GEOPHYSICAL EXPLORATION AND SLIDING SURFACE DISCRIMINANT ANALYSIS OF LARGE-GIANT ANCIENT LANDSLIDES IN MINJIANG RIVER VALLEY, WESTERN SICHUAN
-
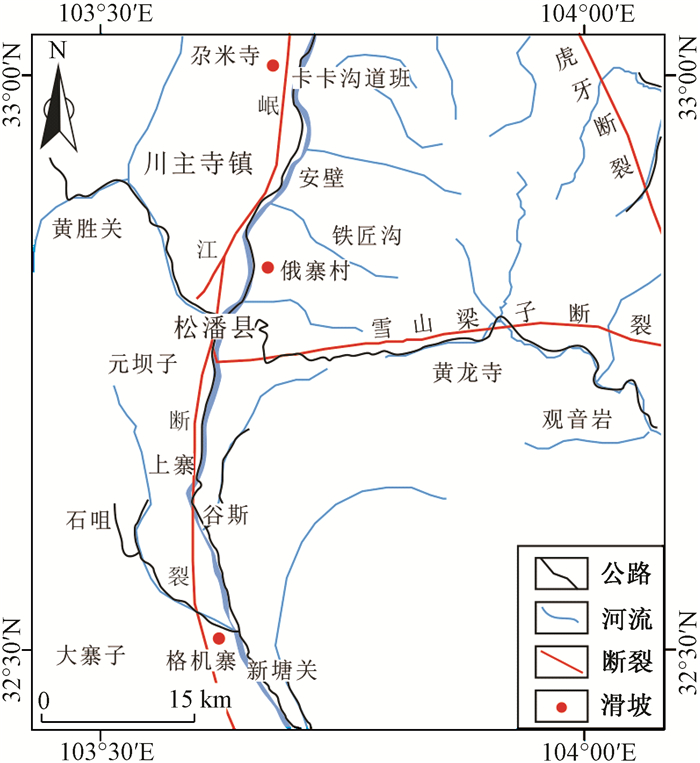
摘要: 在遥感解译、野外调查的基础上,采用高密度电法和电阻率测深法,并结合钻探对川西岷江河谷发育的尕米寺滑坡、俄寨村滑坡、格机寨滑坡等典型大型—巨型古滑坡的空间结构进行了勘探分析,有效确定了古滑坡的空间结构和滑带特征,并认为古滑坡的滑动面多具有高低阻相间的不稳定电性层,且滑坡前缘多位于不稳定电性层变薄收敛的地方。其中,俄寨村滑坡高低阻相间的不稳定电性层厚约0~45 m,为滑坡堆积层,古滑动面紧贴基岩面,滑动面平均埋深约30 m,弱风化基岩面埋深约5.6~61 m,强风化层厚约为3~12 m;尕米寺滑坡高低阻相间的不稳定电性层厚约2.5~43 m,为滑坡堆积层,沿剖面古滑动面平均埋深约35 m,在滑坡中部存在一圈闭的低阻异常体,推测为古河道,并与钻探结果相吻合,其埋深约56~96 m,弱风化基岩面埋深13.3~100 m,强风化及岩溶综合层厚一般约为5~20 m。基于古滑坡的地球物理勘探数据和解译结果,统计分析了川西岷江河谷地区大型—巨型古滑坡空间岩土体的地球物理物性参数,对指导该区滑坡调查分析具有重要的指导意义。Abstract: High density resistivity method and conventional resistivity sounding method are applied in the exploration analysis of the space structure of a series of typical large-giant ancient landslides such as the Gamisi landslide, the Ezhaicun landslide and the Gejizhai landslide. The survey results show that the slip surfaces of ancient landslides are unstable and have low resistance electrical layers. Also the fronts of the landslides are mostly located in the convergence area of the unstable electrically thin layers. Among them, the unstable electrical layer thickness of the Ezhaicun landslide of high and low resistance is about 0~45 m, and it is the landslide accumulation layer. The sliding surface is close to the bedrock surface with the burial depth of about 30 m. The burial depth of weakly weathered bedrock surface is about 5.6~61 m, and the thickness of strong weathered layer is about 3~12 m. The unstable electrical layer thickness of the Gamisi landslide of high and low resistance is about 2.5~43 m, and it is the landslide accumulation layer. The average burial depth of ancient sliding surface along the profile is about 35 m. In the middle of the landslide there is a circle of closed low resistance anomaly bodies, which are speculated as the paleo-channels with the burial depth of about 56~96 m. The burial depth of weakly weathered bedrock surface is about 13.3~100 m, and the thickness of strong weathered and karst complex layer is about 5~20 m. Based on the geophysical exploration data and interpretation results of ancient landslides, the geophysical parameters of spatial rock-soil bodies of large-giant ancient landslides in the Minjiang River Valley were analyzed, which are of great significance to guide the investigation and analysis of landslides in this area.
-
表 1 俄寨村滑坡物性参数
Table 1. Physical parameters of the Ezhaicun landslide
岩土名称 测量电阻率/(Ω·m) 推测位置 碎石土 75~5120 表层 砂砾石土 280~620 滑动面 炭质板岩 70~98 基岩 砂质板岩 191~351 基岩 表 2 尕米寺滑坡物性参数
Table 2. Physical parameters of the Gamisi landslide
岩土名称 测量电阻率/(Ω·m) 推测位置 碎块石土 1564~2726 表层 堆积层 500~1520 滑动面 灰岩 1934~2470 基岩 卵砾石 210~331 古河道 表 3 格机寨滑坡物性参数
Table 3. Physical parameters of the Gejizhai landslide
岩土名称 测量电阻率(Ω·m) 推测位置 黄土 75~320 表层 砂砾石土 500~1520 滑动面 炭质板岩 51~76 基岩 砂质板岩 80~205 基岩 注:表中电阻率是采用对称四极电测深装置采集到的数据统计得到的 -
[1] 黄润秋.中国西部地区典型岩质滑坡机理研究[J].地球科学进展, 2004, 19(3):443~450. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz200403016HUANG Runqiu. Mechanism of large scale landslides in western China[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2004, 19(3):443~450. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz200403016 [2] 刘凤民, 张立海, 刘海青, 等.中国地震次生地质灾害危险性评价[J].地质力学学报, 2006, 12(2):127~131. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060220&flag=1LIU Fengmin, ZHANG Lihai, LIU Haiqing, et al. Danger assessment of earthquake-induced geological disasters in China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2006, 12(2):127~131. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060220&flag=1 [3] 吕擎峰, 卜思敏, 王生新, 等.综合物探法在滑坡稳定性评价中的应用研究[J].岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(S1):142~147. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YTGC2015S1029.htmLV Qingfeng, BU Simin, WANG Shengxin, et al. Application of comprehensive geophysical prospecting method in stability evaluation of landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(S1):142~147. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YTGC2015S1029.htm [4] 郭秀军, 贾永刚, 黄潇雨, 等.利用高密度电阻率法确定滑坡面研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(10):1662~1669. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.10.014GUO Xiujun, JIA Yonggang, HUANG Xiaoyu, et al. Application of multi-electrodes electrical method to detection of slide-face position[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(10):1662~1669. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.10.014 [5] 李来喜.物探在多期次巨型滑坡勘察中的应用[J].工程地球物理学报, 2009, 6(5):575~579. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdqwlxb200905009LI Laixi. Application of geophysical prospecting to multiple and super landslide investigation[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2009, 6(5):575~579. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdqwlxb200905009 [6] 李金玺, 吴有亮, 韩翀, 等.采用高密度电法预测矿山堆积体滑坡面[J].辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 32(1):33~38. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lngcjsdxxb201301009LI Jinxi, WU Youliang, HAN Chong, et al. Prediction of dump landslide using resistivity imaging survey[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science), 2013, 32(1):33~38. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lngcjsdxxb201301009 [7] 熊晋, 王建松, 廖小平, 等.超高密度电法在山区公路滑坡勘探中的应用[J].铁道建筑, 2013, (8):97~100. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tdjz201308031XIONG Jin, WANG Jiansong, LIAO Xiaoping, et al. Application of multi-electrodes electrical method to landslide investigation in mountain area highway[J]. Railway Engineering, 2013, (8):97~100. (in Chinese) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tdjz201308031 [8] 张光保.褚家营巨型滑坡的高密度电法勘察及效果分析[J].地球物理学进展, 2012, 27(6):2716~2721. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.06.052ZHANG Guangbao. Exploration and effectiveness analysis of high-density resistivity method on Chujiaying giant landslide site[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2012, 27(6):2716~2721. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.06.052 [9] 齐信, 邵长生, 陈州丰, 等.江西瑞昌市横岗砖厂断裂探测及其活动特征研究[J].地质力学学报, 2016, 22(3):594~601. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160314&flag=1QI Xin, SHAO Changsheng, CHEN Zhoufeng, et al. Research on detection and activity of the Henggang brickyard fault in Ruichang City, Jiangxi Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 22(3):594~601. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160314&flag=1 [10] 徐兴倩, 苏立君, 梁双庆.地球物理方法探测滑坡体结构特征研究现状综述[J].地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(3):1449~1458. doi: 10.6038/pg20150361XU Xingqian, SU Lijun, LIANG Shuangqing. A review of geophysical detection methods of landslide structure characteristics[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(3):1449~1458. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/pg20150361 [11] Wang P, Zhang B, Qiu W L, et al. Soft-sediment deformation structures from the Diexi paleo-dammed lakes in the upper reaches of the Minjiang River, East Tibet[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 40(4):865~872. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.04.006 [12] 葛永刚, 庄建琦. 5.12汶川地震对岷江上游河道的影响——以都江堰-汶川河段为例[J].地质科技情报, 2009, 28(2):23~28. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb200902005GE Yonggang, ZHUANG Jianqi. River channel change of the upper of Minjiang River By 5.12 Wenchuan earthquake:A case study of the section of Dujiangyan-Wenchuan[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2009, 28(2):23~28. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb200902005 [13] 张斌, 王萍, 王建存.岷江上游堰塞湖沉积中软沉积物变形构造成因讨论[J].地震研究, 2011, 34(1):67~74. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzyj201101011ZHANG Bin, WANG Ping, WANG Jiancun. Discussion of the origin of the soft-sediment deformation structures in Paleo-dammed Lake sediments in the upper reaches of the Minjiang River[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 2011, 34(1):67~74. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzyj201101011 [14] 陈旭, 杜飞翔, 杜宇本, 等.岷江上游河谷重大重力地质灾害分布规律研究[J].铁道工程学报, 2015, 32(8):20~24. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tdgcxb201508004CHEN Xu, DU Feixiang, DU Yuben, et al. Research on the major gravity geological disasters distribution at upper Minjiang River valley[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2015, 32(8):20~24. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tdgcxb201508004 [15] 陈社发, 邓起东, 赵小麟, 等.龙门山中段推覆构造带及相关构造的演化历史和变形机制(一)[J].地震地质, 1994, 16(4):404~421. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzdz404.014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQCHEN Shefa, DENG Qidong, ZHAO Xiaolin, et al. The Latest Pleistocene faulting along the Canfangying segment of the fault zone along the northern margin of Yanqing basin[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1994, 16(4):404~421. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzdz404.014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [16] 赵小麟, 邓起东, 陈社发.龙门山逆断裂带中段的构造地貌学研究[J].地震地质, 1994, 16(4):422~428. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=1309608ZHAO Xiaolin, DENG Qidong, CHEN Shefa. Tectonic geomorphology of the central segment of the Longmenshan Thrust belt, western Sichuan, southwestern China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1994, 16(4):422~428. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=1309608 [17] 张会平, 杨农, 张岳桥, 等.岷江水系流域地貌特征及其构造指示意义[J].第四纪研究, 2006, 26(1):126~135. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj200601016ZHANG Huiping, YANG Nong, ZHANG Yueqiao, et al. Geomorphology of the Minjiang drainage system (Sichuan, China) and its structural implications[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(1):126~135. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj200601016 [18] 乔建平.岷江上游崩塌滑坡分布规律研究[J].长江流域资源与环境, 1994, 3(4):365~370. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb200501011QIAO Jianping. Study on the regularities governing the density distribution of collapses and landslides on the upper Min Jiang River Basin[J]. Resources and Environment in Yangtze Valley, 1994, 3(4):365~370. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb200501011 [19] 孟晖, 张岳桥, 杨农.青藏高原东缘中段地质灾害空间分布特征分析[J].中国地质, 2004, 31(2):218~224. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi200402016MENG Hui, ZHANG Yueqiao, YANG Nong. Analysis of the spatial distribution of geohazards along the middle segment of the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Geology in China, 2004, 31(2):218~224. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi200402016 [20] 朱德兵.工程地球物理方法技术研究现状综述[J].地球物理学进展, 2002, 17(1):163~170. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxjz200201024ZHU Debing. Summarization of engineering geophysics in major of geophysical prospecting and information technique[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2002, 17(1):163~170. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxjz200201024 [21] Vafikis A, Economou N, Ganiatsos Y, et al. Integrated geophysical studies at ancient Itanos (Greece)[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2005, 32(7):1023~1036. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2005.02.007 [22] Pérez-Gracia V, García F, Pujades L G, et al. GPR survey to study the restoration of a Roman monument[J]. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 2008, 9(1):89~96. doi: 10.1016/j.culher.2007.09.003 [23] Hemeda S, Pitilakis K. Serapeum temple and the ancient annex daughter library in Alexandria, Egypt:Geotechnical-geophysical investigations and stability analysis under static and seismic conditions[J]. Engineering Geology, 2010, 113(1/4):33~43. doi: 10.1080/17538947.2011.602119?scroll=top&needAccess=true [24] 刘嵘, 马见青, 李庆春, 等.重磁电综合地球物理探测河套盆地深部结构[J].地质力学学报, 2016, 22(4):943~954. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160412&flag=1LIU Rong, MA Jianqing, LI Qingchun, et al. Gravity, magnetic and electric comprehensive geophysical prospecting for deep structures in Hetao Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 22(4):943~954. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160412&flag=1 [25] 李坚.关于铁路物探疑难技术问题的探讨[J].铁道工程学报, 2014, 31(7):1~6. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tdgcxb201407001LI Jian. Discussion of difficult technical problems about geophysical exploration on railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2014, 31(7):1~6. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tdgcxb201407001 -





 下载:
下载: