GEOMATICS AND EARTH OBSERVATION SCIENCE (EOS) FOR DISASTER MANAGEMENT:AN OVERVIEW
-
摘要: 近年来地球空间信息学(Geomatics)和对地观测学(EOS)的迅速发展, 为灾难管理提供了强有力的支撑技术, 促进了灾难管理效率的提高。在简述地球空间信息学、对地观测学和灾难管理的基础上, 综述了地球空间信息学和对地观测学中多传感技术、高分辨率、多时相的卫星遥感系统的发展不仅满足了灾难管理需求数据的多源性、实时性, 而且提高了遥感影像解译精度和增强了对自然灾害的探测、识别能力; 认为日益完善的空间数据基础设施(SDI)和软件系统功能的增强, 将有利于灾难管理需求数据的可用性、可访问性和数据共享, 加强了灾难管理中海量数据管理、处理、分析和发布能力, 提高了预报和管理决策信息系统的可视化程度, 从而提高灾难管理各个环节的效率和效益。同时, 从技术的角度简述了当前地球空间信息学和对地观测技术在灾难管理应用中的局限性和存在的问题。Abstract: Based on an introduction of disaster management, geomatics and earth observation science (EOS), a discussion has been made on the utility of geomatics and EOS for natural disaster management.It is believed that the development in new techniques on sensors, high-resolution satellite remote sensing system can provides multiple source, timely and accurate spatial data on disaster management can improve the accuracy of satellite image interpretation and strengthen the capability of natural disaster detection and identification.The development in SDI and related techniques, as well as the strengthening function of software, not only drives the ongoing improved data availability, accessibility and data sharing, enhances data management, processing, analysis and dissemination capability, but also improve the quality and visualization of disaster forecasting and decision-making, hence increase efficiency and effectiveness at all levels of disaster management activities.In addition, their limitations and potential research challenges in the current geomatics and EOS for disaster management have been generally discussed.
-
近年来, 自然灾害的发生频率、规模、影响范围与危害程度的增长与加剧, 不仅导致大量了的人员伤亡和财产损失, 而且对社会经济、生态环境造成了长期的负面影响。例如, 2008年5月12日在我国四川省汶川发生的MS =8.0级地震导致了69226死亡, 374640受伤, 17923失踪(截止8月12日), 是建国以来最为严重的地震灾害之一, 给四川、甘肃、陕西等地区的房屋、财产、基础设施和生态环境等造成了严重破坏; 2004年12月印度洋地震与海啸夺走了283106人的生命; 2005年10月的巴基斯坦克什米尔地震导致了80361的伤亡; 2006年2月17日菲律宾南莱特省圣贝尔纳镇的特大滑坡、泥石流事件导致了1800人的死亡。这些重大自然灾害给国家和人民生命财产带来了不可估量的损失, 面对严峻的自然灾害, 国际社会和各国政府都采取了应对措施和国际合作, 其中灾难管理(Disaster management)是国际社会普遍采纳和政府间合作的重点内容。灾难管理是一项系统工程, 它包括对自然灾害的监测、预报、评估、防灾、抗灾、救灾、恢复、教育、保险与综合管理, 每一过程和环节都与空间的地理要素密切相关, 如灾难的时空分布、强度与频度、灾难发生地社会经济易损性及抗灾能力、灾难评估、灾难应急救助措施及预案等。灾难管理是建立在大量空间数据信息基础上的综合评估与决策, 空间数据信息的获取是灾难管理的基础和关键。本文在简述灾难管理、地球空间信息学和对地观测学的基础上, 综述地球空间信息学和对地观测学在灾难管理中的应用进展、技术支撑作用、局限性及发展趋势。
1. 灾难管理
由于自然灾害对社会经济的破坏性影响, 灾难管理成为国际社会广泛认可的一个包括减灾、防灾、应急和恢复四个环节的灾难管理过程, 它涉及到灾害事件发生前、后和期间各个阶段的管理需求。根据国际减灾战略(ISDR)的术语, 分别定义为减灾(Mitigation):采取结构性的工程措施或非结构性的方针政策、法规、教育, 宣传去限制或控制自然灾害、环境退化、人为或技术灾难对社会造成的负面影响; 防灾或抗灾(Preparedness):指的是为确保有效的灾害应急、抢险所采取的措施和活动, 包括及时有效的灾难早期监测、预警, 潜在危险区人员和财产的临时避险场所建设; 救济或应急、抢险(Relief Response):在灾难期间或灾后迅速提供帮助或干预灾害事件(抢险), 以确保灾民的生命和基本生活需求; 恢复(Recovery):在灾后所采取的行动和决策去恢复或提高受灾地区灾前的生活条件和基础设施, 同时鼓励和推动必需的工程措施和政策来降低潜在再次受灾的风险。
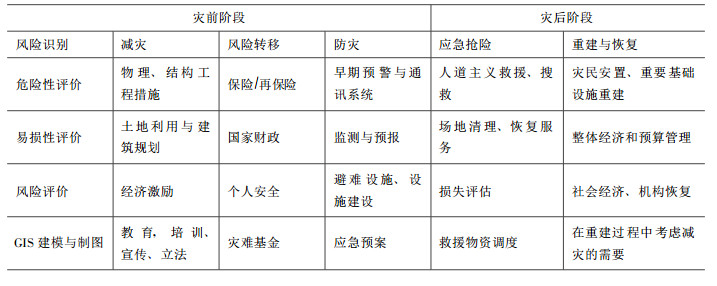
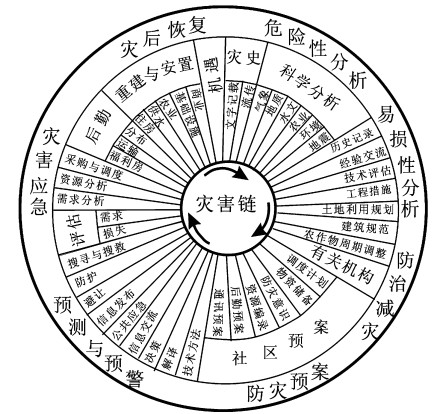
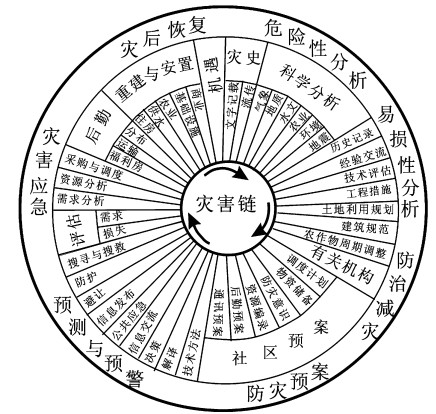
目前, 国际上对灾难管理有不同的具体环节和过程划分, 美国是从突发事件管理的角度来描述灾难管理的各个阶段(图 1), 它包括7个主要环节, 通过对灾难历史和科学的危险性、易损性分析来进行危险性和风险性区划, 以此来制定合理的减灾战略和防灾措施; 合理的防灾规划是建立在机构和社区的基础上, 可靠和实时的灾难预测和早期预警可以减少伤亡; 及时有效的应急抢险可以将灾难人员和财产损失最小化; 灾后恢复包括长期的灾后重建, 后勤保障和社会经济的恢复。欧洲从事灾难管理科学研究的学者, 如荷兰学者Van Westen等[1]将灾难管理的主要过程分为灾前风险识别、减灾、风险转移、防灾和灾后的应急抢险和重建恢复, 并将各个环节的主要构成细化(表 1), 认为风险识别是建立在危险性、易损性、风险评估及灾害地理信息系统建模和制图的基础上, 采取适宜的减灾工程措施, 合理的土地利用和建筑规划, 通过经济激励、教育、宣传和立法来减灾, 降低灾害风险; 以经济和社会、个人保险的手段来转移风险; 为更好地防灾、抗灾, 采取早期灾害监测预警、预报, 避难场所建设及抢险预案的编制以防灾害事件的发生; 灾后阶段主要有灾害应急、抢险、人道救援、场地清理和建筑破坏、损失评估、救灾物资的调度等; 灾后恢复包括基础设施的重建和社会经济活动的恢复。
2. 地球空间信息学与对地观测学
目前国际上, 对于地球空间信息学的表达为“Geomatics”一词, 国际标准化组织(ISO)给出的简明定义:“Geomatics是一个新的科学术语, 是指量测、分析、管理和显示空间数据的集成技术方法”, 对应的中文译名为“地球空间信息学”[2], 与之相同或相近的术语有“Geoinformatics”, “Geoinformation science”[1, 3], “geospatial technology”等, 这些术语都囊括了空间数据(Spatial data)、遥感(RS)、地理信息系统(GIS)、全球定位系统(GPS)技术, 反映了现代测绘科学、遥感、地理信息学等学科与现代计算机科学、信息科学相结合的多学科集成, 以满足对空间信息的要求[2]。1996年国际标准化组织给出的定义:地球空间信息学是采集、量测、分析、存储、管理、显示和应用空间数据的集成方法, 它所涵盖的学科范围包括(但不限于)地图学、控制测量、数字测图、大地测量、地理信息系统, 水文测量、土地信息管理、土地测量、矿藏调查和遥感。它的广泛应用和发展主要得益于:①美国政府对GPS信号限制的放宽, 使民用空间定位可以接收到更多的高精度信息; ②由于美国和俄罗斯政府对卫星影像的保密级别降低及高精度卫星的商业化运行, 使遍及全球的、达到军用高精度的卫星影像的民用化逐渐普及; ③具有友好界面、功能强大的地球空间信息软件系统和价格低、网络驱动的个人电脑系统的发展[3]。
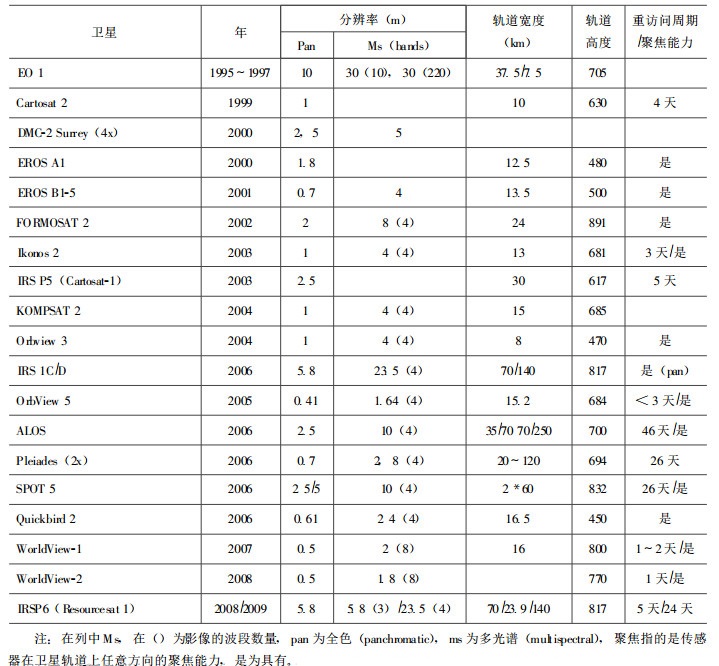
“EOS” (Earth Observation Science的英文缩写)中文为“对地观测学”, 是指从空间观测地球, 并将得到的数据和信息通过计算机网络以地理信息系统的形式存储、管理、分发、流通和应用的科学技术[4]。利用对地观测新技术, 不仅可以开展气象预报、资源勘探、环境监测、土地利用等工作, 还可以用于沙尘暴、台风、洪水、地震、火灾、滑坡和泥石流等自然灾害的预测、预报和防治。由于相关技术的进步和一些国家重大计划的成功, 如美国国家航空与航天局(NASA)开展的地球观测系统(EOS)计划, 对地观测技术步入了新的发展时期, 其重要标志是1999年底和2000年初新一代对地观测传感器, 如Terra卫星的发射上天, 以及现今在轨运行和规划的民用高分辨率卫星系统(表 2), 这些传感器针对当前地学研究和国土资源调查中对空间数据的实际需求, 以几天为周期, 重复获取全球地表高分辨率数据, 这对动态监测和合理规划国土资源意义重大。由这些传感器每天发回的海量数据, 将通过超级计算等手段, 定量模拟地球动态过程, 并把地球上的大气圈、水圈、岩石圈等自然营力和人类活动产生的影响作为整体进行研究, 将全球变化研究建立在长期的观测数据基础之上, 使全球变化研究水平得到了根本性提高。
表 2 现今和未来的民用光学高分辨率卫星系统(据瑞士地理信息中心)Table 2. Current and forthcoming civil optical high-resolution satellite system (SwissTopo)
3. 地球空间信息学与对地观测学在灾难管理中的应用研究
在灾难管理的各个环节, 需要大量不同尺度的空间信息, 如地形、地质和土壤图、地表植被覆盖、道路交通网络、建筑位置与类型、航空影像、卫星影像和全球卫星定位系统。地球空间信息学可以为灾难管理所需的快速有效的数据管理、处理、分析、发布和决策提供强有力的支撑技术[5]。在防灾阶段, 地理信息系统和遥感可以用来开展灾难危险和风险制图, 建立承灾体数据库, 自然现象的建模与模拟可以帮助成灾机理和灾难诱发条件的理解。在灾难应急阶段, 集成地理信息系统和遥感不仅能够监测和早期预警灾难, 而且可以对灾难过程进行制图, 例如火灾蔓延态势及趋势分析图, 洪水淹没区及预测分析图; 可以帮助决策者对灾难影响区救灾资源的调度和合理分配。全球定位系统可以为对建筑损失评估所需要的地面观测提供定位信息; 集成全球定位系统和地理信息系统可以为人道救援和搜救行动提供重要的信息[6]。在灾后恢复阶段, 地理信息系统可以用来管理建筑破坏信息、人口分布统计制图、建筑规划、选址等。
3.1 地球空间信息学的发展对灾难管理的促进
地球空间信息学的最新发展对灾难管理的促进主要表现在两个方面:(1)空间数据基础设施(SDI)及其相关技术的发展增强和提高了灾难管理中所需数据的共享性、可用性、协同性和集成性; (2)计算机软件和各种建模工具能力的增强为自然灾害建模、模拟、仿真分析提供了强大的引擎。
空间数据基础设施是一个空间数据管理架构, 为空间数据可利用性, 可获取性和集成性提供一个切实可行的环境。同时, “随着网络地理信息系统技术的发展, 空间数据基础设施可以协助灾难管理机构提高决策质量, 提高灾难管理各个环节的效率和效益”[7]。可用性、可访问性和利用可靠的, 最新、精确的空间数据依然是当前灾难管理的瓶颈, 尤其表现在灾害应急中。及时, 最新和精确的空间数据信息描述的救灾境况, 例如可用资源, 可通行的道路, 受灾区域需求的物资和急需的灾难应急行动, 对成功处置突发灾难事件极为重要。而且, 这些信息必须是可用的, 可以访问的且能够在短期内被利用“任何问题或拖延数据收集, 访问, 利用和发布都会影响救灾决策质量, 从而影响到整个灾难应急的成败”[7]。
地理信息系统是空间数据处理和分析的支撑技术, 具有集成各种空间数据类型的能力, 而且可以与信息和通讯技术(ICT)集成, 如决策支持系统(DSS)、专家系统、网络、无线应用、全球定位系统、遥感技术以及模拟器。为此, 地理信息系统在全球广泛应用于自然灾难管理中的减灾、防灾、应急和恢复的各个环节, 利用空间数据取得高效率和效益的灾难管理。桌面地理信息系统软件(如ArcGIS, MircoStation等)的显著发展和移动地理信息系统技术, 网络地理信息系统和组件式地理信息系统技术的不断发展提高和增强了利用地理信息系统技术从事灾难管理的效率和能力。灾害建模和预测能力的提高, 计算和数据处理技术的发展在以下几个方面:①更好的时空监测和预测在自然现象发展成极端灾害事件中, 例如对台风的形成, 移动轨迹和登陆地点的预测; ②更好的软件工具以用来集成影响或控制灾害的因素, 为正在逼近的灾害事件进行模拟, 对其影响进行分析; ③为灾难管理决策和模拟提供了更好的虚拟现实环境。然而, 需要指出的是不管是地理信息系统还是建模工具软件仅能够提供灾害模拟分析的虚拟场景和软件工具, 这些结果很大程度上依赖于输入数据质量和对各种灾害的成灾、诱发机理的研究程度和建模能力。
3.2 对地观测学的发展对灾难管理的促进
卫星遥感系统因其覆盖范围大, 具有周期性影像获取能力, 在自然灾难管理中具有举足轻重的地位。随着对地观测学的新技术的发展及新的对地观测系统投入运营, 例如极高空间分辨率的(< 1m)的可见光和热红外影像IKONOS、Quick bird、IRS CartoSat-1、ALOS、星载干涉雷达(INSAR)和差分干涉雷达(DINSAR) Radarsat、ERS、Envisat、TerraSAR-X、Cosmo SkyMed、ALOS等, 微波卫星Ple’ iades、DMC、RapidEye、机载激光高度测量议和差分干涉雷达技术等, 不管是机载, 星载或地面传感器都极大地提高了灾难管理所需的全天候、实时的数据获取能力。地球观测学的发展对灾难管理的促进主要体现在以下几个方面:
(1) 地表或地形模拟和可视化:数字地形模型(DTM), 数字高程模型(DEM)和数字表面模型(DSM)
地表和地形的模拟是灾难管理所需的关键要素之一, 尤其是受地形条件控制和影响的山地灾害, 如滑坡、泥石流灾害。地球观测学的发展对地表和地形模拟方面, 促进了数字地形模型、数字高程模型和数字表面模型的生成手段的多样化和精度的提高, 主要表现在:①基本覆盖全球的均一的NASA SRTM 90m空间分辨率的数字高程模型, 使得地形模拟简易化, 其数据的全球免费共享促成SRTM DEM数据在灾难管理中的应用普及; ②高级空载热发射和反射辐射计(ASTER)是搭载在1999年发射的Terra平台上的5个传感器之一, 它提供的立体像对可用来生成15m空间分辨率的数字高程模型, 可以用来生成全球高质量数字地形, 而且其成本费用较低; 从高分辨率传感器, 如IKONOS提供的立体像对生成的数字高程模型具有较高的精度和具有对微地形的模拟和刻画能力, 而且在大面积上立体卫星影像像对要比航空影像像对更为划算[8]; ③干涉雷达作为快速、精确(毫米级)地形数据获取的技术日益受到重视, 很多星载干涉雷达已经投入运营(ERS, ENVISAT, RADARSAT), 或处于计划和发射执行阶段; ④配置了高精度差分全球定位系统(DGPS)和实时导航系统(INS)的激光扫描仪可以全天候实时生成高精度数字表面模型。所有的这些技术, 都可以应用到灾难管理各个阶段所需要的地形、地表信息以及快速灾害制图, 如利用干涉雷达或激光扫描仪生成的城市地区高精度数字表面模型, 可以用来开展自然灾害如地震、海啸后的建筑损失评估。
(2) 灾害风险探测、识别、监测和预警手段的多样化
多传感器技术基本能覆盖所有大气窗口的, 从全色、多光谱、高光谱, 到可见光、近红外、短波红外、热红外、主动微波传感器、激光测高仪、雷达等传感器类型, 具有高空间、光谱和时间分辨率的卫星影像, 丰富了利用遥感技术开展灾害危险探测, 风险识别的选择: ①越来越多的研究根据遥感波谱特征来探测和分类自然灾害的控制或影响因素, 开展成灾体制图, 例如SPOT和IRS-1C用来进行灾害变化探测和危险性制图[8~10]; 高光谱影像可用于详细的矿物、岩石、土和植被的类型光谱识别, 如Hyperspectral Mapper (HyMap)成功应用于土类型划分和膨胀性黏土的识别[11]; ②高精度全天候的卫星合成孔径雷达(SAR)、干涉合成孔径雷达(INSAR)、差分干涉雷达(DINSAR)可以用来监测滑坡的活动, 地表变形和地面沉降[12~13], 而且这些测量方法可以提供达到毫米级精度的空间上的变形连续观测; ③利用微震实地监测, 大地测量, 高精度的数字地面模型(如通过干涉雷达, 激光雷达或数字摄影测量技术)和影像波谱学(如利用ASTER, MODIS及Hyperion)开展火山活动危险和风险评估[14]。
(3)灾害应急所需及时、精确数据可获取性
随着卫星和传感器的增多, 装配有高级传感器的对地观测系统以星群的形式出现, 大大提高了影像获取的时间分辨率, 在航空和地基系统的配合下能够为灾难应急提供及时数据。在2008年5.12汶川地震、2004年印度洋海啸、2006年印度尼西亚地震等灾害事件中高分辨率IKONOS和Quickbird影像被广泛应用于灾难应急所需的灾后快速制图服务和城市建筑损失评估[15~16]。其次, 国际空间信息团体间以政府或非政府形式的合作, 为在重大灾难事件期间和灾后提供空间数据和信息支持, 如灾害的快速制图, 灾情监测和预测、预报有力地提高了灾害应急和抢险能力等。这些国际合作组织主要有International Charter on Space & Major Disasters, 其主要目的在于通过建立发展民用救灾机构与空间技术机构长期的工作关系来提高利用空间技术从事灾难管理的效率[3]; UNOSAT的宗旨是鼓励、推动、促进和拓展在降低灾害易损性、危机管理、灾后重建和可持续发展中应用从对地观测卫星影像获取的专业级高精度地理信息; RESPOND Consortium在其网站首页写道“GMES服务支持人道救援、减灾和灾后重建”, 联合国人道救援办公室官员Verjee认为“ RESPOND Consortium致力于通过提高图、卫星影像和地理信息的开放性使人道救援机构越来越容易获取地球空间信息”[3]。这些机构在近年来的重大灾难事件的救灾应急中, 如2003年伊朗巴姆地震、2004年印度洋海啸、2005年巴基斯坦地震、2008年5.12汶川地震中, 不仅提供遥感影像的快速获取, 处理和灾害专题图的快速制图服务, 而且还参与了基于遥感技术的灾情、损失评估和灾害的实时跟踪, 监测和制图, 为减灾救灾做出了杰出的贡献。
总之, 多传感技术、高分辨率、多时相的卫星遥感系统的不断发展, 可以满足灾难管理需求数据的多源性、实时性, 提高遥感影像解译精度和增强遥感技术对自然灾害的探测能力; 日益完善的空间数据基础设施, 软件系统功能的增强, 以及针对重大灾难事件的国际空间信息合作。
3.3 局限性及发展趋势
地球空间信息学和对地观测科学的发展为灾难管理提供了新的工具, 但地球空间信息学在灾难管理方面的应用还需要逐步完善, Mansourian等[7]指出了在空间数据基础设施方面需要重视的问题, 包括:①制定相关的政策, 法规, 标准和服务, 从灾难管理需求的角度考虑支持各相关机构的数据在地理信息系统环境下的适用性, 各机构系统的兼容性和数据的集成性; ②强化灾难管理机构或社团的技术能力, 尤其是在空间技术, 如地理信息系统、全球定位系统、遥感、激光扫描、激光雷达等的应用, 利用遥感探测生命线、主要交通线和车辆跟踪的解决方案, 网络和通讯设施的应用; ③为突发事件处置中心配置数据分析所需的软、硬件设施, 提供决策支持系统。
虽然随着对地观测技术的发展, 对地观测能够提供全天候、宽光谱范围、高精度的立体影像, 但是在灾难管理方面还存在一些技术瓶颈:①影像处理、解译的能力和精度, 目前计算机自动解译的水平较低, 影像解译精度受解译人员的经验和专业背景知识影响大; ②适时的卫星数据接收, 有时由于云层的覆盖了有限的自由视角, 卫星轨道不容许对某一地区从几天到几个星期, 甚至几个月进行拍照。较差的天气条件, 主要是云层覆盖是受灾区域难以获得充分的卫星影像的主要原因; ③针对某一特定需求数据的合理选取, 确定决策过程所需的数据。针对数目繁多的卫星影像数据, 如何利用有限的灾难管理资金选取性价比合理的数据, 这个问题日益突出; ④ “即使是高分辨率影像(< 1m), 在特定灾难应急中所需的探测详细的真三维建筑结构破坏的能力有限”[17]; ⑤除了技术层面的局限, 还存在“从事灾难管理人员与遥感技术间的鸿沟, 尤其是在发展中国家”[1], 也就是相关人员专业知识的匮乏; 而且⑥高昂的数据花费, 有限的立体影像能力, 难以获取有效的地面控制点(GCPs)在一定程度上是应用对地观测技术于灾难管理的障碍。李德仁院士认为地球空间信息学“未来发展方向是'四化', 即'时空信息获取的天地一体化和全球化'、'时空信息加工与处理的自动化、智能化与实时化'、'时空信息管理和分发的网格化'以及'时空信息服务的大众化' ”[4]。这“四化”的实现将从根本上解决上述局限和问题, 极大地提高灾难管理的水平。
4. 结论
地球空间信息学和对地观测学的最新技术发展推动了灾难管理水平的提高, 为灾难管理提供了海量数据的多源化, 增强了数据的集成、可用性和可访问性, 为数据管理、分析处理、灾害建模、动态监测、模拟和预警提供了新的技术支撑体系, 为构建了灾难管理信息平台提供了良好的软硬件平台。但需要指出的是技术的进步和发展虽能够为灾难管理提供引擎, 但还需要相关的政策、法规支持, 以及对成灾机理和过程的深入研究。
-
表 2 现今和未来的民用光学高分辨率卫星系统(据瑞士地理信息中心)
Table 2. Current and forthcoming civil optical high-resolution satellite system (SwissTopo)
-
[1] Van Westen C.Geoinformation Science and Earth Observationfor municipal risk management[J].The SLARIMProject, 2003. [2] 李德仁.论"GEOMATICS"的中译名[J].测绘通报, 1998, 27(2). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=chtb199807005 [3] Verjee F.The Application of Geomaticsin Complex Humanitarian Emergencies[J].SEAS Fellow&Research Associate Institutefor Crisis, Disaster&Risk Management, the George Washington University, 2004. [4] 李德仁.对地观测与地理信息系统[J].地球科学进展, 2001, 16(5):689~703. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2001.05.013 [5] Montoya L.Geo-data acquisition through mobile GIS and digital video:an urban disaster management perspective[J].Environmental Modeling&Software, 2003, 18(10):869~876. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ025746966/ [6] Van Westen C. Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systemsfor Natural Disaster Management In Skidmore[M]. A. ed. Environmental Modeling with GIS and Remote Sensing. London: Taylor&Francis, 2002. 200~226. [7] Mansourian A. A, Rajabifard, et al. Using SDI and web-based systemto facilitate disaster management[J]. Computers&Geosciences, 2006, 32(3): 303~315. [8] Nichol J E, Shaker A, et al.Application of high-resolution stereo satellite images to detailed landslide hazard assessment[J].Geomorphology, 2006, 76(1~2):68~75. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ024972165 [9] McKean J, Roering J.Objective landslide detection and surface morphology mapping using high-resolution airborne laser altimetry[J].Geomorphology, 2004, 57(3~4):331~351. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ026153955/ [10] Metternicht G, Hurni L, et al.Remote sensing of landslides:An analysis of the potential contribution to geo-spatial systems forhazard assessment in mountainous environments[J].Remote Sensing of Environment, 2005, 98(2~3):284~303. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2005.08.004 [11] Waheed T, Bonnell R B, et al.Measuring performance in precision agriculture:CART——A decision tree approach[J].Agricultural Water Management, 2006, 84(1~2):173~185. [12] Raucoules D, Maisons C, et al.Monitoring of slowground deformation by ERS radar interferometry on the Vauvert salt mine(France):Comparison with ground-based measurement[J].Remote Sensing of Environment, 2003, 88(4):468~478. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2003.09.005 [13] Singhroy V, Molch K.Characterizing and monitoringrockslides fromSARtechniques[J].Advances in Space Research, 2004, 33(3):290~295. doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(03)00470-8 [14] Tralli DM, Blom RG, et al.Satellite remote sensing of earthquake, volcano, flood, landslide and coastal inundation hazards[J].ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2005, 59(4):185~198. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2005.02.002 [15] Luca Gusella C K H, Beverley J. Adams, Sungbin Cho, Hung Chung. Damage Assessment with Very-High Resolution OpticalImagery Followingthe December 26, 2003 Bam, Iran Earthquake. 2004. [16] Keiko Saito RS, M. EERI, Terence Ade CFoley. Visual Damage Assessment Using High-Resolution Satellite Images Followingthe 2003 Bam, Iran, Earthquake[J]. Earthquake Spectra, 2005, 21: 309~318. [17] Kerle N, Stekelenburg R. Advanced structural disaster damage assessment based on aerial oblique video imagery and integratedauxiliary data sources. Paper presented at the ISPRS 2004 Istanbul conference, 2004. -






 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载: