STUDY ON FLUID INCLUSIONS AND GENETIC TYPE OF HAOYAOERHUDONG GOLD DEPOSIT, INNER MONGOLIA
-
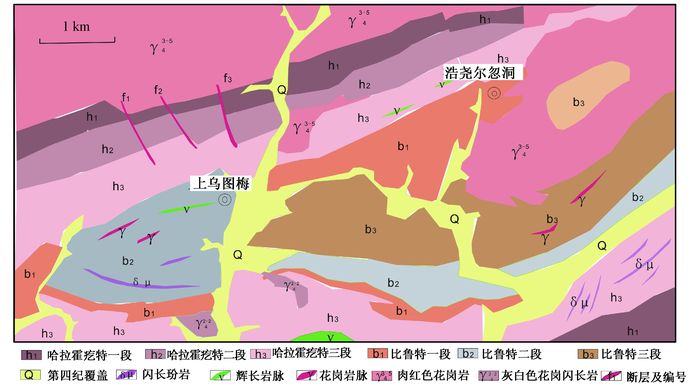
摘要: 内蒙浩尧尔忽洞金矿中比鲁特岩组一、二岩性段是主要的赋矿层位,岩石类型有炭质变粉砂岩、粉砂质板岩、炭质板岩和千枚岩等。该组中Au含量是地壳丰度值的7.14倍,且碳含量较高,介于1%~7%之间。矿化过程分为4个阶段:早期石英脉阶段包裹体均一温度245.2~323.3℃,石英-黄铁矿阶段均一温度为236.9~317.5℃,石英-多金属硫化物阶段均一温度231.7~324.5℃,石英-碳酸盐阶段均一温度187.6~312.9℃。激光拉曼显微探针分析结果显示,气液两相包裹体中液相成分主要为H2O,含少量CO2;气相成分主要为CO2,含少量的CH4和N2。氢、氧同位素特征表明成矿流体与岩浆热液关系密切。气相成分中大量有机成分可能是岩浆上侵促使地层中有机质发生热降解而生成的。矿床类型属于黑色岩系型金矿,与中亚成矿带的黑色岩系型金矿具有很高的可比性。Abstract: The first and second members of Bilute formation are the major ore-bearing horizons in Haoyaoerhudong gold deposit. The rock types contain carbonaceous meta-siltstone, silty slate, carbonaceous slate and phyllite, etc. Au content is 7.14 times of the crustal abundance in the formation and the carbon content is higher, with values of 1% to 7%. The metallogenic process can be divided into four stages:The homogenization temperature of fluid inclusions in the early quartz vein stage and the quartz-pyrite stage are from 245.2 to 323.3℃ and from 236.9 to 317.5℃ respectively; And the homogenization temperature are between 231.7 and 324.5℃ in the quartz-polymetallic sulfide stage and between 187.6 and 312.9℃ in the quartz-carbonate stage. According to the results of laser raman microprobe, The main liquid phase composition are H2O with minor amounts of CO2 and the main gas phase composition are CO2 with minor amounts of CH4 and N2 in fluid inclusions. Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic features indicate that the ore-forming fluid is closely related to magmatic hydrothermal. A large number of organic compounds in the gas phase composition may be generated in the thermal degradation of organic matter prompted by the magma invasion. The deposit type belongs to the black rock-hosted gold, with a high comparability of that in central Asian metallogenic belt.
-
Key words:
- Bilute formation /
- fluid inclusion /
- Raman microprobe /
- black rock-hosted gold
-
表 1 浩尧尔忽洞金矿流体包裹体显微测温结果
Table 1. Microthemometric data of fluid inclusions of Haoyaoerhudong gold deposit
样品编号 寄主矿物 数量 均一温度/℃ 冰点/℃ 盐度/% 流体密度/(g·cm-3) 成矿阶段 hr007-3 石英 18 245.2~323.3 -5.8~-9.2 10.58~16.59 0.78~0.92 早期石英脉阶段 hr007-5 石英 12 236.9~317.5 -7.6~-11.2 14.00~21.29 0.84~0.91 石英-黄铁矿阶段 hr007-4 石英 21 231.7~324.5 -5.8~-8.7 10.58~15.80 0.75~0.93 石英-硫化物阶段 hr007-13 石英 24 187.6~312.9 -3.9~-7.5 7.04~13.84 0.79~0.97 石英-方解石阶段 -
[1] 王玉峰.内蒙古浩尧尔忽洞金矿区岩体地球化学特征及其成矿意义[D].北京:中国地质大学,2012:30~40. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1012365086.htmWANG Yu-feng. The geochemical characteristics and its ore-forming significance of the pluton in the Haoyaoerhudong gold deposit of Inner Mongolia[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 2012:30~40. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1012365086.htm [2] 王建平,刘家军,江向东,等.内蒙古浩尧尔忽洞金矿床黑云母氩氩年龄及其地质意义[J].矿物学报,2011,(增刊):643~644. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2011S1335.htmWANG Jian-ping, LIU Jia-jun, JIANG Xiang-dong, et al. The argon-argon age of black mica in Haoyaoerhudong gold deposit and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Journal, 2011, (Supp.):643~644. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2011S1335.htm [3] 肖伟,聂凤军,刘翼飞,等.内蒙古长山壕金矿区花岗岩同位素年代学研究及地质意义[J].岩石学报,2012,28(2):535~543. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201202016.htmXIAO Wei, NIE Feng-jun, LIU Yi-fei, et al. Isotope geochronology study of the granitoid intrusions in the Changshanhao gold deposit and its geological implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(2):535~543. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201202016.htm [4] 赵百胜,刘家军,王建平,等.内蒙古长山壕金矿矿床地球化学特征与成因研究[J].现代地质,2012,25(6):1077~1086. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201106006.htmZHAO Bai-sheng, LIU Jia-jun, WANG Jian-ping, et al. Geological-geochemical characteristics and genesis of Changshanhao gold deposit in Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 25(6):1077~1086. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201106006.htm [5] 杨理华,李钦祖.华北地区地壳应力场[M].北京:地震出版社,1980:39~41.YANG Li-hua, LI Qin-zu. Crustal stress field in north China[M]. Beijing:Seismological Publishing House, 1980:39~41. [6] 崔盛芹.华北陆块北缘构造运动序列及区域构造格局[M].北京:地质出版社,2000:179~183.CUI Sheng-qin. The tectonic movement sequence and regional structure pattern in the northern margin of North China Landmass[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2000:179~183. [7] 胡桂明,王守伦.华北陆台北缘地体构造与铁金矿产[M].北京:地质出版社,1998:50~56.HU Gui-ming, WANG Shou-lun. The terrene tectonics and gold minerals in the northern margin of North China Landmass[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1998:50~56. [8] Hall D L, Stemer S M, Bodnan R J. Freezing point depression of NaCl-KCl-H2O solutions[J]. Economic Geology, 1988, 83:197~202. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.83.1.197 [9] 刘斌,段光贤.NaCl-H2O溶液包裹体的密度式和等容式及其应用[J].矿物学报,1987,7(4):345~351. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB198704010.htmLIU Bin, DUAN Guang-xian. The density and isochoric formulae for NaCl-H2O fluid inclusions and their applications[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1987, 7(4):345~351. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB198704010.htm [10] 邵洁涟.金矿找矿矿物学[M].北京:中国地质大学出版社,1990.SHAO Jie-lian. Gold prospecting mineralogy[M]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences Press, 1990. [11] 孙丰月,金巍,李碧乐,等.关于脉状热液金矿床成矿深度的思考[J].长春科技大学学报,2000,30(增刊):27~30.SUN Feng-yue, JIN Wei, LI Bi-le, et al. Considerations on the mineralizing depth of hydrothermal lode gold deposits[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2000, 30(Supp.):27~30. [12] 徐九华,谢玉玲,丁汝福,等.CO2-CH4流体与金成矿作用——以阿尔泰山南缘和穆龙套金矿为例[J].岩石学报,2007,23(8):2026~2032. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200708022.htmXU Jiu-hua, XIE Yu-ling, DING Ru-fu, et al. CO2-CH4 fluids and gold mineralization:Southern margin of Altay, China and Muruntau of Uzbekistan[J]. Acta Petrologica Sirnica, 2007, 23(8):2026~2032. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200708022.htm [13] Nadon J. Role of methane and carbon dioxide in gold deposition[J]. Nature, 1989, 342:793~795. doi: 10.1038/342793a0 [14] Shayakubov T, Islamov F, Kremenetsky A, et al. Excursion guide book:Au, Ag and Cu deposits of Uzbekistan[M]. London/Tashkent:GeoForschungs Zentrum Potsdam, 1999:1~74. [15] Kempe U, Belyats B V, Krymsky R S, et al. Sm-Nd and Sr isotope systematics of scheelite from the giant Au(-w)deposit Munmtau (Uzbekistan):Implications for the age and sources of Au mineralization[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2001, 36:379~392. doi: 10.1007/s001260100156 [16] Yakubchuk A, Cole A, Seltmann R, et al. Tectonic setting, characteristics and regional exploration criteria for gold mineralization in the Altaid orogenic collage:The Tienshan province as a key example[C]//Goldfarb R, Nielsen R L. Integrated methods for discovery:Global exploration in the 21st Century. United States:Society of Economic Geologists, 2002:177~201. [17] 鲍庆中,王宏,沙德铭,等.新疆和静县大山口金矿床成矿流体地球化学特征研究[J].西北地质,2003,36(2):43~49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI200302006.htmBAO Qing-zhong, WANG Hong, SHA De-ming, et al. Study on the geochemical characteristics of ore-forming fluid inclusion of Dashankou gold deposit in Xinjiang[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2003, 36(2):43~49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI200302006.htm [18] 陈华勇,张莉,李登峰,等.南天山萨瓦亚尔顿金矿床稀土微量元素特征及其成因意义[J].岩石学报,2013,29(1):159~166. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201301013.htmCHEN Hua-yong, ZHANG Li, LI Deng-feng, et al. Characteristics of rare earth and trace elements of the Sawayaerdun gold deposit, Southwest Tianshan:Implications for ore genesis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(1):159~166. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201301013.htm [19] 谭娟娟,朱永峰.穆龙套金矿地质和地球化学[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报,2008,27(4):391~398. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200804013.htmTAN Juan-juan, ZHU Yong-feng. Geology and geochemistry of Muruntau gold deposit[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2008, 27(4):391~398. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200804013.htm [20] 陈喜峰,彭润民,刘家军,等.吉尔吉斯斯坦库姆托尔超大型金矿床地质特征[J].黄金,2010,34(12):15~19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1277.2010.12.004CHEN Xi-feng, PENG Run-min, LIU Jia-jun, et al. Geological characteristics of Kumtor super large gold deposit in Kyrgyzstan[J]. Gold, 2010, 34(12):15~19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1277.2010.12.004 -





 下载:
下载: