THE EFFECT OF 1668 TANCHENG M8.5 EARTHQUAKE ON THE SEISMIC ACTIVITY OF THE VICINITY FROM COSEISMIC AND POSTSEISMIC DEFORMATION
-
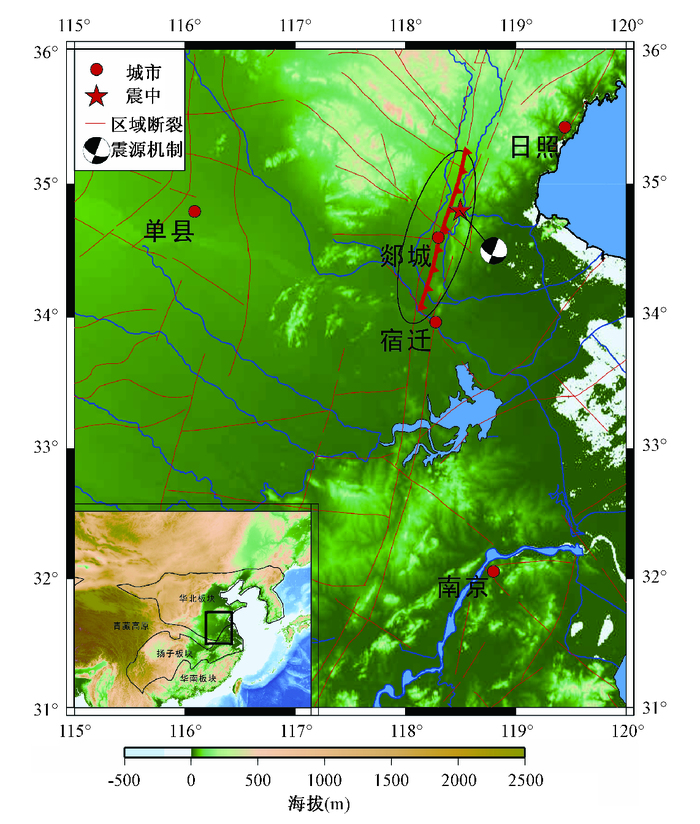
摘要: 以山东郯城1668年大地震为例,以前人地表地质调查结果为约束,利用弹性位错理论初步获取了该地震的同震破裂模型;在此基础上,基于粘弹性分层模型分析了该地震的同震和震后形变,同时以主震断层为接收断层计算了库仑应力分布,进一步讨论了地幔不同粘滞性系数对地表形变和库仑应力变化的影响。计算结果显示,该地震是一个右旋走滑为主兼有一定逆冲性质的地震,其同震位移巨大,能量释放较彻底;同震破裂造成震中郯城县西北、东北和南部部分断层库仑应力增加,而震后形变使得这些断层库仑应力进一步增加,在单县、宿迁和日照等地,地震后350 a库仑应力变化量达到+1bar-+1MPa量级;地幔粘滞性系数不同,形变量和库仑应力变化达到稳定的时间不同,但最终趋于稳定的数值基本一致。Abstract: The Tanlu fault zone is an important active fault zone in east China. Many great earthquakes have occurred along it. The 1668 M8.5 Tancheng earthquake is the largest recorded event. With the constraint of surface rupture, we get a coseismic rupture model based on the elastic dislocation theory. In addition, we calculate the coseismic, postseismic deformation and Coulomb stress change of this earthquake with a viscoelastic multilayered model. The results show that the rupture fault of the earthquake is adextral strike-slip fault, which has slight thrust. The coseismic displacement of this event is very large. The accumulated energy is released thoroughly. The coseismic rupture of the 1668 Tancheng earthquake increased the Coulomb stress on the northwest, northeast and southeast faults of Tanlu fault zone. The Coulomb stress increases further due to the postseismic deformation. After 350 years of the Tancheng earthquake, the Coulomb stress changes in Shanxian, Suqian and Rizhaoget to +1bar-+1MPa. When the mantle is imposed different viscosities, the duration time which the deformation and Coulomb changes become stable will be different. However, the stable values of them are generally same.
-
表 1 分层模型及参数
Table 1. Parameters of the multilayer crustal model
序号 深度范围/km P波速度/(km·s-1) S波速度/(km·s-1) 密度/(kg·m-3) 粘滞系数/(Pa·s) 1 0~10 5.00 2.89 2100 ∞ 2 10~15 6.16 3.56 2500 ∞ 3 15~20 6.20 3.58 2800 ∞ 4 20~30 6.35 3.67 2850 ∞ 5 30~35 6.32 3.66 2950 1.0×1018 6 35~40 6.50 3.76 3000 1.0×1018 7 >40 8.18 4.73 3100 1.0×1018 -
[1] 马玉香, 钟普裕.1668年山东郯城8.5级地震综述[J].国际地震动态, 2009, (2):9~18.MA Yu-xiang, ZHONG Pu-yu.Summarization of the Tancheng Earthquake with 8.5 in 1668[J]. Recent developments in World Seismology, 2009, (2):9~18. [2] 高维明, 郑朗荪, 李家灵, 等.1668年郯城8.5级地震的发震构造[J].中国地震, 1988, 4(3):9~15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD198803002.htmGAO Wei-ming, ZHENG Lang-sun, LI Jia-ling.The triggering structure of the Ms8.5 earthquake of Tan Cheng in 1668[J].Earthquake Research in China, 1988, 4(3):9~15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD198803002.htm [3] 鞠林雪. 1668年郯城8. 5级地震发震断层构造特征与应力场分析[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2012. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKX201203021.htmJU Lin-xue.The research on the structure of triggring faults and stress field in 1668:The Tancheng earthquake[D]. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology, 2012. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKX201203021.htm [4] 李清河, 张元生, 鲍海英, 等.据地壳速度结构推测1668年山东郯城8.5级大地震震中[J].中国地震, 2014, 30(1):30~42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD201401005.htmLI Qing-he, ZHANG Yuan-sheng, BAO Hai-ying, et al. Crust veolcity structure of the epicenter of M8.5 earthquake at Tancheng, Shandong, China, in 1668[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 2014, 30(1):30~42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD201401005.htm [5] 李永红, 胡新亮, 许萍, 等.以双差定位方法对郯城8.5级地震震中附近现代小震重新定位[J].西北地震学报, 2011, 33(1):71~75. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ201101014.htmLI Yong-hong, HU Xin-liang, XU Ping, et al. Relocation of modern small earthquakes near the epicenter of Tancheng 8.5 earthquake using the Double Difference Earthquaake Location Algorithm[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 2011, 33(1):71~75. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ201101014.htm [6] 王华林, 耿杰.1668年郯城8.5级地震震源参数及其讨论[J].地震学刊, 1996, (4):27~33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXK604.005.htmWANG Hua-lin, GENG Jie. Discussion about focus parameters of Tancheng earthquake of Ms8.5 in 1668[J]. Journal of Seismology, 1996, (4):27~33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXK604.005.htm [7] 王华林.1668年郯城8.5级地震断裂的全新世滑动速率, 古地震和强震复发周期[J].西北地震学报, 1995, 17(4):1~12, 22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYJ602.012.htmWANG Hua-lin. Holocene displacement rate, paleoearthquakes and recurrence intervals of strong earthquakes along the 1668 Tancheng Earthquake (Ms=8.5) Fault[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 1995, 17(4):1~12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYJ602.012.htm [8] 王启鸣.三维有限元方法估算郯城8.5级大震重复周期[J].中国地震, 1988, 4(3):54~58. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD198803009.htmWANG Qi-ming. The calculation of recurrence intervals of the Ms8.5 earthquake in Tancheng by the three dimension finite element method[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 1988, 4(3):54~58. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD198803009.htm [9] 万永革, 吴忠良, 周公威, 等.地震应力触发研究[J].地震学报, 2002, 24(5):533~551. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXB200205010.htmWAN Yong-ge, WU Zhong-liang, Zhou Gong-wei, et al. Research on seismic stress triggering[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 2002, 24(5):533~551. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXB200205010.htm [10] 魏光兴.郯庐带地震活动性研究[M].北京:地震出版社, 1993.WEI Guang-xing. Research on the seismic activity of Tanlu earthquake belt[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 1993. [11] Okada Y. Surface deformation to shear and tensile faults in a halfspace[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1985, 75(4):1135~1154. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.484.8168 [12] Pollitz F F. Postseismic relaxation theory on a spherical Earth[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1992, 82(1):422~453. http://www.bssaonline.org/content/82/1/422.abstract [13] 付广裕, 孙文科.球体位错理论计算程序的总体设计与具体实现[J].地震, 2012, 32(2):73~87. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZN201202010.htmFU Guang-yu, SUN Wen-ke. Overall design and special strctures of the computing codes for coseismic deformations on a layered sperical earth[J]. Earthquake, 2012, 32(2):73~87. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZN201202010.htm [14] 石耀霖.关于应力触发和应力影概念在地震预报中应用的一些思考[J].地震, 2001, 21(3):1~7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZN200103000.htmSHI Yao-lin. Sress triggers and stress shadows How to apply these concepts to earthquake prediction[J]. Earthquake, 2001, 21(3):1~7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZN200103000.htm [15] Wang R, Lorenzo-Martín F, Roth F. PSGRN/PSCMP:A new code for calculating co-and post-seismic deformation, geoid and gravity changes based on the viscoelastic-gravitational dislocation theory[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2006, 32:527~541. doi: 10.1007/s11589-013-0001-8 [16] Freed A M. Earthquake triggering by static, dynamic, and postseismic stress transfer[J]. Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 2005, 33:335~367. http://www.oalib.com/references/20004531 [17] 孙玉军, 董树文, 范桃园, 等.从同震和震后形变分析日本东北Mw 9.0级大地震对近场地震活动性的影响[J].地球物理学进展, 2013, 28(3):1131~1139. doi: 10.6038/pg20130304SUN Yu-jun, DONG Shu-wen, FAN Tao-yuan, et al. The effect of Tohotu Mw 9.0 earthquake on the near field seismic activity from coseismic and postseismic deformation[J]. Progress in Geophys, 2013, 28(3):1131~1139. doi: 10.6038/pg20130304 [18] 江国焰. 利用库仑破裂准则评估活动断层地震危险性[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2013.JIANG Guo-yan. Assessing the seismic hazards of active faults using Coulomb Failure Criterion[D]. Wuhan:Wuhan University, 2013. [19] Okada Y. Internal deformation due to shear and tensile fault in a half space[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1992, 92:1018~1040. http://www.oalib.com/references/18999619 [20] King G C P, Stein R S, Lin J. Static stress changes and the triggering of earthquakes[J]. Bull.seismol.soc.amer, 1994, 84:935~953. http://www.academia.edu/3661471/STATIC_STRESS_CHANGES_AND_THE_TRIGGERING_OF_EARTHQUAKES [21] 周翠英, 刁桂苓, 耿杰, 等.1668年郯城大地震震源断层三维特征反演[J].地球物理学进展, 2013, 28(6):2814~2824. doi: 10.6038/pg20130602ZHOU Cui-ying, DIAO Gui-ling, GENG jie, et al. 3-D characteristics inversion of hypocenter fault-plane of the 1668 Tancheng great earthquake[J]. Progress in Geophys, 2013, 28(6):2814~2824. doi: 10.6038/pg20130602 -





 下载:
下载: