GENESIS AND SOURCES OF NON-CONVENTIONAL WATER SOLUBLE METHANE GAS IN GUSHI SAG
-
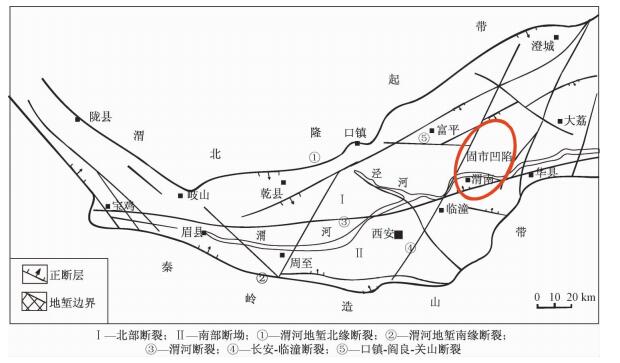
摘要: 针对渭河盆地固市凹陷水溶甲烷气的成因类型进行分析研究。对地层水溶甲烷气碳同位素δ13C1及重烃的含量研究发现,不同层位的水溶甲烷气成因类型不同。新近系张家坡组水溶甲烷气主要为有机成因的生物气,来源于本层含碳质较高的灰黑色泥灰岩生物分解,为自生自储式;下部蓝田—灞河组水溶甲烷气以未成熟的煤型热解气(煤型腐殖型)为主,来源于下部地层。对CO2碳同位素的分布范围和含量进行分析得出,δ13CCO2 < -10‰,为典型的壳源型有机成因,证明蓝田—灞河组水溶甲烷气和CO2来源于下部地层的混合型气,结合乙烷碳同位素分析,得出下部地层可能存在有机成因的煤型热解气层系。Abstract: The genetic types of water soluble methane gas in Gushi sag in Weihe Basin were studied. Research on carbon isotope δ13C1 and content of heavy hydrocarbon in water soluble gas methane showed that the genetic types of water soluble methane gas in different formations were different. Water soluble gas in Neogene Zhangjiapo Formation was mainly biogenetic. It came from biological decomposition of dark grey muddy limestone with higher content of carbon, which was self-generated and self-reserved. Water soluble methane gas in the Lantian-Bahe Formation was mainly immature coal-type pyrolysis gas (coal humic pyrolysis gas), which came from the lower layer. Analysis of the carbon isotope of CO2 showed that δ13CCO2 < -10‰, being typical crust source type of organic origin. This proved that the water soluble methane and CO2 in the Lantian-Bahe Formation came from the lower strata. Combining the above results and ethane carbon isotope analysis, the authors concluded that the biogenetic pyrolysis gas probably existed in the lower strata.
-
Key words:
- Gushi Sag /
- water-soluble methane /
- genetic type /
- biogas /
- shell source type
-
表 1 珠江组及其相邻地层概况(据文献[9]修改)
Table 1. Stratigraphic profiles about Zhujiang Formation and the adjacent strata
演化阶段 天然气类型 Ro/% δ13CCH4/‰ 计算值 确定值 生物化学作用带 生物化学气 ≤0.3 ≤-58.6 ≤-60 生物化学作用带 生物—热催化过渡气 0.3~0.6 -58.6~-44.9 -65~-45 热催化作用带 煤型热解气 0.6~2.0 -44.9~-28.0 -45~-28 热裂解作用带 煤型裂解气 ≥2.0 ≥-28.0 ≥-28 表 2 固市凹陷天然气碳同位素分析结果
Table 2. Analysis results of the natural gas in Gushi Sag
井名 取样地层 δ13 CCH4/‰ δ13 CCO2/‰ δ13 CC2H6/‰ WN1 蓝田—灞河组 -34.9 -11.4 -21.6 WN2 蓝田—灞河组 -33.8 -11.6 -26.4 WN3 蓝田—灞河组 -39.8 -10.0 -25.9 WN4 蓝田—灞河组 -28.8 -14.0 -26.2 WN5 蓝田—灞河组 -28.1 -13.1 WN6 张家坡组 -65.6 -15.2 -53.2 WN7 蓝田—灞河组 -28.4 -14.0 -26.2 表 3 固市凹陷水溶天然气组分
Table 3. Water soluble gas composition in Gushi Sag
井号 甲烷/% 乙烷/% 丙烷/% 异丁烷/% 正丁烷/% 异戊烷/% 正戊烷/% 全烃/% CO2/% 1 82.44 3.405 0.343 0.012 0.064 0.013 0.021 86.29 8.824 2 89.74 3.093 0.556 0.035 0.167 0.01 0.035 93.85 1.913 3 43.17 2.300 0.545 0.115 0.185 0.039 0.048 46.40 45.678 4 12.52 0.134 0.020 0.002 0.005 0.001 0.002 12.68 17.992 5 47.52 0.442 0.053 0.006 0.013 0.003 0.004 48.43 8.241 6 98.51 0.076 0.013 0.002 0.001 0 0 98.60 1.237 7 99.03 0.092 0.014 0.004 0.001 0.001 0 99.14 0.316 8 62.77 0.018 0.002 0 0.001 0 0 62.79 15.336 9 72.20 2.727 0.536 0.040 0.166 0.016 0.044 75.73 19.830 10 98.90 0.076 0.013 0.005 0.001 0.001 0 98.99 1.249 11 84.91 0.072 0.018 0.007 0.002 0.001 0.001 85.01 0.411 12 31.17 0.420 0.160 0.028 0.025 0.009 0.009 35.10 0.256 13 95.90 0.059 0.012 0.006 0.002 0.002 0 95.98 1.292 平均 70.68 0.993 0.176 0.020 0.049 0.007 0.013 72.23 9.429 表 4 固市凹陷与柴达木三湖地区生物气资源类比
Table 4. Comparison of biogas resources in Gushi Sag and Qaidam Sanhu area
地区 地质年代 沉积速率/(mm·a-1) 有机碳含量/% 地层温度/℃ 地温梯度/(℃/100 m) 地层压力/MPa 储层孔隙度/% 砂层厚度/m 生物气资源量/108 m3 δ13 C1/‰ 固市凹陷 N2z 0.740 0.55 65.75 3.43 15 30 200 11784 -65.6 柴达木三湖地区 Q1s 0.715 0.3~0.4 63 3.78 16.8 25~41 300 11210 -60.58~-66.38 表 5 陆相烃源岩有机质丰度评价指标
Table 5. Evaluation indicators of organic matter abundance in continental hydrocarbon source rocks
指标 湖盆水体类型 非烃源岩 烃源岩类型 差 中等 好 最好 总有机碳/% 淡水—半咸水 <0.4 0.4~0.6 >0.6~1.0 >1.0~2.0 >2.0 咸水—超咸水 <0.2 0.2~0.4 >0.4~0.6 >0.6~0.8 >0.8 氯仿沥青"A"/% <0.015 0.015~0.050 >0.050~0.100 >0.100~0.200 >0.200 HC/10-6 <100 100~200 >200~500 >500~1000 >1000 (S1+S2)/(mg·g-1) <2 2~6 >6~20 >20 表 6 固市凹陷张家坡组有机碳、氯仿沥青"A"含量
Table 6. Contents of organic carbon and chloroform bitumen "A" in Zhangjiapo Formation in Gushi Sag
井号 有机碳/% 氯仿沥青"A"/% 烃源岩类型 沉积相带 样品数 最小—最大/平均值 样品数 最小—最大/平均值 渭1井 12 0.112~0.858/0.47 12 0.0063~0.0674/0.032 差—中 浅湖 渭3井 36 0.034~0.423/0.18 5 0.0029~0.0241/0.0113 差—非 浅湖 渭参1井 6 0.212~0.459/0.30 2 0.0139~0.0142/0.0141 差—好 浅湖 渭参2井 8 0.060~0.143/0.10 1 0.0037 非 河湖 渭参3井 5 0.326~0.408/0.36 5 0.0107~0.0225/0.0174 差 浅湖 渭参4井 25 0.083~1.185/0.48 28 0.0021~0.257/0.0362 差—中 较深湖 渭参5井 18 0.239~0.786/0.45 21 0.0044~0.348/0.0468 差—中 较深湖 渭深12井 27 0.24~0.92/0.52 27 0.0011~0.0663/0.0275 差—好 较深湖 渭深16井 23 0.08~1.17/0.50 23 0.0025~0.0368/0.0174 差—好 较深湖 渭深17井 16 0.22~1.3/0.69 24 0.0059~0.045/0.0181 差—好 较深湖 渭南1井 1 0.59 1 0.1195 中—好 较深湖 渭南2井 1 0.56 1 0.0256 差—中 较深湖 渭南3井 2 0.08~0.30/0.19 2 0.0061~0.0072/0.00665 差—非 浅湖 渭南4井 1 0.41 1 0.0115 差—非 较深湖 渭南5井 2 0.26~0.33/0.295 2 0.0082~0.0090/0.0086 差—非 较深湖 渭南6井 2 0.65~0.82/0.735 2 0.061~0.089/0.075 中—好 较深湖 表 7 固市凹陷张家坡组烃源岩热解分析数据
Table 7. Pyrolysis analysis data of hydrocarbon source rock in Zhangjiapo Formation in Gushi Sag
样品号 井号 井深/m 岩性 可溶烃
S1/(mg·g-1)热解烃
S2/(mg·g-1)最高峰温
Tmax/℃产油潜率
(S1+S2)/(mg·g-1)wh-1 渭南5 1764.75 灰黑色泥岩 0.05 2.84 430 2.89 wh-2 渭南6 1687.85 灰黑色泥岩 0.02 0.97 421 0.99 wh-3 渭南11 1673.76 灰黑色泥岩 0.05 2.42 432 2.47 wh-4 1669.76 灰黑色泥岩 0.03 1.32 422 1.35 wh-5 渭南10 1479.16 灰黑色泥岩 0.01 0.17 426 0.18 wh-6 1610.15 灰黑色泥岩 0.01 0.24 428 0.25 wh-7 渭南8 1843.54 深灰色泥页岩 0.01 0.49 430 0.50 wh-8 1845.83 深灰色泥岩 0 0.03 431 0.03 wh-9 渭南9 1543.26 深灰色泥岩 0.01 0.16 431 0.17 表 8 固市凹陷张家坡组镜质体反射率分析结果
Table 8. Vitrinite reflectance of hydrocarbon source rock in Zhangjiapo Formation in Gushi Sag
样品号 井号 井深/m 岩性 测点数 Ro/% 最小值 最大值 平均值 wh-1 渭南5 1764.75 灰黑色泥岩 5 0.50 0.65 0.58 wh-2 渭南6 1687.85 灰黑色泥岩 5 0.49 0.62 0.54 wh-3 渭南11 1673.76 灰黑色泥岩 1 0.53 wh-4 1669.76 灰黑色泥岩 1 0.49 wh-5 渭南10 1479.16 灰黑色泥岩 1 0.59 wh-6 1610.15 灰黑色泥岩 1 0.48 wh-7 渭南8 1843.54 深灰色泥页岩 10 0.52 0.64 0.57 wh-8 1845.83 深灰色泥岩 1 0.60 wh-2 渭南9 1543.26 深灰色泥岩 8 0.50 0.68 0.59 -
[1] 陈万川, 陈家弦, 云琼英, 等. 汾渭盆地石油普查阶段地质成果报告[R]. 咸阳: 第三普查大队301分队, 1977.CHEN Wan-chuan, CHEN Jia-xuan, YUN Qiong-ying, et al. Petroleum reconnaissance report for the Fenwei Basin[R]. Xianyang: No. 301 Branch of the Third Exploration Group, 1977. [2] 杨申镳, 张肖兰, 王雪吾, 等.水溶性天然气勘探与开发[M].山东:石油大学出版社, 1997:1~142.YANG Shen-shu, ZHANG Xiao-lan, WANG Xue-wu, et al. Water soluble gas exploration and development[M].Shandong: University of Petroleum Press, 1997:1~142. [3] 戴金星.天然气碳氢同位素特征和各类天然气鉴别[J].天然气地球科学, 1993, 4(2/3):1~40. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX1993Z1000.htmDAI Jin-xing. Carbon and hydrogen isotopic characteristics of natural gas and identification of types of natural gas[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 1993, 4(2/3): 1~40. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX1993Z1000.htm [4] 张景廉.论石油的无机成因[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2001:1~305.ZHANG Jing-lian. On inorganic origin of petroleum[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2001: 1~305. [5] 何家雄. 中国东部及近海陆架盆地CO2成因及运聚规律与有利成藏富集区预测[D]. 广州: 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所, 2007: 21.HE Jia-xiong. Genesis, migration and accumulation of CO2 in the offshore shelf basins in eastern China and prediction of favorable concentration area[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry of China Academy of Science, 2007: 21. [5] 刚文哲, 高岗, 郝石生, 等.论乙烷碳同位素在天然气成因类型研究中的应用[J].石油实验地质, 1997, 19(2):164~167. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199702164GANG Wen-zhe, GAO Gang, HAO Shi-sheng, et al. Carbon isotope of ethane applied in the analyses of genetic types of natural gas [J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 1997, 19(2): 164~167. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199702164 [6] 张福礼, 孙启邦. 固市凹陷张家坡组生物气及资源定量评价[R]. 咸阳: 第三普查大队, 2013.ZHANG Fu-li, SUN Qi-bang. Biogas in the Zhangjiapo Formation in Gushi sag and its quantitative evaluation[R]. Xianyang: The Third Exploration Brigade, 2013. [7] 权新昌.渭河盆地断裂构造研究[J].中国煤田地质, 2005, 17(3):1~8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT200503001.htmQUAN Xin-chang. Weihe basin faulted structure study[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2005, 17(3): 1~8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT200503001.htm [8] 李玉宏, 卢进才, 李金超, 等.渭河盆地天然气成因特征及其意义[J].西安石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2011, 26(5):11~16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201105005.htmLI Yu-hong, LU Jin-cai, LI Jin-chao, et al. Genesis characteristics and significance of the natural gas in Weihe Basin [J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University: Natural Science Edition, 2011, 26(5): 11~16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201105005.htm [9] 王景明.渭河地堑断裂构造研究[J].地质论评, 1984, 30(3):217~223. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP198403002.htmWANG Jing-ming. A study on the tectonics of the Weihe River Graben [J]. Geological Review, 1984, 30(3): 217~223. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP198403002.htm -





 下载:
下载: