APPLICATION OF FLUVIAL DEPOSITIONAL SYSTEM ANALYSIS DURING THE QUATERNARY GEOLOGICAL SURVEY IN THE SHALLOW COVERED AREA: A CASE STUDY OF 1: 50000 GEOLOGICAL MAPPING IN THE HETAO REGION OF INNER MONGOLIA
-
摘要: 随着国家大比例尺地质调查(1:50000)向特殊地质地貌区的开展,已有第四纪填图方法已不能满足覆盖区填图的实际需求,地质工作者面临着第四纪大比例尺填图“填什么、如何填”的问题。选取典型覆盖区——河套平原为研究区,以河流沉积理论为指导,通过钻孔揭露方法,建立了全新世以来的河流沉积体系,并以此作为区域地质图骨架,提出了河道亚相、堤坝亚相、泛滥平原亚相的填图单元,应用“逐步逼近原则”确定地质界线,划分出区内三期河道及其相应的沉积体系,解决了覆盖区第四纪地质调查中填图单元稀少,地质图表达单调的问题,为覆盖区第四纪地质调查提供了一套可行方案。Abstract: With the conduction of the national large-scale (1:50000) geological survey in special geological and geomorphic areas, traditional Quaternary mapping methods could not meet the needs of modern geological mapping in the coverage areas. Therefore, "What can we do" and "How can we do" become the key issues for the geological workers during the Quaternary geological mapping. In order to test even find some new geological mapping methods, we select typical coverage area-Hetao plain as our study area. Under the guidance of theories in fluvial sedimentlogy, combined with drilling column, we build the fluvial sedimentary system since the Holocene. Regard these subfacies as the sedimentary frame for the geological sketch frame, we recognize fluvial subfacies, embankments subfacies, and flood plain subfacies. The principle of step by step approximation was applied to determine the geological boundary. Besides that, three periods of fluvial deposits and corresponding sedimentary systems were recognized. Therefore, the problem of lacking geological units during the Quaternary geological survey in covered area might be solved, and a set of feasible scheme could be provided.
-
Key words:
- shallow covered area /
- mapping methods /
- fluvial system /
- sedimentary facies analyzation /
- Hetao plain
-
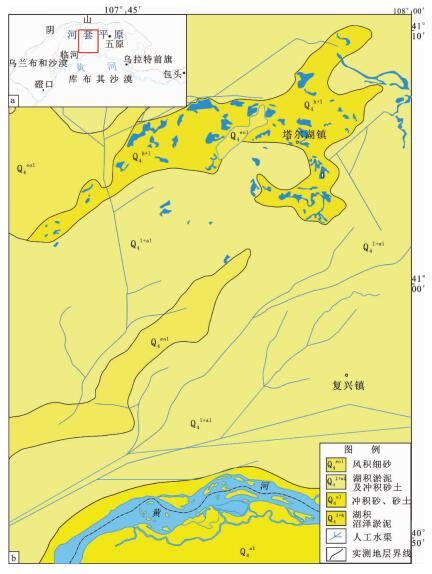
图 1 研究区地质图(a修改自[23]; b修改自临河县幅1:200000地质图)
Figure 1. Geological map of study area
表 1 主要填图单元特征
Table 1. Characteristies of main mapping units
填图单元
(沉积亚相)主要沉积物 沉积特点 地表形态 沉积物粒度特征 河道亚相 中砂、细砂、粉细砂 沉积厚层砂体 整体为长条状 三段式及两段式跳跃及悬浮组分为主 堤坝亚相 粉砂、黏土 粉砂黏土互层或厚层粉砂, 斜层理 伴随河道, 并沿河道方向延伸 三段式及两段式跳跃及悬浮组分组合, 悬浮组分为主 泛滥平原亚相 黏土, 粉砂质黏土 红棕色厚层黏土沉积 无规则分布, 常被其他沉积相切割掩埋 两段式为主悬浮组分占优势 表 2 河道亚相沉积特征
Table 2. Sedimentary characteristics of channel subfacies
典型沉积相(点4090) 分层描述 沉积组合(▲代表取样位置)及粒度曲线 ① 层为耕作土
沉积组合特征:较厚细砂层"二元结构"
② 229~130 cm, 灰黄色黏土质粉砂 
③ 3131~200 cm, 灰棕色细砂 
分析:概率累计曲线得到样品为两段式和三段式, 跳跃组分和悬浮组分占优势; 频率曲线得到分层沉积物来源均一, 中值粒径分别为50 μm、157 μm; 平均粒径分别为52 μm、166 μm, 沉积物相对较粗, 整体呈现上细下粗的"二元结构", 较厚细砂的出现, 成为河道亚相标志层。 表 3 堤坝亚相沉积特征
Table 3. Sedimentary characteristics of embankment subfacies
典型沉积相(点4094) 分层描述 沉积组合(▲代表取样位置)及粒度曲线 ① 层:耕作土
沉积组合特征:粉砂黏土互层
② 层:22~80 cm, 红棕色黏土 
③ 层:80~117 cm, 棕黄色黏土质粉砂 
④ 层:117~200 cm, 红棕色黏土, 质地均匀, 可塑性较强 
分析:概率累计曲线得到样品均为两段式, 以跃移和悬移为主, 悬移组分比例较大, 形成水动力较弱。频率曲线得到分层沉积物来源一致, 中值粒径分别为7 μm、26 μm、6 μm; 平均粒径分别为9 μm、26 μm、8 μm。 表 4 泛滥平原亚相沉积特征
Table 4. Depositional feature of flood plain
典型沉积相(点4096) 分层描述 沉积组合(▲代表取样位置)及粒度曲线 ① 层:耕作土
② 层:34~67 cm, 黄棕色含粉砂黏土
沉积组合特征:棕红色黏土为主
③ 层:67~84 cm, 棕黄色黏土质粉砂 
④ 层:84~200 cm, 棕红色黏土 
分析:概率累计曲线得到样品均为两段式, 以悬浮组分占优势。频率曲线得到分层沉积物来源一致, 中值粒径分别为16 μm、7 μm; 平均粒径分别为17 μm、8 μm, 沉积物整体较细, 以较厚棕红色黏土层为标志层, 氧化色明显。 -
[1] 浅覆盖区区域地质调查工作细则(1: 50000) DZ/T 0158-95[S].Regional geological survey of shallow coverage area(1:50000) DZ/T 0158-95[S]. [2] 胡道功.探索适合我国地质特点的地质填图新方法[N].中国国土资源报, 2014-07-24005.HU Dao-gong.Explore new method of geological mapping for geological characteristics in China[N]. China land and Resources News, 2014-07-24005. [3] 赵希涛, 胡道功, 吴中海.晚新生代地质填图理论与方法的新探索[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(10):1419~1429. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.10.008ZHAO Xi-tao, HU Dao-gong, WU Zhong-hai. An exploration to the theory and methodology of Late Cenozoic geological mapping[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2009, 28(10):1419~1429. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.10.008 [4] 王保良.覆盖区的岩性组合(岩相组合)填图法[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(12):890. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.12.013WANG Bao-liang.Coverage area lithologic (lithofacies) mapping method[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2002, 21(12):890. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.12.013 [5] 周宗尧, 董学发, 余国春, 等.浅覆盖城市经济区立体填图最新进展——浙江1:5万鸣鹤镇、澥浦镇、慈城镇、鄞江镇、姜山镇幅区调项目成果[J].资源调查与环境, 2013, 34(4):211~215. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ201304002.htmZHOU Zong-rao, DONG Xue-fa, YU Guo-chun, et al.New progresses of stereoscopic geological mapping in shallow covered urban economic regions:A case study of the 1:50000 scale regional geological survey of Minghe town, Xiepu town, Cicheng town, Yinjiang town and Jiangshan town sheets in Zhejiang Province[J]. Resources Survey and Environment, 2013, 34(4):211~215. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ201304002.htm [6] 周飞飞, 杨健.现代地质填图, 走向特殊地质地貌区[N].中国国土资源报, 2016-01-26006.ZHOU Fei-fei, YANG Jian. Modern geological mapping, to the special geological features area[M]. China Land and Resources Reported, 2016-01-26006. [7] 张晔卿, 谷永昌.成因地层分析方法在陆相盆地填图中的应用——以冀北滦平陆相火山-沉积盆地为例[J].华北地质矿产杂志, 1999, (2):288~294. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDZ199902033.htmZHANG Ye-qin, GU Yong-chang. The application of method about genetic analysis in continental basin mapping:Using continental volcanic-sedimentary basin in Luanping[J]. NORTH magazine Geology and Mineral Resources, 1999, (2):288~294. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDZ199902033.htm [8] 郭盛乔, 张祥云, 葛云, 等. 1:25万区调中第四系深覆盖区野外工作方法研究——以淮安市幅为例[J].地质学刊, 2013, 37(4):509~514. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ201304001.htmGUO Sheng-qiao, ZHANG Xiang-yun, GE Yun, et al, Study of field investigation method for 1:250000 scale regional geological survey in quaternary deep overburden area:A case study of Huaian City[J]. Journal of Geology, 2013, 37(4):509~514. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ201304001.htm [9] 王涛, 计文化, 胡健民, 等.专题地质填图及有关问题讨论[J].地质通报, 2016, 35(5):633~641. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201605001.htmWANG Tao, JI Wen-hua, HU Jian-min, et al. Geological mapping for special issues and a discussion on related topics[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2016, 35(5):633~641. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201605001.htm [10] 吕鹏, 张炜, 刘国, 等.国外重要地质调查机构三维地质填图工作进展[J].国土资源情报, 2013, (3):13~18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTZQ201303005.htmLÜ Peng, ZHANG Wei, LIU Guo, et al.Geological survey agencies dimensional geological mapping important progress abroad[J].Land and Resources Information, 2013, (3):13~18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTZQ201303005.htm [11] 王随继, 任明达.根据河道形态和沉积物特征的河流新分类.沉积学报, 1999, 17(2):240~246. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB902.012.htmWANG Sui-ji, RENG Ming-da.A New classification of fluvial rivers according to channel planform and sediment characteristics[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1999, 17(2):240~246. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB902.012.htm [12] 王随继, 倪晋仁, 王光谦.河流沉积学研究进展及发展趋势[J].应用基础与工程科学学报, 2000, (4):362~369. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJGX200004003.htmWANG Sui-ji, NI Jing-ren, WANG Guang-qian.The evolution and direction of research in fluvial sedimentology[J].Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2000, (4):362~369. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJGX200004003.htm [13] 谢庆宾, 朱筱敏, 管守锐等.中国现代网状河流沉积特征和沉积模式[J].沉积学报, 2003, 21(2):219~227. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200302004.htmXIE Qing-bin, ZHU Xiao-min, GUAN Shou-rui, et al. Depositional characteristics and models of the modern anastomosing river in China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2003, 21(2):219~227. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200302004.htm [14] 廖保方, 张为民, 李列等.辫状河现代沉积研究与相模式——中国永定河剖析[J].沉积学报, 1998, 16(1):34~39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199801005.htmLIAO Bao-fang, ZHANG Wei-min, LI Lie, et al. Study on modern deposit of a braided stream and facies model:Taking the Yongding River as an example[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1998, 16(1):34~39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199801005.htm [15] 郭峰, 郭岭, 姜在兴等.潮白河现代沉积特征与沉积模式[J].大庆石油学院学报, 2010, 34(2):7~10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY201002001.htmGuo Feng, Guo Ling, Jiang Zai-xing, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and depositional model of modern Chaobai River[J]. Journal of Daqing Petroleum Institute, 2010, 34(2):7~10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY201002001.htm [16] 何乃华, 朱宣清.河北平原曲流河现代沉积模式[J].地理研究, 1991, 10(1):65~72. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLGT199002010.htmHE Nai-hua, ZHU Xuan-qing.Present depositional feature and depositional model of meandering Streams in Hebei Plain[J]. Geographical Research, 1991, 10(1):65~72. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLGT199002010.htm [17] 常文会, 赵永刚, 卢松.曲流河环境沉积微相和测井相特征分析[J].天然气工业, 2010, 30(2):48~51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201002009.htmCHANG Wen-hui, ZHAO Yong-gang, LU Song. Features of sedimentary microfacies and electrofacies of meandering river deposits[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2010, 30(2):48~51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201002009.htm [18] 郭岭, 贾超超, 朱毓, 等.现代渭河西安段沉积体沉积相与岩相特征[J].沉积学报, 2015, 33(3):543~550. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201503014.htmGUO Ling, JIA Chao-chao, ZHU Yu, et al. Characteristics of sedimentary facies and lithofacies of modern Weihe river in Xi'an[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(3):543~550. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201503014.htm [19] 谭程鹏, 于兴河, 李胜利, 等.辫状河-曲流河转换模式探讨——以准噶尔盆地南缘头屯河组露头为例[J].沉积学报, 2014, 32(3):450~458. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201403006.htmTAN Cheng-peng, YU Xing-he, LI Sheng-li, et al. Discussion on the model of braided river transform to meandering river:An example of Toutunhe Formation in southern Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(3):450~458. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201403006.htm [20] 时志强, 韩永林, 赵俊兴, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地中南部中侏罗世延安期沉积体系及岩相古地理演化[J].地球学报, 2003, 24(1):49~54. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200301008.htmSHI Zhi-qiang, HAN Yong-lin, ZHAO Jun-xing, et al.Depositional system and paleogeographic evolution of the Middle Jurassic Yan'an Stage in the central and southern Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2003, 24(1):49~54. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200301008.htm [21] 巴彦淖尔盟志编纂委员会.巴彦淖尔盟志[M].呼和浩特:内蒙古人民出版社, 1997:167~170, 438~440.Bayannaoer Chi Compilation Committee. Bayannaoer Chi[M]. Hohhot:Inner Mongolia People's Publishing House. 1997:167~170, 438~440. [22] Jia L, Zhang X, He Z, et al. Late Quaternary climatic and tectonic mechanisms driving river terrace development in an area of mountain uplift:A case study in the Langshan area, Inner Mongolia, northern China[J]. Geomorphology, 2015, 234:109~121. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.12.043 [23] 张翼龙, 曹文庚, 于娟, 等.河套地区典型剖面地下水砷分布及地址环境特征研究[J].干旱区资料与环境, 2010, 24(12):167~171. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201012030.htmZHANG Yi-long, CAO Wen-geng, YU Juan, et al. The geological environment characteristics and distribution of groundwater arsenic in the typical section of Hetao Plain[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2010, 24(12):167~171. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201012030.htm [24] 江娃利.内蒙狼山一色尔腾山山前活动断裂古地震事件识别及同震垂直位移[J].地壳构造与地壳应力文集, 2002, 15:42~51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEIS200300005.htmJIANG Wa-li. Paleo-earthquake event and co-seismic vertical deformation recognition along the Langshan-Sertenshan pediment fault, Inner Mongolia[J]. Collection of Crustal Tectonics and Crustal Stress, 2002, 15:45~52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEIS200300005.htm [25] 国家地震局鄂尔多斯周缘活动断裂系课题组, 鄂尔多斯周缘活动断裂系, 地震出版社, 1988, 39~44.The research group on"active fault system around Ordos massif", State Seismological Bureau. Active fault system around Ordos massif[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 1988:39~44. [26] Jia L, Zhang X, Ye P, et al. Development of the alluvial and lacustrine terraces on the northern margin of the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia, China:Implications for the evolution of the Yellow River in the Hetao area since the late Pleistocene[J]. Geomorphology, 2016, 263:87~98. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.03.034 [27] 张小瑾. 河套地区(内蒙古磴口)晚冰期以来古气候演化初步研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2011. http://xueshu.baidu.com/s?wd=paperuri%3A%28c3bc88a29184f25afe2f7203798a1799%29&filter=sc_long_sign&tn=SE_xueshusource_2kduw22v&sc_vurl=http%3A%2F%2Fcdmd.cnki.com.cn%2FArticle%2FCDMD-11415-1011078081.htm&ie=utf-8&sc_us=5263684923296925796ZHANG Xiao-jin. Preliminary study of paleoclimate changes in Hetao area since late glacial:A case study in Dengkou County of Inner Mongolia[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 2011. http://xueshu.baidu.com/s?wd=paperuri%3A%28c3bc88a29184f25afe2f7203798a1799%29&filter=sc_long_sign&tn=SE_xueshusource_2kduw22v&sc_vurl=http%3A%2F%2Fcdmd.cnki.com.cn%2FArticle%2FCDMD-11415-1011078081.htm&ie=utf-8&sc_us=5263684923296925796 [28] 王随继.黄河流域河型转化现象初探[J].地理科学进展, 2008, 27(2):10~17. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2008.02.002WANG Sui-ji. Analysis of river pattern transformations in the Yellow River basin[J]. Progress in Geography, 2008, 27(2):10~17. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2008.02.002 [29] 陈建强, 周洪瑞, 王训练.沉积学及古地理学教程(第二版)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2015:97~107.CHENG Jian-qiang, ZHOU Hong-rui, WANG Xun-lian. Sedimentology and Palaoeogeography (2nd edition)[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2015:97~107. [30] 邓金宪, 刘正宏, 徐仲元, 等.包头地区晚更新世-全新世地层划分对比及环境变迁[J].地层学杂志, 2007, 31(2):133~140. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ200702005.htmDENG Jin-xian, LIU Zheng-hong, XU Zhong-yuan, et al. Subdivision and correlation of the late Pleistocene-Holocene strata in the Baotou area and its paleoenvironment variation[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2007, 31(2):133~140. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ200702005.htm [31] 刘哲, 赵华, 王成敏等.临河凹陷晚更新世以来沉积地层的光释光年龄[J].干旱区地理, 2014, 03:439~446. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL201403005.htmLIU Zhe, ZHAO Hua, WANG Cheng-min, et al.OSL ages of sedimentary layers in Linhe Depression since Late Pleistocene[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2014, 03:439~446. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL201403005.htm [32] 王兆义.槽型钻在浅覆盖区地质调查中的使用及其推广意义[J].科技风, 2013, (6):150. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJFT201306127.htmWANG Zhao-yi. Application and popularization significance of groove drill in geological survey of shallow cover area[J].Technology Wind, 2013, (6):150. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJFT201306127.htm -





 下载:
下载: