CHARACTERISTICS AND CONTROLLING FACTORS OF FRACTURES IN RESERVOIRS OF XUJIAHE FORMATION IN ZITONG AREA, SICHUAN BASIN
-
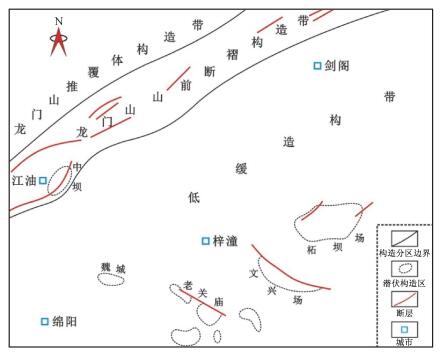
摘要: 基于野外露头、岩心、薄片及样品实验测试等资料, 对四川盆地梓潼地区须家河组储集层裂缝特征与控制因素进行了精细分析与解释。须家河组致密砂岩储集层主要发育3种类型的裂缝, 分别为构造裂缝、成岩裂缝以及与异常流体高压有关的裂缝, 并以构造裂缝为主。裂缝走向主要为近东西向、近南北向和北西向, 平均密度0.56条/m, 多为层内发育。平面上, 沿老关庙—文兴场—柘坝场构造, 裂缝密度依次减小; 纵向上, 以须四段裂缝最为发育。有效裂缝比例在老关庙地区最低, 向北东至柘坝场构造呈带状递增趋势。该区储集层裂缝的分布主要受岩性、岩层厚度、构造部位及异常流体压力等因素控制, 其中断层对裂缝分布的控制作用最为显著。细粒级、薄层砂岩更容易产生裂缝, 断裂带附近与构造高部位也是该区裂缝发育的有利区域, 且断层对裂缝的控制作用远大于构造高部位的影响作用。此外, 异常流体高压的存在也有利于该区裂缝的发育, 尤其是张裂缝, 其密度在高压区明显增大; 异常高压也能导致早期闭合缝重新开启, 并且对裂缝中矿物的充填程度与溶蚀强度有重要的控制作用。Abstract: Based on the data of outcrops, cores, thin sections and experimental analysis, the development characteristics and controlling factors of fractures in tight sandstone reservoirs of Xujiahe Formation in Zitong Area, Sichuan Basin were analysed and interpreted. There are three types of fractures, i.e. tectonic fractures, diagenetic fractures and fractures related to abnormal high pressure of fluid in the tight sandstone reservoirs. Among them, the tectonic fractures are the main part. There are main three sets fractures of nearly EW, nearly SN and NW-SE orientations. The fractures in study area have an average density of 0.56/m and are mostly confined within the single layer. In the plane, fractures density decreases along the Lao Guanmiao-Wen Xingchang-Zhe Bachang area. While, the fractures of T3x4 are most developed. The proportion of effective fracture is the lowest around the Lao Guanmiao area and increases along the direction of NW to Zhe Bachang area. The distribution of these fractures in study area were controlled by such factors as the lithology, layer thickness, structures and abnormal high pressure of fluid. Sandstone with fine particle and thin layer are favorable for fractures development. Where near the faults and the high part of the structure also are the favorable areas for tectonic fractures development. The control action of faults on the forming and distribution of fractures plays a dominant role. Moreover, the abnormal high pressure of fluid is beneficial to the development of fractures, especially for the extension fractures, the fractures density in abnormal high pressure belts increases significantly. The abnormal high pressure also causes some fractures which were closed in early stage to open and plays important roles in increasing the extent of mineral filling and corrosion increases of fractures.
-
Key words:
- reservoir fractures /
- controlling factor /
- tight sandstone /
- Xujiahe Formation /
- Zitong area /
- Sichuan basin
-
表 1 不同含气构造须家河组地层压力系数与张裂缝密度统计
Table 1. Statistical table of formation pressure coefficient and the density of tension fissure in Xujiahe Formation of different gas bearing structure
含气构造区 须二段压力系数 须四段压力系数 张裂缝密度/(条·m-1) 老关庙地区 1.6~2.2 1.7~2.3 0.21 文兴场地区 1.8~2.1 1.7~2.1 0.18 柘坝场地区 1.8~2.0 1.7~2.0 0.17 剑门地区 1.8~2.0 1.7~2.0 0.17 中坝地区 <1.4 <1.4 0.04 -
[1] 兰大樵, 张豫, 戴鸿鸣.川西北地区上三叠统油气勘探方向[J].天然气工业, 2005, 25(11):4~6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2005.11.002LAN Da-qiao, ZHANG Yu, DAI Hong-ming. Reservoiring conditions and exploratory targets of Upper Triassic Series in northwest Sichuan Basin area[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2005, 25(11): 4~6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2005.11.002 [2] 杨克明.川西坳陷须家河组天然气成藏模式探讨[J].石油与天然气地质, 2006, 27(6):786~793. doi: 10.11743/ogg20060609YANG Ke-ming. Gas reservoiring mode in Xujiahe Formation of western Sichuan depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2006, 27(6):786~793. doi: 10.11743/ogg20060609 [3] 戴朝成, 郑荣才, 朱如凯, 等.四川类前陆盆地中西部须家河组储层特征[J].天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(1):47~55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201101009.htmDAI Chao-cheng, ZHENG Rong-cai, ZHU Ru-kai, et al. Reservoir characteristics of Xujiahe Formation in Central West Sichuan Analogous Foreland Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2011, 22(1):47~55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201101009.htm [4] 裴森奇, 李跃纲, 张本健, 等.川西地区上三叠统天然气成藏主控因素及勘探方向[J].天然气工业, 2012, 32(10):6~13. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2012.10.002PEI Sen-qi, LI Yue-gang, ZHANG Ben-jian, et al. Major controlling factors of gas pooling and exploration directions in the Upper Triassic in the western Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2012, 32(10):6~13. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2012.10.002 [5] 邱宗湉, 何鹏.九龙山气田须二气藏工业气井的控制因素分析[J].天然气工业, 1990, 10(4):7~10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG199004001.htmQIU Zong-tian, HE Peng. Analysis of the Controlling Factors of the Commercial Gas Wells in Xu-2Reservoir in Jiulongshan Gas Field[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 1990, 10(4):7~10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG199004001.htm [6] 罗文军, 彭军, 杜敬安, 等.川西坳陷须家河组二段致密砂岩储层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J].石油与天然气地质, 2012, 33(2):287~295. doi: 10.11743/ogg20120215LUO Wen-jun, PENG Jun, DU Jing-an, et al. Diagenesis and porosity evolution of tight sand reservoirs in the 2nd member of Xujiahe Formation, western Sichuan Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2012, 33(2):287~295. doi: 10.11743/ogg20120215 [7] 曾联波.低渗透砂岩储层裂缝的形成与分布[M].北京:科学出版社, 2008.ZENG Lian-bo. Formation and distribution of fractures in low-permeability sandstone reservoirs[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008. [8] 张闻林, 何颐婷, 文龙, 等.川西北地区上三叠统异常高压探讨[J].天然气勘探与开发, 2002, 25(2):7~12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT200202002.htmZHANG Wen-lin, HE Yi-ting, WEN Long, et al. Research on the abnormal high pressures in upper Triassic in NorthWestern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2002, 25(2):7~12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT200202002.htm [9] 刘埃平, 文龙, 张闻林, 等.川西前陆盆地上三叠统异常高压的分布特征及形成机制研究[J].天然气勘探与开发, 2004, 27(4):3~8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT200404001.htmLIU Ai-ping, WEN Long, ZHANG Wen-lin, et al. Distributive characteristic and forming mechanism of abnormally high pressures in upper Triassic of West Sichuan foreland basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2004, 27(4):3~8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT200404001.htm [10] 王震亮, 孙明亮, 张立宽, 等.川西地区须家河组异常压力演化与天然气成藏模式[J].地质科学, 2004, 29(4):433~439. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200404008.htmWANG Zhen-liang, SUN Ming-liang, ZHANG Li-kuan, et al. Evolution of abnormal pressure and model of gas accumulation in Xujiahe Formation, Western Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2004, 29(4):433~439. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200404008.htm [11] 罗啸泉, 宋进.川西地区须家河组异常高压分布与油气富集[J].中国西部油气地质, 2007, 3(1):35~40. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBYD200701007.htmLUO Xiao-quan, SONG Jin. Distribution characteristics of abnormal high pressure of Xujiahe Formation in the Western Sichuan[J]. West China Petroleum Geosciences, 2007, 3(1):35~40. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBYD200701007.htm [12] Cooke M L. Fracture termination and step-over at bedding interfaces due to frictional slip and interface opening[J].Journal of Structural Geology, 2001, 23(2/3):223~238. [13] 曾联波, 漆家福, 王永秀.低渗透储层构造裂缝的成因类型及其形成地质条件[J].石油学报, 2007, 28(4):52~56. doi: 10.7623/syxb200704010ZENG Lian-bo, QI Jia-fu, WANG Yong-xiu. Origin type of tectonic fractures and geological conditions in low-permeability reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(4):52~56. doi: 10.7623/syxb200704010 [14] 周新桂, 张林炎, 屈雪峰, 等.沿河湾探区低渗透储层构造裂缝特征及分布规律定量预测[J].石油学报, 2009, 30(2):195~200. doi: 10.7623/syxb200902006ZHOU Xin-gui, ZHANG Lin-yan, QU Xue-feng, et al. Characteristics and quantitative prediction of distribution laws of tectonic fractures of low-permeability reservoirs in Yanhewan area[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(2):195~200. doi: 10.7623/syxb200902006 [15] GROSHONG R H. Forced folds and fractures: geological society special publication[J]. Tectonophysics.2001, 334(5):57~59. [16] 曾联波, 李跃纲, 张贵斌, 等.川西南部上三叠统须二段低渗透砂岩储层裂缝分布的控制因素[J].中国地质, 2007, 34(4):622~627. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200704011.htmZENG Lian-bo, LI Yue-gang, ZHANG Gui-bin, el at. Controlling factors for fracture distribution in the low-permeability sandstone reservoir of the Second Member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the south of western Sichuan[J]. Geology in China, 2007, 34(4):622~627. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200704011.htm [17] 刘树根, 何鹏, 邓荣贵, 等.川西九龙山构造须二段岩石力学性质与裂缝发育规律研究[J].天然气工业, 1996, 16(2):1~4. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG199602003.htmLIU Shu-gen, HE Peng, DENG, Rong-gui, et al. Rock mechanics and fracture distribution of Xu2 Member in Jiulongshan structure of western Sichuan basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 1996, 16(2):1~4. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG199602003.htm -





 下载:
下载: