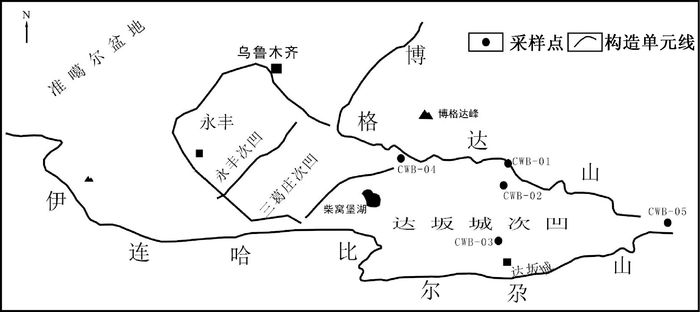
THE GEOCHEMICAL AND MINERALOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF SHALES IN CHAIWOBU DEPRESSION, SOUTHERN MARGIN OF JUNGGAR BASIN
-
摘要: 利用XRD、Rock-eval和气相色谱—质谱仪对准格尔南缘柴窝堡凹陷上石炭统、上二叠统及下侏罗统的泥页岩进行了地球化学和矿物学特征分析。有机地球化学实验结果指示,柴窝堡凹陷石炭纪至二叠纪经历了较长时期的淡水—微咸水沉积环境,有机质来源具有相似的母源输入特征,干酪根类型具有Ⅱ型混合母质特征;有机质热演化特征表明,下侏罗统泥页岩处于低熟阶段,上石炭统与上二叠统泥页岩具有机质丰度较高、有机质类型丰富、热演化处于成熟—高成熟阶段等特点;矿物学特征显示,上二叠统泥页岩长石、石英等脆性矿物含量为73%,粘土矿物次之,指示其脆性指数较高,具有较好的可压裂性和粘土表面吸附性。结合前人认识,预测该段泥页岩中可能蕴藏着一定规模的页岩气资源,具有较好的页岩气资源前景和勘探潜力。Abstract: Using XRD, Rock-eval and GC-MS, kerogen type, organic geochemical characteristics and inorganic mineralogy features of shales in upper Carboniferous, upper Permian, and lower Jurassi from the Chaiwobu depression at southern margin of Junggar Basin were analyzed. The organic geochemical index shows that from Carboniferous to Permian, it has been a long period of fresh-brackish water sedimentary environment in Chaiwobu depression. The sources of organic matter shared the similar source input characteristics, and kerogen type were mainly featured by type Ⅱ. The thermal evolution of organic matter indicates that shales in lower Jurassic were in low mature stage while shales in upper Carboniferous and upper Permian showed the features of high abundance, rich in types and mature-high mature stage in the thermal evolution. The mineralogical characteristics show that the content of brittle minerals feldspar and quartz in upper Permian shales is 73%, followed by clay mineral, indicating a high brittleness index and good property of fracturing and adsorption. Combined with the previous studies, it is predicted that a certain scale of shale gas resources may be contained in shales of this member with a good prospect and potential for exploration.
-
Key words:
- Chaiwobu Depression /
- shale /
- biomarker /
- mineralogy /
- shale gas
-
表 1 样品的基础地球化学参数
Table 1. Basic geochemical parameters of the shale samples
样品 层位 岩性 TOC/% TMAX/℃ S1/(mg/g) S2/(mg/g) PI/(S1/(S1+S2)) IH/(mg/g) IO/(mg/g) CWB-3 J1b 褐色泥页岩 3.27 436 0.03 6.15 0.01 188 110 CWB-2 P2h 碳色泥岩 0.31 449 0.01 0.02 0.65 6 135 CWB-1 P1j 炭质泥岩 0.30 448 0.08 0.03 0.28 10 157 CWB-5 C2sh 灰质泥岩 0.93 538 0.01 0.00 0.81 0 67 CWB-4 C2sh 灰质泥岩 0.29 446 0.01 0.00 0.66 0 121 表 2 样品氯仿沥青“A”族组成特征
Table 2. Composition characteristics of chloroform bitumen "A" group samples
样品 层位 饱和烃/% 芳烃/% 非烃/% 沥青质/% 非+沥/% 饱芳比 非沥比 CWB-03 J1b 12.07 1.45 81.13 5.35 86.48 8.32 15.16 CWB-02 P2h 24.73 5.49 43.41 26.37 69.78 4.50 1.65 CWB-01 P1j 14.06 13.53 27.07 45.34 72.41 1.04 0.60 CWB-05 C2sh 3.23 2.15 68.82 25.81 94.62 1.50 2.67 CWB-04 C2sh 16.88 8.44 42.86 31.82 79.86 2.00 1.35 表 3 正构烷烃和类异戊二烯烷烃生物标志化合物参数
Table 3. Biomarker parameters of n-alkanes and isoprenoid
样品 层位 碳数 峰型 主峰 Pr/Ph Pr/nC17 Ph/nC18 ∑C22-/∑C23+ OEP25-29 CWB-03 J1b 12~33 双峰 17/25 1.44 0.30 0.26 0.67 4.04 CWB-02 P2h 13-31 双峰 17/23 1.17 0.70 0.68 1.19 1.13 CWB-01 P1j 14-32 双峰 17/27 1.00 0.73 0.72 0.18 1.04 CWB-05 C2sh 14-31 双峰 17/25 1.03 0.87 0.86 1.02 0.90 CWB-04 C2sh 14-30 双峰 17/25 1.03 0.60 0.71 1.38 1.13 表 4 烃源岩萜烷和甾类化合物参数
Table 4. Parameters of terpane compounds and sterane compounds in source rock
样品
编号萜烷 甾烷 ∑三环萜烷/
∑藿烷Ts/Tm G/C30H C3122S/
(S+R)C3222S/
(S+R)C29H/
C30HC29ββ/
(αα+ββ)C2920S/
(S+R)相对含量/% C27 C28 C29 CWB-03 0 0.13 0.01 0.08 0.60 0.37 0.34 0.15 32.59 24.44 42.96 CWB-02 2.59 0.89 0.09 0.60 0.67 0.68 0.40 0.47 45.74 24.47 29.79 CWB-01 1.26 0.85 0.16 0.56 0.63 0.76 0.49 0.50 26.44 32.18 41.38 CWB-05 3.02 0.86 0.11 0.58 0.67 0.78 0.40 0.43 44.44 22.22 33.33 CWB-04 3.08 0.89 0.11 0.59 0.60 0.79 0.40 0.45 39.71 26.47 33.82 -
[1] 李玉喜, 聂海宽, 龙鹏宇.我国富含有机质泥页岩发育特点与页岩气战略选区[J].天然气工业, 2009, 29(12): 115~118, 152~153. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2009.12.034LI Yuxi, NIE Haikuan, LONG Pengyu. Development characteristics of organic-rich shale and strategic selection of shale gas exploration area in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2009, 29(12): 115~118, 152~153. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2009.12.034 [2] 汪新伟, 汪新文, 马永生.新疆博格达山的构造演化及其与油气的关系[J].现代地质, 2007, 21(1): 116~124. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200701014.htmWANG Xinwei, WANG Xinwen, MA Yongsheng. The tectonic evolution of Bogda Mountain, Xinjiang, Northwest China and its relationship to oil and gas accumulation[J]. Geoscience, 2007, 21(1): 116~124. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200701014.htm [3] 俞仁连, 杨树生, 韩军.新疆天山构造带中小型山间盆地构造特征及油气勘探方向[J].新疆石油地质, 1996, 17(1): 18~23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD601.002.htmYU Renlian, YANG Shusheng, HAN Jun. Characteristics of moderate-small-size intermont basins structures and prospects for oil-gas exploration in Tianshan Mountain structural belts[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 1996, 17(1): 18~23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD601.002.htm [4] 郭建军, 陈践发, 朱忠云, 等.柴窝堡凹陷达坂城次凹上二叠统烃源岩的地球化学特征及勘探方向[J].沉积学报, 2006, 24(3): 446~455. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200603018.htmGUO Jianjun, CHEN Jianfa, ZHU Zhongyun, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Upper Permian source rocks and exploration directions in Dabancheng sub-depression of Chaiwopu depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(3): 446~455. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200603018.htm [5] 张逊, 庄新国, 涂其军, 等.柴窝堡凹陷二叠系芦草沟组页岩气烃源岩评价[J].新疆地质, 2016, 34(2): 280~285. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201602024.htmZHANG Xun, ZHUANG Xinguo, TU Qijun, et al. Source rock evaluation of shale gas of Lucaogou Formation in Chaiwopu Sag, southern of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2016, 34(2): 280~285. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201602024.htm [6] 旷理雄, 郭建华, 宋阳, 等.柴窝堡凹陷油气藏形成条件及成藏模式研究[J].西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 20(4): 5~9, 16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200504001.htmKUANG Lixiong, GUO Jianhua, SONG Yang, et al. Studies on the forming conditions and patterns of the reservoirs in Chaiwopu Sag[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 2005, 20(4): 5~9, 16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200504001.htm [7] 俞仁连, 杨树生, 赵立群.准噶尔盆地柴窝堡凹陷达坂城次凹构造特征及油气勘查方向[J].石油实验地质, 1996, 18(3): 237~243, 273. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199603237YU Renlian, YANG Shusheng, ZHAO Liqun. Structural characteristics and oil/gas exploration targets of Dabancheng sub-depression of the Juggar Basin[J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 1996, 18(3): 237~243, 273. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199603237 [8] 陈嘉明, 吴宝凤, 段艳秋.新疆柴窝堡盆地构造样式及勘探思路[J].天然气勘探与开发, 2002, 25(2): 31~36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT200202006.htmCHEN Jiaming, WU Baofeng, DUAN Yanqiu. Structural style and prospect routine of Chaiwopu sag in Xinjiang[J]. Natural Gas Exploration & Development, 2002, 25(2): 31~36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT200202006.htm [9] 沈建林.柴窝堡盆地的石油地质特征[J].新疆石油地质, 1990, 11(4): 297~310. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI200204040.htmSHEN Jianlin. The characteristics of petroleum geology in Chaiwopu Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 1990, 11(4): 297~310. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI200204040.htm [10] 吴光红, 巴秀娥, 冯永宏, 等.柴窝堡凹陷石油地质特征及勘探方向[J].新疆石油地质, 2003, 24(6): 523~526. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200306011.htmWu Guanghong, Ba Xiue, Feng Yonghong, et al. Petroleum characteristics and prospecting target in Chaiwopu Seg, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2003, 24(6): 523~526. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200306011.htm [11] 郭建军, 朱忠云, 李广才, 等.柴窝堡凹陷柴参1侧1井烃源岩的地球化学特征[J].天然气地球科学, 2004, 15(6): 652~654. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200406020.htmGUO Jianjun, ZHU Zhongyun, LI Guangcai, et al. The geochemistry characteristics of source rock in well Chaican 1 ce 1 in Chaiwopu Sag[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2004, 15(6): 652~654. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200406020.htm [12] 旷理雄, 郭建华, 王英明, 等.柴窝堡凹陷达坂城次凹油气成藏条件及勘探方向[J].天然气地球科学, 2005, 16(1): 20~24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200501005.htmKUANG Lixiong, GUO Jianhua, WANG Yingming, et al. Studies on the oil & gas reservoir formation conditions and exploration bearing in Daban Town sub-depression of Chaiwopu depression[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2005, 16(1): 20~24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200501005.htm [13] 王怡然, 吴天琦, 田继军, 等.准噶尔盆地南缘页岩气形成条件与有利区预测[J].中国地质, 2016, 43(1): 288~297. doi: 10.12029/gc20160121WANG Yiran, WU Tianqi, TIAN Jijun, et al. Formation conditions and favorable exploration zones of shale gas on the southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(1): 288~297. doi: 10.12029/gc20160121 [14] 高劲, 曹喆.准噶尔盆地下侏罗统页岩气形成条件[J].西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 38(1): 37~45. doi: 10.11885/j.issn.1674-5086.2014.03.15.01GAO Jin, CAO Zhe. Shale gas accumulation conditions of lower Jurassic in Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2016, 38(1): 37~45. doi: 10.11885/j.issn.1674-5086.2014.03.15.01 [15] 王铁冠, 钟宁宁, 候读杰, 等.中国低熟油的几种成因机制[J].沉积学报, 1997, 15(2): 75~83. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB702.015.htmWANG Tieguan, ZHONG Ningning, HOU Dujie, et al. Several genetic mechanisms of immature crude oils in China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1997, 15(2): 75~83. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB702.015.htm [16] Peters K E, Walters, C C. Moldowan, J M. The biomarker guide[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005, 499~662. [17] 王作栋, 陶明信, 梁明亮, 等.三塘湖盆地上二叠统芦草沟组烃源岩地球化学特征[J].沉积学报, 2012, 30(5): 975~982. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201205023.htmWANG Zuodong, TAO Mingxin, LIANG Mingliang, et al. Characteristics of organic geochemistry of Lucaogou formation source rocks, Upper Permian, Santanghu Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(5): 975~982. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201205023.htm [18] 梁明亮, 王作栋, 郑建京, 等.辽河断陷烃源岩有机地球化学特征[J].岩性油气藏, 2014, 26(4): 110~116. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201404021.htmLIANG Mingliang, WANG Zuodong, ZHENG Jianjing, et al. Organic geochemistry characteristics of source rocks in Liaohe depression[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2014, 26(4): 110~116. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201404021.htm [19] 张立平, 黄第藩, 廖志勤.伽马蜡烷-水体分层的地球化学标志[J].沉积学报, 1999, 17(1): 136~140. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB901.021.htmZHANG Liping, HUANG Difan, LIAO Zhiqin. Gammacerane-geochemical indicator of water column stratification[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1999, 17(1): 136~140. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB901.021.htm [20] 龚大兴, 林金辉, 唐云凤, 等.上扬子地台北缘古生界海相烃源岩有机地球化学特征[J].岩性油气藏, 2010, 22(3): 31~37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201003008.htmGONG Daxing, LIN Jinhui, TANG Yunfeng, et al. Organic geochemical characteristics of Paleozoic marine source rocks in northern margin of Upper Yangtze platform[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2010, 22(3): 31~37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201003008.htm [21] 刘军, 罗小平, 李辉, 等.查干凹陷下白垩统烃源岩地球化学特征[J].岩性油气藏, 2013, 25(1): 75~80, 87. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201301021.htmLIU Jun, LUO Xiaoping, LI Hui, et al. Geochemical characteristics of hydrocarbon source rocks of the lower Cretaceous in the Chagan Sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2013, 25(1): 75~80, 87. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201301021.htm [22] Volkman J K. Sterols and other triterpenoids: source specificity and evolution of biosynthetic pathways[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2005, 36(2): 139~159. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2004.06.013 [23] 任军虎, 王万春, 康晏.有机地球化学指标的分析[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2006, 25(3): 266~271. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200603008.htmREN Junhu, WANG Wanchun, KANG Yan. The analysis of organic geochemistry indexes[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2006, 25(3): 266~271. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200603008.htm [24] 刘小平, 刘庆新, 刘杰, 等.黄骅坳陷沧东凹陷孔二段富有机质泥页岩地球化学特征[J].岩性油气藏, 2015, 27(6): 15~22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201506003.htmLIU Xiaoping, LIU Qingxin, LIU Jie, et al. Geochemical characteristics of organic-rich shales of the second member of Kongdian Formation in Cangdong Sag, Huanghua depression[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2015, 27(6): 15~22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201506003.htm [25] 傅家谟, 盛国英, 许家友, 等.应用生物标志化合物参数判识古沉积环境[J].地球化学, 1991, 20(1): 1~12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX199101000.htmFU Jiamo, SHENG Guoying, XU Jiayou, et al. Application of biomarker compounds in assessment of paleo-environments of Chinese terrestrial sediments[J]. Geochimica, 1991, 20(1): 1~12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX199101000.htm [26] 郑建京, 温德顺, 孟仟祥, 等.煤系烃源岩热模拟演化过程的地球化学参数特征――以准噶尔盆地侏罗系煤系烃源岩为例[J].天然气地球科学, 2003, 14(2): 134~139. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2003.02.134ZHENG Jianjing, WEN Deshun, MENG Qianxiang, et al. Characteristics of geochemical parameters of coal measures source rock in the thermal simulation experiment[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2003, 14(2): 134~139. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2003.02.134 [27] 李新景, 胡素云, 程克明.北美裂缝性页岩气勘探开发的启示[J].石油勘探与开发, 2007, 34(4): 392~400. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200704003.htmLI Xinjing, HU Suyun, CHENG Keming. Suggestions from the development of fractured shale gas in North America[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2007, 34(4): 392~400. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200704003.htm [28] 吉利明, 马向贤, 夏燕青, 等.黏土矿物甲烷吸附性能与微孔隙体积关系[J].天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(2): 141~152. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201402002.htmJI Liming, MA Xiangxian, XIA Yanqing, et al. Relationship between methane adsorption capacity of clay minerals and micropore volume[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(2): 141~152. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201402002.htm [29] 刘洪林, 王红岩, 刘人和, 等.中国页岩气资源及其勘探潜力分析[J].地质学报, 2010, 84(9): 1374~1378. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201009011.htmLIU Honglin, WANG Hongyan, LIU Renhe, et al. China shale gas resources and prospect potential[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(9): 1374~1378. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201009011.htm -





 下载:
下载: