EVALUATION OF THE HYDROCARBON GENERATION POTENTIAL OF SOURCE ROCKS OF THE JURASSIC YAOJIE FORMATION IN MULI DEPRESSION OF QILIAN MOUNTAINS
-
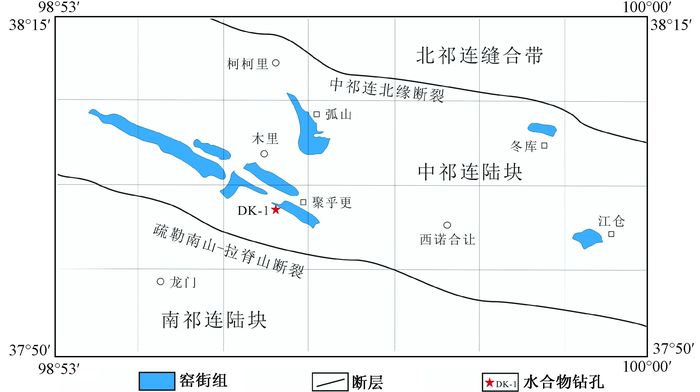
摘要: 祁连山木里坳陷侏罗系窑街组煤系泥岩和煤有机质丰度、有机质类型和有机质成熟度分析结果表明, 窑街组煤系泥岩为好的烃源岩, 有机质类型为Ⅱ1型, 处于成熟阶段, 以生油为主, 生气为辅; 煤为差等烃源岩, 有机质类型为Ⅲ型, 处于成熟阶段, 富氢基质镜质体含量高, 具有一定的生烃潜力。综合其它层位烃源岩分析结果, 认为窑街组煤系泥岩和晚三叠世尕勒得寺组湖相泥岩为祁连山木里地区天然气水合物的主要气源岩。Abstract: The research results of the abundance, types and maturity of the organic matter of mudstone and coal seam of Yaojie coal-bearing formation in Muri depression of Qilian Mountains show that the mudstone of Yaojie coal-bearing formation is good hydrocarbon source rock and the organic matter type is sapropelic-humic (Ⅱ1) during the mature stage in which gas generation is predominant. While the coal seams are relatively poor hydrocarbon source rocks, with the organic matter of humic type (Ⅲ) at the mature stage, which have a certain hydrocarbon generating potential. Based on the analysis of hydrocarbon source rocks in others formation, it is concluded that the mudstone of Yaojie coal-bearing formation and the lacustrine mudstone of Galedesi formation in late Triassic are the main source rocks of gas hydrates in Muri depression.
-
Key words:
- Yaojie Formation /
- hydrocarbon generation potential /
- Muli depression /
- Qilian Mountains
-
表 1 窑街组烃源岩参数统计
Table 1. Parametric statistics of source rocks in Jurassic Yaojie Formation
采样点 岩性 TOC/% (S1+S2)/(mg·g-1) IH/(mg·g-1) Ro/% Tmax/℃ D/% a b c d a b c d a b c d a b c d a b c d a b c d 聚
乎
更
煤
区一露天 泥岩 5 1.28 5.89 3.29 5 1.23 11.22 4.37 5 57 178 99 / / / / 5 447 462 455 5 5.67 19.8 9.67 煤 56 42.00 88.26 85.31 56 28.72 166.5 98.8 56 111 254 194 5 0.96 1.1 1.03 56 425 471 452 56 9.57 27.2 16.9 二露天 煤 8 44.84 78.21 62.28 8 11.84 84.37 33.54 8 88 168 125 4 0.51 0.83 0.71 8 429 438 433 8 7.47 14.5 10.9 三露天 泥岩 3 2.17 4.45 3.01 3 3.11 7.23 4.68 3 147 160 156 / / / / 3 448 449 448 3 14.3 14.9 14.7 煤 13 38.59 87.71 69.56 13 9.14 187.43 111.62 13 70 382 240 4 0.48 0.85 0.67 13 424 447 437 13 5.97 32.0 20.3 四井田 泥岩 4 1.93 4.58 3.3 4 2.32 12.27 6.49 3 99 408 211 1 0.83 0.83 0.83 4 448 460 454 3 8.78 35.4 18.4 煤 14 68.64 87.03 80.9 14 63.86 171.47 131.38 14 171 298 237 3 0.89 0.95 0.91 14 439 454 448 14 14.7 25.8 20.6 冬库矿区 煤 5 80.53 85.24 82.76 5 40.1 53.7 44.58 5 131 170 150 2 0.74 0.87 0.8 5 433 438 436 5 11.8 15.5 13.4 弧山矿区 煤 8 39.33 90.28 72.55 8 11.21 27.95 17.88 8 24 58 39 5 1.53 2.06 1.86 8 516 531 524 8 2.05 4.94 3.27 江仓矿区 煤 17 65.08 91.46 82.66 17 66.74 161.75 119.38 17 107 359 224 5 0.87 1.44 1.09 17 454 482 467 17 9.03 30.4 19 全区
平均值泥岩 12 1.28 5.89 3.22 12 1.23 12.27 5.18 11 57 408 149 1 0.83 0.83 0.83 12 447 462 453 11 5.67 35.4 13.4 煤 121 38.59 92.9 80.26 121 9.14 187.43 94.93 121 24 382 191 28 0.48 2.51 1.06 121 424 531 455 121 2.5 32 16.5 注:TOC—总有机碳;S1+S2—生烃潜量;IH—氢指数;Ro—镜质体反射率;Tmax—岩石热解峰温;D—降解率;a—样品数;b—最小值;c—最大值;d—平均值 表 2 侏罗系窑街组煤显微组分组成
Table 2. Coal macerals in the Jurassic Yaojie Formation
显微组分 样品件数 最小值 最大值 平均值 镜质组/% 28 80.74 97.74 87.90 惰性组/% 28 1.75 16.84 10.43 壳质组/% 28 0 5.26 1.10 腐泥组/% 28 0 5.26 0.53 基质镜质体/% 28 21.43 71.97 51.51 类型指数(Ti) 28 -79.21 -59.65 -75.27 类型 Ⅲ 表 3 窑街组煤干酪根碳同位素
Table 3. The δ13C analysis of kerogen in the coal of Yaojie Formation
样品 δ13C/‰ B038-1 -24.8 H040 -23.6 H073 -25.3 B302-2 -24.1 H342 -24.0 H344 -23.7 B349-1 -23.3 H361 -23.8 H683 -24.0 H379 -24.2 -
[1] 曹代勇, 刘天绩, 王丹, 等.青海木里地区天然气水合物形成条件分析[J].中国煤炭地质, 2009, 21(9):3~6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT200909005.htmCAO Dai-yong, LIU Tian-ji, WANG Dan, et al. Analysis of formation conditions of natural gas hydrate in Muli coalfield, Qinghai Province[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2009, 21(9): 3~6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT200909005.htm [2] 王佟, 刘天绩, 邵龙义, 等.青海木里煤田天然气水合物特征与成因[J].煤田地质与勘探, 2009, 37(6):26~30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT200906008.htmWANG Tong, LIU Tian-ji, SHAO Long-yi, et al. Characteristics and origins of the gas hydrates in the Muli coalfield of Qinghai[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2009, 37(6): 26~30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT200906008.htm [3] 祝有海, 刘亚玲, 张永勤.祁连山多年冻土区天然气水合物的形成条件[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(1/2):58~63. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2006Z1010.htmZHU You-hai, LIU Ya-ling, ZHANG Yong-qin. Formation conditions of gas hydrates in permafrost of the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China[j]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(1/2): 58~63. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2006Z1010.htm [4] 祝有海, 张永勤, 文怀军, 等.祁连山冻土区天然气水合物及其基本特征[J].地球学报, 2010, 31(1):7~16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201001004.htmZHU You-hai, ZHANG Yong-qin, WEN Huai-jun, et al. Gas hydrates in the Qilian Mountain permafrost and their basic characteristics[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(1): 7~16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201001004.htm [5] 卢振权, 祝有海, 张永勤, 等.青海祁连山冻土区天然气水合物的气体成因研究[J].现代地质, 2010, 24(3):581~588. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201003024.htmLU Zhen-quan, ZHU You-hai, ZHANG Yong-qin, et al. Study on genesis of gases from gas hydrate in the Qilian Mountain permafrost, Qinghai[J]. Geoscience, 2010, 24(3): 581~588. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201003024.htm [6] 张雪亭, 杨生德.青海省区域地质概论[M].北京:地质出版社, 2007.ZHANG Xue-ting, YANG Sheng-de. Introduction to regional geology of Qinghai Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007. [7] 符俊辉, 周立发.南祁连盆地石炭—侏罗纪地层区划及石油地质特征[J].西北地质科学, 1998, 19(2):47~54. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBFK199802003.htmFU Jun-hui, ZHOU Li-fa. Carboniferous-Jurassic staratigraphic provinces of the southern Qilian basin and Their petro-geological features[J]. Northwest Geoscience, 1998, 19(2): 47~54. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBFK199802003.htm [8] 白旭东, 咸发美, 张志青, 等.青海木里地区晚三叠世—早中侏罗世烃源岩特征初探[J].中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2013, 33(15):134~135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2013.15.127BAI Xun-dong, XIAN Fa-mei, ZHANG Zhi-qing, et al. Features of hydrocarbon source rock of Late Triassic-Early Middle Jurassic in Muli depression in Qilian Mountains[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2013, 33(15): 134~135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2013.15.127 [9] 青海江仓能源发展有限责任公司. 青海省木里煤田江仓矿区四井田勘探报告[R]. 西宁: 青海江仓能源发展有限责任公司, 2006.Qinghai Jiangcang Energy Development Limited Company. The exploration report on the No. 4 Well of Jiangcang mine area in Muli Coalfield, Qinghai Province[R]. Xining: Qinghai Jiangcang Energy Development Limited Company, 2006. [10] 陈建平, 赵长毅, 何忠华.煤系有机质生烃潜力评价标准探讨[J].石油勘探与开发, 1997, 24(1):1~5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK199701000.htmCHEN Jian-ping, ZHAO Chang-yi, HE Zhong-hua. Criteria for evaluating the hydrocarbon generating potential of organic matter in coal measures[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1997, 24(1): 1~5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK199701000.htm [11] 汪生秀, 张枝焕, 张志平, 等.二连盆地侏罗系烃源岩地球化学特征及油源贡献[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2012, 31(4):396~403. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201204011.htmWANG Sheng-xiu, ZHANG Zhi-huan, ZHANG Zhi-ping, et al. Geochemical characteristics and oil-source correlation of the Jurassic source rocks in the Erlian Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2012, 31(4): 396~403. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201204011.htm [12] Hunt J M. Generation of gas and oil from coal and other terrestrial organic matter[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1991, 17(6): 673~680. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(91)90011-8 [13] Snowdon L R. Oil Irom Type Ⅲ organic matter: Resinite revisited[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1991, 17(6): 743~747. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(91)90018-F [14] Mukhopadhyay P K, Hatcher P G. Composition of coa1[C]//Law B E, Rice D D. Hydrocarbons Irom coal. Tulsa: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 1993: 79~118. [15] 程克明, 王铁冠.天然气源岩地球化学特征[J].天然气地球科学, 1993, (2):49~94. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201503017.htmCHENG Ke-ming, WANG Tie-guan. The natural gas source rock geochemistry[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 1993, (2): 49~94. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201503017.htm [16] 成海燕, 李安龙, 龚建明.陆相烃源岩评价参数浅析[J].海洋地质动态, 2007, 24(2):6~10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT200802003.htmCHENG Hai-yan, LI An-long, GONG Jian-ming. Evaluation parameters of source rock of continental facies[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2007, 24(2): 6~10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT200802003.htm [17] 宋换新, 曾艳涛, 文志刚. 祁连山冻土区烃源岩生烃潜力评价[R]. 北京: 中国地质科学院地质力学研究所, 2014.SONG Huan-xin, ZENG Yan-tao, WEN Zhi-gang. Evaluation of hydrocarbon generating potential in permafrost of the Qilian Mountains[R]. Beijing: Institute of Geomechanics, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2014. -





 下载:
下载: