EXTRACTION OF TECTONIC GEOMORPHOLOGIC PARAMETRES BASED ON DEM AND ANALYSIS OF DIFFERENCE ON TECTONIC ACTIVITY ABOUT LANGSHAN MOUNTAIN, INNER MONGOLIA
-
摘要: 基于30 m分辨率DEM数据, 利用ArcGIS10.0对内蒙古狼山东南坡河流流域地貌参数进行提取, 精确计算了其中15条规模较大的北西—南东向河流的面积-高程积分值(HI), 并据此对河流发育阶段以及构造运动进行分析。研究结果显示有8条河流的HI值处于0.3~0.6之间, 属于河流发展的壮年阶段; 7条河流的HI值大于0.6, 为幼年期, 未出现老年期河流。狼山西南部河流河谷V1—V14的HI值变化平缓, 波动幅度不大, 构造运动呈现出先增强后减弱的态势; 中北部河流V14—V22的HI值变化较剧烈, 尤其是V14—V19, 呈明显上升趋势, 河流受侵蚀后残存体积增多, 构造运动活跃性下降; V19以北HI值持续下降, 其构造运动的活跃性增加。由此认为狼山从西南到东北总体呈现增强—减弱—增强的差异性运动状态, 该结论与前人所做山前构造地貌研究结果较为一致。
-
关键词:
- 新构造运动 /
- DEM /
- 河流地貌面积-高程积分 /
- 内蒙古狼山 /
Abstract: This paper extracted the drainage basins of 15 rivers on the southeast slope of Langshan Mountain and narrowly calculated their HI values using ArcGIS10.0 based on 30 meter resolution DEM data, then analysed the tectonic activities and geomophological evolutions in this region. The results showed that the HI values of 8 rivers were between 0.3 and 0.6, indicating that these rivers were in their mature stage; the HI values of 7 rivers were greater than 0.6, stating clearly that these rivers were in their juvenile stage. Moreover, there were no rivers in old age. The HI values of V1~V14 changed gently, with the tectonic movement first increasing and then decreasing. The area-altitude points of V14~V22 changed tempestuously, especially rivers V14~V19, which showed a clear upward trend and the river eroded remnant volume increased in the result the tectonic activity decreased. HI values the rivers north of V19 continued to decline, and its tectonic activity increased. The Langshan Mountain was suggested in enhanced-weakening-enhanced diversity state of motion from the southwest to the northeast with the conclusion of previous work in tectonic geomorphology of the consistent results.-
Key words:
- neotectonics /
- DEM /
- fluvial geomorphology /
- hypsometric integral (HI) /
- Langshan Mountain
-
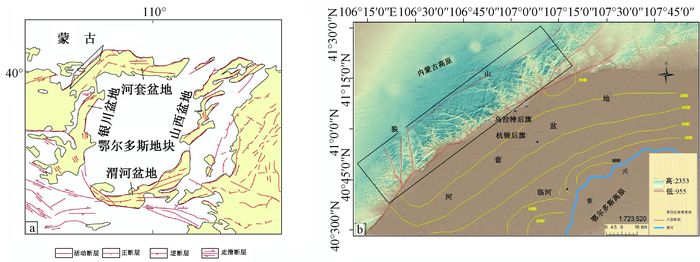
图 1 研究区概况(据文献[23]修改)
Figure 1. Sketch map of study area
表 1 各流域参数
Table 1. Parameters of every valley
河谷序号 流域面积/km2 河网总长度/km 平均高程/m 河网密度 HI值 高差/m V2 66.55 40.23 1570 0.605 0.680 649 V3 34.77 20.63 1517 0.593 0.598 676 V4 71.48 38.66 1568 0.541 0.639 698 V5 218.14 119.53 1664 0.548 0.584 920 V7 243.11 131.75 1706 0.542 0.562 1050 V9 63.35 38.76 1688 0.612 0.581 1008 V10 113.05 60.07 1800 0.531 0.650 1053 V13 55.85 30.16 1693 0.540 0.582 1033 V14 149.51 83.72 1852 0.560 0.647 1141 V15 140.34 77.28 1935 0.551 0.674 1217 V18 142.68 71.79 1990 0.503 0.711 1254 V19 376.46 199.58 1893 0.530 0.638 1265 V20 86.13 44.57 1746 0.517 0.585 1110 V21 66.85 37.40 1661 0.559 0.514 1116 V22 123.67 65.53 1692 0.530 0.505 1215 -
[1] 汤国安.我国数字高程模型与数字地形分析研究进展[J].地理学报, 2014, 69, (09):1305~1325 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB201409007.htmTANG Guo-an.Progress of DEM and digital terrain analysis in China[J].Acta Geographica Sinica, 2014, 69(09):1305~1325. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB201409007.htm [2] 单菊萍. 基于DEM的雅鲁藏布江河流地貌特征的研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京), 2007 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199805011.htmSHAN Ju-ping.Research on the Morphological Features of YarlungZangbo River Based on DEM[D].China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2007. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199805011.htm [3] 李利波, 徐刚, 胡健民, 等.基于DEM渭河上游流域的活动构造量化分析[J].第四纪研究, 2012, 32(5):866~879 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201205008.htmLI Li-bo, XU Gang, HU Jian-min, et al. Quantitative analysis of relative active tectonics of the upstream region of Weihe River based on DEM [J].Quaternary Sciences, 2012, 32(5):866~879. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201205008.htm [4] 韩海辉. 基于SRTM-DEM的青藏高原地貌特征分析[D]. 兰州大学, 2009 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10730-1015334753.htmHAN Hai-hui. Analysis of geomorphological features of the Tibetan Plateau based on DEM[D].Lanzhou University, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10730-1015334753.htm [5] A. Demoulin. An automated method to extract fluvial terraces from digital elevation models: The Vesdre valley, a case study in eastern Belgium. Geomorphology, 2007, 91:51~64. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2007.01.020 [6] M. Font, D. Amorese, J.-L. Lagarde, . DEM and GIS analysis of the stream gradient index to evaluate effects of tectonics: the Normandy intraplate area (NW France) [J].Geomorphology, 2010, 119: 172~180. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2010.03.017 [7] John T. Hack. Stream-profile analysis and stream-gradient index [J]. U.S. Geological Survey Journal Research, 1: 421~429. http://catalogue.nla.gov.au/Record/3770826 [8] 何祥丽, 张绪教, 何泽新.基于构造地貌参数的新构造运动研究进展与思考[J].现代地质, 2014, 28(1):119~127 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201401012.htmHE Xiang-li, ZHANG Xu-jiao, HE Ze-xin. Neotectonics Research Based on Tectonic Geomorphologic Parameters: Progress and Discussion[J].Geoscience, 2014, 28(1):119~127. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201401012.htm [9] 宋效东, 刘学军, 汤国安, 等DEM与地形分析的并行计算[J].地理与地理信息科学, 2012, 28, (4):1~7 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLGT201204002.htmSONG Xiao-dong, LIU Xue-jun, Tang Guo-an, etal.Parallel Computing of the Digital Elevation Model and Digital Terrain Analysis[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2012, 28, (4):1~7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLGT201204002.htm [10] 王岩, 刘少峰, 高明星, 等.洮河水系流域地貌特征及其构造指示意义[J].地学前缘, 2010, 17, (4):43~49 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201004007.htmWANG Yan, LIU Shao-feng, GAO Ming-xing, et al. Geomorphology of the Taohe River drainage system and its structural implications.Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(4):43~49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201004007.htm [11] 胡小飞, 潘保田, KIRBY Eirc, 等.河道陡峭指数所反映的祁连山北翼抬升速率的东西差异[J].科学通报, 2010, 55(23):2329~2338 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201023016.htmHU Xiao-fei, Pan Bao-tian, KIRBY Eirc, et al. Spatial differences in rock uplift rates inferred from channel steepness indices along the northern flank of the Qilian Mountain, northeast Tibetan Plateau [J]. Science China Press, 2010, 55(23):2329~2338. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201023016.htm [12] 宋卓沁. 青藏高原东缘典型河流地貌及其活动构造指示[D]. 中国地震局地震预测研究所, 2014 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DKXB201502020.htmSONG Zhuo-qin.The Geomorphology of the Typical Rivers in the Eastern Tibet and their Active Tectonic Implications[D].Institute of Earthquake Science China, China Earthquake Administration, 2014. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DKXB201502020.htm [13] 常直杨, 王建, 白世彪, 等.基于DEM的白龙江流域构造活动定量分析[J].第四纪研究, 2014, 34, (2):292~301 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201402003.htmCHANG Zhi-yang, WANG Jian, BAI Shi-biao, et al.Research on Quantitative Geomorphologic indices of Bailongjiang drainage basin in the eastern Tibet Plateau based on Digital Elevation Models[J].Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 34, (2):292~301. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201402003.htm [14] 信忠保, 许炯心, 马元旭.黄土高原面积-高程分析及其侵蚀地貌学意义[J].山地学报, 2008, 26, (3):356~363 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA200803024.htmXIN Zhong-bao, XU Jong-xin, MA Yuan-xu. Hypsometric integral analysis and its sediment yield implications in the Plateau, China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2008, 26(3): 356~363. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA200803024.htm [15] 施炜.黄河中游晋陕峡谷的DEM流域特征分析及其新构造意义[J].第四纪研究, 2008, 28, (2):288~298 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200802013.htmSHI Wei. DEM drainage analysis of the ShanXi-ShaanxiGorge in the middle reaches of the Huanghe River and its neotectonic implications[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2008, 28(2):288~298. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200802013.htm [16] 高明星, 徐锡伟, 谭锡斌. 地貌参数指示的龙门山最新活动的特征[C] //中国地球物理2012. 北京: 中国地球物理学会, 2012: 269 http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Column/Paper?q=%E4%BD%9C%E8%80%85%3A%22Tan%20Xibin%22GAO Ming-xing, XU Xi-wei, TAN Xi-bin.Geomorphic indices indicated recent tectonic activity of the Longmensha[C] //The Chinese Geophysics 2012. Beijing: Geophysical Society of China, 2012:269. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Column/Paper?q=%E4%BD%9C%E8%80%85%3A%22Tan%20Xibin%22 [17] 郑光佑. 台湾西部麓山带前缘流域面积高度积分之构造意义研究[D]. 台北国立高雄大学, 2002. 33~37 http://edu.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/Detail/dsjyj201501006ZHENG Guang-you.The Implications of Hypsometric Integral for River Basins in the Mountain Front of Western Taiwan[D].National Kaohsiung NormalUniversity, 2002, 33~37. http://edu.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/Detail/dsjyj201501006 [18] Martin D. Hurst, Simon M. Mudd, Mikael Attal, et al.Hillslopes record the growth and decay of landscapes[J].Science, 2013, 341: 868~871. http://www.geos.ed.ac.uk/homes/mattal/CVAttal_Aug16.pdf [19] 何泽新, 张绪教, 贾丽云, 等.内蒙古狼山山前台地成因及其新构造运动意义[J].现代地质, 2014, 28(1):98~108 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201401010.htmHE Ze-xin, ZHANG Xu-jiao, JIA Li-yun, et al.Genesis of Piedmont Terraces and Its Neotectonic Movement SignificanceinLangshan Mountain Area, Inner Mongolia[J].Geoscience, 2014, 28(1):98~108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201401010.htm [20] 江娃利.内蒙狼山—色尔腾山山前活动断裂古地震事件识别及同震垂直位移[J].地壳构造与地壳应力文集, 2003, 15: 45~52 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEIS200300005.htmJIANG Wa-li. Paleo-Earthquake Event and Co-Seismic Vertieal Deformation Recognition along the Langshan-Sertenshan Pediment Fault, Inner Mongolia[J].Crustal tectonics and crustal stress, 2003, 15:45~52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEIS200300005.htm [21] LI YunJia. Late Quaternary climatic and tectonic mechanisms driving river terrace development in an area of mountain uplift: A case study in the Langshanarea, Inner Mongolia, northern China.Geomorphology, 2015, 234:109~121. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.12.043 [22] 彭润民, 翟裕生, 韩雪峰, 等.内蒙古狼山造山带构造演化与成矿响应[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(3):679~688 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200703016.htmPENG Run-min, ZHAI Yu-sheng, Han Xue-feng, et al.Mineralization response to structural evolution in the Langshan orogenic belt, Inner Mongolia[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(3):679~688. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200703016.htm [23] 毕丽思. 基于DEM的活动构造地貌参数研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所, 2011 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Area/CDMDUnitArticle-85402-2011-1.htmBI Li-si, A Study on the Geomorphologic Indexes in Active Tectonics Based on DEM Data[D].Beijing: Institute of Geology China Earthquake Administrations, 2011. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Area/CDMDUnitArticle-85402-2011-1.htm [24] 张敬春, 李川川, 张梅等.格尔木河流域面积-高程积分值的地貌学分析[J].山地学报, 2011, 29(3):257~268 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201103001.htmZHANG Jing-chun, LI Chuan-chuan, ZHANG Mei, et al.Geomorphologic analysis of the Golmud River drainage basin based on Hypsometric-Intrgral Value[J].Journal of Mountain Science, 2011, 29(3):257~268. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201103001.htm [25] Strahler A N.Hypsometric (area-altitude) analysis of erosional topography [J].Bulletin of the Geological Society of America, 1952, 63(1): 1117~1142. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1952GSAB...63.1117S [26] Pike R J.Wilson S E. Elevation-relief ratio, hypsometric integral and geomorphic area-altitude analysis [J].Geological Society of America Builetin.1971, 82:1079~1084. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1971)82[1079:ERHIAG]2.0.CO;2 [27] 张天琪, 王振, 吕红华.北天山乌鲁木齐河流域面积-高程积分及其地貌意义.第四纪研究, 2015, 35(1):60~70 http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj201501006ZHANG Tian-qi, WANG Zhen, LV Hong-hua, et al.Hypsometric integral analysis of the Urumqi River drainage basin and its implications for topographic evolution[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 34(2): 281~291. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj201501006 [28] Lifton N A, Chase C G. Tectonic, climatic and lithologic influences on landscape fractal dimension and hypsometry: Implications for landscape evolution in the San Gabriel Mountains, California[J]. Geomorphology, 1992, 5: 77~114. doi: 10.1016/0169-555X(92)90059-W [29] 邵建崇, 李勇, 赵国华.基于面积-高程积分对龙门山南段山前河流的构造地貌研究.现代地质, 2015, 29(4):727~737 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201504001.htmSHAO Chong-jian, LI Yong, ZHAO Guo-hua. Tectonic geomorphology analysis of piedmont rivers of the southen section LongMen Shan based on Area-Altitude points[J].Geoscience, 2015, 29(4):727~737. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201504001.htm [30] 何祥丽, 张绪教, 何泽新, 等.内蒙古狼山地区晚第四纪泥石流发育特征及其构造意义[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(9):1735~1748 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201509015.htmHE Xiang-li, ZHANG xu-jiao, HE Ze-xin. Development features of the Late Quaternary debris flow and their tectonic significance in Langshan area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(9):1735~1748. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201509015.htm -





 下载:
下载: