THE PRINCIPLE OF GEOCHEMICAL ANOMALY DELINEATION BASED ON THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOCHEMICAL EXPLORATION DATA METHOD AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE
-
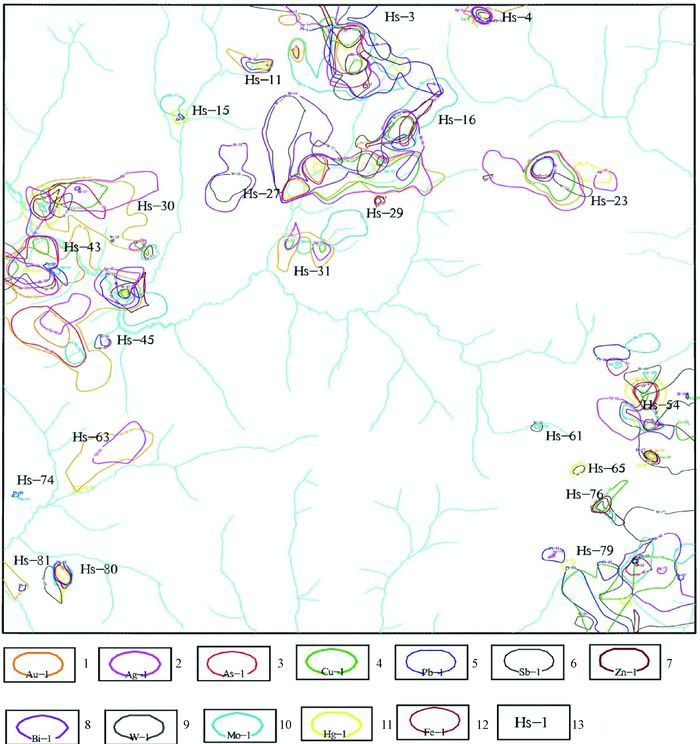
摘要: 以往传统的化探异常圈定,均采用二维化探数据计算方法,这种数据处理方法在勘查地球化学行业已应用多年,到目前为止也仍然是生产中勘查地球化学规范执行标准。但在采样和景观差异较大的前提下,这种数据处理方法在找矿方面尚有不足之处。为弥补这些不足,我们提出了一种新的化探数据处理方法,即增加高程要素的三维数据处理成图方法。通过试验证明该方法对综合异常的圈定效果较好,异常物质流向更为清楚。三维数据处理法圈定的范围小、浓集中心明显,有利于准确布置地表探矿工程,并可以节约勘查成本,提高找矿命中率。在地球化学环境分析和地球化学找矿评价方面具有重要的现实意义。
-
关键词:
- 三维数据处理成图方法 /
- 化探数据计算方法 /
- 化探异常圈定 /
- 浓集中心
Abstract: Two-dimensional geochemical data calculation method, as the traditional method in geochemical exploration anomaly delineation, has been used in the geochemical exploration industry for many years. However, this data processing method has some deficiencies in the prospecting and prospecting area in the premise of sampling and landscape differences. In order to compensate for these shortcomings, three-dimensional data processing and mapping method is proposed, which added elevation elements. It is proved by experiments that this method is better for comprehensive anomaly delineation and the abnormal material flows are clearer. The delineation range of the 3D data processing and mapping method is relatively small with obvious concentration center, which is conducive to the accurate arrangement of surface exploration engineering, saving prospecting cost and improving the accuracy of prospecting. -
表 1 某些金属离子的水解pH值
Table 1. Hydrolyzed pH values of certain metal ions
元素 Fe3+ Zn3+ Sn2+ Ce4+ Hg+ In3+ Th4+ Al3+ U4+ Cr3+ Cu3+ Fe2+ Be2+ Pb2+ pH 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.7 3.0 3.4 3.5 4.1 4.2 5.3 5.3 5.5 5.7 6.0 元素 Cd2+ Ni2+ Cu2+ Y3+ Sm3+ Zn2+ Nd3+ Pb3+ Hg2+ Ce3+ La3+ Ag+ Mn2+ Mg2+ pH 6.7 6.7 6.8 6.8 6.8 7.0 7.0 7.1 7.3 7.4 8.4 7.5~8.0 8.5~8.8 10.5 -
[1] 熊光强, 赵洪涛, 刘敏, 等.内蒙古四子王旗黑脑包岩体年代学与地球化学特征及其构造演化[J].地质力学学报, 2013, 19(2): 162~177. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130206&flag=1XIONG Guangqiang, ZHAO Hongtao, LIU Min, et al.Geochronology and geochemistry of the Heinaobao pluton in Siziwangqi, Inner Mongolia and its tectonic evolution[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2013, 19(2): 162~177. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130206&flag=1 [2] 丁文君, 陈正乐, 陈柏林, 等.河北迁安杏山铁矿床地球化学特征及其对成矿物质来源的指示[J].地质力学学报, 2009, 15(4): 363~373. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090405&flag=1DING Wenjun, CHEN Zhengle, CHEN Bolin, et al. Geochemical characters of band iron formations from Xingshan iron deposit in Qian'an area, Hebei Province:implication for their origin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 15(4): 363~373. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090405&flag=1 [3] 许淑梅. 长江口外缺氧区及其邻近海域氧化还原敏感性元素的分布规律及环境指示意义[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2005. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10423-2005140382.htmXU Shumei. The distribution and environmental significance of redox sensitive elements off the Changjiang Estuary hypoxia zone and its contiguous sea area[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2005. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10423-2005140382.htm [4] 穆振永. 判定物质氧化性强弱的十种方法[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2005. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/jt/Magazine?magazineId=jxygl&yearIssue=2004_6MU Zhenyong.Ten methods for determining the oxidation resistance of materials[D]. Qingdao:Ocean University of China, 2005. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/jt/Magazine?magazineId=jxygl&yearIssue=2004_6 [5] 王为, 许刘兵, 林志海, 等.海岸壶穴与风化坑的成因差异及证据——以广东沙扒镇和庙湾岛海岸为例[J].第四纪研究, 2013, 33(5): 1016~1033. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201305019.htmWANG Wei, XU Liubing, LIN Zhihai, et al. Evidences for the origin of coastal weathering pits and marine potholes on the coast of Guangdong——a case study in Shapa Town and Miaowan Island, China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33(5): 1016~1033. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201305019.htm [6] 薛传东, 刘星, 亓春英, 等.滇池近代沉积物的元素地球化学特征及其环境意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2007, 26(6): 582~590. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200706019.htmXUE Chuandong, LIU Xing, QI Chunying, et al. Element geochemical characteristics of modern sediments in the Dianchi Lake, Kunming, and their environmental significance[J]. ActaPetrologicaetMineralogica, 2007, 26(6): 582~590. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200706019.htm [7] 郑国东, 付碧宏.断裂带构造地球化学研究[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(S1): 436~437. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-2005107171.htmZHENG Guodong, FU Bihong. Tectonic geochemistry of fault zone[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2008, 27(S1): 436~437. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-2005107171.htm [8] 胡丰产.新疆某铜矿区化探数据异常下限确定方法对比研究[J].矿业工程, 2012, 10(2): 4~6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWKS201202004.htmHU Fengchan. Geochemical data abnormality lower-limit determining methods and their comparison for a copper ore deposit in Xinjiang[J]. Mining Engineering, 2012, 10(2): 4~6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWKS201202004.htm [9] 程小昆. 广西珊瑚钨锡矿床地球化学异常特征及找矿预测[D]. 桂林: 桂林理工大学, 2009. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1479501CHENG Xiaokun.Geochemical anomalies and prospecting prediction of the coral tungsten tin deposit, Guangxi[D].Guilin:Guilin University of Technology, 2009. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1479501 [10] 李艳芳, 王加晶, 许丹妮.黑龙江省生物多样性评价[J].环境科学与管理, 2012, 37(12): 153~157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2012.12.038LI Yanfang, WANG Jiajing, XU Danni. Evaluation on biodiversity in Heilongjiang province[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2012, 37(12): 153~157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2012.12.038 [11] 杨少平, 焦保权, 孙忠军, 等. 森林沼泽景观区区域化探异常追踪方法技术[A]. 第八届全国勘察地球化学学术讨论会论文集[C]. 昆明: 中国地质学会, 2009. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Conference?id=Conference_6848449YANG Shaoping, JIAO Baoquan, SUN Zhongjun, et al. Regional forest swamp landscape area geochemical anomaly tracing method[A]. The National Survey and Geochemical Symposium[C].Kunming: Geological Society of China, 2009. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Conference?id=Conference_6848449 [12] 高珍权. 东天山铜金多金属成矿学及找矿系统工程学[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2002. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD902.006.htmGAO Zhenquan. Copper-gold polymetalmetallogenyand prospecting systematic engineering of East Tianshan, Xinjiang, China[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2002. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD902.006.htm [13] 薛水根.地球化学异常的查证方法及效果[J].江苏地质, 2002, 26(1): 13~18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ200201004.htmXUE Shuigen.Determination methods and effect for geochemical anomaly[J]. JiangsuGeology, 2002, 26(1): 13~18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ200201004.htm [14] 王学求, 孙宏伟, 迟清华, 等.地球化学异常再现性与可对比性[J].中国地质, 2005, 32(1): 135~140. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200501018.htmWANG Xueqiu, SUN Hongwei, CHI Qinghua, et al. Reproducibility and Comparison of geochemical anomalies[J].Geology in China, 2005, 32(1): 135~140. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200501018.htm [15] 姚涛, 陈守余, 廖阮颖子.地球化学异常下限不同确定方法及合理性探讨[J].地质找矿论丛, 2011, 26(1): 96~101. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201101019.htmYAO Tao, CHEN Shouyu, LIAORUAN Yingzi.Methods for determination of the lower geochemical anomaly limit and the rationality discussion[J].Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2011, 26(1): 96~101. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201101019.htm -





 下载:
下载: