AN OVERVIEW ON EARTHQUAKE-INDUCED LANDSLIDE RESEARCH
-
摘要: 地震滑坡是大陆内部山区大地震活动中最为常见的地震地质灾害类型,不仅数量多、规模大,而且危害性极大,常会对人类活动造成特别严重的损害,分析研究地震滑坡对地震灾害危险性评价和防震减灾工作极为重要。通过系统总结和梳理国内外地震滑坡的研究现状,对地震滑坡的发育规律、动力机理以及“3S”技术在地震滑坡研究中的应用等方面进行了较为全面的论述。Abstract: Earthquake induced landslide is one of the most common geological disasters in great earthquake of continent internal mountain. It not only has large amount and great scale, but also causes serious damage for human activities. So, it is extraordinarily significant to analysis the earthquake induced landslide for evaluating the seismic risk. This paper scientifically concludes the research status of landslide at domestic and overseas, based on the law of earthquake induced landslide development and dynamics mechanism. Then, it summarizes the 3S technique specific application to the landslides.
-
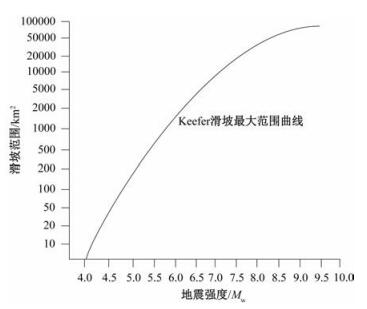
图 1 震级与地震滑坡范围趋势线[1]
Figure 1. Trend line of earthquake magnitude and landslide scope
表 1 中国南北地震带及邻区历史上典型ML 7.5及以上大地震的地震滑坡参数统计
Table 1. Statistical parameters of landslides caused by typical ML 7.5 and above earthquakes in north-south seismic belt of China and its adjacent region in history

表 2 西南11个典型地震事件中滑坡统计
Table 2. Landslide statistics for 11 typical seismic events in the southwest of China

-
[1] Keefer D K. Landslides caused by earthquakes[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1984, 95(4):406~421. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1984)95<406:LCBE>2.0.CO;2 [2] 李为乐, 伍霁, 吕宝雄.地震滑坡研究回顾与展望[J].灾害学, 2011, 26(3):103~108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU201103021.htmLI Wei-le, WU Ji, LÜ Bao-xiong. Research on landslide triggered by earthquake:Review and prospect[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2011, 26(3):103~108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU201103021.htm [3] 黄润秋.汶川8.0级地震触发崩滑灾害机制及其地质力学模式[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(6):1239~1249. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200906023.htmHUANG Run-qiu. Mechanism and geomechanical modes of landslide hazards triggered by Wenchuan 8.0 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(6):1239~1249. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200906023.htm [4] 李树德.活动断层分段研究[J].北京大学学报:自然科学版, 1999, 35(6):768~773. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ199906006.htmLI Shu-de. Study on segmentation of active faults[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 1999, 35(6):768~773. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ199906006.htm [5] Keefer D K, Wilson R C. Predicting earthquake-induced landslides, with emphasis on arid semi-arid environments[C]//Sadler P M, Morton D M. Landslides in a semi-arid environment with emphasis on the inland Valleys of Southern California. California:Publications of the Inland Geological Society, 1989. [6] Rodíigueza C E, Bommer J J, Chandler R J. Earthquake-induced landslides:1980-1997[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 1999, 18(5):325~346. doi: 10.1016/S0267-7261(99)00012-3 [7] Papadopoulos G A, Plessa A. Magnitude-distance relations for earthquake-induced landslides in Greece[J]. Engineering Geology, 2000, 58(3-4):377~386. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00043-0 [8] Prestininzi A, Romeo R. Earthquake-induced ground failures in Italy[J]. Engineering Geology, 2000, 58(3-4):387~397. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00044-2 [9] 李天池. 地震与滑坡的关系及地震滑坡预测探讨[C]//滑坡文集, 第二集. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 1979: 127~132.LI Tian-chi. The relationship between earthquakes and landslides and explore seismic landslide forecast[C]//Landslide Anthology, Episode 2. Beijing:China Railway Publishing House, 1979:127~132. [10] 周本刚, 王裕明.中国西南地区地震滑坡的基本特征[J].西北地震学报, 1994, 16(1):95~103. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ401.016.htmZHOU Ben-gang, WANG Yu-ming. Some characteristics of earthquake-induced landslide in southwestern China[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 1994, 16(1):95~103. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ401.016.htm [11] 孙崇绍, 蔡红卫.我国历史地震时滑坡崩塌的发育及分布特征[J].自然灾害学报, 1997, 6(1):25~30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH701.004.htmSUN Chong-shao, CAI Hong-wei. Developing and distributing characteristics of collapses and landslides during strong historic earthquake in China[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 1997, 6(1):25~30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH701.004.htm [12] 辛鸿博, 王余庆.岩土边坡地震崩滑及其初判准则[J].岩土工程学报, 1999, 21(5):591~594. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC199905014.htmXIN Hong-bo, WANG Yu-qing. Earthquake induced landslide and avalanche[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1999, 21(5):591~594. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC199905014.htm [13] Owen L A, Kamp U, Khattak G A, et al. Landslides triggered by the 8 October 2005 Kashmir earthquake[J]. Geomorphology, 2008, 94(1-2):1~9. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2007.04.007 [14] Masahiro Chigira, Hiroshi Yagii. Geological and geomorphological characteristics of landslides triggered by the 2004 Mid Niigta prefecture earthquake in Japan[J]. Engineering Geology, 2006, 82(4):202~221. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.10.006 [15] Liao H W, Lee C T. Landslides triggered by the Chi-Chi earthquake, Asian association on remote sensing, Asian conference on remote sensing ACRS 2000[EB/OL]. (2002-01-13)[2010-10-23]. http://www.gisdevelopment.net/aars/acrs/2000/ts8/hami0007.asp. [16] Hiroshi P S, Hiroyuki H, Fujiwara S, et al. Interpretation of landslide distribution triggered by the 2005 Northern Pakistan earthquake using SPOT5 imagery[J]. Landslides, 2007, 4(2):113~122. doi: 10.1007/s10346-006-0069-5 [17] 康来迅.昌马断裂带滑坡之研究[J].内陆地震, 1988, 2(4):376~381. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LLDZ198804005.htmKANG Lai-xun. Study on the characteristics of landslide of Changma fault zone[J]. Inland Earthquake, 1988, 2(4):376~381. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LLDZ198804005.htm [18] 黄润秋, 李为乐."5. 12"汶川大地震触发地质灾害的发育分布规律研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(12):2585~2592. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.028HUANG Run-qiu, LI Wei-le. Research on development and distribution rules of geohazards induced by Wenchuan earthquake on 12th May, 2008[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(12):2585~2592. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.028 [19] 许强, 李为乐.汶川地震诱发大型滑坡分布规律研究[J].工程地质学报, 2010, 18(6):818~826. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201006002.htmXU Qiang, LI Wei-le. Distribution of large-scale landslide induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(6):818~826. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201006002.htm [20] 吴树仁, 石菊松, 姚鑫, 等.四川汶川地震地质灾害活动强度分析评价[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(11):1900~1906. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.11.020WU Shu-ren, SHI Ju-song, YAO Xin, et al. Analysis and evaluation of geohazard intensity of the Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(11):1900~1906. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.11.020 [21] 刘洪兵, 朱晞.地震中地形放大效应的观测和研究进展[J].世界地震工程, 1999, 15(3):20~25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDC199903002.htmLIU Hong-bing, ZHU Xi. Advances on topographic amoplification effects of seismic response[J]. World Information on Earthquake Engineering, 1999, 15(3):20~25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDC199903002.htm [22] Celebi M. Topographic and geological amplification determined from strong motion and aftershock records of 3 March 1985 Chile earthquake[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1987, 77(4):1141~1147. [23] Hartzell S H, Carver D L, King K W. Initial investigation of site and topographic effects at Robinwood Ridge, California[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1994, 84(5):1336~1349. [24] Hutchinson J N. General report:Morphological and geotechnical parameters of landslides in relation to geology and hydrogeology[C]//Bonnard C. Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Landslides. Lausanne:Rotterdam/Brookfield, 1988:3~35. [25] 周维垣.高等岩石力学[M].北京:水利电力出版社, 1990.ZHOU Wei-yuan. Advanced rock mechanics[M]. Beijing:China Water Power Press, 1990. [26] 胡广韬.滑坡动力学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1995.HU Guang-tao. Landslide dynamics[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1995. [27] 张倬元, 王士天, 王兰生.工程地质分析原理[M].北京:地质出版社, 1993.ZHANG Zhuo-yuan, WANG Shi-tian, WANG Lan-sheng. Principle of engineering geological analysis[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1993. [28] 毛彦龙, 胡广韬, 毛新虎, 等.地震滑坡启程剧动的机理研究及离散元模拟[J].工程地质报, 2001, 9(1):74~80. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200101012.htmMAO Yan-long, HU Guang-tao, MAO Xin-hu, et al. Mechanism of set-out violent-slide of slope mass during earthquake and its simulation by using discrete element method[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2001, 9(1):74~80. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200101012.htm [29] 祁生文, 伍法权, 刘春玲, 等.地震边坡稳定性的工程地质分析[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(16):2792~2796. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.16.024QI Sheng-wen, WU Fa-quan, LIU Chun-ling, et al. Engineering geology analysis of seismic slope stability[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(16):2792~2796. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.16.024 [30] Shin Aoi, Takashi Kunugi, Hiroyuki Fujiwara. Trampoline effect in extreme ground motion[J]. Science, 2008, 322:727~730. doi: 10.1126/science.1163113 [31] 唐春安, 左宇军, 秦泗凤, 等. 汶川地震中的边坡浅层散裂与抛射模式及其动力学解释[C]//第十届全国岩石力学与工程学术大会论文集. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2009: 258~262.TANG Chun-an, ZUO Yu-jun, QIN Si-feng, et al. Slope in Wenchuan earthquake shallow spallation and projectile model and dynamic interpretation[C]//Proceedings of the 10th Academic Conference of Rock Mechanics and Engineering. Beijing:China Electric Power Press, 2009:258~262. [32] 殷跃平.汶川八级地震地质灾害研究[J].工程地质学报, 2008, 16(4):433~444. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGYJ200904001024.htmYIN Yue-ping. Researchs on the geo-hazards triggered by Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2008, 16(4):433~444. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGYJ200904001024.htm [33] 黄润秋, 李为乐.汶川地震触发地质灾害的断层效应分析[J].工程地质学报, 2009, 17(1):19~28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSDI201508040.htmHUANG Run-qiu, LI Wei-le. Faulty effect analysis of geo-hazard triggered by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(1):19~28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSDI201508040.htm [34] 黄润秋, 向喜琼, 巨能攀.我国区域地质灾害评价的现状及问题[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(11):1078~1082. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.11.005HUANG Run-qiu, XIANG Xi-qiong, JU Neng-pan. Assessment of China's regional geohazards:Present situation and problems[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2004, 23(11):1078~1082. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.11.005 [35] Terzaghi K, Peek R B. Soil mechanics in engineering practice[M]. New York:John Wile, 1948. [36] Seed H B. Landslides during earthquakes due to soil liquefaction[J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, 1968, 94(SM5):1053~1122. [37] 丁彦慧, 王余庆, 孙进忠.地震崩滑与地震参数的关系及其在边坡震害预测中的应用[J].地球物理学报, 1999, 42(S1):101~107. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX1999S1014.htmDING Yan-hui, WANG Yu-qing, SUN Jin-zhong. Correlation between landslides and seislides and seismic parameters and its application in predicting slope earthquake disaster[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 1999, 42(S1):101~107. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX1999S1014.htm [38] Newmark N M. Effects of earthquake on dams and embankments[J]. Geotechnique, 1965, 15(2):139~160. doi: 10.1680/geot.1965.15.2.139 [39] Wieczorek G F, Wilson R C, Harp E L. Map showing slope stability during earthquakes in San Mateo County, California[C]//US Geological Survey. Miscellaneous investigation maps. Reston:USGS, 1985:I-1257-E. [40] Jibson R W, Keefer D K. Analysis of the seismic origin of landslide:Examples from the New Madrid seismic zone[J]. Geological Society of American Bulletin, 1993, 105(4):521~536. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1993)105<0521:AOTSOO>2.3.CO;2 [41] Broecker W S. Abrupt climate change:Causal constraints provided by the paleoclimate record[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2000, 51(1-4):137~154. doi: 10.1016/S0012-8252(00)00019-2 [42] Ambraseys N N, Menu J M. Earthquake-induced ground displacements[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 1988, 16(7):985~1006. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-9845 [43] Jibson R W. Predicting earthquake-induced landslide displacement using Newmarks Sliding Block Analysis[M]//Transportation Research Board Business Office. Transportation research record No.1411:Earthquake-induced ground failure hazards. Washington, DC:Transportation Research Board, 1993:9~17. [44] 黄润秋.灾害性崩滑地质过程的全过程模拟[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 1994, (增1):11~17, 29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH4S1.001.htmHUANG Run-qiu. Full-course Simulation of Hazardous Rockfalls and Avalanches[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1994, (Supp.1):11~17, 29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH4S1.001.htm [45] 刘忠玉, 马崇武, 苗天德, 等.高速滑坡远程预测的块体运动模型[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2000, 19(6):742~746. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200006011.htmLIU Zhong-yu, MA Chong-wu, MIAO Tian-de, et al. Kinematic block model of long run-out prediction for high-speed landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2000, 19(6):742~746. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200006011.htm [46] 邬爱清, 林绍忠, 马贵生, 等.唐家山堰塞坝形成机制DDA模拟研究[J].人民长江, 2008, 39(22):91~95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2008.22.033WU Ai-qing, LIN Shao-zhong, MA Gui-sheng, et al. DDA simulation research for formation mechanism of Tangjiashan barrier lake[J]. Yangtze River, 2008, 39(22):91~95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2008.22.033 [47] 崔芳鹏, 胡瑞林, 殷跃平, 等.纵横波时差耦合作用的斜坡崩滑效应离散元分析——以北川唐家山滑坡为例[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(2):319~327. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201002015.htmCUI Fang-peng, HU Rui-lin, YIN Yue-ping, et al. Discrete element analysis of collapsing and sliding response of slope triggered by time difference coupling effects of P and S seismic waves:Taking Tangjiashan landslide in Beichuan County for Example[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(2):319~327. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201002015.htm [48] 曹琰波, 戴福初, 许冲, 等.唐家山滑坡变形运动机制的离散元模拟[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2011, 30(增1):2878~2887. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2011S1039.htmCAO Yan-po, DAI Fu-chu, XU Chong, et al. Discrete element simulation of deformation mechanism of Tangjiashan landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(Supp.1):2878~2887. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2011S1039.htm [49] 王兰民, 孙军杰, 徐舜华, 等.爆破模拟地震动条件下黄土场地震陷研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(5):913~921. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200805008.htmWANG Lan-min, SUN Jun-jie, XU Shun-hua, et al. Characteristics of seismic subsidence of loess induced by blasting ground motion[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(5):913~921. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200805008.htm [50] 许冲, 戴福初, 徐锡伟.汶川地震滑坡灾害研究综述[J].地质论评, 2010, 56(6):860~874. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201006014.htmXU Chong, DAI Fu-chu, XU Xi-wei. Wenchuan earthquake-induced landslides:An overview[J]. Geological Review, 2010, 56(6):860~874. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201006014.htm [51] 郝立贞, 白世彪, 徐红波, 等.基于CBERS-02卫星数据的地震滑坡识别——以青川县为例[J].防灾科技学院学报, 2010, 12(4):46~52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZJS201004010.htmHAO Li-zhen, BAI Shi-biao, XU Hong-bo, et al. Landslide identification after earthquake based on CBERS-02 remote sensing data:The case of Qingchuan[J]. Journal of Institute of Disaster Prevention, 2010, 12(4):46~52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZJS201004010.htm [52] 沈永林, 李晓静, 吴立新.基于航空影像和LiDAR数据的海地地震滑坡识别研究[J].地理与地理信息科学, 2011, 27(1):16~20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLGT201101005.htmSHEN Yong-lin, LI Xiao-jing, WU Li-xin. Detection of Haiti earthquake induced landsides from aerial images and LiDAR data[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2011, 27(1):16~20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLGT201101005.htm [53] 石菊松, 吴树仁, 石玲.遥感在滑坡灾害研究中的应用进展[J].地质论评, 2008, 54(4):505~514. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJZF201508104.htmSHI Ju-song, WU Shu-ren, SHI Ling. Remote sensing for landslide study:An Overview[J]. Geological Review, 2008, 54(4):505~514. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJZF201508104.htm [54] 曾庆利, 张西娟, 杨志法.云南虎跳峡"滑石板"岩质滑坡的基本特征与成因[J].自然灾害学报, 2007, 16(3):1~6.ZENG Qing-li, ZHANG Xi-juan, YANG Zhi-fa. Principal characteristics and formation mechanism of plate type rock landslide in Hutiao-Gorge, Yunnan[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2007, 16(3):1~6. [55] 杨文涛, 汪明, 史培军.利用NDVI时间序列识别汶川地震滑坡的分布[J].遥感信息, 2012, 27(6):45~56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXX201206010.htmYANG Wen-tao, WANG Ming, SHI Pei-jun. Identification of landslides in Wenchuan earthquake affected region using NDVI time series[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2012, 27(6):45~56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXX201206010.htm [56] 花利忠, 崔胜辉, 李新虎, 等.汶川大地震滑坡体遥感识别及生态服务价值损失评估[J].生态学报, 2008, 28(12):5909~5916. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.12.017HUA Li-zhong, CUI Sheng-hui, LI Xin-hu, et al. Remote sensing identification of earthquake trigged landsides and their impacts on ecosystem services:A case study of Wenchuan County[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(12):5909~5916. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.12.017 [57] Hervás J, Barredo J I, Rosin P L, et al. Monitoring landslides from optical remotely sensed imagery:The case history of Tessina landslide, Italy[J]. Geomorphology, 2003, 54(1-2):63~75. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(03)00056-4 [58] LIN Wen-Tzu, CHOU Wen-Chieh, LIN Chao-Yuan, et al. Vegetation recovery monitoring and assessment at landslides caused by earthquake in Central Taiwan[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2005, 210(1-3):55~66. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2005.02.026 [59] 万保峰, 袁水华, 苏建平.基于纹理分析的滑坡遥感图像识别[J].地矿测绘, 2009, 25(2):11~14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKCH200902003.htmWAN Bao-feng, YUAN Shui-hua, SU Jian-ping. Remote sensing image recognition of landslide based on texture analysis[J]. Surveying and Mapping of Geology and Mineral Resource, 2009, 25(2):11~14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKCH200902003.htm [60] 李松, 李亦秋, 安裕伦.基于变化检测的滑坡灾害自动识别[J].遥感应用, 2010, (1):27~31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXX201001007.htmLI Song, LI Yi-qiu, AN Yu-Lun. Automatic recognition of landslides based on change detection[J]. Remote Sensing Application, 2010, (1):27~31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXX201001007.htm [61] 傅文杰, 洪金益.基于支持向量机的滑坡灾害信息遥感图像提取研究[J].水土保持研究, 2006, 13(4):120~122. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY200604037.htmFU Wen-jie, HONG Jin-yi. Discussion on application of support vector machine technique in extraction of information on landslide hazard from remote sensing images[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006, 13(4):120~122. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY200604037.htm [62] 陈晓利, 赵健, 叶洪.应用径向基概率神经网络研究地震滑坡[J].地震地质, 2006, 28(3):430~439. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200603010.htmCHEN Xiao-li, ZHAO Jian, YE Hong. Application of rbpnn in the research of earthquake-induced landslide[J]. Seismology and geology, 2006, 28(3):430~439. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200603010.htm [63] Biswajeet Pradhan, Saro Lee. Utilization of optical remote sensing data and GIS tools for regional landslide hazard analysis using an artificial neural network model[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14(6):143~152. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5791(08)60008-1 [64] Kamp U, Growley B J, Khattak G A, et al. GIS-based landslide susceptiblility mapping for the 2005 Kashmir earthquake region[J]. Geomorphology, 2008, 101(4):631~642. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.03.003 [65] 许冲, 徐锡伟, 于贵华.基于证据权方法的玉树地震滑坡危险性评价[J].地震地质, 2013, 35(1):151~164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201301015.htmXU Chong, XU Xi-wei, YU Gui-hua. The Yushu earthquake triggered landslide hazard evaluation based on weight of evidence method[J]. Seismology and geology, 2013, 35(1):151~164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201301015.htm [66] Ali Uromeihy, Maryam Fattahi. Landslide hazard zonation of Babolrood Watershed, Iran[C]//Asia-Pacific Chemical, Biological & Environmental Engineering Society. Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology. Singapore:IACSIT Press, 2011:318~320. [67] 王余庆, 高艳平, 辛鸿博.用灰色聚类方法预测边坡稳定性研究[J].工业建筑, 2002, 32(6):44~47. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYJZ200206014.htmWANG Yu-qing, GAO Yan-ping, XIN Hong-bo. A research on prediction of seismic stability of slopes by grey clustering method[J]. Industrial Construction, 2002, 32(6):44~47. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYJZ200206014.htm [68] 许冲, 戴福初, 徐素宁, 等.基于逻辑回归模型的汶川地震滑坡危险性评价与检验[J].水文地质工程地质, 2013, (3):98~104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201303021.htmXU Chong, DAI Fu-chu, XU Su-ning, et al. Application of logistic regression model on the Wenchuan earthquake triggered landslide hazard mapping and its validation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2013, (3):98~104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201303021.htm [69] 高艳平, 王余庆, 辛鸿博.神经元网络在预测边坡地震稳定性中的应用[J].辽宁工程技术大学学报:自然科学版, 2001, 20(4):431~433. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXKY200104015.htmGAO Yan-ping, WANG Yu-qing, XIN Hong-bo. The application of the artificial neural network in prediction of slope seismic stability[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University:Natural Science Edition, 2001, 20(4):431~433. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXKY200104015.htm [70] 樊伟, 杨军, 刘廷廷.灰色神经网络组合模型及在滑坡预测中的应用[J].人民长江, 2005, 36(11):48~50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2005.11.018FAN Wei, YANG Jun, LIU Ting-ting. Gray neural network model and its application in landslide forecast[J]. Yangtze River, 2005, 36(11):48~50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2005.11.018 [71] Yesilnacar E, Topal T. Landslide susceptibility mapping:A comparison of logistic regression and neural networks methods in a medium scale study, Hendek region, Turkey[J]. Engineering Geology, 2005, 79(3-4):251~266. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.02.002 [72] 庄涛.我国地震防灾减灾科普教育的瓶颈及对策分析[J].国际地震动态, 2013, (4):30~34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJZT201304008.htmZHUANG Tao. Bottleneck and countermeasures of the popular science education on earthquake disaster prevention and mitigation in China[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology, 2013, (4):30~34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJZT201304008.htm -





 下载:
下载: