MAGNETOSTRATIGRAPHY AND HEAVY MINERALS RECORDS OF TZK9 CORE IN SUBEI BASIN
-
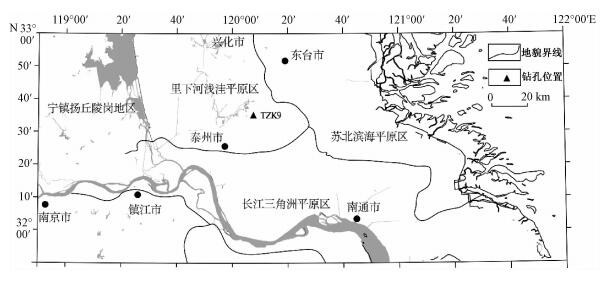
摘要: 通过对苏北盆地TZK9孔的磁性地层和重矿物组合分析,探索了该地区晚上新世以来沉积物的物源变化特征。古地磁结果显示,TZK9孔的M/G界线位于250.3 m,B/M界线位于78.5 m,并很好记录了2次正极性亚时(Jaramillo和Olduvai),分别位于129.0~150.2 m与172.55~192.80 m,通过沉积速率外推获得该钻孔的底界年龄约为3.0 Ma。对TZK9孔重矿物组合、特征指数进行分析,并结合淮河及长江下游的重矿物组合特征,揭示在距今3.0~2.6 Ma其沉积物主要来自于淮河流域。而相比晚上新世,第四纪的磷灰石、锆石、金红石、电气石含量增加,表明该地区开始受到了长江流域的影响,而第四纪以来重矿物特征指数(ZTR)逐渐增大可能主要受控于全球气候变化。Abstract: The core TZK9 is located in the northeast Taizhou city (N 32°35', E120°6'), the south of Subei Basin. The main kinds of lithology in the core are clay and silty clay. Some silt, sand and coarse sand are also found. In this study, 382 samples at 30~60 cm intervals were taken for paleomagnetic measurements, and 17 samples for heavy minerals test. Magnetostratigraphic results show that, the M/G and B/M are found at the depth of 250.3 and 78.5 m, respectively. Extrapolation with accumulation rates suggest that the basal ages for sediments in this core is about 3.0 Ma. ATi index was from 50.97 to 100, while GZI index was 11.48 to 77.81, indicating that the source was metamorphic and igneous rocks. During 3.0~2.6 Ma, the main heavy minerals of TZK9 core were ilmenite, epidote, magnetite, garnet and zircon. Comparing the heavy minerals of the TZK9 core with Huai river and Yangtze river, it shows that the sediment came from the Huai river during this time. During 2.6~0 Ma, the main heavy minerals are ilmenite, epidote, zircon, apatite, garnet and magnetite. The content of zircon, apatite, tourmaline, rutile increases compared to the previous period, and it indicates that the Yangtze river begin to influence this area in this period. And the ZTR index gradually increased since 2.6 Ma, which may be related to the change of global climate.
-
Key words:
- Late Pliocene /
- magnetic stratigraphy /
- heavy minerals /
- the Subei Basin
-
表 1 TZK9孔中主要重矿物含量(%)的垂向变化特征
Table 1. Variations of main heavy minerals content in core TZK9
深度/m 年龄/Ma 锆石 磷灰石 金红石 白钛石 石榴子石 电气石 赤褐铁矿 榍石 6.4 0.06 9.52 1.22 4.41 1.22 3.64 0.38 1.15 1.16 16.6 0.16 6.73 3.73 1.00 0.59 5.11 2.64 3.79 0.09 29.6 0.29 5.11 7.54 3.23 0.49 2.18 3.57 2.98 0.10 37.8 0.38 3.32 5.25 0.72 0.09 1.81 1.09 2.18 0.25 56.0 0.56 10.33 6.46 2.13 2.13 2.94 2.01 1.70 2.13 73.0 0.73 8.33 1.26 2.36 0.38 5.74 1.21 2.42 1.38 89.1 0.82 7.00 10.30 2.47 0.58 2.38 0.85 4.42 0.88 110.3 0.91 5.69 6.69 4.31 0.88 2.44 1.87 4.87 0.69 128.6 0.99 6.57 2.11 1.14 0.59 3.97 0.76 4.74 0.91 142.7 1.04 3.46 1.81 0.47 1.23 7.52 0.41 10.98 3.09 169.2 1.67 10.34 7.68 1.61 1.52 2.56 0.67 1.75 0.19 204.2 2.07 7.34 3.94 2.88 1.58 0.95 1.11 4.44 0.99 223.7 2.29 5.30 1.39 2.47 1.53 1.35 1.35 4.06 0.82 249.7 2.57 7.28 3.93 1.42 0.76 2.90 1.99 3.26 0.41 253.3 2.61 3.01 2.06 0.19 0.55 4.54 0.95 2.27 1.55 273.4 2.84 5.13 1.75 0.48 1.30 4.38 1.01 5.39 1.27 285.5 2.97 1.96 0.34 0.35 0.32 6.86 0.00 6.86 0.17 表 2 TZK9孔中主要重矿物含量及特征参数的变化
Table 2. Variations of main heavy minerals content and mineral indices in core TZK9
深度/m 钛铁矿 磁铁矿 绿帘石 辉石 角闪石 ATI GZI ZTR 风化指数 6.4 43.68 0.00 20.50 2.87 0.00 76.15 27.64 14.32 0.35 16.6 25.68 3.29 21.40 11.69 0.00 58.58 43.15 10.36 0.63 29.6 32.34 0.00 29.96 3.18 0.00 67.86 29.92 11.91 0.58 37.8 25.51 14.25 17.38 12.85 0.00 82.83 35.24 5.13 0.56 56.0 30.98 0.23 26.18 1.08 2.17 76.22 22.18 14.47 0.48 73.0 38.24 14.38 8.16 3.02 4.08 50.97 40.82 11.89 0.20 89.1 26.90 8.15 24.86 1.19 0.00 92.38 25.38 10.32 0.41 110.3 35.22 2.75 23.04 0.00 1.69 78.12 29.97 11.88 0.38 128.6 33.00 11.15 20.48 1.07 4.58 73.42 37.70 8.47 0.40 142.7 28.26 8.47 19.32 2.24 3.25 81.69 68.47 4.34 0.38 169.2 27.57 2.00 24.07 0.94 0.54 91.94 19.82 12.63 0.46 204.2 31.55 4.70 20.77 0.00 0.32 78.05 11.48 11.34 0.35 223.7 40.14 0.00 31.33 0.00 0.85 50.62 20.36 9.12 0.55 249.7 37.70 4.03 26.64 0.00 0.36 66.36 28.48 10.70 0.42 253.3 32.56 10.75 27.26 1.14 3.60 68.48 60.19 4.14 0.55 273.4 35.52 4.71 28.11 0.34 0.67 63.43 46.02 6.63 0.48 285.5 51.73 5.83 16.13 0.00 0.00 100.00 77.81 2.31 0.22 -
[1] 包汉勇, 郭战峰, 黄亚平, 等.苏北盆地晚白垩世以来的构造热演化[J].高校地质学报, 2013, 19(4):574~579. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201304002.htmBAO Han-yong, GUO Zhan-feng, HUANG Ya-ping, et al. Tectonic-thermal evolution of the Subei Basin since the Late Cretaceous[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2013, 19(4):574~579. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201304002.htm [2] 陈友飞, 严钦尚, 许世远.苏北盆地沉积环境演变及其构造背景[J].地质科学, 1993, 28(2):151~160. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199302006.htmCHEN You-fei, YAN Qin-shang, XU Shi-yuan. Evolution of the sedimentary environments in north Jiangsu Basin and its tectonic setting[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinaca, 1993, 28(2):151~160. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199302006.htm [3] 邱海峻, 许志琴, 乔德武.苏北盆地构造演化研究进展[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(9/10):1117~1120. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2006Z2022.htmQIU Hai-jun, XU Zhi-qin, QIAO De-wu. Progress in the study of tectonic evolution of the Subei Basin, Jiangsu, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(9/10):1117~1120. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2006Z2022.htm [4] 张喜林, 朱筱敏, 钟大康, 等.苏北盆地高邮凹陷古近系戴南组沉积相及其对隐蔽油气藏的控制[J].古地理学报, 2005, 7(2):207~218. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200502006.htmZHANG Xi-lin, ZHU Xiao-min, ZHONG Da-kang, et al. Sedimentary facies and its controlling on subtle oil and gas reservoirs of the Dainan Formation of Paleogene in Gaoyou sag, Subei Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2005, 7(2):207~218. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200502006.htm [5] 钱基.苏北盆地油气田的形成与分布特征[J].石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2000, 24(4):21~25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200004004.htmQIAN Ji. Formation and distribution of oil and gas fields in Subei Basin[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 2000, 24(4):21~25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200004004.htm [6] 高丽坤, 林春明, 姚玉来, 等.苏北盆地高邮凹陷古近系戴南组沉积相及沉积演化[J].沉积学报, 2010, 28(4):706~716. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201004007.htmGAO Li-kun, LIN Chun-ming, YAO Yu-lai, et al. Sedimentary facies and evolution of Paleogene Dainan Formation in Gaoyou sag, Subei Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(4):706~716. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201004007.htm [7] 杨守业, 李从先, 张家强.苏北滨海平原全新世沉积物物源研究——元素地球化学与重矿物方法比较[J].沉积学报, 1999, 17(3):458~463. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199903019.htmYANG Shou-ye, LI Cong-xian, ZHANG Jia-qiang. Provenance study of holicene sediments in subei coastal Plain-Comparison between elemental geochemistry and heavy mineral methods[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1999, 17(3):458~463. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199903019.htm [8] 冯金顺, 孙磊, 葛云, 等.江苏省里下河(兴化-泰州)地区浅表沉积物特征及古地理环境演变[J].江苏地质, 2007, 31(2):101~107. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ200702005.htmFENG Jin-shun, SUN Lei, GE Yun, et al. On shallow sediment properties and paleogeographic evolvement in Xinghua-Taizhou, Jiangsu[J]. Jiangsu Geology, 2007, 31(2):101~107. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ200702005.htm [9] 舒强, 李才林, 赵志军, 等.苏北盆地浅钻沉积物磁化率与粒度记录的末次冰消期以来的环境变化[J].沉积学报, 2009, 27(1):111~117. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200901016.htmSHU Qiang, LI Cai-lin, ZHAO Zhi-jun, et al. The records of mass susceptibility and grain size for climate changes in Subei Basin during the last deglaciation[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(1):111~117. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200901016.htm [10] 舒强, 张茂恒, 赵志军, 等.苏北盆地XH-1钻孔晚新生代沉积记录特征及其与长江贯通时间的关联[J].地层学杂志, 2008, 32(3):308~314. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ200803012.htmSHU Qiang, ZHANG Mao-heng, ZHAO Zhi-jun, et al. Sedimentary record from the XH-1 core in north Jiangsu Basin and its implication on the Yangtze river run-through time[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2008, 32(3):308~314. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ200803012.htm [11] Garzanti E, Andò S. Heavy mineral concentration in modern sands:implications for provenance interpretation[J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 2007, 58:517~545. doi: 10.1016/S0070-4571(07)58020-9 [12] Garzanti E, Andò S, Vezzoli G. Settling equivalence of detrital minerals and grain-size dependence of sediment composition[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 273(1):138~151. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X0800397X [13] Heroy D C, Kuehl S A, Goodbred S L. Mineralogy of the Ganges and Brahmaputra Rivers:implications for river switching and Late Quaternary climate change[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2003, 155(3):343~359. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0037073802001860 [14] Ogg J G, Smith A G. The geomagnetic polarity time scale[M]. Massachusetts:Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, 2004. [15] Morton A C, Hallsworth C R. Processes controlling the composition of heavy mineral assemblages in sandstones[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1999, 124(1):3~29. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0037073898001183 [16] 赵红格, 刘池洋.物源分析方法及研究进展[J].沉积学报, 2003, 21(3):409~415. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200303006.htmZHAO Hong-ge, LIU Chi-yang. Approaches and prospect of provenance analysis[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinaca, 2003, 21(3):409~415. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200303006.htm [17] Morton A, Hurst A. Correlation of sandstones using heavy minerals:an example from the Statfjord Formation of the Snorre Field, northern North Sea[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1995, 89(1):3~22. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1995.089.01.02 [18] 和钟铧, 刘招君. 柴达木盆地北缘大煤沟剖面重矿物分析及其地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2001, 20(3): 279~284. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ200103011.htmHE Zhong-hua, LIU Zhao-jun, Guo Wei. The heavy mineral analysis and its geological significance of dameigou section in northern Caidam Basin[J]. World Geology, 2001, 20(3):279~284. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ200103011.htm [19] 陆洁民, 郭召杰, 赵泽辉, 等.新生代酒西盆地沉积特征及其与祁连山隆升关系的研究[J].高校地质学报, 2004, 10(1):50~61. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200401003.htmLU Jie-min, GUO Zhao-jie, ZHAO Ze-hui, et al. Cenozic sedimentation characteristics of Jiuxi Basin and uplift history of northern Qilian mountain[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2004, 10(1):50~61. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200401003.htm [20] 郑良烁. 苏北兴化2孔晚中新世以来重矿物物源示踪研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10319-1013333493.htmZHENG Liang-shuo. The provenance study of the heavy mineral of 2 core since the late Miocene, in Xinghua, Subei Basin[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Normal University, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10319-1013333493.htm [21] 王腊春, 陈晓玲, 储同庆.黄河、长江泥沙特性对比分析[J].地理研究, 1997, 16(4):71~79. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ704.009.htmWANG La-chun, CHEN Xiao-ling, CHU Tong-qing. A contrast analysis on the loads character of the Yangtze River and the Yellow River[J].Geographical Research, 1997, 16(4):71~79. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ704.009.htm [22] 江苏省地质矿产局.江苏省及上海市区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1984:1~857.Jiangsu Geology & Mineral Exploration Bureau. Regional geology of Jiangsu Province and Shanghai[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1984:1~857. [23] Zachos J C, Dickens G R, Zeebe R E. An early Cenozoic perspective on greenhouse warming and carbon-cycle dynamics[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7176):279~283. doi: 10.1038/nature06588 [24] De Boer B, Van de Wal R S W, Bintanja R, et al. Cenozoic global ice-volume and temperature simulations with 1-D ice-sheet models forced by benthic δ18O records[J]. Annals of Glaciology, 2010, 51(55):23~33. doi: 10.3189/172756410791392736 [25] Yancheva G, Nowaczyk N R, Mingram J, et al. Influence of the intertropical convergence zone on the East Asian monsoon[J]. Nature, 2007, 445(7123):74~77. doi: 10.1038/nature05431 [26] Wan S, Li A, Clift P D, et al. Development of the East Asian monsoon:mineralogical and sedimentologic records in the northern South China Sea since 20 Ma[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2007, 254(3):561~582. [27] Oppo D W, Sun Y. Amplitude and timing of sea-surface temperature change in the northern South China Sea:Dynamic link to the East Asian monsoon[J]. Geology, 2005, 33(10):785~788. doi: 10.1130/G21867.1 [28] Miller K G, Kominz M A, Browning J V, et al. The Phanerozoic record of global sea-level change[J]. Science, 2005, 310(5752):1293~1298. doi: 10.1126/science.1116412 [29] 王扬扬, 范代读.长江三角洲晚第四纪地层沉积物源特征及其对季风气候变化的响应[J].古地理学报, 2013, 15(6):853~863. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2013.06.070WANG Yang-yang, FAN Dai-du. Provenance characteristics of the late Quaternary in the Yangtze River Delta and its response to monsoon climate change[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2013, 15(6):853~863. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2013.06.070 -





 下载:
下载: