STUDY ON THE VARIATION LAW OF CRUSTAL STRESS FIELD IN TIGHT RESERVOIR UNDER MULTI FIELD COUPLING
-
摘要: 地应力是储层改造方案设计、提高油气勘探开发效率的重要指标。致密储层所处环境复杂,需要综合考虑温度-应力-渗流多场耦合作用的影响。为此,以准噶尔盆地中部4区块某三维区致密储层为例,基于COMSOL Multiphyics软件,建立了温度-应力-渗流耦合控制方程,研究了多场耦合作用下研究区致密储层地应力场的变化规律。研究结果表明:研究区最大水平主应力范围在113~134 MPa之间,最小水平主应力范围在106~124 MPa之间,均表现为压应力;在油气开采过程中,最大水平主应力先增大后趋于稳定,随着油气开采的深入,应力变化范围逐渐由井口周围向附近断层延展,并且优先沿着断层的开裂方向发展;在断层的破碎过渡区应力值最小,断层核部应力值介于破碎过渡区与连续地层之间;随着油气开采的深入,致密储层会发生竖向变形,储层最大竖向变形出现在井口附近,位移量超过10 cm,随着距离变远,沉降量不断减小。Abstract: Crustal stress is an important index of reservoir reconstruction scheme design and improvement to oil and gas exploration and development efficiency. Due to the complex environment in which tight reservoirs are located, the multi field coupling of temperature, stress and seepage should be considered comprehensively. Therefore, the tight reservoir in Block 4 three-dimensional area of central Junggar Basin was taken as an example, the THM coupled control equation was established based on the COMSOL Multiphyics software, and the variation law of crustal stress field in tight reservoir under multi field coupling was studied. The result shows that:The maximum horizontal principal stress ranges from 113 to 134 MPa, and the minimum horizontal principal stress from 106 to 124 MPa, all showing as compressive stress. In the process of oil and gas exploitation, the maximum horizontal principal stress increases first and then tends to be stable. With the deepening of oil and gas exploitation, the range of stress change gradually extends from the wellhead to the nearby fault, and preferentially develops along the fracture direction of the fault. In the fault transition zone, the stress value is minimum, and the stress at the core of the fault is between the broken transition zone and the continuous stratum. With the deepening of oil and gas exploitation, the vertical deformation will occur in tight reservoirs. The maximum vertical deformation of the reservoir occurs near the wellhead, the displacement is more than 10cm, and the settlement decreases as the distance increasing.
-
表 1 最优化反演数据表
Table 1. Optimized inversion data sheet
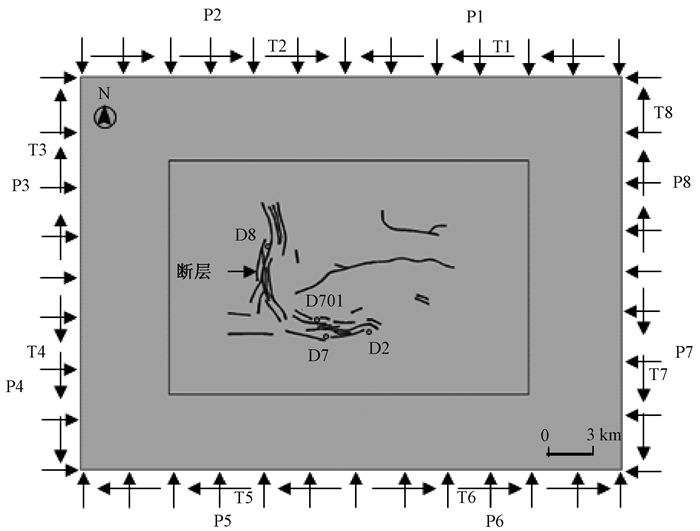
边界荷载 反演最优值/MPa 边界荷载 反演最优值/MPa 边界荷载 反演最优值/MPa 边界荷载 反演最优值/MPa P1 149.47 P5 107.61 T1 -93.93 T5 89.08 P2 91.55 P6 123.66 T2 64.19 T6 -14.19 P3 77.72 P7 131.6 T3 -58.59 T7 69.59 P4 138.54 P8 86.51 T4 16.51 T8 -22.67 表 2 计算参数表
Table 2. Calculation parameter list
介质 密度/(kg/m3) 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 热熔系数/(J·kg-1·K-1) 热传导系数/(W·m-1·K-1) 热膨胀系数/$\frac{1}{{\rm{K}}}$ 孔隙率/% 连续地层 2700 28 0.22 923 2.47 5.3×10-5 0.06 过渡区 2100 16.8 0.314 923 2.61 6.2×10-5 0.35 断层核部 2800 28.8 0.21 923 2.45 5.2×10-5 0.03 液相 1070 - - 4200 随温度变化 2.08×10-4 - 表 3 模拟结果与计算结果对比表
Table 3. Comparison between simulation results and calculation results
井号 最大水平主应力/MPa 模拟值 计算值 误差% D2 115.34 120.36 4.163 D7 112.89 123.14 8.323 D701 127.81 121.02 5.611 D8 115.80 120.73 4.083 -
[1] 曾溅辉, 杨智峰, 冯枭, 等.致密储层油气成藏机理研究现状及其关键科学问题[J].地球科学进展, 2014, 29(6):651-661. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201406001ZENG Jianhui, YANG Zhifeng, FENG Xiao, et al. Study status and key scientific issue of tight reservoir oil and gas accumulation mechanism[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2014, 29(6):651-661. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201406001 [2] 谷江锐, 刘岩.国外致密砂岩气藏储层研究现状和发展趋势[J].国外油田工程, 2009, 25(7):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-641X.2009.07.001GU Jiangrui, LIU Yan. Present study and development trend of foreign tight gas sandstone reservoirs[J]. Foreign Oil Field Engineering, 2009, 25(7):1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-641X.2009.07.001 [3] 董晓霞, 梅廉夫, 全永旺.致密砂岩气藏的类型和勘探前景[J].天然气地球科学, 2007, 18(3):351-355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2007.03.007DONG Xiaoxia, MEI Lianfu, QUAN Yongwang. Types of tight sand gas accumulation and its exploration prospect[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2007, 18(3):351-355. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2007.03.007 [4] 徐向荣, 马利成, 唐汝众.地应力及其在致密砂岩气藏压裂开发中的应用[J].钻采工艺, 2000, 23(6):17-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-768X.2000.06.006XU Xiangrong, MA Licheng, TANG Ruzhong. Application of formation stress in fracturing development for tight sandstone reservoir[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2000, 23(6):17-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-768X.2000.06.006 [5] ECKERT A. 3D multi-scale finite element analysis of the crustal state of stress in the Western US and the Eastern California Shear Zone, and implications for stress-fluid flow interactions for the Coso geothermal field[D]. Karlsruhe: Institute of Geophysics, University of Karlsruhe, 2007. [6] MATSUKI K, NAKAMA S, SATO T. Estimation of regional stress by FEM for a heterogeneous rock mass with a large fault[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2009, 46(1):31-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.03.005 [7] 丁文龙, 曾维特, 王濡岳, 等.页岩储层构造应力场模拟与裂缝分布预测方法及应用[J].地学前缘, 2016, 23(2):63-74. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201602008DING Wenlong, ZENG Weite, WANG Ruyue, et al. Method and application of tectonic stress field simulation and fracture distribution prediction in shale reservoir[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(2):63-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201602008 [8] 李春林, 郭鹏, 任德生.大民屯凹陷构造应力场及其与油气运聚关系[J].油气地质与采收率, 2012, 19(6):47-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2012.06.011LI Chunlin, GUO Peng, REN Desheng. Relationship between tectonic stress field and migration and accumulation of oil and gas in Damintun depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2012, 19(6):47-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2012.06.011 [9] 张建良.金湖凹陷卞东油田灰岩-砂岩混积岩储层应力场模拟及裂缝预测研究[J].石油天然气学报, 2012, 34(5):30-34, 48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2012.05.006ZHANG Jianliang. Stress field simulation and fracture forecast in lime-sandstone Diamictite reservoirs of Biandong oilfield in Jinhu sag[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2012, 34(5):30-34, 48. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2012.05.006 [10] 徐珂, 戴俊生, 商琳, 等.高尚堡油田深层油藏南区现今地应力场预测及应用[J].中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(6):19-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2018.06.003XU Ke, DAI Junsheng, SHANG Lin, et al. Prediction of current in-situ stress filed and its application of southern area of deep reservoir in Gaoshangpu Oilfield[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2018, 42(6):19-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2018.06.003 [11] 柴军瑞.岩体渗流-应力-温度三场耦合的连续介质模型[J].红水河, 2003, 22(2):18-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-408X.2003.02.005CHAI Junrui. Continuum model for coupled seepage, stress and temperature fields in rock mass[J]. Hongshui River, 2003, 22(2):18-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-408X.2003.02.005 [12] 刘建军, 冯夏庭.我国油藏渗流-温度-应力耦合的研究进展[J].岩土力学, 2003, 24(S1):645-650. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/6735995LIU Jianjun, FENG Xiating. Advance of studies on thermo-hydro-mechanical interaction in oil reservoir in China[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2003, 24(S1):645-650. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/6735995 [13] 王群嶷.大庆油田三维地应力研究与低渗油气资源经济开发[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2009.WANG Qunyi. Study on 3-D stress field for economical effective development low permeability oil and gas resources in Daqing oil field[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 曾春雷.高温、高压和渗流耦合作用下软岩力学行为的研究[D].青岛: 青岛科技大学, 2007. https://max.book118.com/html/2015/1112/29267217.shtmZENG Chunlei. Study on mechanical behavior of soft rock in coupled effect of high temperature, high pressure and seepage[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Science & Technology, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://max.book118.com/html/2015/1112/29267217.shtm [15] 盛金昌.多孔介质流-固-热三场全耦合数学模型及数值模拟[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(S1):3028-3033. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb2006z1066SHENG Jinchang. Fully coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical model of saturated porous media and numerical modelling[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(S1):3028-3033. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb2006z1066 [16] 李娟.复合场作用下的碳酸盐岩裂缝预测研究[D].青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2014.LI Juan. The prediction of fractures in carbonate rocks in the composite fields[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 刘善利.饱和岩体热流固耦合模型研究[D].南京: 河海大学, 2007.LIU Shanli. Thermo-hydro-mechanical coupling model research in saturated rock mass[D]. Nanjing: Hohai University, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] BONACINA C, COMINI G, FASANO A, et al. Numerical solution of phase-change problems[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1973, 16(10):1825-1832. doi: 10.1016/0017-9310(73)90202-0 [19] 张立松, 闫相祯, 杨秀娟, 等.致密碎屑岩裂缝性储层裂缝发育定量预测[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(2):501-506. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zngydxxb201402024ZHANG Lisong, YAN Xiangzhen, YANG Xiujuan, et al. Quantitative prediction of natural fracture development for tight fractured clastic rock reservoir[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(2):501-506. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zngydxxb201402024 [20] 刘向君, 罗平亚, 孟英峰.地应力场对井眼轨迹设计及稳定性的影响研究[J].天然气工业, 2004, 24(9):57-59. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2004.09.017LIU Xiangjun, LUO Pingya, MENG Yingfeng. Influence of ground stress field on borehole trajectory design and wellface stability[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2004, 24(9):57-59. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2004.09.017 -





 下载:
下载: