BROADBAND GROUND MOTION SIMULATION IN TIANSHUI BASIN BASED ON A HYBRID METHOD
-
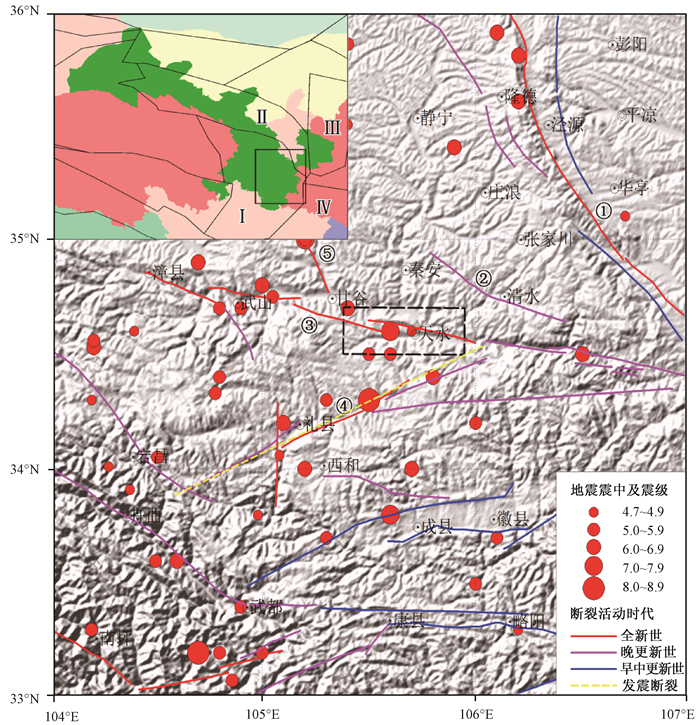
摘要: 本文采用有限差分和随机振动合成结合的复合方法,模拟了当礼县—罗家堡断裂发生矩震级Mw7.7级大地震时,在天水盆地产生的宽频带地震动场,分析了在设定地震条件下盆地内的地震动分布特征,为该区黄土地震滑坡分析提供了地震动参数结果。结果显示:(1)有限差分法和随机振动合成法可以很好地互补,得到盆地内地表宽频带地震动;(2)地震在盆地区域产生了强烈地震动,PGA(峰值加速度)介于150~900 gal,离断层较近的区域东南角的PGA最大,随着断层距的增加,PGA逐渐减小。河谷南侧的PGA值相比北侧较大,具备诱发滑坡的强大动力条件;(3)盆地区域PGV(峰值速度)最大为120 cm/s。受第四系覆盖层放大效应和地形放大效应共同影响,水平向地震动在盆地区域东侧和中部具有较大PGV,而西侧PGV相对较小。竖向地震动在盆地区域东侧较弱,而在中部和西侧较强,特别是最西侧陡峭的山坡上,PGV达到了最大值。此外,竖向地震动明显受到覆盖层厚度的影响,譬如在盆地区域南侧的中间部位,也具有较大的PGV。Abstract: Taking Lixian-Luojiabao fault as a causative fault of an Mw 7.7 scenario earthquake, a hybrid numerical method combining finite difference method with random vibration synthesis method is adopted to simulate broadband ground motion field in Tianshui basin, and the ground motion characteristics in the basin are analyzed, providing ground motion parameters for analyzing seismic loess landslides. The following conclusions are acquired:(1)Finite difference method and random vibration synthesis method are complementary to get broadband ground motion in the basin. (2)The scenario earthquake causes intensive ground motion in the basin, with PGA (peak ground acceleration) of 150~900 gal. The largest PGA is located in the southeastern corner of the basin where is nearest to causative fault, and it decreases with the distance from causative fault. Compared to the north side of river valley, the south side has larger PGA to induce landslides. (3)The largest PGV is 120cm/s in the basin. Affected by Quaternary covering layer amplification effect and terrain amplification effect, PGV in the east and the central parts of the basin are larger than those in the west part. (4)The vertical ground motion shows smaller PGV in the east part of the basin but larger ones in the west and central parts. Especially at the western most steep mountains, PGV reaches the maximum. In addition, the vertical ground motion can also reflect the influence of loess layer, for example, the PGV is also larger in the central part of the south side of the basin.
-
Key words:
- Tianshui basin /
- scenario earthquake /
- hybrid method /
- numerical simulation /
- ground motion parameters
-
表 1 天水盆地地下介质的计算参数
Table 1. Calculation parameters of underground media in Tianshui basin
介质层 第四系覆盖层 沉积层 上地壳 中地壳 下地壳 介质密度/g·cm-3 2.00 2.25~2.65 2.80 2.90 3.00 纵波速度/km·s-1 2.0 3.0~5.8 5.9~6.5 6.6~7.0 7.0~7.2 横波速度/km·s-1 1.0 1.5~3.3 3.4~3.8 3.8~4.1 4.1~4.2 介质品质因子 100 150~330 340~380 380~410 410~420 层介质埋深/km 0~0.09 0~6.5 6.5~24 24~38 38~40 -
[1] 程小杰, 杨为民, 向灵芝, 等.基于Newmark模型的天水市北山地震黄土滑坡危险性评价[J].地质力学学报, 2017, 23(2):296~305. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170213&flag=1CHENG Xiaojie, YANG Weimin, XIANG Lingzhi, et al. Risk assessment of seismic loess landslide based on Newmark model in Beishan, Tianshui city[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 23(2):296~305. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170213&flag=1 [2] 田尤, 杨为民, 黄晓, 等.天水市麦积区幅黄土滑坡发育分布特征及其孕灾因素分析[J].地质力学学报, 2016, 22(1):25~38. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160103&flag=1TIAN You, YANG Weimin, HUANG Xiao, et al. Distribution characteristics and inducing factors of loess landslide in Maiji Mappable Unit, Tianshui[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 22(1):25~38. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160103&flag=1 [3] 雷中生, 袁道阳, 葛伟鹏, 等. 734年天水7级地震考证与发震构造分析[J].地震地质, 2007, 29(1):51~62. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/95728X/200701/24197791.htmlLEI Zhongsheng, YUAN Daoyang, GE Weipeng, et al. Textual research on the Tianshui M7 earthquake in 734 AD and analysis of its causative structure[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2007, 29(1):51~62. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/qk/95728X/200701/24197791.html [4] 李传友, 张培震, 张剑玺, 等.西秦岭北缘断裂带黄香沟段晚第四纪活动表现与滑动速率[J].第四纪研究, 2007, 27(1):54~63. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj200701007LI Chuanyou, ZHANG Peizhen, ZHANG Jianxi, et al. Late-Quaternary activity and slip rate of the western Qinling fault zone at Huangxianggou[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27(1):54~63. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj200701007 [5] 邵延秀, 袁道阳, 王爱国, 等.西秦岭北缘断裂破裂分段与地震危险性评估[J].地震地质, 2011, 33(1):79~90. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/71135X/201107/37861335.htmlSHAO Yanxiu, YUAN Daoyang, WANG Aiguo, et al. The segmentation of rupture and estimate of earthquake risk along the north margin of western Qinling fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2011, 33(1):79~90. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/71135X/201107/37861335.html [6] 张波, 何文贵, 袁道阳, 等.西秦岭北缘断裂带西端晚第四纪活动特征及其西延问题[J].地震, 2012, 32(1):136~143. http://www.doc88.com/p-3147137415870.htmlZHANG Bo, HE Wengui, YUAN Daoyang, et al. Late Quaternary activities of the west segment of northern margin of western Qinling fault zone and its western extension[J]. Earthquake, 2012, 32(1):136~143. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.doc88.com/p-3147137415870.html [7] 刘白云. 甘东南地区两次8. 0级历史疑难地震发震构造及发震机制研究[D]. 兰州: 中国地震局兰州地震研究所, 2012.LIU Baiyun. A study on causative structure and mechanism of two Ms8.0 earthquakes in the southeast area of Gansu[D]. Lanzhou:Lanzhou Institute of Seismology, CEA, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 杨晓平, 冯希杰, 黄雄南, 等.礼县-罗家堡断裂晚第四纪活动特征:兼论1654年礼县8级地震孕震机制[J].地球物理学报, 2015, 58(2):504~519. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150214YANG Xiaoping, FENG Xijie, HUANG Xiongnan, et al. The Late Quaternary activity characteristics of the Lixian-Luojiabu fault:A discussion on the seismogenic mechanism of the Lixian M8 earthquake in 1654[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(2):504~519. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/cjg20150214 [9] Kamae K, Irikura K, Pitarka A. A technique for simulating strong ground motion using hybrid green's function[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1998, 88(2):357~367. http://bssa.geoscienceworld.org/content/88/2/357.abstract [10] Viens L, Laurendeau A, Bonilla L F, et al. Broad-band acceleration time histories synthesis by coupling low-frequency ambient seismic field and high-frequency stochastic modelling[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2014, 199(3):1784~1797. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggu362 [11] Virieux J. P-SV wave propagation in heterogeneous media:velocity-stress finite-difference method[J]. Geophysics, 1986, 51(4):889~901. doi: 10.1190/1.1442147 [12] Levander A R. Fourth-order finite-difference P-SV seismograms[J]. Geophysics, 1988, 53(11):1425~1436. doi: 10.1190/1.1442422 [13] Graves R W. Simulating seismic wave propagation in 3D elastic media using staggered-grid finite differences[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1996, 86(4):1091~1106. http://gji.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/ijlink?linkType=ABST&journalCode=ssabull&resid=86/4/1091 [14] Robertsson J O A. A numerical free-surface condition for elastic/viscoelastic finite-difference modeling in the presence of topography[J]. Geophysics, 1996, 61(6):1921~1934. doi: 10.1190/1.1444107 [15] Ohminato T, Chouet B A. A free-surface boundary condition for including 3D topography in the finite-difference method[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1997, 87(2):494~515. http://www.bssaonline.org/content/87/2/494.short [16] 张伟. 含起伏地形的三维非均匀介质中地震波传播的有限差分算法及其在强地面震动模拟中的应用[D]. 北京: 北京大学, 2006.ZHANG Wei. Finite difference seismic wave modelling in 3D heterogeneous media with surface topography and its implementation in strong ground motion study[D]. Beijing:Beijing University, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] Motazedian D, Atkinson G M. Stochastic finite-fault modeling based on a dynamic corner frequency[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 2005, 95(3):995~1010. doi: 10.1785/0120030207 [18] 李少华, 王彦宾, 梁子斌, 等.甘肃东南部地壳速度结构的区域地震波形反演[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(4):1186~1197. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94718X/201204/41917210.htmlLI Shaohua, WANG Yanbin, LIANG Zibin, et al. Crustal structure in southeastern Gansu from regional seismic waveform inversion[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(4):1186~1197. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94718X/201204/41917210.html [19] 王周元, 范世宏, 姬凤英, 等.甘肃地区地壳速度的非均匀分布[J].西北地震学报, 1996, 18(2):18~25. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=2139711WANG Zhouyuan, FAN Shihong, JI Fengying, et al. The inhomogeneity of crustal velocity in Gansu region[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 1996, 18(2):18~25. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=2139711 [20] 彭聪.中国西部布格重力异常特征和地壳密度结构[J].地球学报, 2005, 26(5):417~422. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=20302075PENG Cong. Bouguer anomalies and crustal density structure in western China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2005, 26(5):417~422. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=20302075 [21] 杨光亮, 申重阳, 吴桂桔, 等.金川-芦山-犍为剖面重力异常和地壳密度结构特征[J].地球物理学报, 2015, 58(7):2424~2435. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150719YANG Guangliang, SHEN Chongyang, WU Guiju, et al. Bouguer gravity anomaly and crustal density structure in Jinchuan-Lushan-Qianwei profile[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(7):2424~2435. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/cjg20150719 [22] 赵翠萍, 陈章立, 华卫, 等.中国大陆主要地震活动区中小地震震源参数研究[J].地球物理学报, 2011, 54(6):1478~1489. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94718X/201106/38668355.htmlZHAO Cuiping, CHEN Zhangli, HUA Wei, et al. Study on source parameters of small to moderate earthquakes in the main seismic active regions, China mainland[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(6):1478~1489. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94718X/201106/38668355.html [23] 沈建文, 邱瑛, 赵志贺.震级-破裂长度关系与断层破裂模型[J].地球物理学报, 1990, 33(2):242~248. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94718X/199002/228526.htmlSHEN Jianwen, QIU Ying, ZHAO Zhihe. Rupture length magnitude relationship and fault-rupture model[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 1990, 33(2):242~248. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94718X/199002/228526.html [24] Somerville P, Irikura K, Graves R, et al. Characterizing crustal earthquake slip models for the prediction of strong ground motion[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 1999, 70(1):59~80. doi: 10.1785/gssrl.70.1.59 [25] 王海云. 近场强地震动预测的有限断层震源模型[D]. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所, 2004.WANG Haiyun. Finite fault source model for predicting near-field strong ground motion[D]. Harbin:Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration, 2004. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] 王海云, 陶夏新.近场强地震动预测中浅源地震的Asperity模型特征[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2005, 37(11):1533~1539. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.2005.11.022WANG Haiyun, TAO Xiaxin. Characterizing a shallow earthquake asperity model for predicting near field strong ground motion[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2005, 37(11):1533~1539. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.2005.11.022 [27] Gallovič F, Brokešová J. On strong ground motion synthesis with k-2 slip distributions[J]. Journal of Seismology, 2004, 8(2):211~224. doi: 10.1023/B:JOSE.0000021438.79877.58 [28] Mai P M, Beroza G C. A spatial random field model to characterize complexity in earthquake slip[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2002, 107(B11):ESE 10-1-ESE 10-21. doi: 10.1029/2001JB000588 [29] Hisada Y. A theoretical omega-square model considering the spatial variation in slip and rupture velocity[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 2000, 90(2):387~400. doi: 10.1785/0119990083 [30] Hisada Y. A theoretical omega-square model considering spatial variation in slip and rupture velocity. Part 2:Case for a Two-Dimensional source model[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 2001, 91(4):651~666. doi: 10.1785/0120000097 [31] Frankel A. Modeling strong-motion recordings of the 2010Mw 8.8 Maule, Chile, earthquake with high stress-drop subevents and background slip[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 2017, 107(1):372~386. doi: 10.1785/0120160127 [32] Allmann B P, Shearer P M. Global variations of stress drop for moderate to large earthquakes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2009, 114(B1):B01310, doi: 10.1029/2008JB005821. [33] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB 18306-2015中国地震动参数区划图[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB 18306-2015 Seismic ground motion parameters zonation map of China[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: