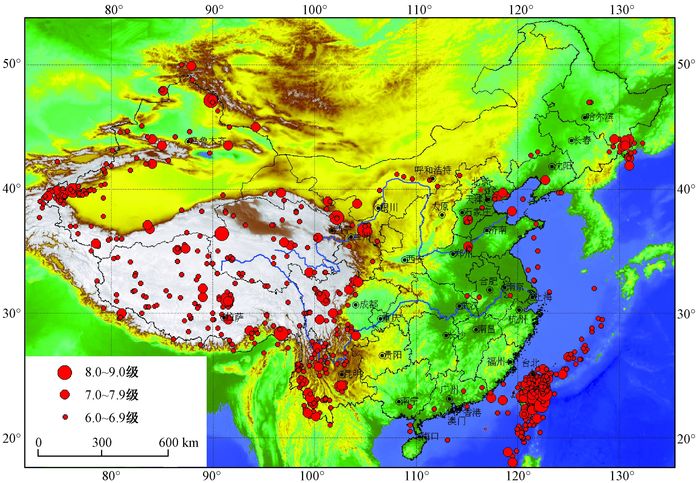
NEW GENERATION 1:5000000 MAP OF REGION STABILITY EVALUATION IN CHINA
-
摘要: 新一代中国区域稳定性评价图(1:500万)是利用近年来我国在新构造运动、地质灾害等方面的最新研究成果, 在综合分析中国新构造运动基本规律的基础上, 利用现代构造运动理论, 进行区域稳定性评价, 编制全国范围的区域稳定性评价图, 进一步完善我国的基础地质信息, 提高我国在区域稳定性评价研究方面的研究水平, 为国家重大工程建设、区域城市群建设、西部大开发战略以及振兴东北老工业基地和政府的宏观决策、国民经济的可持续发展服务。Abstract: Based on the latest research results of neotectonic movements and geological hazards, a new 1:5000000 map of region stability evaluation in China is compiled which uses the theory of modern tectonic movement to evaluate region stability in the comprehensive analysis of basic laws of China's neotectonic movement. The new map aims to further perfect our basic geological data and improve the level of region stability evaluation research, in the service of the construction of major national projects and the regional city group, the western development strategy and the promotion of the northeastern old industrial base, the macroscopic decision of government and the sustainable development of national economy.
-
表 1 中国区域地壳稳定性综合评价等级和指标体系
Table 1. Comprehensive evaluation grade and indicators system of region crustal stability in China
评价指标
(权重)评价等级和评价指标分值 稳定 基本稳定 次不稳定 不稳定 7.5 6 4.5 3 50年超越概率10%地震动峰值加速度(0.2) <0.05 g 0.05~0.15 g 0.20~0.30 g ≥0.40 g 活动断裂(0.2) 远离活动断裂带,无活动断裂通过 有新近纪断裂通过,但断裂在全新世活动不明显 有活动断裂通过,但断裂规模较小、活动较弱 位于大的活动断裂带上或活动断裂带交汇处,断裂活动强烈 地应力(最大主应力值)(0.1) ≤5.0 MPa 5.0~15.0 MPa 15.0~22.5 MPa ≥22.5 MPa 岩石圈结构(0.2) 地壳、岩石圈各界面平缓,无低速层和高导层,布格重力异常梯度值较小。布格重力水平导数模量小于1 mGal/km 莫霍面和上地幔隆起较缓,无低速层和高导层。布格重力异常梯度值中等,布格重力水平导数模量1~2 mGal/km 莫霍面和上地幔隆起,发育低速层或高导层,但处于低速层或高导层的中部。布格重力异常梯度值较大,布格重力水平导数模量2~3 mGal/km 处于莫霍面和上地幔隆起的梯度带、低速层和高导层的梯度带上或岩石圈各界面的错断带上。布格重力异常梯度值大,布格重力水平导数模量大于3 mGal/km 地面垂直运动速率(0.1) 0~2 mm/a 2~5 mm/a 5~8 mm/a >8 mm/a 地质灾害(0.1) 单元内无地质灾害分布,也不在地质灾害影响区 地貌基本有利,物理地质作用不太明显 发育小型地质灾害,地貌反差明显,河流冲刷、切割强烈,松散堆积物发育 发育中—大型崩塌、滑坡、泥石流、地裂缝、坍塌等地质灾害 场地工程地质特性(0.1) 场地地质体为各种坚硬的基岩 场地地质体为各种半胶结的岩类和碎裂岩类 场地地质体为各种松散的碎石土、中粗砂砾、黏土(包括黄土) 场地地质体为各类特殊土,包括软黏土、饱和软黏土、松散粉细砂、饱和粉细砂、淤泥、淤泥质土、人工填土等 表 2 区域稳定性综合评价分级标准
Table 2. Comprehensive evaluation classification standard of regional stability
区域稳定性级别 代码 指数范围 评价结果/% 稳定 1 0~0.2 23.6 基本稳定 2 0.2~0.5 44.5 较不稳定 3 0.5~0.8 29.5 不稳定 4 0.8~1.0 2.4 -
[1] 李四光.论地震[M].北京:地质出版社, 1977.LI Si-guang. 1977. On the Earthquake[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. [2] 胡海涛, 殷跃平.区域地壳稳定性评价"安全岛"理论及方法[J].地学前缘, 1996, 3(1/2):57~68. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY601.008.htmHU Hai-tao, YIN Yue-ping. Theory and evaluation methods of regional crust stability "safety island"[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1996, 3(1/2): 57~68. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY601.008.htm [3] 李兴唐, 许兵.区域地壳稳定性研究理论与方法[M].北京:地质出版社, 1987.LI Xing-tang, XU Bing. Research theories and methods of regional crust stability[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. [4] 孙叶, 谭成轩, 李开善, 等. 区域地壳稳定性定量化评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998.SUN Ye, TAN Cheng-xuan, LI Kai-shan, SHAO Yun-hui, YE Ding-heng, ZUO Wen-zhi, ZHANG Hui-lan. 1998. Quantitative assessment and research of regional crustal stability[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. [5] 胡海涛.区域地壳稳定性评价的"安全岛"理论及方法[J].地质力学学报, 2001, 7(2):97~103. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY601.008.htmHU Hai-tao. The theory and methods of evaluation of regional crustal stability based on concept of "safe island"[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2001, 7(2): 97~103. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY601.008.htm [6] 杜建军, 马寅生, 谭成轩, 等. 京津地区区域地壳稳定性评价[J]. 地球学报, 2008, 29(4): 502~509. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200804013DU Jian-jun, MA Yin-sheng, TAN Cheng-xuan, GONG Ming-quan, SHI Wei. 2008. The evaluation of regional crustal stability in Beijing and Tianjin area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 29(4): 502~509. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200804013 [7] 廖椿庭, 吴满路, 张春山, 等. 青藏高原昆仑山和羊八井现今地应力测量及其工程意义[J]. 地球学报, 2002, 23(4): 353~357. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200204012LIAO Chun-ting, WU Man-lu, ZHANG Chun-shan, WU Gang. Recent ground stress measurement of the Kunlun Mountains and Yangbajing area in Qinghai-Tibet plateau and its engineering significance[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2002, 23(4): 353~357. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200204012 [8] 马寅生, 廖椿庭, 张业成, 等.黄河上游新构造活动与地质灾害风险评价[M].北京:地质出版社, 2003.MA Yin-sheng, LIAO Chun-ting, ZHANG Ye-cheng, et al. The neotectonic activity and the evaluation of geological hazards risk in the upper reaches of the Yellow River[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2003. [9] 吴满路, 张春山, 廖椿庭, 等. 风火山隧道地应力测量及工程稳定性分析[J]. 地球学报, 2005, 26(1): 71~74. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200501011WU Man-lu, ZHANG Chun-shan, LIAO Chun-ting, et al. Stress measurement and engineering stability analysis at Fenghuoshan tunnel[J]. 2005, 26(1): 71~74. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200501011 [10] 任纪舜, 王作勋, 陈炳蔚, 等.新一代中国大地构造图[J].中国区域地质, 1997, 16(3):225~230. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200301000.htmREN Ji-shun, WANG Zuo-xun, CHEN Bing-wei, et al. A new generation tectonic map of china[J]. Regional geology of china, 1997, 16(3): 225~230. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200301000.htm [11] 任纪舜.新一代中国大地构造图[J].地球学报, 2003, 24(1):1~2. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200301000.htmREN Ji-shun. A new generation tectonic map of china[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2003, 24(1): 1~2. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200301000.htm [12] GB 18306-2001, 中国地震动峰值加速度区划图(1: 400万)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2001.GB 18306-2001, China Earthquake Administration. Seismic peak ground acceleration zonation map of China (1:4000000)[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2001. [13] 叶定衡.中国及毗邻海区新构造图(1:500万)[M].北京:地质出版社, 1996.YE Ding-heng. The map of neotectonic in china and its adjacent sea area(1:5000000)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1996. [14] 邓起东, 冉勇康, 杨晓平, 等.中国活动构造图(1:400万)[M].北京:地震出版社, 2007.DENG Qi-dong, RAN Yong-kang, YANG Xiao-ping, et al. The map of activity tectonics in china (1:4000000)[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 2007. -





 下载:
下载: