PREDICTION OF CRUSTAL STRESS OF DEEP-BURIED TUNNELS BASED ON BP ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK
-
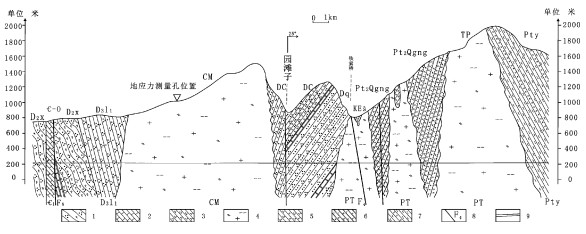
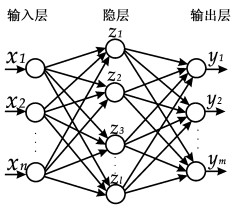
摘要: 深部地应力的测量一直是工程界难题之一。由于研究手段和测试技术的限制, 深部地应力很难测到, 或者部分数据不理想。本文将BP神经网络方法引入地应力场研究, 选取深度、岩芯密度(天然密度)、岩芯弹模、岩芯的三轴抗压强度(10MPa围压)、岩芯的声发射地应力测值、岩芯裂隙率6个参数作为地应力预测研究的主要指标, 在此模型的基础上对秦岭深埋隧洞地应力测量数据进行了拟合分析, 并对深部的地应力做了预测。结果表明用BP神经网络模型进行深埋隧洞地应力大小的预测是可行的。Abstract: The measurement of the crustal stress at depth is a difficult problem in geological engineering projects.The crustal stress is hard to determine or measuring data are not ideal because of the limitation of unduly simple research means and measuring techniques.On the other hand, satisfying results can be achieved by artificial neural network (ANN)even though the data have deficiencies such as data noise, partial absence, lack of cognition because of the native advantages:self-learning, self-adaptability, robust, error tolerance and generalization.Based on the BP artificial neural network method, this paper provides a prediction model for the crustal stress values using 6 factors:depth, field density, elastic modulus, triaxial compressive strength (10 MPa confining pressure), acoustic emission stress measurements and fissure density.The authors made hydrofracturing stress measurements in the Qinling deep-buried long tunnel by using the BP artificial neural network model, perpormed a fitting analysis of the measured data and predicted the crustal stress at depth.The main conclusion is that the BP artificial network model is feasible in the prediction of the crustal stress value of deep-buried tunnels.
-
表 1 秦岭深埋隧洞地应力测量BP神经网络预测的样本数据
Table 1. Sample data for ANN prediction of crustal stress in the Qinling deep-buried tunnel

表 2 秦岭深埋隧洞地应力测量BP神经网络训练结果数据表
Table 2. Comparison of ANN training data with measurements

表 3 BP神经网络预测结果与地应力实测数据的比较
Table 3. Comparison between the resulds of prediction and measured data

-
[1] 黄润秋, 王贤能.深埋隧道工程主要灾害地质问题分析[J].水文地质工程地质, 1998, (4):21~24. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jzgcjsysj2015120304 [2] 孙叶, 谭成轩等.区域地壳稳定性定量化评价[M].北京:地质出版社, 1998. [3] 谭成轩, 孙叶, 王连捷.地应力测量值得注意的问题探讨[J].地质力学学报, 2003, 9 (3):275~280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2003.03.010 [4] 阎平凡, 张长水.人工神经网络与模拟进化计算(第二版)[M].北京:清华大学出版社, 2005. [5] Simon Haykin (叶世伟, 史忠植译). 神经网络原理(第二版)[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2004. [6] Hecht-Nielsen R.Theory of the back propagation neural network[J]. Proc.of ICNN, 1989, 1:593~603. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_204986640668fdf28de7614b3c8459f9 [7] 王洪元, 史国栋.人工神经网络技术及其应用[M].北京:中国石油化工出版社, 2002. [8] 周志华, 曹存根.神经网络及其应用[M].北京:清华大学出版社, 2004. [9] 罗四维.大规模人工神经网络基础[M].北京:北方交通大学出版社, 2004. [10] McCulloch WS, Pitts W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity[J].Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics, 1943, 5:115~133. doi: 10.1007/BF02478259 [11] 张永双, 曲永新, 等.硬土-软岩工程地质信息管理分析系统及其应用[J].地球学报, 2001, vol.22:277~ 282. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200103010 [12] Rumelhart D, Ninton G, Willianms J. Learning Internal Representation by Error Propagation[M].Cambridge, MA:MIT Press, 1986. -





 下载:
下载: