THE FEATURES AND AGES OF LAKE BEACH ROCK AROUND SAYRAM LAKE IN WESTERN TIAN SHAN AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE ON LAKE LEVEL FLUCTUATION DURING THE LAST INTERGLACIAL EPOCH MIS3
-
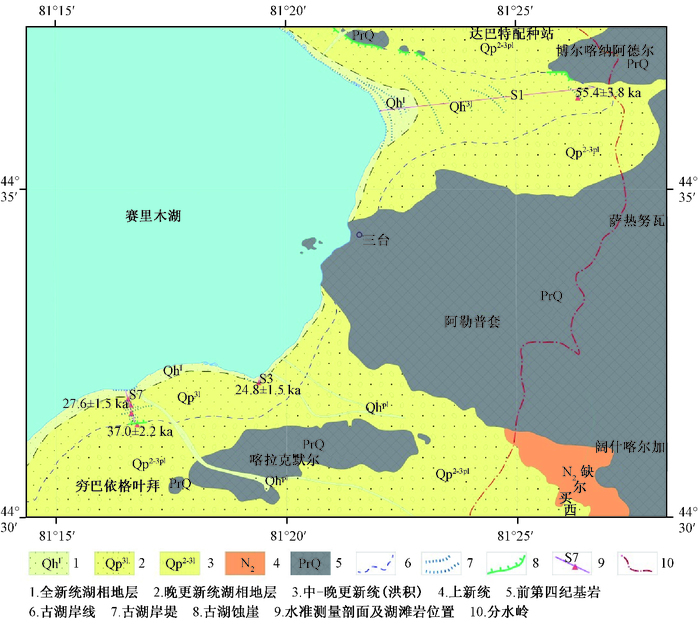
摘要: 在对西天山赛里木湖盆地进行第四纪地质调查与5万填图基础上,发现沿该湖泊的不同湖岸阶地上都不同程度地发育了可指示湖面变化的湖滩岩。水准测量结果表明,典型的湖滩岩最常见于高出现今湖面7.1~9.4 m和33.4~39.4 m的低、高两级湖积台地上。对湖滩岩样品进行岩石学和矿物学研究进一步揭示,湖滩岩主要由内碎屑、藻团块、陆源碎屑、胶结物和填隙物等构成,胶结物主要为亮晶方解石,夹少量文石,表明赛里木湖周边的湖滩岩为典型的方解石胶结砂屑砾屑岩。湖滩岩样品的U系年代测试结果表明,低、高两级台地上的湖滩岩主要形成于距今24.8±1.5 ka至27.6±1.5 ka和55.4±3.8 ka的晚更新世晚期,大致对应末次冰期间冰阶MIS3阶段早期和末期的相对暖湿气候阶段。湖滩岩及其测年结果指示,赛里木湖最近一期最高湖面出现在距今55.4 ka左右末次间冰阶早期,其后由于气候的干旱化,湖面整体处于逐步下降过程,在相对暖湿期间经历了多次湖面相对稳定期并形成湖滩岩。Abstract: Lake beach rock is one of the products which can reflect the land and sea interactions, of great significance for studying the ancient lake level fluctuations, lakeshore zone evolution and paleoclimatic change. On the basis of Quaternary geological survey and 1 :50000 scale geological mapping for Sayram Lake Basin in western Tianshan, we found lake beach rocks on the different shore terraces, indicating lake level fluctuations. The levelling result showed that the concentration distribution of typical lake beach rock was mainly on the fluvial terraces above the lake level 7.1~9.4 m and 33.4~39.7 m. The Petrologic and mineralogical study further showed that the lake beach rocks were mainly composed of intraclast, algal briquette, terrigenous clastic, cement and filler content, etc., and the cement mainly for the sparry calcite with a small amount of aragonite, which proved that the Sayram Lake beach rocks were typical calcite cementation sand gravel chip rocks. According to the U series dating results of lake beach rock samples, the lake beach rocks on the fluvial terraces were formed from 24.8±1.5 ka to 27.6±1.5 ka and 55.4±3.8 ka, late of the late Pleistocene, roughly corresponding to the relatively warm climate stage of early and late in last glacial interglacial epoch MIS3 stage.The lake beach rocks and dating results indicated that the recent highest level of Sayram Lake appeared in the distance of about 55.4 ka, early in the last interglacial epoch. Due to the subsequent drying climate, the lake level was overall in the process of decline gradually. During the relatively warm moist period, the lake level underwent multiple relatively stable periods, and resulted in lake beach rock formed.
-
Key words:
- the West Tianshan /
- the Sayram Lake /
- lake level fluctuation /
- lake beach rock /
- the last glacial period
-
图 4 赛里木湖周缘湖滩岩显微特征
a—湖滩岩手标本,可观察到其结构为典型的砂质含砾胶结岩,块状构造,接触式胶结;b—镜下观察湖滩岩薄片,岩石为含砂砾质砂屑砾屑结构(-),基底式接触式胶结。内碎屑由泥晶灰岩、粉晶灰岩等构成,次棱角—浑圆状,具方向性分布。陆源碎屑由岩屑、石英构成。岩屑主见硅质岩、石英岩、(含铁炭质)粘土质板岩、花岗斑岩、蚀变岩等,大小不等。胶结物由亮晶方解石及少量文石构成,粒径<0.1mm。亮晶方解石、文石主呈纤状、刃状等;c—镜下观察湖滩岩薄片,岩石由内碎屑、藻团块、藻球粒、陆源碎屑、填隙物构成。陆源碎屑由岩屑、石英构成,棱角-次棱角状为主,零散分布。岩屑主见硅质岩、石英岩、粘土质板岩等,大小0.02~8.0 mm不等;d—镜下观察湖滩岩样品中的藻团块特征。藻团块呈团状,有的边缘不规则,0.2~1.0 mm,由泥晶方解石及藻类构成,色暗;e—镜下观察湖滩岩胶结物特征,胶结物由亮晶方解石及少量文石构成,亮晶方解石、文石主要呈纤状、刃状等,垂直碎屑生长,构成栉壳结构,局部由多层纤状方解石与有机质混杂构成玛瑙纹状构造,基底式及接触式胶结;f—镜下观察湖滩岩的泥晶填隙物。湖滩岩中的内碎屑及陆源碎屑之间的填隙物由亮晶方解石胶结物、文石及泥晶方解石填隙物构成
Figure 4. Micro-characteristics of the lacustrine-beach rock around south-east Sayram Lake
表 1 赛里木湖湖滩岩出露高程及铀系测试结果
Table 1. Elevations and U-series dates of the lacustrine-beach rock around the Sayram Lake
样品编号 剖面地点与采样部位 拔湖高度/m 高程/m 岩性 年龄/ka S0811-7 S1剖面最高湖岸堤顶部 34.72 2107 钙质胶结砂砾石 55.4±3.8 S0814-5 S7剖面第9测点小湖岸堤顶 9.38 2082 钙质胶结砾石 27.6±1.5 S0814-9 湖岸阶地后缘上覆洪积扇前缘 44.85 2118 钙质胶结含砂砾石 37.0±2.2 S0814-17 S8剖面2080 m湖岸堤顶部 7.14 2080 钙质胶结砾石 24.8±1.5 -
[1] 王树基.关于赛里木湖的形成、演变与第四纪古冰川作用的关系[J].干旱区地理, 1978, 1(1):47~55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL197801004.htmWANG Shu-ji. The relationship between Sayram Lake and paleo-glacier[J]. Arid Land Geography, 1978, 1(1): 47~55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL197801004.htm [2] 赵彩龙, 阎顺, 宋旭东, 等.新疆赛里木湖地质公园旅游开发研究[J].干旱区地理, 2009, 32(4):638~644. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL200904024.htmZHAO Cai-long, YAN Shun, SONG Xu-dong, et al. Tourism development of Sayram Lake Geopark, Xinjiang[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2009, 32(4): 638~644. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL200904024.htm [3] 李永春.青海湖全新世湖相碳酸盐胶结岩湖滩岩的发现及意义[J].青海地质, 1989, (1):22~26.LI Yong-chun. The discovery and significance of lake beach rock-the Holocene lacustrine carbonate cementation rock of Qinghai Lake[J]. Qinghai geology, 1989, (1): 22~26. [4] Allaby A, Allaby M. The concise Oxford Dictionary of earth sciences[M]. Beijing: Seismic Publishing House, 1998: 57. [5] 朱大岗, 赵希涛, 孟宪刚, 等.西藏纳木错晚更新世湖滩岩[J].地质论评, 2003, 49(4):432~439. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200304013.htmZHU Da-gang, ZHAO Xi-tao, MENG Xian-gang, et al. Late Pleistocene lacustrine-beach rock around the Nam Co in Xizang[J]. Geological Review, 2003, 49(4): 432~439. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200304013.htm [6] 朱大岗, 孟宪刚, 赵希涛, 等.西藏纳木错和藏北高原古大湖晚更新世以来的湖泊演化与气候变迁[J].中国地质, 2001, 31(3):269~277. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200403004.htmZHU Da-gang, MENG Xian-gang, ZHAO Xi-tao, et al. Evolution and climatic change of Nam Co of Tibet and an ancient large lake in the northern Tibetan Plateau since the late Pleistocene[J]. Geology in China, 2001, 31(3): 269~277. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200403004.htm [7] 赵希涛, 朱大岗, 严富华, 等.西藏纳木错末次间冰期以来的气候变迁与湖面变化[J].第四纪研究, 2003, 23(1):41~52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200301004.htmZHAO Xi-tao, ZHU Da-gang, YAN Fu-hua, et al. Climatic change and lake-level variation of NAM CO, Xizang since the last interglacial state[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2003, 23(1): 41~52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200301004.htm [8] Given R K, WIL Kinson B H. Kinetic control of morphology, composition, and mineralogy of abiotic sedimentary carbonates[J]. Sediment Petrol, 1985, 55(1): 109~119. [9] Robbert L F. The natural history of crystalline calcium carbonate: Effect of magnesium content and salinity[J]. J Sediment Petrol, 1974, 44(1): 40~53. [10] 赵希涛, 沙庆安, 冯文科.海南岛全新世海滩岩[J].地质科学, 1978, (2):163~173. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB198603010.htmZHAO Xi-tao, SHA Qing-an, PENG Wen-ke. Holocene beach rocks at Hainan Island[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1978, (2): 163~173. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB198603010.htm [11] 胡东生.现代沉积环境中形成的海滩岩、湖滩岩、河滩岩[J].青海环境, 1991, 1(1):34~38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHHJ199101010.htmHU Dong-sheng. The beach rock, lake beach rock, river beach rock formed in the modern sedimentary environment[J]. Journal of Qinghai Environment, 1991, 1(1): 34~38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHHJ199101010.htm [12] 李永春.闽南海滩岩与青海湖湖滩岩的比较研究[J].泉州师范学院学报:自然科学版, 2003, 21(4):43~47. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QZXB200304010.htmLI Yong-chun. Comparing research the Bbeachrocks in the south of Fujian Province with that in Qinghai Lake[J]. Journal of Quanzhou Normal University, 2003, 21(4): 43~47. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QZXB200304010.htm [13] 朱大岗, 赵希涛, 孟宪刚, 等.西藏纳木错第四纪湖泊沉积与湖成地貌——兼论藏北高原古大湖问题[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2003, 33(2):156~161. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200302009.htmZHU Da-gang, ZHAO Xi-tao, MENG Xian-gang, et al. On the Quaternary lacustrine deposits and the lacustrine landform of NAM CO, Xizang (Tibet) [J]. Journal of JiLin University: Earth Science Edition, 2003, 33(2): 156~161. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200302009.htm [14] 马志邦, 赵希涛, 朱大岗, 等.西藏纳木错湖相沉积的铀系年代学研究[J].地球学报, 2002, 23(4):311~316. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200204004.htmMA Zhi-bang, ZHAO Xi-tao, ZHU Da-gang et al. U-series chronology of lacustrine deposits from the Nam Co Lake, north Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Geosicientia Sinica, 2002, 23(4): 311~316. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200204004.htm [15] 黄金森, 朱袁智, 沙庆安.西沙群岛现代海滩岩岩石学初见[J].地质科学, 1978, 4:358~363. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX197804005.htmHUANG Jin-sen, ZHU Yuan-zhi, SHA Qing-an. Preliminary study of petrology on recent beach rocks in the Xisha Islands, Guangdong Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1978, 4: 358~363. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX197804005.htm [16] Beier J A. Diagenesis of Quaternary Bahamian beachrock: Petrographic and isotopic evidence[J]. Sediment Petrol, 1985, 55: 755~761. doi: 10.1007%2F1-4020-3880-1_44.pdf [17] Calvet F, Cabrer M C, Carracedo J C. Beachrocks from the island of La Palma (Canary Islands, Spain)[J]. Mar Geol, 2003, 197: 75~93. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00090-2 [18] Gischler E, Lomando A J. Holocene cemented beach deposits in Belize[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1997, 110: 277~297. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(96)00088-7 [19] Spurgeon D, Davisa J R A, Shinn E A. Formation of beachrocks at Siesta Key, Florida and its influence on barrier island development[J]. Mar Geol, 2003, 200: 19~29. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00162-2 [20] 孙金龙, 徐辉龙.中国的海滩岩研究与进展[J].热带海洋学报, 2009, 28(2):103~108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDHY200902017.htmSUN Jin-long, XU Hui-long. Advances of beach rock research in China[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2009, 28(2): 103~108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDHY200902017.htm [21] Imbrie J, Hays J G, Martinson D S, et al. The orbital theory of Pleistocene climate: Support from a revesed chronology of the marine δ18O record[C]//Berger A, Imbrie J, Hays J G, et al. Milankovich and Climate. Dordrecht (Holland): Reidel Publish Company, 1984: 269~305. [22] Antje H L V. Global distribution of centennial-scale records for Marine Isotope Stage (MIS) 3: A data base[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2002, 21(10): 1185~1212. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00139-1 [23] 王有清, 姚檀栋.冰芯记录中末次间冰期冰期旋回气候突变事件的研究进展[J].冰川冻土, 2002, 24(5):550~558. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT200205016.htmWANG You-qing, YAO Tan-dong. Progresses in the studies of abrupt climatic change events recorded in ice cores during the Last Glacial-Interglacial Cycle[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geoctryology, 2002, 24(5): 550~558. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT200205016.htm [24] 陈一萌, 饶志国, 张家武, 等.中国黄土高原西部马兰黄土记录的MIS3气候特征与全球气候记录的对比研究[J].第四纪研究, 2004, 24(3):359~365. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200403017.htmCHEN Yi-meng, RAO Zhi-guo, ZHANG Jia-wu, et al. Comparative study of MIS3 climatic features recorded in Malan Loess in the western part of the loess plateau and global records[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2004, 24(3): 359~365. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200403017.htm [25] 李世杰, 张宏亮, 施雅风, 等.青藏高原甜水海盆地MIS3阶段湖泊沉积与环境变化[J].第四纪研究, 2008, 28(1):122~131. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200801014.htmLI Shi-jie, ZHANG Hong-liang, SHI Ya-feng, et al. A high resolution MIS3 environmental change record from lacustrine deposit of Tianshuihai lake, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2008, 28(1): 122~131. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200801014.htm [26] 施雅风, 姚檀栋.中低纬度MIS3b(54~44 ka BP)冷期与冰川前进[J].冰川冻土, 2002, 24(1):1~9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT200201000.htmSHI Ya-feng, YAO Tan-dong. MIS3b (54~44 ka BP) cold period and glacial advance in middle and low latitudes [J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2002, 24(1): 1~9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT200201000.htm [27] 朱芸, 赵志军, 陈晔, 等.神农架泥炭记录的MIS3阶段环境变化及千年尺度气候波动[J].第四纪研究, 2013, 33(1):155~166. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201301021.htmZHU Yun, ZHAO Zhi-jun, CHEN Ye, et al. Record of environmental and millennial scale climatic changes during MIS3 by peat at Shennongjia[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33(1): 155~166. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201301021.htm -





 下载:
下载: