EARTHQUAKE RISK ANALYSIS IN THE ENGINEERING AREA OF BOHAI STRAIT CROSS-SEA CHANNEL
-
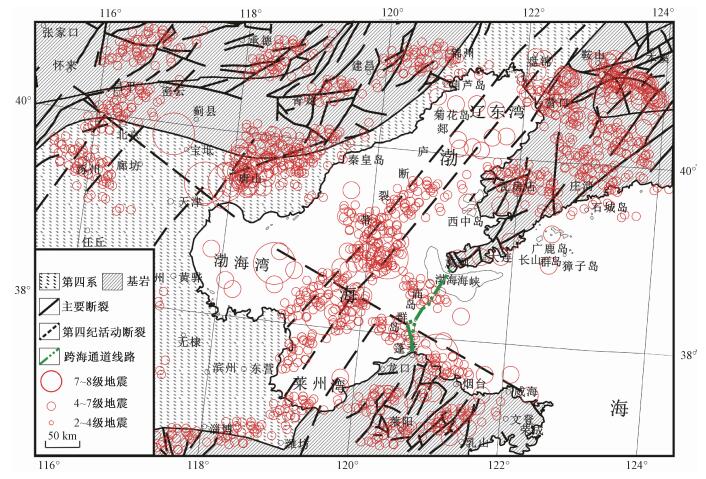
摘要: 研究渤海海峡地区区域历史地震时空分布特征,分析渤海海峡地区的地震发生位置及其发震规律,论述历史地震对工程场地的影响,为渤海海峡跨海通道的选址提供依据,使选址时尽量避开活动断层以减少地震对跨海通道的影响,增加评判工程稳定性的因子,使评判结论更加可靠。Abstract: Spatial temporal features for regional historical earthquake of Bohai Strait area has been studied, and location and law of the earthquake been analyzed. We discussed the impact of the historical earthquake to the construction area, and provided a theoretical basis for the site choice of the Bohai Strait Cross-Sea Channel, so that the construction area could avoid active faults to the greatest extent, reduced the influence of earthquake to the Bohai Strait Cross-Sea Channel, increased the factor of engineering stable judgment, and made the evaluation more exactly and reliable.
-
Key words:
- Bohai Strait Cross-Sea Channel /
- earthquake /
- risk analysis /
- earthquake trend /
- prediction
-
表 1 渤海地区Ms≥2.0级地震统计
Table 1. Seismic classification statistical table for the area of Bohai

表 2 海城地震等震线参数
Table 2. Isoseismal parameter of Haicheng earthquake

表 3 工程区震级-频度关系拟合曲线
Table 3. Fitting curve of magnitude to frequency for the construction area

-
[1] 中央地震工作小组办公室.中国地震目录[M].北京:科学出版社, 1971.TheCentral Earthquake Working Group Office. China earthquake catalogue[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1971. [2] 顾功叙.中国地震目录(公元1970-1979年)[M].北京:地震出版社, 1984.GU Gong-xu. China earthquake catalogue (1970-1979)[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 1984. [3] 刁守中, 晁洪太.中国历史有感地震目录[M].北京:地震出版社, 2008.DIAO Shou-zhong, CHAO Hong-tai. Inductive earthquake catalogue in Chinese history[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 2008. [4] 彭华, 崔巍, 马秀敏, 等.南水北调西线第一期工程调水区水压致裂地应力测量及其工程意义[J].地质力学学报, 2006, 12(2):182~190. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20060227&journal_id=dzlxxbPENG Hua, CUI Wei, MAXiu-min, et al. Hydro fracturing in-situ stress measurements of the water diversion area in the first stage of the South-North Water Diversion Project (Western Line)[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2006, 12(2):182~190. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20060227&journal_id=dzlxxb [5] 马秀敏, 彭华, 李金锁, 等.新疆西部地应力测量在隧道工程中的应用[J].地质力学学报, 2005, 11(4):386~393. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20050455&journal_id=dzlxxbMA Xiu-min, PENG Hua, LI Jin-suo, et al. Application of hydraulic fracturing in-situ stress measurements in tunneling in western Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2005, 11(4):386~393. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20050455&journal_id=dzlxxb [6] 蔡克明.1548年蓬莱地震[J].地震地质, 1987, (2):95~96. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXK198701011.htmCAI Ke-ming. Penglai earthquake of 1548[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1987, (2):95~96. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXK198701011.htm [7] 张肇诚.中国震例(1966-1975)[M].北京:地震出版社, 1988.ZHANG Zhao-cheng, China earthquake cases (1966-1975)[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 1988. [8] 赵成斌, 孙振国, 刘保金, 等.邢台地震浅部构造特征及其与深部构造的耦合关系[J].地震地质, 1999, 21(4):417~424. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ199904016.htmZHAO Cheng-bin, SUN Zhen-guo, LIU Bao-jin, et al, A study of the shallow structural characteristics and the coupling relation between deep and shallow structures in Xingtai earthquake area[J]. Seismology and geology 1999, 21(4):417~424. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ199904016.htm [9] 虢顺民, 李志义, 程绍平, 等.唐山地震区域构造背景和发震模式的讨论[J].地质科学, 1977, (4):305~320. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX197704000.htmGUO Shun-min, LI Zhi-yi, CHENG Shao-ping, et al. Discussion on the regional structural background and the seismogenic model of the Tangshan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1977, (4):305~320. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX197704000.htm [10] 向宏发, 方仲景, 徐杰, 等.三河-平谷8级地震区的构造背景与大震重复性研究[J].地震地质, 1988, 10(1):15~37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ198801002.htmXIANG Hong-fa, FANG Zhong-jing, XU Jie, et al. A magnitude 8 earthquake in Sanhe-Pinggu tectonic background and strong earthquakes in repetitive research[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1988, 10(1):15~37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ198801002.htm [11] 中国地震局地质研究所.地震危险性预测研究(1999年度)[M].北京:地震出版社, 1998.Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration. Seismic risk prediction research (1999)[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 1998. [12] 中国地震局分析预报中心.中国地震趋势预测研究(2003年度)[M].北京:地震出版社, 2002.Center of Earthquake Analysis and Prediction, China Earthquake Administration. Chinese earthquake prediction research (2003)[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 2002. [13] Xiang Hongfa, Zhang Wanxia, Li Rucheng. Deformation zone of the l679 Sanhe-Pinggu M=8.0 earthquake and burried active faults[C]//Proceedings of the 30th International Geological Congress. Beijing, 1996. [14] King C Y. Episodic radon change in subsurface soil:Gasalong active faults and possible relation to earthquakes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1980, 85(B6):3065~3078. doi: 10.1029/JB085iB06p03065 [15] 建筑抗震设计规范GBJ 11-89[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1990.Current China Seismic Design Code of Buildings GBJ 11-89[S]. Beijing:China Architecture & Building Press, 1990. -





 下载:
下载: