3D digital modelling and detailed anatomy of tight sandstone reservoir outcrop with oil-bearing heterogeneity: A case study of Angou outcrop of Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin
-
摘要: 由于缺少典型油砂露头,客观认识砂体内部受控于构型界面的储层含油非均质性受到制约,有效素材的缺乏一直阻碍着表征砂体内部含油非均质性及其与构型界面具体关系的认识。位于鄂尔多斯盆地东南部的安沟露头中致密砂岩含油非均质性表现明显,是储层含油非均质性和表征其与不同构型界面具体关系的有效素材。利用无人机多点位航拍对安沟油砂露头进行了三维数字露头建模,并对其三维数字模型进行了沉积−层序−成岩解剖,结果发现露头中原油充注仅分布于单层砂体内部,而砂体顶、底部并不含油。对实测剖面进行沉积相及层序地层分析,结果表明含油致密砂岩的沉积环境为曲流河水道,底面对应延长组7(长7)油层组和延长组6(长6)油层组界限的三级层序界面。砂体内含油非均质性与水道叠置、砂坝垂向加积和底形(交错层)构型界面关系密切。手持切割机对长7和长6油层组露头进行连续取样和岩石薄片镜下观察,研究发现单砂层顶、底和内部截然不同的结构、物性和成岩特征是造成安沟露头差异化含油的根本原因。安沟油砂露头的发现为客观认识砂体内部受控于构型界面的储层含油非均质性提供了难得的野外实例。该露头的详细解剖为致密砂岩储层含油非均质性明显受控于沉积作用和差异化的成岩作用提供了直接的地质证据。Abstract:
Objective Our understanding of architecture-controlled oil-bearing heterogeneity shown in tight sandstone reservoirs is hindered by scarcity of large-scale oil-bearing outcrops. Triassic lacustrine delta and fluvial succession exposed in a quarry near Angou village (Yanchang county, northern Shannxi province) is an analog for buried oil-bearing tight sandstones in the Ordos basin. Methods In this study, 3D digital outcrop modeling was carried out on the oil-bearing sandstone outcrop of Angou by using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle(UAV) multi-point aerial photography, and then the depositional sequence diagenetic anatomy and field anatomy were carried out on the 3D digital model of Angou oil-bearing sandstone outcrop. Based on field observations, drone-based measurement and digital outcrop modelling, continuous sampling using Husquvarna power cutter and petrographic and diagenesis analysis under section, a 2D architectural heterogeneity model incorporating spatial configuration of effective reservoir was created. Results The UAV 3D digital outcrop modeling and field dissection revealed that the oil charging was only distributed within the interior, but not at the top or bottom of sand body. The configuration and nature of bounding surface underlying this succession was reconstructed with reference to lateral tracing for distinctive markers and a detailed measured profile with facies and sequence stratigraphic analysis. The results show that the sedimentary environment of oil-bearing tight sandstone is curved river channel. In the quarry, fluvial sandstone succession is underlain by a regional surface interpreted as a third-order sequence boundaries on the basis of abrupt landward facies change and locally developed incised valleys <20 m deep. Architectural heterogeneity within the amalgamated sandbody is expressed by multiple fifth-order storey surfaces, sixth-order barform and seventh-order bedform. Continuous sampling and thin-section observation of outcrops show that the completely different structural properties and diagenetic characteristics of the top, bottom and interior of a single sand layer are the fundamental reasons for the different oil bearing in outcrops. The discovery of the Angou oil-bearing outcrop provides a rare field example for the objective understanding of the oil-bearing heterogeneity of the reservoir controlled by the configurational interface in the sand body. Conclusion In this study, the specific characteristics of oil-bearing heterogeneity in oil-bearing sandstone outcrop are described, the sedimentary background and possible levels of different configuration interfaces of extremely thick oil-bearing sandstone are revealed, and the causes of oil-bearing heterogeneity developing in sand bodies are qualitatively understood. [ Significance ] Of importance, the discovery and detailed anatomy of Angou outcrop provide direct geological evidence showing that sedimentation and diagenesis exert a strong control on the quality and heterogeneity of most tight clastic reservoirs. -
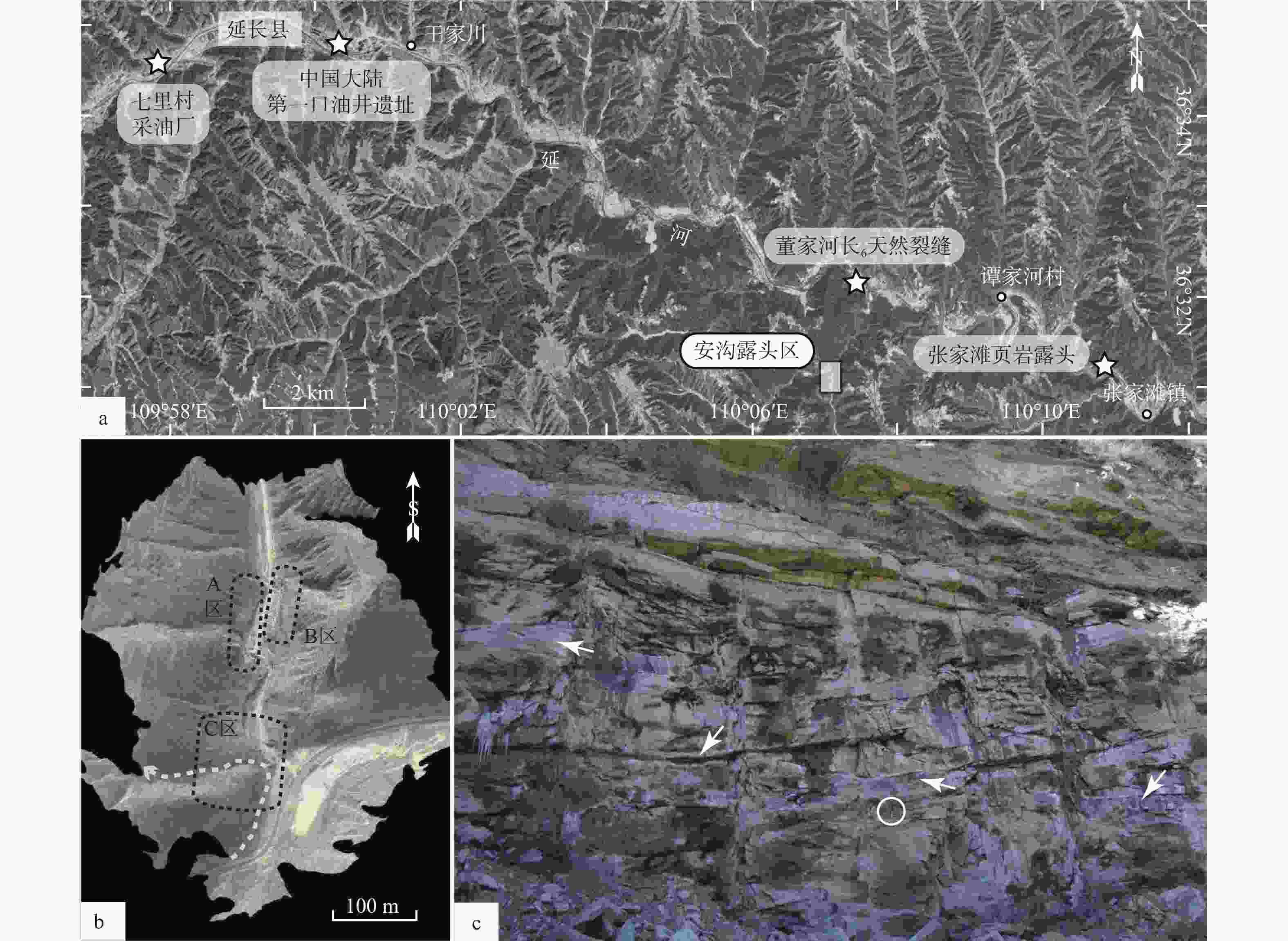
图 2 安沟露头野外特征
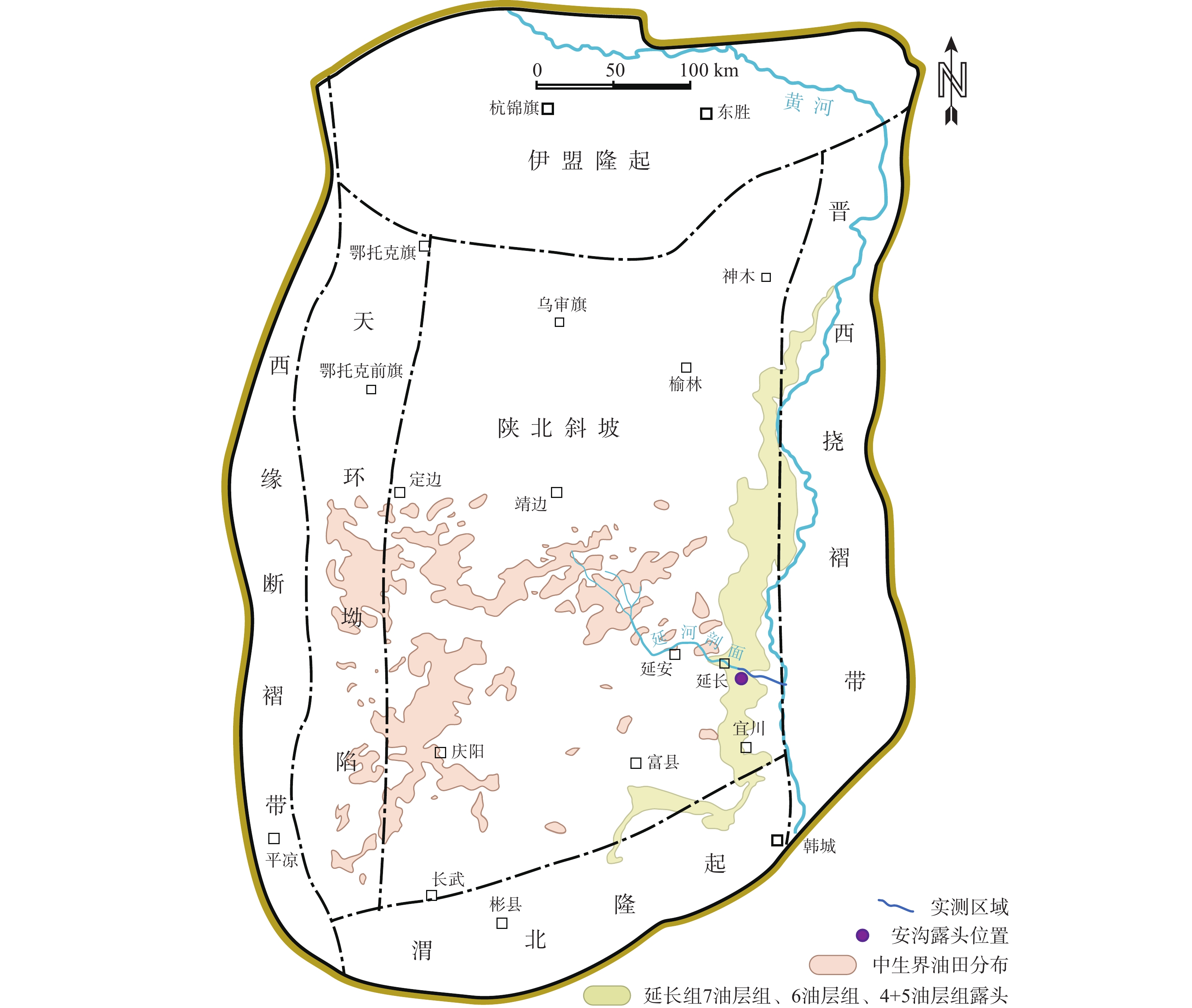
a—三叠系延长组正层型(延河)剖面和安沟露头区位置图;b—安沟露头区三维点云模型及分区解剖方案(白色虚线为图3剖面实测路线);c—B区露头致密砂岩中含油非均质性特征(箭头所指为结合型砂岩中灰白色不含油区域,其余棕色区域均普遍含油;白圈内为比例尺)
Figure 2. Field characteristics og Angou outcrop
(a) Location map of the stratotype (Yan river) section of Triassic Yanchang Formation and the Angou outcrop; (b) Low resolution point-cloud dataset showing the extent of three studied surfaces of the Angou outcrop (black dotted round rectangle) and location of measured section (white dotted line); (c) Close-up view of B-surface showing the heterogeneity of oil charging(The most brown areas are oil-bearing, whereas others are oil-free (white arrows);proportional scale in the white circle)
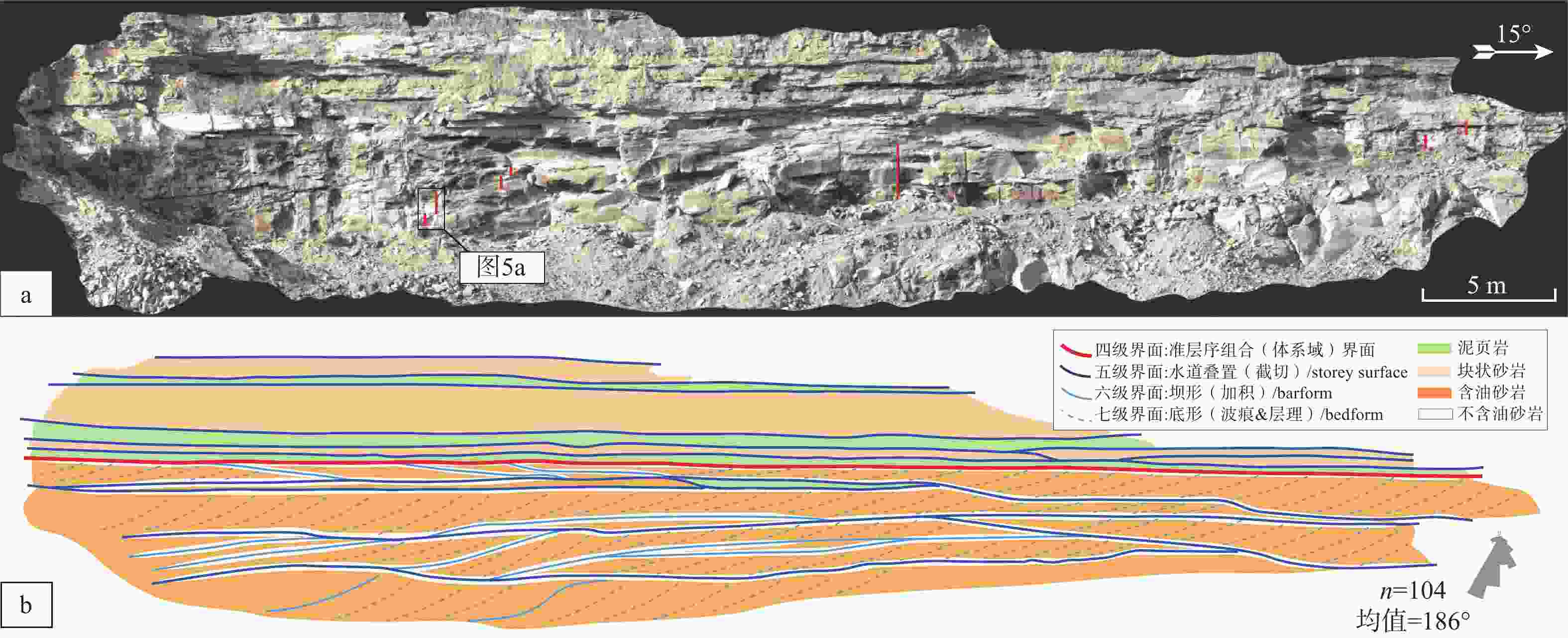
图 3 安沟露头致密砂岩储层结构非均质性模型
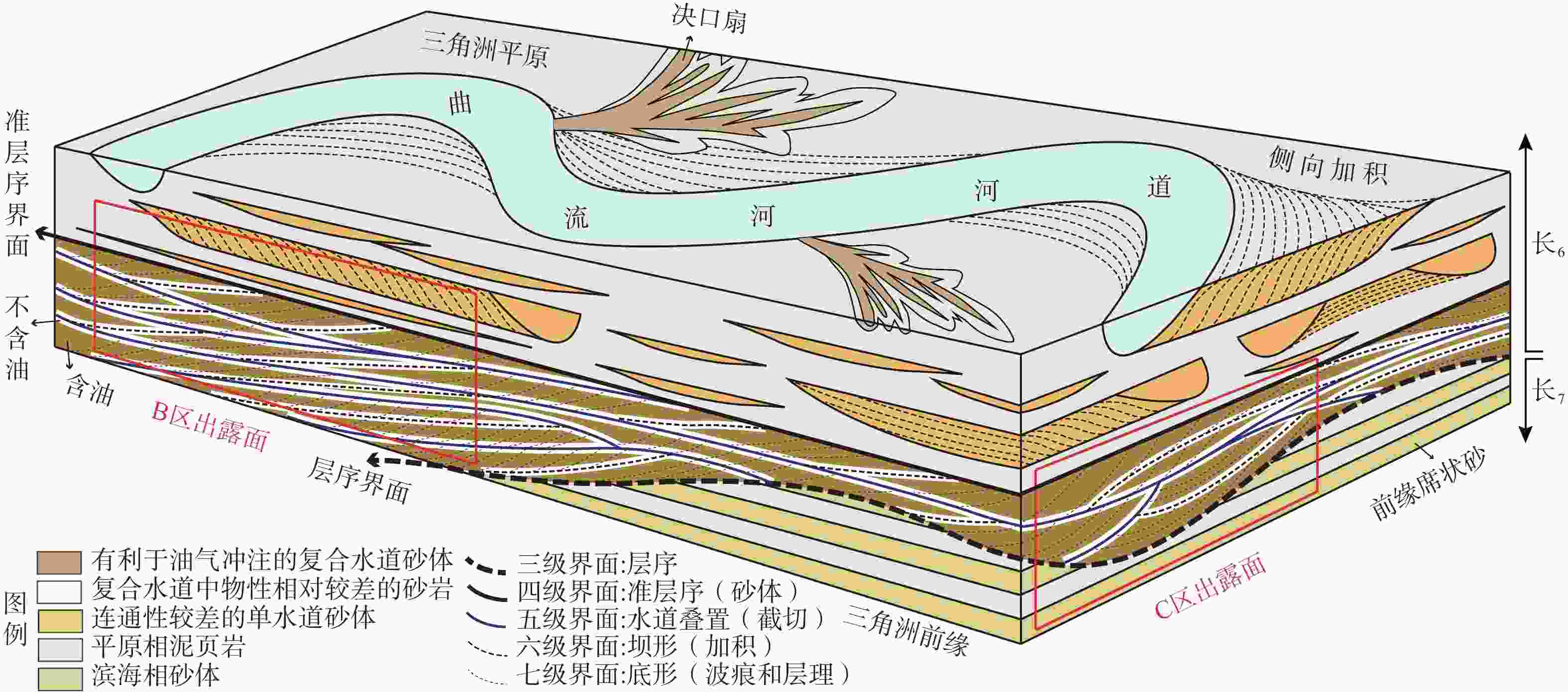
a—B区露头三维点云模型面向105°方位的正射影像(红色条带为野外手持切割机连续取样位置);b—结合型致密砂岩储层中不同级别构型界面和含油非均质性特征示意图(其中水道叠置和砂坝加积界面为写实,交错层等底形界面仅为示意,n代表古流向测量数值,玫瑰花图显示古流向)
Figure 3. Model for architectural heterogeneity in tight sandstone reservoir exposed in the Angou outcrop
(a) Digital orthophoto of 3D point-cloud model of B-surface facing 105-degree, area of continuous sampling using Husquvarna power cutter is denoted by red bands; (b) Diagram showing different-scale architectural boundaries and heterogeneity of oil charging in amalgamated tight sandstone reservoir (For simplicity, storey and barform surfaces are depicted explicitly, whereas bedform surfaces are shown schematically, n represents the measured number of paleo-flows, and the rose diagram shows the paleo-flows)
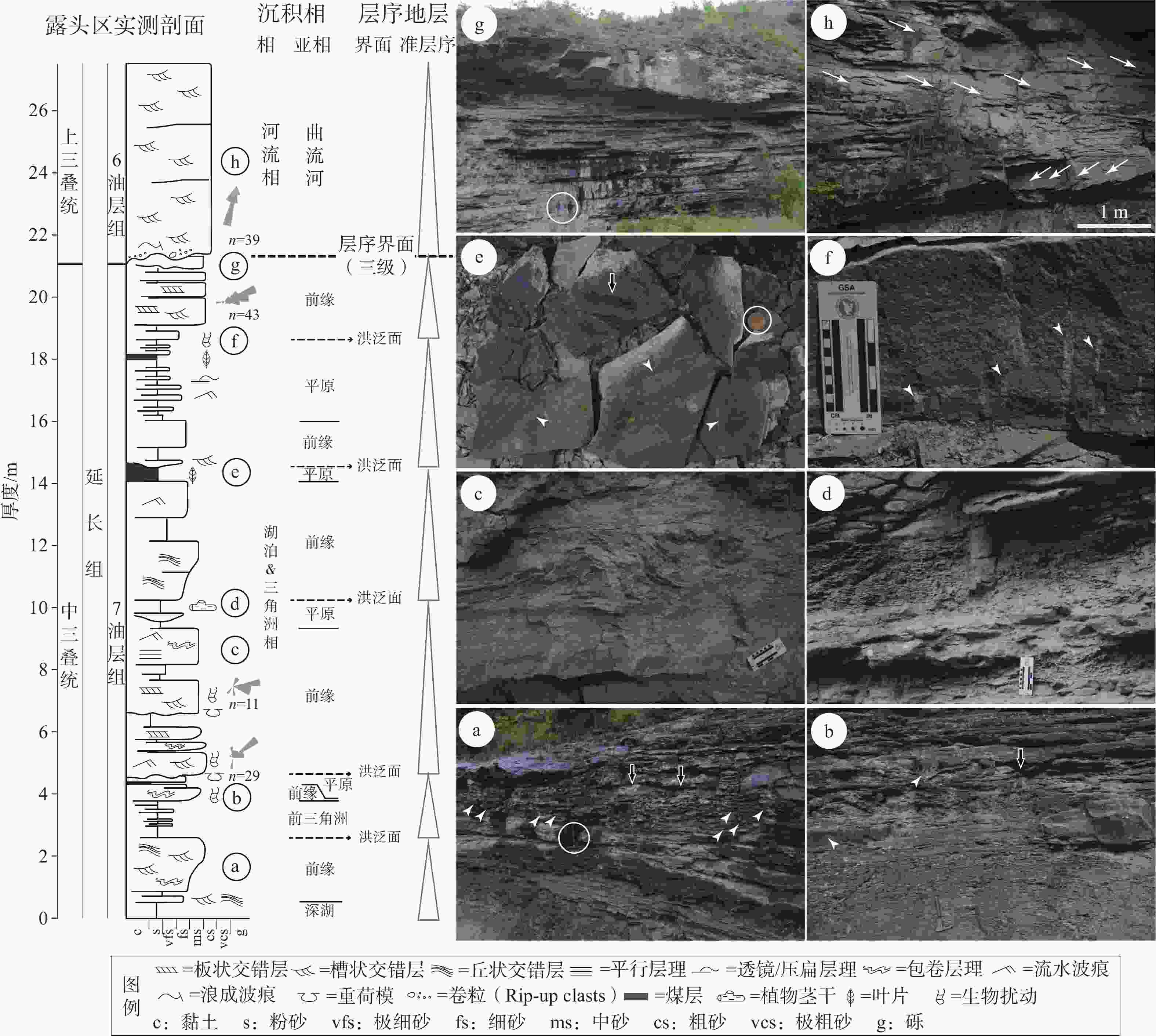
图 4 安沟露头C区实测地层剖面柱状图及典型岩相野外照片
n代表古流向测量数据a—实测剖面底部的深湖相长7张家滩页岩及上覆三角洲前缘亚相发育槽状交错层(白色箭头所指)和丘状交错层(黑色箭头所指)的灰白色巨厚层中粒石英岩屑砂岩;b—三角洲前缘亚相砂岩底部发育的重荷模(白色箭头所指)及内部发育的泄水构造(黑色箭头所指);c—三角洲前缘亚相砂岩内部发育的包卷层理;d—三角州平原相粉砂质泥岩中直立的芦木化石;e—三角州平原亚相劣质煤层中大量保存的植物茎干(白色箭头所指)和叶片(黑色箭头所指);f—三角洲前缘亚相砂岩内部发育的垂直虫孔;g—长6和长7地层界限上下不同方向的槽状交错层(箭头所指);h—长6地层底部河流相砂岩底部发育的大型下切侵蚀面
Figure 4. Columnar diagram of measured stratigraphic section and field photographs of typical petrographic facies in Area C of Angou outcrop
(a) Profundal facies Zhangjiatan shale (lower-left corner) and trough (white arrows) and hummocky (black arrows) cross-stratifications and in overlying delta front facies sandstone; (b) Load casts (white arrows) and dewatering structures (black arrows) in delta front facies sandstone; (c) Convolute lamination in delta front facies sandstone; (d) Trunk of calamite fossil preserved in delta plain facies silty mudstone; (e) Stems and leaves of unidentified plant fossils in delta plain facies coal-bearing beds; (f) Rooting or unidentified burrowing (white arrows) in delta front facies sandstone; (g) Channelized incision surface developed on the top of delta front facies deposits of Chang 7 member, Overlying facies are coarser fluvial facies of Chang 6 member; (h) The stratigraphic boundary between Chang 6 and 7 members underlain and overlain by delta and fluvial facies sandstone with NEE- and SSW-oriented trough cross-stratifications (white arrows) n represents the number of measured paleo-flows
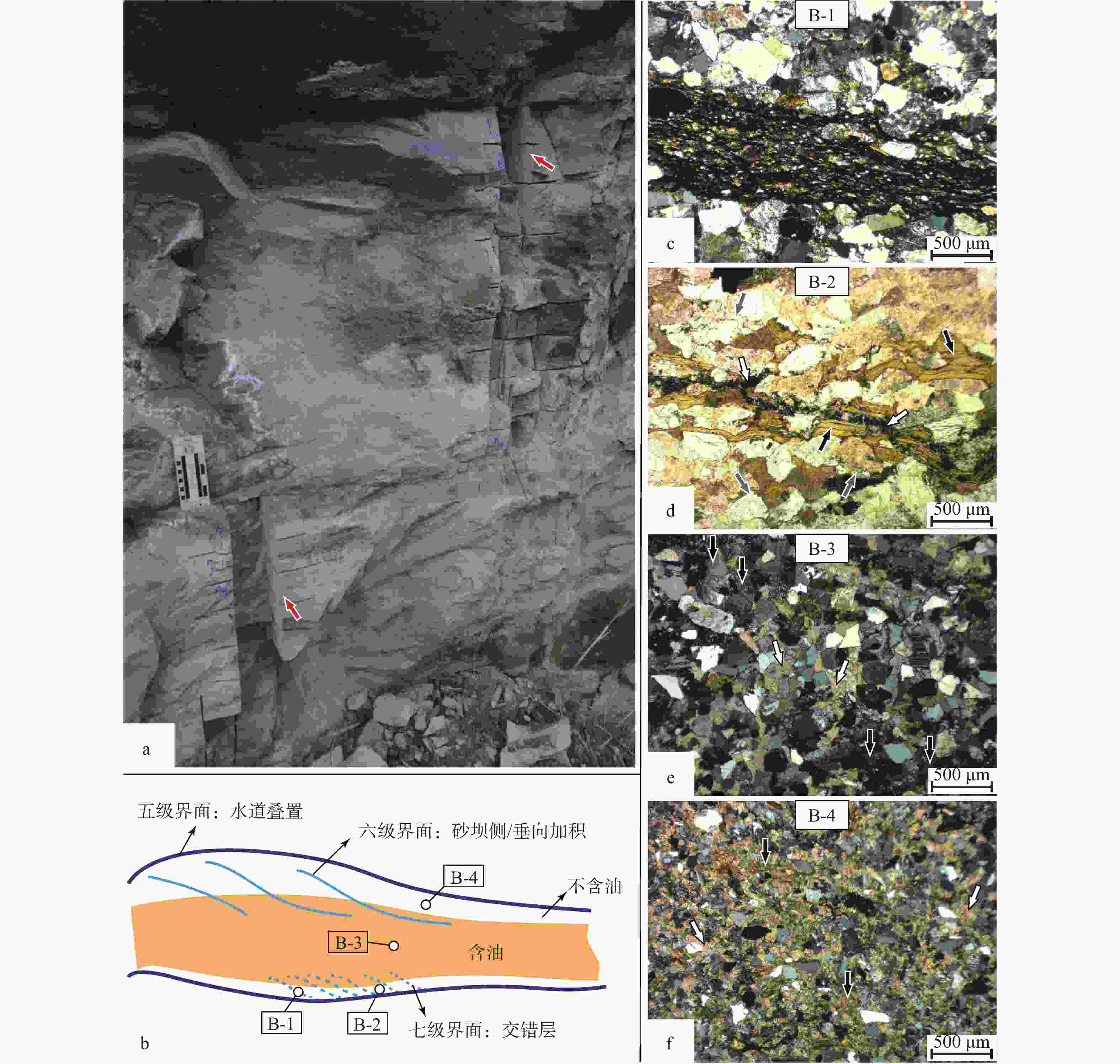
图 5 局部露头含油非均质性以及单层砂岩不同部位的物性与成岩特征
a—单层砂岩含油特征露头近照及连续取样记录,采样位置(红色箭头);b—单层砂岩含油非均质性示意图及薄片样品位置;c—单层砂岩底部样品,发育有机质纹层的中粒长石砂岩,正交偏光;d—单层砂岩底部样品,发育假杂基(黑色箭头)、长石自生加大(灰色箭头)和黄铁矿胶结(白色箭头)的中粒长石砂岩,单偏光;e—单层砂岩中部样品,发育方解石和浊沸石连晶式胶结的细粒长石砂岩,正交偏光;f—单层砂岩顶部发育亮晶(白色箭头)和泥晶(黑色箭头)方解石基底式胶结的极细粒长石砂岩,正交偏光
Figure 5. Details of oil-bearing heterogeneity in local outcrops and physical properties and diagenetic characteristics in different parts of individual sandstone layer
(a) Close-up view of oil-bearing characteristic of each sandstone bed and record of continuous sampling for detailed observation, sampling location (red arrows); (b) Schematic diagram showing heterogeneity of oil charging in single bed of tight sandstone and positions of representative samples for thin-section; (c)The bottom sample of single-layer sandstone, medium grained arkose sandstone with organic lamination, cross-polarized light, sample B-1; (d) The bottom sample of single-layer sandstone is a mediumgrained arkose with pseudoheterobasic (black arrow), autogenetic extension of feldspar (gray arrow) and pyrite cement (white arrow), plane polarized light, sample B-2; (e)The central sample of single-layer sandstone developed fine grained arkose with calcite and turbidite intergranular cementation, cross-polarized light, sample B-3; (f)The top of the singlelayer sandstone is a very finegrained arkose with sparry (white arrow) and micrite (black arrow) calcite basement cement, cross-polarized light, sample B-4
-
[1] BEKELE E, PERSON M, DE MARSILY G, 1999. Petroleum migration pathways and charge concentration: a three-dimensional model: discussion[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 83(6): 1015-1019. [2] BRYANT I D, FLINT S S, 1992. Quantitative clastic reservoir geological modelling: problems and perspectives[M]//FLINT S S, BRYANT I D. The geological modelling of hydrocarbon reservoirs and outcrop analogues. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications: 1-20. CATUNEANU O, 2019. Scale in sequence stratigraphy[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 106: 128-159. [3] CATUNEANU O,2019. Scale in sequence stratigraphy[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,106:128-159. [4] CATUNEANU O, 2022. Sequence stratigraphic framework[M]// CATUNEANU O. Principles of Sequence Stratigraphy . Amsterdam: Elsevier: 295-336. [5] CHEN F, LUO P, ZHANG X Y, et al., 2010. Stratigraphic architecture and sequence stratigraphy of Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in the eastern margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 17: 330-338. (in Chinese) [6] CHEN H Q, WANG J, DU Y J, 2017. Advances of research methods on reservoir heterogeneity[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 23(1): 104-116. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] CHEN J J, ZHAO J Z, LIU Z Y, et al. , 2023. Influencing Factors of Physical Properties of Chang 6 Reservoir in the Qilicun Oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Geology and Exploration 59(3): 647-656. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] CHEN Q H, LI W H, GAO Y X, et al., 2007. Deep lacustrine sedimentary relationship of Yanchang Formation, Upper Triassic, Ordos Basin[J]. Science in China Press, 31(S1): 39-48. (in Chinese) [9] CUI J W, ZHU R K, WU S T, et al., 2013. Heterogeneity and lower oily limits for tight sandstones: a case study on Chang-7 oil layers of the Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 34(5): 877-882. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] DALRYMPLE R W, BOYD R, ZAITLIN B A, 1994. Incised-valley systems: origin and sedimentary sequences[M]. Tulsa: SEPM Society for Sedimentary Geology. [11] DENG S H, LU Y Z, LUO Z, et al., 2018. Subdivision and age of the Yanchang Formation and the Middle/Upper Triassic boundary in Ordos Basin, North China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 61(10): 1419-1439. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9215-3 [12] DENG X Q, LI W H, LIU X S, 2009. Discussion on the stratigraphic boundary between Middle Triassic and Upper Triassic[J]. Acta geologica Sinica, 83(8): 1089-1096. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] DU G C, SHI L H, MA X F, et al., 2019. Laumontite cementation characteristics and their influences on reservoir physical properties in Chang 6 member of Qilicun oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 40(2): 174-180. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] DUTTON S P, WHITE C D, WILLIS B J, et al., 2002. Calcite cement distribution and its effect on fluid flow in a deltaic sandstone, Frontier Formation, Wyoming[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 86(12): 2007-2021. [15] ENGE H D, BUCKLEY S J, ROTEVATN A, et al., 2007. From outcrop to reservoir simulation model: workflow and procedures[J]. Geosphere, 3(6): 469-490. doi: 10.1130/GES00099.1 [16] FISCHER C, GAUPP R, DIMKE M, et al., 2007. A 3D high resolution model of bounding surfaces in aeolian-fluvial deposits: an outcrop analogue study from the Permian Rotliegend, northern Germany[J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 30(3): 257-273. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-5457.2007.00257.x [17] FITCH P J R, LOVELL M A, DAVIES S J, et al., 2015. An integrated and quantitative approach to petrophysical heterogeneity[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 63: 82-96. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.02.014 [18] FU J H, GUO Z Q, DENG X Q, 2005. Sedimentary facies of the Yanchang Formation of Upper Triassic and petroleum geological implication in southwestern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 7(1): 34-44. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] HODGETTS D, 2013. Laser scanning and digital outcrop geology in the petroleum industry: a review[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 46: 335-354. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.02.014 [20] HOWELL J A, MARTINIUS A W, GOOD T R, 2014. The application of outcrop analogues in geological modelling: a review, present status and future outlook[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 387(1): 1-25. doi: 10.1144/SP387.12 [21] JI L M, XU J L, SONG Z G, 2012. Lacustrine cyanobacteria from the Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin and its implication of oil source[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 29(3): 270-281. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] JIANG D X, WANG Y D, WEI J, 2006. Palynoflora and its environmental significance of the Late Triassic in Tongchuan, Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 8(1): 24-33. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] LAPPONI F, CASINI G, SHARP I, et al., 2011. From outcrop to 3D modelling: a case study of a dolomitized carbonate reservoir, Zagros Mountains, Iran[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 17(3): 283-307. doi: 10.1144/1354-079310-040 [24] LONGMAN M W, 1980. Carbonate diagenetic textures from nearsurface diagenetic environments[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 64(4): 461-487. [25] LUO J L, LUO X R, BAI Y B, et al., 2016. Impact of differential diagenetic evolution on the chronological tightening and pore evolution of tight sandstone reservoirs: a case study from the Chang-7 tight turbidite sandstone reservoir in the southwestern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 38(1): 79-92. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] LUO X R, 2011. Simulation and characterization of pathway heterogeneity of secondary hydrocarbon migration[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 95(6): 881-898. doi: 10.1306/11191010027 [27] LUO X R, HU C Z, XIAO Z Y, et al., 2015. Effects of carrier bed heterogeneity on hydrocarbon migration[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 68: 120-131. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.08.015 [28] LUO X R, WANG Z N, LEI Y H, et al., 2016a. Heterogeneity characteristics and accumulation model of ultra-low permeability sandstone reservoirs: a case study of the lower part of Yanchang Formation in the western Ordos Basin, China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 37(S1): 87-98. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] LUO X R, ZHANG L K, LEI Y H, et al., 2016b. Structural heterogeneity of reservoirs and its implication on hydrocarbon accumulation in deep zones[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 21(1): 28-36. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] MA L Y, HU C Z, QIU G Q, et al., 2020. Heterogeneity and structural pattern of Chang 8 reservoir in Zhenjing Area, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 38(5): 1088-1098. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] MIALL A D, 1996. The Geology of Fluvial Deposits: Sedimentary Facies, Basin Analysis and Petroleum Geology[M]//GEORGE P. Sedimentary Geology. Berlin: Springer-Verlag: 149-150. [32] MIALL A D, 2010. TimeinSequence Stratigraphy[M]//ANDREW M. The Geology of Stratigraphic Sequences. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer: 381-389. [33] MIKES D, GEEL C R, 2006. Standard facies models to incorporate all heterogeneity levels in a reservoir model[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 23(9-10): 943-959. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2005.06.007 [34] MORAD S, AL-RAMADAN K, KETZER J M, et al., 2010. The impact of diagenesis on the heterogeneity of sandstone reservoirs: a review of the role of depositional facies and sequence stratigraphy[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 94(8): 1267-1309. doi: 10.1306/04211009178 [35] NESBIT P R, BOULDING A D, HUGENHOLTZ C H, et al., 2020. Visualization and sharing of 3D digital outcrop models to promote open science[J]. GSA Today, 30(6): 4-10. doi: 10.1130/GSATG425A.1 [36] ONYENANU G I, JACQUEMYN C E M M, GRAHAM G H, et al., 2018. Geometry, distribution and fill of erosional scours in a heterolithic, distal lower shoreface sandstone reservoir analogue: Grassy member, Blackhawk Formation, Book Cliffs, Utah, USA[J]. Sedimentology, 65(5): 1731-1760. doi: 10.1111/sed.12444 [37] OWEN A, EBINGHAUS A, HARTLEY A J, et al., 2017. Multi‐scale classification of fluvial architecture: an example from the Palaeocene–Eocene Bighorn Basin, Wyoming[J]. Sedimentology, 64(6): 1572-1596. doi: 10.1111/sed.12364 [38] PORTER R J, ROJAS A M, SCHLÜTER M, 2018. The impact of heterogeneity on waterflood developments in clastic inner shelf reservoirs: an example from the Holland Greensand member, Rotterdam Field, The Netherlands[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 469(1): 457-477. doi: 10.1144/SP469.20 [39] POSAMENTIER H W, ALLEN G P, 1999. Siliciclastic sequence stratigraphy—concepts and applications[M]. Tulsa: SEPM Society for Sedimentary Geology. [40] PRANTER M J, REZA Z A, BUDD D A, 2006. Reservoir-scale characterization and multiphase fluid-flow modelling of lateral petrophysical heterogeneity within dolomite facies of the Madison Formation, Sheep Canyon and Lysite Mountain, Wyoming, USA[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 12(1): 29-40. doi: 10.1144/1354-079305-660 [41] PRINGLE J K, WESTERMAN A R, CLARK J D, et al., 2004. 3D high-resolution digital models of outcrop analogue study sites to constrain reservoir model uncertainty: an example from Alport Castles, Derbyshire, UK[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 10(4): 343-352. doi: 10.1144/1354-079303-617 [42] QU H J, YANG X C, CAO J Z, et al., 2011. Oil accumulation rules in deep zones of Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 32(2): 243-248. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] RASHID B, MUGGERIDGE A H, BAL A, et al., 2012. Quantifying the impact of permeability heterogeneity on secondary-recovery performance[J]. SPE Journal, 17(2): 455-468. doi: 10.2118/135125-PA [44] SCHLAGER W, 2004. Fractal nature of stratigraphic sequences[J]. Geology, 32(3): 185-188. doi: 10.1130/G20253.1 [45] VAN WAGONER J C, MITCHUM R M, CAMPION K M, et al. , 1990. Siliciclastic sequence stratigraphy in well logs, cores, and outcrops: concepts for high-resolution correlation of time and facies[M]. Tulsa: American Association of Petroleum Geologists. [46] VAN WAGONER J C, 1995. Sequence stratigraphy and marine to nonmarine facies architecture of foreland basin strata, Book Cliffs, Utah, U. S. A. [M]//VAN WAGONER J C, BERTRAM G T. Sequence stratigraphy of foreland basin deposits: outcrop and subsurface examples from the cretaceous of north America. Tulsa: American Association of Petroleum Geologists. [47] WANG D Y, XIN B S, YANG H, et al., 2014. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age and geological implications of tuff at the bottom of Chang-7 member of Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 57(12): 2966-2977. doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4979-0 [48] WEBER K J, 1978. Computation of initial well productivities in aeolian sandstone on the basis of a geological model, Leman gas field, U K [M]//TILLMAN R W, WEBER K J. Reservoir Sedimentology. Tulsa, Oklahoma, U. S. A: Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists: 333-354. [49] WEBER K J, 1986. How heterogeneity affects oil recovery[M]//LAKE L W, CARROLL JR H B. Reservoir characterization. New York: Academic Press: 487-544. [50] WORDEN R H, ARMITAGE P J, BUTCHER A R, et al., 2018. Petroleum reservoir quality prediction: overview and contrasting approaches from sandstone and carbonate communities[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 435(1): 1-31. doi: 10.1144/SP435.21 [51] WU C D, LIU J M, WANG J, et al., 2003. The reservoir heterogeneity and analysis of sedimentary architecture in river deposits[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 38(1): 60-73. (in Chinese with English abstract [52] WU S H, JI Y L, YUE D L, et al., 2013. Discussion on hierarchical scheme of architectural units in clastic deposits[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 19(1): 12-22. (in Chinese with English abstract [53] ZEITO G A, 1956. Interbedding of shale breaks and reservoir heterogeneities[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology,, 17((10):): 1223-1228. doi: 10.2118/1128-PA [54] ZHANG X H, XIN H G, CAO R R, et al., 2023. Differences in Microscopic Pore-Throat Structure of Reservoirs and Their Significance for Hydrocarbon Accumulation of Chang 8 Reservoir in the Nanliang-Huachi Area, Ordos Basin[J]. Geology and Exploration, 59(2): 418-432. (in Chinese with English abstract [55] ZHAO J Z, YANG X C, WU F L, et al., 2006. Controlling of uplifts on the Triassic petroleum accumulation and distribution in north Shaanxi Slope, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(5): 648-655. (in Chinese with English abstract [56] ZHOU Y, JI Y L, XU L M, et al., 2016. Controls on reservoir heterogeneity of tight sand oil reservoirs in Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in Longdong Area, southwest Ordos Basin, China: implications for reservoir quality prediction and oil accumulation[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 78: 110-135. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.09.006 [57] ZHU X M, PAN R, ZHU S F, et al., 2018. Research progress and core issues in tight reservoir exploration[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 25(2): 141-146. (in Chinese with English abstract [58] 陈飞,罗平,张兴阳,等,2010. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘上三叠统延长组砂体结构与层序地层学研究[J]. 地学前缘,17(1):330-338. [59] 陈欢庆,王珏,杜宜静,2017. 储层非均质性研究方法进展[J]. 高校地质学报,23(1):104-116. [60] 陈军军,赵靖舟,柳朝阳,等,2023. 鄂尔多斯盆地七里村油田长6油层储层物性影响因素[J]. 地质与勘探,59(3):647-656. [61] 陈全红,李文厚,高永祥,等,2007. 鄂尔多斯盆地上三叠统延长组深湖沉积与油气聚集意义[J]. 中国科学D辑:地球科学,31(S1):39-48. [62] 崔景伟,朱如凯,吴松涛,等,2013. 致密砂岩层内非均质性及含油下限:以鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段为例[J]. 石油学报,34(5):877-882. [63] 邓胜徽,卢远征,罗忠,等,2018. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组的划分、时代及中—上三叠统界线[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,48(10):1293-1311. [64] 邓秀芹,李文厚,刘新社,等,2009. 鄂尔多斯盆地中三叠统与上三叠统地层界线讨论[J]. 地质学报,83(8):1089-1096. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.08.005 [65] 杜贵超,石立华,马晓峰,等,2019. 七里村油田长6油层浊沸石胶结特征及其对物性影响[J]. 新疆石油地质,40(2):174-180. [66] 付金华,郭正权,邓秀芹,2005. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南地区上三叠统延长组沉积相及石油地质意义[J]. 古地理学报,7(1):34-44. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2005.01.004 [67] 吉利明,徐金鲤,宋之光,2012. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组湖相蓝藻及其油源意义[J]. 微体古生物学报,29(3):270-281. [68] 江德昕,王永栋,魏江,2006. 陕西铜川晚三叠世孢粉植物群及其环境意义[J]. 古地理学报,8(1):23-33. [69] 罗静兰,罗晓容,白玉彬,等,2016. 差异性成岩演化过程对储层致密化时序与孔隙演化的影响:以鄂尔多斯盆地西南部长7致密浊积砂岩储层为例[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,38(1):79-92. [70] 罗晓容,王忠楠,雷裕红,等,2016a. 特超低渗砂岩油藏储层非均质性特征与成藏模式:以鄂尔多斯盆地西部延长组下组合为例[J]. 石油学报,37(S1):87-98. [71] 罗晓容,张立宽,雷裕红,等,2016b. 储层结构非均质性及其在深层油气成藏中的意义[J]. 中国石油勘探,21(1):28-36. [72] 马立元,胡才志,邱桂强,等,2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地镇泾地区长8段储层非均质性及其结构模式[J]. 沉积学报,38(5):1088-1098. [73] 屈红军,杨县超,曹金舟,等,2011. 鄂尔多斯盆地上三叠统延长组深层油气聚集规律[J]. 石油学报,32(2):243-248. [74] 王多云,辛补社,杨华,等,2014. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长7底部凝灰岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,44(10):2160-2171. [75] 吴朝东,刘建民,王军,等,2003. 河流沉积单元分析与储层宏观非均质性[J]. 地质科学,38(1):60-73. [76] 吴胜和,纪友亮,岳大力,等,2013. 碎屑沉积地质体构型分级方案探讨[J]. 高校地质学报,19(1):12-22. [77] 张晓辉,辛红刚,曹润荣,等,2023. 鄂尔多斯盆地南梁-华池地区长8储层微观孔喉结构差异及成藏意义[J]. 地质与勘探,59(2):418-432. [78] 赵靖舟,杨县超,武富礼,等,2006. 论隆起背景对鄂尔多斯盆地陕北斜坡区三叠系油藏形成和分布的控制作用[J]. 地质学报,80(5):648-655. [79] 朱筱敏,潘荣,朱世发,等,2018. 致密储层研究进展和热点问题分析[J]. 地学前缘,25(2):141-146. -




 下载:
下载: