geology, 2003, 69(3): 331~343. [4] FORSTER A, JENKINS G. The assessment of landslide hazard potential as a guide to land use and planning in the South Wales Coalfield[J]. Urban Geology in Wales, 2005, 24: 81~87. [5] WOOTEN R M, LATHAM R S, WITT A C, et al. Landslide hazards and landslide hazard mapping in North Carolina [J]. Geological Society of America, 2006, 38(3): 28. [6] 殷坤龙, 朱良峰.滑坡灾害空间区划及GIS应用研究[J].地学前缘, 2001, 8(2):279~284. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200102012.htmYIN Kun-long, ZHU Liang-feng. Landslide hazard zonation and application of GIS [J]. Earth science Frontiers, 2001, 8(2): 279~284. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200102012.htm [7] 许冲, 戴福初, 姚鑫, 等.GIS支持下基于层次分析法的汶川地震区滑坡易发性评价[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(2):3978~3985. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2009S2104.htmXU Chong, DAI Fu-chu, YAO Xin, et al. GIS based landslide susceptibility assessment using analytical hierarchy process in Wenchuan earthquake region [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(2): 3978~3985. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2009S2104.htm [8] 范林峰, 胡瑞林, 曾逢春, 等.加权信息量模型在滑坡易发性评价中的应用——以湖北省恩施市为例[J].工程地质学报, 2012, 20(4):508~513. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201204005.htmFAN Lin-feng, HU Rui-lin, ZENG Feng-chun et al. Application of weighted information value model to landslide susceptibility assessment a case study of Enshi city Hubei province [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(4): 508~513. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201204005.htm [9] 王佳佳, 殷坤龙, 肖莉丽.基于GIS和信息量的滑坡灾害易发性评价——以三峡库区万州区为例[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(4):797~808. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201404018.htmWANG Jia-jia, YIN Kun-long, XIAO Li-li. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on GIS and weighted information value: a case study of Wanzhou district, three gorges reservoir [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(4): 797~80. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201404018.htm [10] 孟兴民, 陈冠, 郭鹏, 等.白龙江流域滑坡泥石流灾害研究进展与展望[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(4):1~15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201304004.htmMENG Xin-ming, CHEN Guan, GUO Peng, et al. Research of landslides and debris flows in Bailong river basin progress and prospect [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(4): 1~15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201304004.htm [11] 杨为民, 黄晓, 张春山, 等.白龙江流域坪定—化马断裂带滑坡特征及其形成演化[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2014, 44(2):574~583. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201402017.htmYANG Wei-min, HUANG Xiao, ZHANG Chun-shan, et al. Deformation behavior of landslides and their formation mechanism along Pingding-Huama aclive fault in Bailong river region [J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2013, 33(4): 1~15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201402017.htm [12] 张茂省, 黎志恒, 王根龙, 等.白龙江流域地质灾害特征及勘查思路[J].西北地质, 2011, 44(3):1~9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201103003.htmZHANG Mao-sheng, LI Zhi-heng, WANG Gen-long, et al. The geological hazard characteristics and exploration ideas of the Bailong River Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2011, 44(3): 1~9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201103003.htm -





 下载:
下载: