EXPLORATION OF GEOLOGICAL MAPPING METHODS ON COVERED AREA OF FAULTED BASIN IN THE NORTHWEST CHINA: A MAPPING PRACTICE IN THE BARKOL BASIN, XINJIANG
-
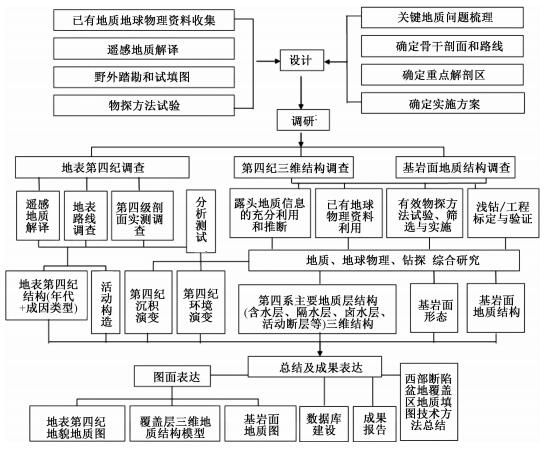
摘要: 西部断陷盆地覆盖区覆盖层与基岩面地质结构及盆山关系是当今覆盖区区域地质调查研究需解决的重点与难点。基于新疆巴里坤山间断陷盆地覆盖区地质填图试点实践,梳理出断陷盆地区地质填图的基本内容和填图目标;强调覆盖区地质调查必须针对需解决的关键地质问题,贯彻地表地质调查-地球物理探测-钻孔验证相结合的基本工作思路;确定出普适性的填图技术路线和围绕填图目标及基本内容的针对性填图方法组合;最后以巴里坤断陷盆地填图为例,从调研目标的确定到物探工作及方法组合优选和钻探布设,系统介绍了巴里坤断陷盆地覆盖区地质填图的方法体系,并最终落实到地质填图成果的体现,成为西部断陷盆地覆盖区地质填图的示范。Abstract: The geological texture of bedrock surface and overburden cover, and the basin-mountain coupling relationship are the key and difficult points in the regional geological survey of the covered areas of faulted-basin in the western China. In this paper we sorted out the mapping target and mapping contents to the covered region of faulted-basin based on the geological mapping practice in the Barkol basin, emphasized that the geological survey in the covered region must be aimed to solve the key geological problems and combination of surface geological survey, geophysical exploration and drilling verification, and determined the general mapping technical route and the combination of mapping methods. As an example, this paper also systematically introduced the mapping methods in the Barkol faulted-basin, including determining mapping targets and contents, optimizing geophysical exploration methods, and laying out drilling work.
-
表 1 测区钻探工作布设
Table 1. Disposition of drill holes in the work area
钻孔号 物探异常 钻探目的 ZK1 重力异常高 揭示第四系、古—新近系厚度、基岩面顶面深度和基岩岩性 ZK2 重力异常高 揭示第四系、古—新近系厚度、基岩面顶面深度和基岩岩性 ZK3 磁力高异常 揭示第四系、古—新近系厚度、基岩面顶面深度和基岩岩性; 磁异常成因 ZK4 重力异常中等 探索孔, 探索拗陷带第四系、古—新近系沉积结构和厚度 ZK5 C线大地电磁低阻层隆起区 揭示第四系、古—新近系厚度、基岩面顶面深度和基岩岩性; 验证标定低阻层隆起区 ZK6 重力异常低 探索孔, 探索第四系覆盖层厚度 -
[1] 李锦轶, 何国琦, 徐新, 等.新疆北部及邻区地壳构造格架及其形成过程的初步探讨[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(1):148~168. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200601020.htmLI Jin-Yi, HE Guo-qi, XU Xin, et al. Crustal tectonic framework of northern Xinjiang and adjacent regions and its formation[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2006, 80(1):148~168. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200601020.htm [2] 刘训.中国西北盆山地区中-新生代古地理及地壳构造演化[J].古地理学报, 2004, 6(4):448~458. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200404006.htmLIU Xun. Palaeogeography of the Meso-Cenozoic and crustal tectonic evolution of basin-mountain area in northwestern China[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2004, 6(4):448~458. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200404006.htm [3] 高洪雷, 刘红旭, 何建国, 等.东天山地区中-新生代隆升-剥露过程:来自磷灰石裂变径迹的证据[J].地学前缘, 2014, 21(1):249~260. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201401026.htmGAO Hong-lei, LIU Hong-xu, HE Jian-guo, et al. Mesozoic-Cenozoic uplift-exhumation history of East Tianshan:Evidence from apatite fission track[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(1):249~260. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201401026.htm [4] 舒良树, 郭召杰, 朱文斌, 等.天山地区碰撞后构造与盆山演化[J].高校地质学报, 2004, 10(3):393~404. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200403009.htmSHU Liang-shu, GUO Zhao-jie, ZHU Wen-bin, et al. Post-collision tectonism and basin-range evolution in the Tianshan belt[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2004, 10(3):393~404. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200403009.htm [5] 肖克炎, 邢树文, 丁建华, 等.全国重要固体矿产重点成矿区带划分与资源潜力特征[J].地球学报. 2016, 90(7):1269~1280. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201607001.htmXIAO Ke-yan, XING Shu-wen, DING Jian-hua, et al. Division of major mineralization belts of China's key solid mineral resources and their mineral resource potential[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 2016, 90(7):1269~1280. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201607001.htm [6] Allen M B, Windley B F, Zhang C, et al. Basin evolution within and adjacent to the Tienshan range, NW China[J]. Journal of the Geological Society. 1991, 148(2):369~378. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.148.2.0369 [7] 李锦轶, 王克卓, 李亚萍, 等.天山山脉地貌特征、地壳组成与地质演化[J].地质通报, 2006, 25():895~909. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200608001.htmLI Jin-yi, WANG Ke-zhuo, LI Ya-ping, et al. Geomorphological features, crustal composition and geological evolution of the Tianshan Mountains[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(8):895~909. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200608001.htm [8] 顾明光, 汪庆华, 卢成忠, 等.杭州城市平原区三维第四系结构调查研究方法探讨[J].中国地质, 2008, 35(2):232~238. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200802007.htmGU Ming-guang, WANG Qing-hua, LU Cheng-zhong, et al. Method for the investigation of 3D Quaternary structure in the plain region of Hangzhou City[J]. Geology in China, 2008, 35(2):232~238. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200802007.htm [9] Tian G, Steeples D W, Xia J H, et al. Multichannel analysis of surface wave method with the autojuggie[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2003, 23(3):243~247. [10] 李嘉, 郭成超, 王复明, 等.探地雷达应用概述[J].地球物理学进展. 2007, 22(2):629~637.LI Jia, GUO Cheng-chao, WANG Fu-ming, et al. The summary of the surface ground penetrating radar applied in subsurface investigation[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007, 22(2):629~637. [11] 王宗秀, 李涛, 张进, 等.博格达山链新生代抬升过程及意义[J].中国科学D辑:地球科学, 2008, 38(3):312~326. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200803005.htmWANG Zong-xiu, LI Tao, ZHANG Jin, et al. The uplift progresses of the Bogda Moutain and its significance[J]. Science in China Series D:Geoscience, 2008, 38(3):312~326. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200803005.htm -





 下载:
下载: