METALLOGENIC MODEL OF THE XIANGSHAN URANIUM ORE FIELD, JIANGXI PROVINCE
-
摘要: 本文在阐述相山矿田区域地质背景和成矿特征的基础上, 分析了成矿物质来源、成矿溶液来源及成矿物质迁移途径, 建立了相山矿田铀成矿模式。认为相山矿田铀成矿是受区域地质背景控制的特定时空域内的客观产物, 区域富铀地层是成矿的物质基础, 成矿溶液源自岩浆水和混入的雨水, 岩浆及期后热液是铀迁移的载体。铀成矿模式强调了火山岩成岩过程是成矿物质的富集过程, 火山岩浆期后成矿热液系统演化孕育了相山火山盆地50Ma的成矿过程, 流体降温、浓缩、混合等成矿机制的耦合, 促使了铀沉淀、成矿。Abstract: The authors studied the regional geological setting and metallogenic characteristics of the Xiangshan ore field and analyzed the sources of ore substances and ore fluids and channels for transport of ore substances, and on that basis, they constructed a uranium metallogenic model for the Xiangshan ore field. Uranium metallogenesis of the Xiangshan ore field took place in a specific temporal-spatial domain controlled by the regional geological setting; regional uranium-rich strata provided substances for metallogenesis; and ore fluids derived from magmatic water, mixed meteoric water, magma and postmagmatic hydrothermal fluids were carriers of uranium transport. The uranium metallogenic model emphasizes that the formation process of volcanic rocks was a process of ore substance concentration. The evolution of the volcanic postmagmatic hydrothermal ore system gave birth to ore-forming processes with a time span of 50 Ma in the Xiangshan volcanic basin. The coupling of metallogenic mechanisms such as temperature decline, concentration and mixing of fluids promoted uranium precipitation and ore formation.
-
前人在相山矿田业已提出了“双混合”成矿模式[1]、古水热系统排泄区成矿模式[2]、碱交代作用成矿模式[3]等, 可见, 不同的研究者对相山矿田成矿模式有着诸多不同的认识。成矿模式是对同一类(或相似的)矿床的地质、构造、地球物理、地球化学和其他基本特征进行概括, 是反映对矿床成矿规律的认识。为此, 本文根据相山矿田区域地质背景和成矿特征, 结合成矿物质来源、成矿溶液来源、成矿物质迁移、富集及矿质沉淀机理综合分析, 对相山铀矿田成矿模式进行探讨。
1. 区域地质背景及矿田铀成矿特征
1.1 区域地质背景
江西省相山矿田位于华南铀成矿省北部赣杭构造火山岩铀成矿带的南西端, 受制于相山大型塌陷式火山盆地。赣杭构造带的大地构造位置处于扬子板块与华南板块的交接部位, 它经历了长期复杂的地质发展历史, 构造运动和岩浆活动频繁, 尤以中生代强烈的火山活动最为显著。燕山中期(晚侏罗世)强烈挤压运动导致大规模的火山活动, 形成赣杭火山岩带; 燕山晚期(白垩纪)火山活动减弱并向东迁移, 区域构造环境由挤压转为拉张[4, 5], 这一时期在赣杭构造火山岩带发生了高强度、大规模、短时限的铀成矿作用, 形成了相山、盛源、大洲铀矿田及数十个铀矿床, 相山铀矿田是其典型代表。
相山火山盆地基底地层为南华系-震旦系浅变质岩, 岩性以千枚岩、片岩为主; 下石炭统华山岭组砂岩及上三叠统安源组煤系仅在火山盆地东侧出露。盖层为一套上侏罗统火山岩系及出露于火山盆地西侧的白垩纪红层, 火山岩系由酸性、中酸性火山熔岩、火山碎屑岩及少量正常沉积夹层构成, 总厚度大于2000m, 分为打鼓顶组(J3d)和鹅湖岭组(J3e), 每组的特点总体是由沉积到爆发再到喷溢式侵出, 由此构成一个大的火山喷发旋回, 下部打鼓顶组由砂砾岩、砂岩、熔结凝灰岩、流纹英安岩等组成, 上部鹅湖岭组由砂砾岩、晶玻屑凝灰岩和巨厚层碎斑熔岩组成。大规模火山活动期后次火山岩侵入, 以不规则的弧形和半环形围绕盆缘的北、东、南部出露, 岩性主要为花岗斑岩。
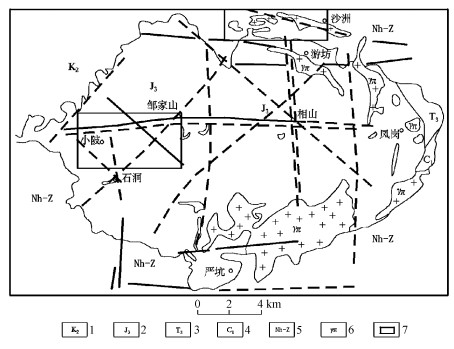
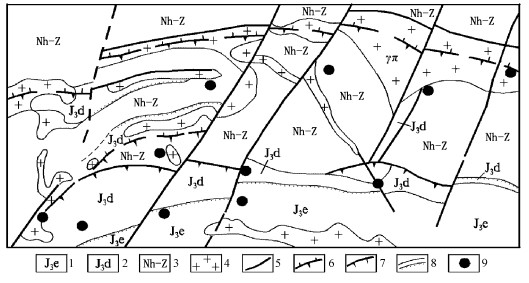
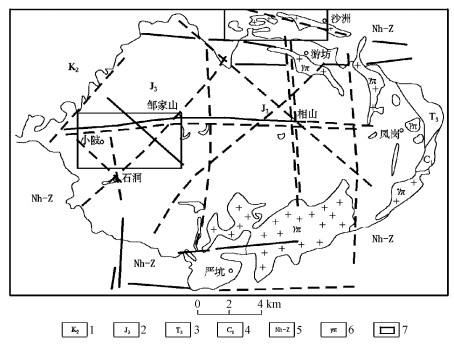
据相山火山盆地重力资料多高度上延处理及遥感TM数据增强处理结果[6], 火山盆地基底构造有EW、SN、NE、NW向四组(图 1)。在重力资料各上延高度, EW向构造重力场信息均明显; 当上延高度为5km时, SN向构造及西部邹家山-石洞NE向构造重力信息存在, 但大多数NE、NW向构造的重力信息已不明显。由此可见, EW向构造为相山火盆基底主构造线, SN向构造次之。
相山火山盆地盖层构造表现为以NE向为主导, NW向次之的线性断裂和火山塌陷环状断裂的构造格局。线性断裂构造多是基底断裂的继承和发展, 火山作用过程中岩浆活动和重力等作用下产生的火山塌陷构造也往往利用、迁就基底构造。
1.2 矿田铀成矿特征
1.2.1 铀矿化空间分布
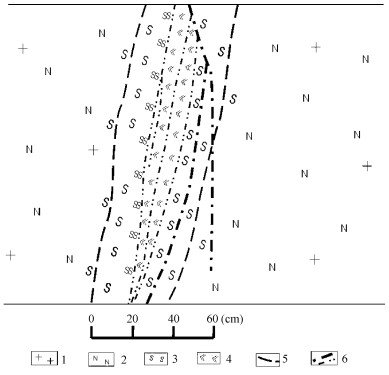
相山火山盆地内业已探明的铀矿床, 在平面上呈两条东西向矿集带形式产于火盆的西部和北部, EW向基底构造与矿集带空间产出相关联(图 1)。西部铀矿床较集中产出于长约7km、宽约3.5km的矿集带内, EW向、NE向、NW向、近SN向构造及火山塌陷构造分别或复合控制矿床定位, 火山岩是主要赋矿岩性, 往往被称为火山岩型铀矿床; 北部的铀矿床相对集中产出于长约6.5km, 宽约1.5km的矿集带内, 矿床多定位于NE向、EW向构造、推覆构造和环状火山塌陷构造复合部位(图 2), 北部多数矿床赋存于次火山岩(花岗斑岩)及其内外接触带中, 习惯上称为次火山岩型铀矿床。铀矿体的空间产出受低级别、低序次的断裂或裂隙密集带控制, 矿体形态以脉状为主, 次为透镜状或似层状。
相山矿田绝大多数矿床的矿化垂深为200 ~ 400m, 少数及个别矿床达600m和1100m, 这仅是目前勘查深度内统计结果的反映。至于铀矿化与岩性间的关系, 事实上, 相山矿田铀矿化对岩性并无绝对的选择性(表 1)。
表 1 相山矿田各类岩石中铀矿平均品位及其资源量占探明资源量的份额Table 1. Average uranium grades and percentages of uranium resources in various types of rocks in the total verified resources of the Xiangshan ore field
据上, 相山矿田铀矿化空间分布特征, 是现有勘探深度内及勘探对象结果的客观反映, 铀矿化的空间分布是成矿作用过程中各种因素相互作用导致的一种“终态”客观实体。
1.2.2 围岩蚀变
相山矿田围岩蚀变具多阶段作用和空间叠加的特点[7]。
成矿前蚀变可分为碱性蚀变和酸性蚀变两种, 前者以钠长石化为代表, 发育于矿田的北部和东部, 花岗斑岩钠长石化极为强烈, 是自变质作用的结果; 后者以水云母化为代表, 发育于矿田西部, 沿火山沿火山塌陷构造、断裂构造可形成宽达几十米至数百米的蚀变带。
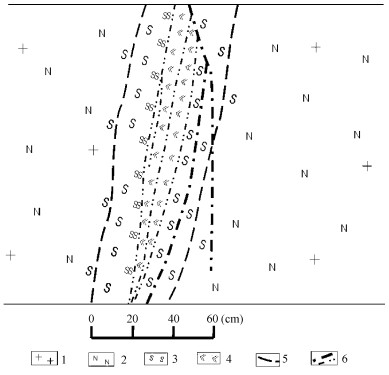
成矿期蚀变可分为早、晚两个阶段, 早阶段以赤铁矿化为主, 并伴随有钠长石化、绿泥石化、水云母化和碳酸盐化; 晚阶段以萤石化、水云母化、绿泥石化为主, 并伴随有碳酸盐化、黄铁矿化。成矿期蚀变具分带性(图 3), 蚀变中心一般为萤石化、水云母化及绿泥石化, 其旁侧为早阶段赤铁矿化、水云母化、绿泥石化、碳酸盐化, 最外侧为成矿前的钠长石化(矿田北、东部)和水云母化(矿田西部)。
矿后期蚀变主要为碳酸盐化、硅化、萤石化等, 呈脉状充填于裂隙之中。
1.2.3 矿石类型
矿田内铀主要以沥青铀矿、钛铀矿、铀钍石、铀石等矿物形式存在矿石中, 其中沥青铀矿多呈斑点状、发丝状、肾状及半圆形胶状体充填在矿石内, 常见有黄铁矿、辉钼矿、方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿等金属矿物与铀矿物相伴生, 为中低温热液型铀矿床①。
① 张金带, 戴民主, 邵飞, 等.华东铀矿地质志.2005
据矿田内与成矿关系最密切、最明显的围岩蚀变对矿石类型进行划分, 矿田内主要铀矿石类型有:铀-赤铁矿型、铀—绿泥石型、铀—萤石型和铀—硫化物型(表 2)。尽管各矿床一般有几种矿石类型, 但主要类型为1 ~ 2种, 值得指出的是, 各矿床中均见有铀—赤铁矿型矿石。矿田西部铀矿床的矿石类型多以铀—萤石型和铀—硫化物型为主, 而北部铀矿床以铀—赤铁矿型和铀—绿泥石型矿石为主。
表 2 相山铀矿田矿石类型及其特征Table 2. Uranium ore types in the Xiangshan uranium ore field and their characteristics
1.2.4 成矿流体性质
不同矿石类型表明其成矿流体性质不同。相山矿田北部与铀成矿有关的流体为富钠碱性热液, 形成碱交代型铀矿化; 矿田西部与铀成矿有关的流体为富氟酸性热液, 形成萤石-水云母型铀矿化②。
② 陈肇博, 等.相山矿田联合科研报告.1980
碱交代型铀矿化, 成矿时成矿流体的压力值约为5 ×107Pa、成矿温度约为200 ℃、盐度为18.36 ~ 31.03wt.%NaCl; 萤石—水云母型铀矿化成矿流体压力值约为2 ×107Pa、成矿温度约为150 ℃、盐度为21.57 ~ 22.09wt.%NaCl[2, 8]。
1.2.5 成矿年龄
据U-Pb同位素资料, 相山矿田铀—赤铁矿型矿石同位素年龄主要介于120 ~ 140Ma之间, 铀—绿泥石型矿石同位素年龄集中于105 ~ 125Ma; 铀-萤石型矿石的成矿年龄为90 ~ 110Ma (表 3)。
表 3 相山矿田部分矿床铀矿石同位素年龄Table 3. Isotopic age data for uranium ore from part of deposits in the Xiangshan ore field
相山矿田不同类型矿石的同位素年龄相对连续, 三种类型矿石各自成矿延续时间约为20Ma, 并且彼此间有5Ma的重叠时间域, 矿田铀成矿累计时间跨度约为50Ma。据此, 矿田铀成矿作用自火山岩浆大规模喷溢和侵出之后, 伴随着次火山岩侵入开始发生。在时间尺度上, 火山岩成岩成矿作用具连续性; 在空间尺度上, 钠交代型铀矿化与火盆北部次火山岩相关联, 萤石-水云母化型铀矿化主要产于西部火山岩中。由此可见, 相山矿田不同阶段高强度成矿作用相应发生于某一时空域内。
2. 成矿物质来源
相山矿田成矿物质来源始终存在争议, 以往的研究多侧重于相山火山盆地内岩、矿石分析数据的推认。如前所述, 相山矿田火山岩成岩成矿是相对连续的时间过程, 可以认为相山火山盆地仅是成矿物质的汇聚区, 应从更大时空尺度去寻找成矿物质来源, 不应将汇聚区内成矿物质迁移及再分配作为分析成矿物质来源的途径。基于此, 本文从区域铀物质时空分布特征对铀源进行判定。
华南地区自元古宙到中生代沉积、变质岩铀含量分析结果表明, 早寒武世地层铀含量高达16.53 ×10-6 ~ 91.56 ×10-6, 而其他时代地层铀含量一般不超过7 ×10-6[9]。区域地层现代实测的铀含量经过了长期地质和地球化学作用改造, 若改造的结果导致高铀含量地层中铀大量迁出、贫化而接近区域平均水平, 就不可能为其后的铀成矿提供物质来源。早寒武世地层中的铀现在仍表现为较高值, 显然其可构成华南地区区域铀源层。
我国华南地区已探明了13个花岗岩型和火山岩型铀矿田, 其中有4个火山岩型和8个花岗岩型铀矿田的基底地层及岩体外围地层分布有早寒武世区域铀源层, 这种关联现象支持区域铀源层可能为铀成矿提供物质来源。尽管相山火山盆地基底地层中目前缺失早寒武世区域铀源层, 但同属于赣杭火山岩带、位于相山矿田北东方向约150km的盛源火山岩型铀矿田基底地层中有早寒武世富铀地层出露; 位于相山矿田南部约120km、与相山矿田同属大王山—于山成矿带的桃山花岗岩型铀矿田岩体外围广泛分布早寒武世富铀地层, 其铀含量为6.36 ×10-6 ~ 23.0 ×10-6①。据古地理分析[10], 寒武纪时, 包括盛源、相山、桃山等地在内的江西中南部地区古地理环境相同, 寒武纪早世早期沉积了深灰、灰黑色的岩屑砂岩、玻屑凝灰质砂岩、板岩等, 且构成韵律式的复理石建造, 富含磷、钒、铀等元素; 寒武纪早世晚期后, 江西及邻区地处华南海盆, 接受了泥沙质碎屑及碳酸盐沉积。
① 核工业270研究所.华东铀成矿规律及成矿预测.1995
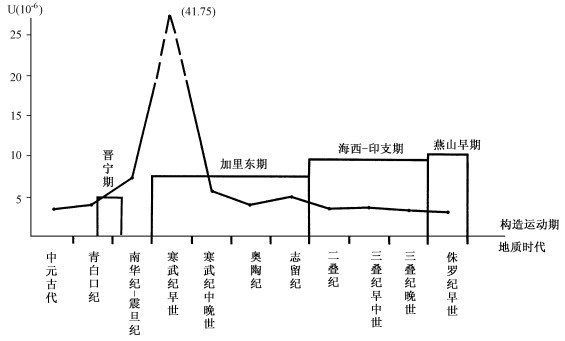
赣杭火山岩带内中酸性火山岩铀平均含量为4.8 ×10-6, 而相山地区、大洲地区火山岩铀平均含量更是高达7.55 ×10-6及8.98 ×10-6②, 其铀含量是地壳平均值的约1.6 ~ 3.0倍, 反映了火山岩的物质来源中混熔了富铀地层, 富铀地层中的铀进入了重熔岩浆。华南地区部分花岗岩体铀含量在时间上的变化有较明显的规律性, 从晋宁期到燕山早期铀含量逐渐增高, 也表明了早寒武世区域富铀层形成之后并被混熔导致花岗岩体的铀含量增高(图 4)。
② 张金带、戴民主、邵飞, 等.华东铀矿地质志.2005
 图 4 华南地区不同时代部分地层及不同构造运动期花岗岩铀含量分布示意图(据章邦桐等, 1990[9]及核工业270研究所1993、1995年资料整理)Figure 4. Distribution of uranium contents in some strata of different ages and granites formed in different tectonic stages in South China
图 4 华南地区不同时代部分地层及不同构造运动期花岗岩铀含量分布示意图(据章邦桐等, 1990[9]及核工业270研究所1993、1995年资料整理)Figure 4. Distribution of uranium contents in some strata of different ages and granites formed in different tectonic stages in South China早寒武世区域铀源层为相山矿田铀成矿提供了物质来源, 火山活动使得相山火山盆地构成了成矿物质的汇聚区, 伴随着火山活动成矿物质在汇聚区发生了迁移和再分配, 并最终发生了铀成矿作用。
3. 成矿溶液来源
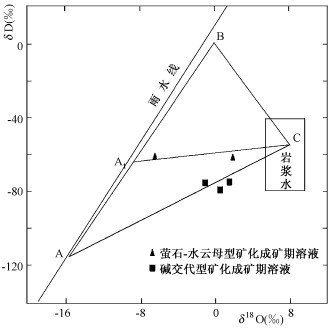
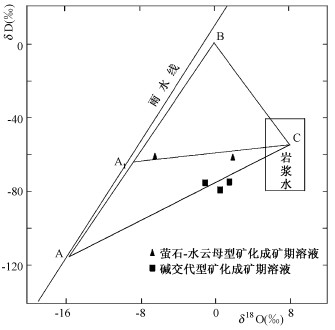
相山矿田不同矿化类型成矿溶液的氢、氧同位素组成不同。碱交代型铀矿化(横涧矿床)成矿溶液的δD值约为-80 ‰, δ18O值介于-1.42 ‰~ +1.24 ‰之间; 萤石-水云母型铀矿化(邹家山矿床)成矿溶液的δD值也较均一, 约为-60 ‰, δ18O值范围为-6.5 ‰~+1.83 ‰。由此可见, 不同矿化类型成矿溶液来源可能不同。
由图 5可以看出, 不同矿化类型成矿溶液的氢、氧同位素组成分别投影于岩浆水的平均氢、氧同位素组成端员(C)和雨水端员(A、A1)的连线上, 表明成矿溶液是岩浆水和雨水的混合[11, 12]。
高盐度、成矿温度和压力相对较高的碱交代型铀矿化, 其成矿溶液雨水端员的氢、氧同位素组成为不同地质时代雨水的平均同位素组成(A), 推认其成矿溶液中雨水成份来源于熔融地层中所含的元古宙、古生代及中生代大气降水, 它们随岩石熔融一道进入岩浆, 导致雨水的氢、氧同位素组成表现为不同地质时代的平均值。成矿温、压值相对较低, 矿岩时差达20 ~ 50Ma的萤石-水云母型矿化, 其成矿溶液中雨水成份表现为成矿期(中生代)大气降水的混入, 但这并不意味着外生水在地形势驱动下直接与高温、高压的岩浆水混合(本文不讨论中生代降水进入岩浆水的运动方式)。
4. 成矿物质的迁移
相山火山盆地岩、矿石稀土元素地球化学特征表明, 盖层火山岩系与基底地层岩石稀土配分模式类似, 且火山岩与次火山岩的稀土配分曲线具彼此平行一致的特征, 显示了火山岩与次火山岩具同源性, 同时也说明火山岩系的形成与陆壳物质具成生联系。火山岩与次火山岩Eu负异常明显, 火山岩浆在通向地表途中受到高度分馏的结晶作用, 由此导致陆壳富铀地层中的铀经熔融作用汇聚于岩浆之中后向岩浆演化晚期热液中迁移; 此外, 岩、矿石微量元素特征及其对比研究, 表明基底片岩及流纹英安岩与岩浆期后热液的相互作用, 导致了岩石中的铀向液相迁移①。
① 邵飞.水—岩相互作用及其与铀成矿关系研究:以相山矿田为例.中国地质大学博士学位论文, 2007
相山火山岩原始岩浆铀含量为10 ×10-6 ~ 13 ×10-6, 而火山岩基质中铀含量仅为2.9 × 10-6 ~ 4.0 ×10-6②, 这也说明有大量的铀在岩浆演化过程中转移到气液中。
② 刘小于, 大陆中酸性火山岩的成因演化与铀成矿作用.核工业北京地质研究院博士学位论文, 1991
总之, 富铀地层的混溶, 不仅使得相山火山盆地成为成矿物质的汇聚区, 也为相山矿田的形成奠定了成矿物质基础。火山岩浆及期后热液是成矿物质迁移的载体, 火山活动过程中成矿物质在汇聚区发生了再迁移及再分配, 最终促使了成矿物质的富集、成矿。
5. 铀成矿模式
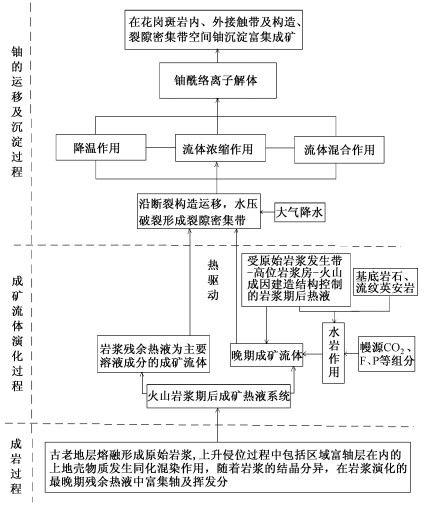
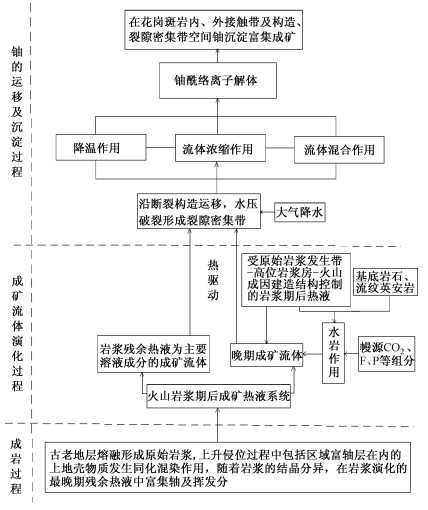
综上所述, 建立图 6所示的相山矿田铀成矿模式, 并着重说明如下:
(1) 相山中生代火山岩浆主要来自地壳物质的部分熔融, 但不排除有一部分源于上地幔[8], 相山晚侏罗世壳内岩浆房的形成深度约为10 ~ 14km①。由此可见, 源于壳-幔过渡带的原始岩浆沿通道上升到高位岩浆房, 继而发生爆发、喷溢及侵入作用, 岩浆上升侵位的成岩作用过程中, 伴随着发生包括富铀地层在内的陆壳物质混染及岩浆结晶分异作用, 即相山火山岩的成岩过程是伴随着成矿物质的富集过程。
① 刘小于.大陆中酸性火山岩的成因演化与铀成矿作用.核工业北京地质研究院博士学位论文, 1991
(2) 火山岩浆期后热液系统的演化过程也是成矿流体演化过程。由于岩浆分异, 岩浆期后热液富含成矿物质-铀; 受原始岩浆发生带-高位岩浆房-火山成因建造垂向结构控制的岩浆期后汽水热液与岩石相互作用, 促使成矿流体演化, 同时由于幔源CO2等组分作用②, 有利于岩石中铀向溶液转移。岩浆期后成矿热液系统持续运转了50Ma, 孕育了相山火山盆地50Ma的成矿过程, 尔后由于区域构造环境变化, 西太平洋俯冲带向洋迁移, 岩浆期后热液系统“能量”供给不足, 铀成矿作用渐趋终止。
② 胡瑞忠, 等.华南中生代以来岩石圈伸展及其与铀成矿关系研究的若干问题.铀矿地质博士论坛论文集, 2006
(3) 含元古宙、古生代及中生代雨水组份的岩浆期后热液, 在热驱动下向花岗斑岩体外侧运移; 受原始岩浆发生带-高位岩浆房-火山成因建造结构系统控制的岩浆期后汽水热液, 在热驱动下, 朝减压方向运移, 运移过程中有中生代降水混入, 由于水力压裂可能形成裂隙密集带。在流体降温、浓缩及混合等成矿机制耦合作用下, 成矿流体中铀酰离子解体、沉淀、成矿, 花岗斑岩体内外接触带、成矿流体运移的断裂构造及其旁侧裂隙密集带为铀成矿提供了空间场所。
-
图 4 华南地区不同时代部分地层及不同构造运动期花岗岩铀含量分布示意图
(据章邦桐等, 1990[9]及核工业270研究所1993、1995年资料整理)
Figure 4. Distribution of uranium contents in some strata of different ages and granites formed in different tectonic stages in South China
表 1 相山矿田各类岩石中铀矿平均品位及其资源量占探明资源量的份额
Table 1. Average uranium grades and percentages of uranium resources in various types of rocks in the total verified resources of the Xiangshan ore field
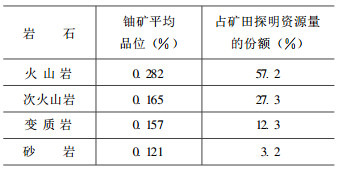
表 2 相山铀矿田矿石类型及其特征
Table 2. Uranium ore types in the Xiangshan uranium ore field and their characteristics
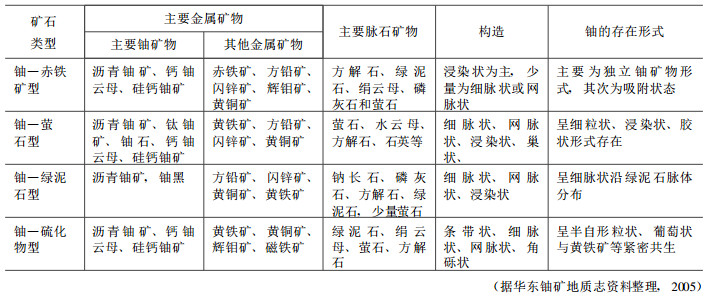
表 3 相山矿田部分矿床铀矿石同位素年龄
Table 3. Isotopic age data for uranium ore from part of deposits in the Xiangshan ore field
-
[1] Chen Zhaobo." Double mixing" genetic model of uranium deposits in volcanic rocks and relationship between China's Mesozoic veintype uranium deposits and Pacific plate tectonics, M etallogensis of Uranium[J].In:Proceedings of the 26th IGC, Geoinstitute, Beogard, 1981, 65~97. [2] 李学礼, 孙占学, 周文斌.古水热系统与铀成矿作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 2000. [3] 杜乐天.中国热液铀矿基本成矿规律和一般热液成矿学[M].北京:原子能出版社, 2001. [4] 张勤文, 黄怀曾.中国东部中、新生代构造-岩浆活化史[J].地质学报, 1982, 2:111~122. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000377655 [5] 王德滋, 杜杨松.东南沿海地区中生代火山-侵入杂岩形成的构造背景[J].矿物岩石地球化学通讯, 1990, 3:186 ~188. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000002008654 [6] 邱爱金.江西相山铀矿田东西向隐伏构造的发现及其地质意义[J].地质论评, 2001, 47 (6):637 ~641. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2001.06.012 [7] 黄志章, 李秀珍, 蔡根庆.热液铀矿床蚀变场及蚀变类型[M].北京:原子能出版社, 1999. [8] 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 张成, 等.相山中生代含铀火山杂岩岩石地球化学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1992. [9] 章邦桐, 张祖还, 倪奇生.内生铀矿床及其研究方法[M].北京:原子能出版社, 1990. [10] 江西省地质矿产局.江西省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1984. [11] 沈渭洲.同位素地质学教程[M].北京:原子能出版社, 1997. [12] 张理刚, 陈振胜, 刘敬秀, 等.两阶段水-岩同位素交换理论及其勘查应用[M].北京:地质出版社, 1995. -






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载: