TECTONIC DEVELOPMENT AND ORE-CONTROLING CHARACTERISTICS OF XIAOQINLING GOLD FIELD
-
摘要: 通过收集和分析小秦岭金矿田地质资料, 重点对典型矿床不同标高探矿工程进行系统研究, 探讨了该矿田的控矿构造特征。研究认为, 受褶皱构造控制, 区内含金石英脉多位于杨砦峪—大月坪—金罗斑复式背形轴部或背形局部侧转处; 矿田内部控矿断裂发育可分为成矿前断裂(早期韧性剪切带)、成矿早期断裂(中期脆韧或韧脆性剪切带)和主成矿期断裂(晚期脆性断裂)3个时期, 主要控矿断裂大致可分为近东西向、北东向、北西向和近南北向共4组; 区内矿体和矿床的大小直接由构造带及单条断裂的规模决定, 同时因构造活动期次、构造变形类型和强度的不同, 造成区内矿脉赋存状态各异以及矿化不均衡现象普遍存在。研究成果可为本区开展大比例尺成矿预测提供借鉴。Abstract: Through analyzing the collected geological data of xiaoqinling gold field, the different levels of exploration engineering on typical ore deposits were studied systematically and the ore-controlling tectonic characteristics of the mine field were discussed. The research shows that under the control of the folds, most auriferous quartz veins are located at the axes or corners of Yangzhaiyu-Dayueping-Jinluoban compound antiform. The development of ore-controlling faults inside the mine field can be divided into three stages: pre-minerogenic faults (the early ductile shear zone), early minerogenic faults (the middle brittle-ductile or ductile-brittle shear zone) and main metallogenic faults (the late brittle fault zone). Accordingly the main ore-controlling faults can be roughly divided into four groups: nearly EW, NE, NW and NS. The sizes of the ore bodies and ore deposits are directly determined by the structural belts and the scale of one single fault in the area, and because of the difference in the tectonic activity stages, tectonic deformation types and strength, the veins are in different occurrence state and the mineralization imbalance phenomenon is widespread. These research results can provide reference for carrying out metallogenetic prediction in large scale in this area.
-
Key words:
- Xiaoqinling /
- gold deposits /
- ore field structure /
- ore-controlling characteristics
-
图 1 小秦岭金矿田区域地质构造略图(据文献[4]修编)
Figure 1. The sketch map showing the regional tectonics of Xiaoqinling gold field
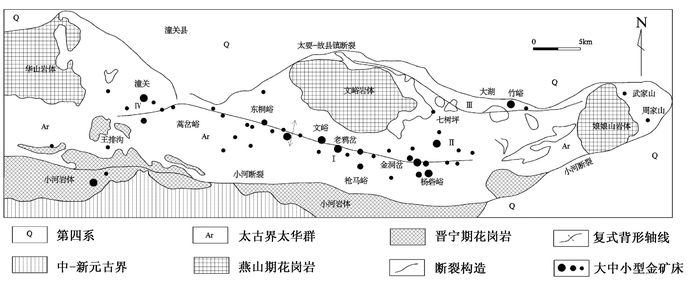
图 2 小秦岭金矿田区域矿产分布略图(据文献[4]修编)
1—第四系;2—中元古界蓟县系;3—中元古界长城系;4—太古界太华群;5—燕山期花岗岩;6—晋宁期花岗岩;7—背形构造;8—向形构造;9—区域边界断裂及编号;10—界面滑脱带;11—地质界线及地层不整合界线;12—大型金矿床;13—中型金矿床;14—小型金矿床;15—小秦岭金矿田
Figure 2. The sketch map showing the regional mineral distribution in Xiaoqinling gold field
图 5 东桐峪一带近东西向断裂不同标高地质特征
a—600中段,晚期脆性断裂叠加早期韧性断裂边缘形成多金属矿化(断面波状弯曲);b—600中段,晚期脆性断裂叠加早期韧性断裂引起的构造膨胀部位形成厚大含矿石英脉;c—400中段,晚期脆性断裂叠加韧脆性断裂引起边缘石英脉碎裂化;d—640中段,含矿石英脉中围岩捕虏体;e—1016中段,含矿石英脉中围岩捕虏体;f—400中段晚期脆性断裂叠加早期形成石英脉,致使内部捕虏体碎裂
Figure 5. Geological characteristics of nearly EW trending faults at different elevation in Dongtongyu area
表 1 断裂构造分类一览表
Table 1. Faults classification
近东西向断裂 北东向断裂 北西向断裂 近南北向断裂 产状 走向/(°) 260~285 35~55 60~70 320~340 350~10 倾向/(°) 170~205 125~130 310~330 150~160 230~250 60 260~280 倾角/(°) 33~65 67~75 35~43 50~70 55~80 50 65~85 断裂性质 压扭性 压扭性 压扭性 张扭性 代表矿脉 Q8,Q8501,Q2051 Q12 Q640-4 Q301 Q3057 Q102 Q315 -
[1] 宫同伦.陕西小秦岭金矿的富化与动力成矿作用的关系[J].西安地质学院学报, 1991, 13(1):8~10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX199101001.htmGONG Tong-lun. The relationship between dynamo-metallogenesis and concentration of the small Qinling gold ore, Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Xi'an College Geology, 1991, 13(1): 8~10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX199101001.htm [2] 徐莉, 刘长命, 盛吉虎, 等.河南小秦岭金矿控矿条件分析及找矿前景[J].河南地质, 1994, 12(1):12~14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDD401.002.htmXU Li, LIU Chang-ming, SHENG Ji-hu, et al. Analyzing of ore-control condition and ore prospecting on Xiaoqinling deposits, Henan Province[J]. Henan Geology, 1994, 12(1): 12~14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDD401.002.htm [3] 祁进平, 陈衍景, 李强之.小秦岭造山型金矿的流体成矿作用分析[J].矿床地质, 2002, 21(增刊):1009~1012. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2002S1267.htmQI Jin-ping, CHEN Yan-jing, LI Qiang-zhi. Synthesis of hydrothermal metallogenesis in Xiaoqinling orogenic gold field[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2002, 21(Supp.): 1009~1012. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2002S1267.htm [4] 陈衍景.造山型矿床、成矿模式及找矿潜力[J].中国地质, 2006, 33(6):1181~1196. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGYT201322155.htmCHEN Yan-Jing. Orogenic deposit, mineral deposit model and ore prospecting[J]. China Geology, 2006, 33(6): 1181~1196. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGYT201322155.htm [5] 魏俊浩, 谭俊. 桐峪金矿矿脉分布规律及成矿预测[R]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2011: 20~89.China University of Geosciences (Wuhan). Golden ore vein distribution and metallogenic prediction of Tongyu[R]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2011: 20~89. [6] 中国人民武装警察部队黄金地质研究所. 东桐峪金矿深部及外围成矿规律研究与成矿预测[R]. 廊坊: 中国人民武装警察部队黄金地质研究所, 2005: 6~17.Institute of Gold Geology, China Peoples Armed Police Force. Metallogenic regularities and metallogenic prognosis of the deep parts and its peripheries of gold ore in Dongtongyu[R]. Langfang: Institute of Gold Geology, China Peoples Armed Police Force, 2005: 6~17. [7] 杨海, 张凯, 任红伟.地质找矿的科学思维模式探析[J].西北地质, 2014, 47(1):262~263. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201401030.htmYANG Hai, ZHANG Kai, REN Hong-wei. Study of scientific thinking pattern of geological prospecting[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2014, 47(1): 262~263. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201401030.htm [8] 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚.秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M].北京:科学出版社, 2001:1~729.ZHANG Guo-wei, ZHANG Ben-ren, YUAN Xue-cheng. Qinling orogenic belt and continental geodynamics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001: 1~729. [9] 张国伟, 孟庆仁, 刘少峰, 等.华北地块南部巨型陆内俯冲带与秦岭造山带岩石圈现今三维结构[J].高校地质学报, 1997, 3(2):129~143. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX702.000.htmZHANG Guo-wei, MENG Qing-ren, LIU Shao-feng, et al. Huge intracontinental subduction zone at south margin of north China block and present 3-D lithospheric framework of the Qinling orogenic belt[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 1997, 3(2): 129~143. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX702.000.htm [10] 胡正国, 钱壮志.小秦岭地质构造新认识[J].地质论评, 1994, 40(4):289~291. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199404000.htmHU Zheng-guo, QIAN Zhuang-zhi. A new idea of geological tectonics in the Xiaoqinling region[J]. Geological Review, 1994, 40(4): 289~291. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199404000.htm [11] 秦鼐.中国金矿主要类型区域成矿条件[M].北京:地质出版社, 1988:17~22.QIN Nai. Discussion on the regional metallogenetic condition about main gold ore field in China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1988: 17~22. [12] 郭福祺, 任崔锁, 杨兴科.小秦岭金矿成矿地质条件分析[J].西安地质学院学报, 1983, (1):51~56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX198301005.htmGUO Fu-qi, REN Cui-suo, YANG Xing-ke. Analysis to the ore-forming geological conditions on Xiaoqinling gold ore field[J]. Journal of Xi'an College of Geology, 1983, (1): 51~56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX198301005.htm [13] 晁援, 朱文怀.对小秦岭金矿田含脉断裂构造带的几何形态及控矿规律的认识[J].陕西地质, 1994, 12(2):1~5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXDY199402000.htmCHAO Yuan, ZHU Wen-huai. An understanding for geometric shape and ore-control regularity of vein-bearing faulted structure belts in gold orefield, Xiaoqinling region[J]. Geology of Shaanxi, 1994, 12(2): 1~5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXDY199402000.htm [14] 栾世伟, 赵宝金.小秦岭金矿糜棱岩成因机理及其与金矿化的关系[J].成都地质学院学报, 1986, 13(8):32~39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG198603004.htmLUAN Shi-wei, ZHAO Bao-jin. The formation of the mylonites and its relationship with gold mineralization in the Xiaoqinling area[J]. Journal of Chengdu College of Geology, 1986, 13(8): 32~39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG198603004.htm [15] 盛吉虎, 徐莉, 尉向东, 等.小秦岭构造岩及其与金矿化关系[J].河南地质, 1996, 14(4):241~248. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDD604.000.htmSHENG Ji-hu, XU Li, YU Xiang-dong, et al. Tectonite on Xiaoqinling and its correlation to auriferous mineralization[J]. Henan Geology, 1996, 14(4): 241~248. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDD604.000.htm [16] 翟裕生.关于矿田构造研究的若干问题[J].地质论评, 1984, 30(1):19~21. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP198401002.htmZHAI Yu-sheng. Some problems on the study of ore field structures[J]. Geological Review, 1984, 30(1): 19~21. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP198401002.htm [17] 毛景文, 华仁民, 李晓波.浅议大规模成矿作用与大型矿集区[J].矿床地质, 1999, 18(4):292~296. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ199904000.htmMAO Jing-wen, HUA Ren-min, LI Xiao-bo. A preliminary study of large-scale metallogenesis and large clusters of mineral deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 1999, 18(4): 292~296. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ199904000.htm [18] 叶天竺, 薛建玲.金属矿床深部找矿中的地质研究[J].中国地质, 2007, 34(5):855~868. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201705102.htmYE Tian-zhu, XUE Jian-ling. Geological study in search of metallic ore deposits at depth[J]. Geology in China, 2007, 34(5): 855~868. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201705102.htm -





 下载:
下载: