Theoretical innovation and applications of ore-field tectonic lithofacies mapping
-
摘要: 开展成矿蚀变−构造岩相解析建相和建模预测研究已成为矿田构造与找矿预测的创新方向之一。文章对国内外8类重要的成矿蚀变−构造岩相模型和形成机制进行论述总结,南美洲智利科皮亚波地区IOCG型矿田受到主岛弧带−弧相关盆地及岩浆叠加−盆地变形样式的复合控制,而中国云南东川沉积岩型铜矿床(SSC型)+IOCG型铁铜矿田受陆缘裂谷盆地、盆地变形构造样式和岩浆叠加侵入构造系统的复合控制。中国内蒙古甲−查浅成低温热液型银铅锌矿田受火山洼地、火山穹隆构造、火山岩岩相类型和火山热液隐爆角砾岩的复合控制,而深成岩浆弧控制了蒙古国南戈壁斑岩型金铜钼−浅成低温热液金银矿田;中国秦岭热水沉积型(SEDEX)银铜铅锌−菱铁矿−重晶石矿田受到陆缘拉分盆地内三级热水沉积盆地、同生断裂带和热水沉积岩相的控制。大陆造山带内不同层次的脆韧性剪切带,控制了金矿田和金钼多金属矿田定位。在新疆塔西盆−山−原镶嵌区盆地系统内,侏罗系煤系烃矿源岩是金属矿田和天然气气田的成矿成藏物质供给源区;乌拉根砂砾岩型天青石−铅锌矿田受到山前挤压—伸展转换盆地、气成热流柱构造和山前冲断褶皱带的复合控制;萨热克铜多金属矿田赋存于旱地扇杂砾岩,受到对冲式厚皮型逆冲推覆断裂带和幔源热流柱带的复合控制。其中在矿集区−矿田尺度上,电气石热流柱构造、岩浆气囊构造、复合岩溶构造岩相等是成矿蚀变−构造岩相的3种新类型;在归纳前期对矿田构造岩相、矿田构造古地理单元和典型矿田构造岩相形成机制研究基础上,文章提出了矿田成矿蚀变−构造岩相类型的新划分方法和划分原则方案,并划分确定了12种变形构造岩相类型。研究成果为矿田构造研究和找矿预测提供了新理论和新方法支撑。Abstract:
Objective In the matter of material architecture, the diagenetic-metallogenic system may be classified into lithofacies of root-feeders (metallogenic material feeders), lithofacies of structural channel (migration of diagenetic-metallogenic material), lithofacies of closed-reservoir space (unloading-enriching room of diagenetic-metallogenic material), and lithofacies of surrounding rock alteration (water–fluid–rock system of diagenetic-metallogenic material). Ore-field tectonic lithofacies mapping and detailed analysis of the formation mechanism of different types of tectonic lithofacies aid in identifying and delineating in-situ diagenetic-metallogenic systems at the scale of ore clusters and ore fields. These approaches also reveal the formation mechanisms of resources, energy, and minerals, marking it as an innovative direction in ore-field structure and prospecting prediction. In order to promote and deepen the research and understanding of tectonic lithofacies and prospecting prediction in ore fields, this article focused on the lithofacies establishment and modeling predictions on the mineralization-alteration-tectonics-lithofacies, discussing and exploring eight important types of mineralization-alteration-tectonics-lithofacies models and their formation mechanisms domestically and internationally. Methods The article carried out ore field tectonic lithofacies mapping and detailed analysis of the formation mechanism of different types of tectonic lithofacies in order to recognize and delineate in situ diagenetic-metallogenic systems at the scale of ore clusters and ore fields. Results Eight models and formation mechanisms for the mineralization-alteration-tectonics-lithofacies at the scale of ore-field tectonic lithofacies were discussed in this study. The IOCG-type ore field in the Copiapo area of Chile is controlled by the main arc belt, arc-related basins, magmatic superimposing and basin–deformation style. However, the SSC-type Cu deposit and the IOCG-type ore field in the Dongchuan area of Yunnan in southwestern China are located at the marginal rift basin with different styles of basin deformation and reworked by the magmatic superimposing tectonic system. The Jia–Cha epithermal Au-Ag-Pb-Zn ore-field in Inner Mongolia of northern China is dominated by volcanic lake-basin, volcanic dome structure, facies-type of volcanic rocks, and volcanic hydrothermal crypto-explosive breccias, whereas porphyry Cu-Mo-Au and epithermal Au-Cu ore-fields in the South Gebi area of Mongolia are formed in the Devonian–Carboniferous plutonic magmatic arc. The Sedex-type Ag-Cu-Pb-Zn-Ba-Fe ore-field in the Qinling orogeny of central China is shaped by the three-order sub-basin, syngenesis fault, and facies of hydrothermal sedimentary rock in the marginal pull-apart basin. However, gold and Au-Mo-polymetallic ore fields are dominated by different scales of the brittle-ductile shear zones in the orogenic belt. Migrations of the ore-reservoir-forming matters for metallic ore field and gas field are derived from the Jurassic coal-measure hydrocarbon-metal-bearing source rocks in the western Tarim of basin-mountain-plateau mosaic structure in western China. The Wulagen glutenite-type celesite-Pb-Zn ore field located at the piedmont compression to extension conversion basin is coupled by the pneumatogenic plume and superimposed by the piedmont thrust-fold belt. The Sareke glutenite-type Cu-polymetallic ore-field hosted at irony glutenite of the dry-fan facies in the tail-end lake basin is reworked by the hedging-style, base-type thrust fold belt and superimposed by mantle-derived hydrothermal plume. Conclusion Eight models and formation mechanisms for the mineralization-alteration-tectonics-lithofacies at the scale of ore field tectonic lithofacies were discussed in this study based on a review of ore-field tectonics. The tourmaline-rich plume tectonics, magmatic gasbag structure, and compound karsting tectonic lithofacies are three new types of mineralization-alteration-tectonics-lithofacies. Ore-field tectonic paleogeographic unit and formation mechanism of important ore-field tectonic lithofacies, new classification methods and principles of the mineralization-alteration-tectonics-lithofacies and 12 different types of deformational tectonic lithofacies were established in this essay. Significance All achievements in this study have established a new foundation for tectonic lithofacies mapping and ore prediction. -
0. 引言
矿田深部构造研究为找矿预测提供了新动力(翟裕生,2007;陈宣华等,2009;陈正乐和陈柏林,2012;韩润生等,2014;杨兴科等,2015;吕古贤,2020;郑义,2022)。目前深部探测、关键矿产和环境资源等前沿领域(Hou and Cook,2009;Hou et al,2015,2020;周永章等,2018;毛景文等,2020;胡瑞忠等,2020;吕志成等,2022;李三忠等,2023)对理论创新的需求更为紧迫。实现矿田深部探测的3种有效途径分别是:①地壳深部探测,可揭示矿集区深部构造特征并实现对成矿系统探测,探测深度(80 km)可达地幔顶部和下地壳(吕庆田等,2019;肖文交等,2022),进行深部物性填图和地质−构造解释性填图。②在深部油气资源远景区,科学深钻有望实现15000 m以浅的科学深钻工程(邹长春等,2023)。在云南东川开展矿田井巷工程三维构造岩相学填图可实现3000 m探测(方维萱等,2018)。③深部探测和浅部勘探相结合并实施钻孔验证,可实现金属矿集区5000 m以浅的深部探测(李天成等,2022)。但目前仍然面临着随深度增加而探测信号减弱和干扰因素增多、成矿地质环境复杂、确定成矿中心难度大等系列难题,同时这些复杂问题也是矿田构造探测研究方向(吕古贤等,2020;张宝林等,2021;杨树锋等,2022;张善明等,2022;郑义,2022;方维萱,2022a,2023)。遵循成矿系统理论(翟裕生,2007),基于构造岩相学理论创新和填图新方法,方维萱等(2018)将成岩成矿系统在物质结构上划分为4个相:根部相(成矿物质供给系统)、构造通道相(成岩成矿流体运移系统)、圈闭储矿相(成矿物质卸载成矿系统)和围岩蚀变相系(成岩成矿水岩反应系统)。矿石类型、围岩蚀变体系、蚀变岩和相关地质体共同记录了成岩成矿系统的形成演化过程和成矿流体−蚀变岩−岩相间的构造−物理−化学作用。对这些矿田构造−蚀变岩进行解析研究和建模预测,有助于资源能源勘查理论和技术方法的创新。
文章在成矿蚀变−矿田构造岩相研究上,聚焦于8类重要的成矿蚀变−构造岩相模型和形成机制,对电气石岩浆隐爆角砾岩筒、岩浆气囊构造、电气石热流柱构造和复合岩溶构造4类重要岩相进行解剖建相,创新矿田构造岩相分带理论,为评价矿田剥蚀程度提供依据。
1. 理论创新研究与实践应用思路
1.1 理论研究的思维方法−协同学原理与方法技术创新
遵循构造岩相学填图的原创理论(方维萱等,2009,2012,2018,2021,2018;方维萱,2012,2019,2020, 2022a,2022b),基于协同放大原理,采用多学科的综合方法和构造岩相学填图创新技术,对(叠加)成岩成矿系统和各单元结构进行探测和重建研究,以实现从成矿系统理论到勘查系统理论与实践(翟裕生,2007)。基于成矿系统的各单元结构和相应的构造岩相学特征,恢复成岩成矿系统总体物质组成及其相应的构造岩相学特征,研究内容包括:①厘定(叠加)成岩成矿系统的物质来源供给系统,识别成矿物质来源区空间位置。②根部相是成矿物质供给系统发生变化并导致矿质开始沉淀且与围岩相互耦合反应的空间部位,常以发育脉带状−筒状−不规则状蚀变岩和富矿囊为标志;厘定和探测成岩成矿系统的根部相,对于重建(叠加)成矿系统组成、评估其剥蚀程度和找矿预测等均具有重要意义。③成矿流体运移通道相和成矿蚀变−构造岩相为载体,它们记录了驱动力类型及运移过程的物理−化学条件,通过构造岩相学+地球化学岩相学解析,揭示成矿系统的时间域—空间域—物质域的7维相体结构与演化规律。④成矿流体卸载成矿物质以圈闭构造和储矿构造岩相学为主。⑤金属矿床与围岩蚀变相体系。⑥矿床开采地质条件、生态环境效应和修复技术,对水文、工程和环境地质类型进行研究,查明主工业组分、共生组分、伴生有价组分和有害杂质组分分布赋存规律。
成矿蚀变−矿田构造岩相填图方法的原创理论(方维萱等,2009,2012a,2018,2021;方维萱,2012,2019,2020, 2022a,2022b)包括以下的11项创新内容之间的逻辑关系:①成岩成矿系统、构造岩相学解析理论与叠加成岩成矿系统的构造岩相学识别方法。②热水沉积盆地分析−盆地动力学类型识别理论与构造岩相学填图新方法。③热水沉积成岩成矿相系分类新方案、构造岩相分带性新理论、构造岩相学填图与识别技术。④沉积盆地内成岩相系划分新方案、盆地动力学演化新理论、叠加成岩成矿相系的构造岩相学筛分和解析新方法。⑤沉积盆地变形构造岩相史、构造岩相学变形筛分和解剖建相新方法。⑥热液角砾岩构造系统理论与构造岩相学填图技术创新。⑦岩浆(叠加)侵入构造系统填图理论与构造岩相学填图技术创新。⑧隐蔽热流柱构造理论与构造岩相学填图创新技术。⑨复杂构造岩相类型解剖建相理论与建模预测新技术。⑩构造岩相“相体−磁性−电性−密度−谱学”原位综合探测理论和深部隐蔽构造岩相识别技术;⑪新类型构造岩相解析建相与识别新技术。
理论创新思维方法包括原发性理论创新、阐述性理论创新、修正性理论创新、发掘性理论创新和方法性理论创新(方维萱等,2018)。①在阐述性理论创新中,遵循矿田构造学理论(翟裕生,2007),依据构造岩相学和地球化学岩相学原理,对IOCG铁铜金成矿系统和沉积岩型铜多金属成矿系统等进行了研究。对秦岭造山带金银铜铅锌−重晶石−菱铁矿矿集区、云南东川铜铁金(IOCG型)−铜钴−金红石矿集区、云南个旧锡铜钨铯铷多金属矿集区、智利科皮亚波铁铜金矿集区、新疆塔西砂砾岩型铜铅锌矿集区、贵州晴隆锑−萤石−金矿集区等进行实证研究,为找矿预测提供了理论依据(方维萱等,2018)。②在方法性理论创新与构造岩相学原理上,主要核心是采用综合信息和精准探测,运用协同学原理进行同一命题研究,采用地质学和构造地质学、岩石岩相学、地球化学、矿床学、地球物理、遥感、谱学探测和综合研究,创立构造岩相学的新理论。③在境外快速评价、找矿预测和矿产勘查实践应用上,从智利科皮亚波地区IOCG矿床选区登记开始,运用构造岩相学−遥感解译−磁法勘探等综合方法,同期开展智利IOCG矿床预测建模研究(方维萱等,2009;方维萱2012),创建并应用了智利航磁数据再度解译研究→境外战略靶区筛选→地面高精度磁法勘探→磁法−电法异常综合解译评价→钻孔验证→系统预测和普查→提交详查报告(李天成等,2022)。
创建基于理论为指导的工程化创新技术体系,提升在战略选区、找矿预测和验证工程中的普适性,包括:①识别并划分成岩成矿系统的根部相、运移相、中心相、外缘相、远端相共5大组成部分,分别建立它们的综合识别标志。②依据成岩相系划分的新方案,建立了地球化学岩相学和构造岩相学识别新方法与技术体系(方维萱,2020)。③依据热液角砾岩构造系统理论(方维萱等,2018),进行构造岩相学填图单元确定,开展构造岩相学填图和找矿预测。④依据岩浆(叠加)侵入构造系统理论,确定构造岩相学填图单元方法,开展矿山立体构造岩相学填图和找矿预测。⑤根据火山岩系在空间域—时间域—物质域内12相系结构理论(方维萱,2022a),在火山岛弧带和弧相关盆地系统内,厘定火山同生构造岩相和岩浆侵入叠加构造岩相样式;恢复正向(负向)火山喷发机构、火山同生断裂带、次火山岩侵入岩体、火山口相(熔结集块岩和熔结火山角砾岩)、火山沉积盆地、火山喷流沉积和火山热液蚀变成岩成矿系统。⑥依据地球化学岩相学理论,建立地球化学岩相学类型识别方法和技术组合,开展找矿预测。通过对构造岩相体的多维地球化学岩相学解剖研究,重建成岩成矿系统的构造岩相学类型和相体结构。⑦地球物理探测方法(如磁化率填图、AMT、CSAMT等)提供深部构造岩相学信息,识别关键构造岩相,进行构造岩相−物性填图。经验证工程,进行建模预测和找矿预测。⑧以云南东川滥泥坪IOCG矿床为例,说明构造岩相填图在矿山隐伏矿预测中发挥显著作用,滥泥坪矿区属基岩覆盖区,传统以寻找东川式铜矿床为主,从2006年初期对磁法异常检查和深部钻孔揭露,发现了铁氧化物铜金型(IOCG)矿体。经解剖建相研究认为在东川地区属新类型,依据理论创新原理(方维萱等,2009),实验性构造岩相学填图取得了显著的找矿预测效果(方维萱等, 2012),创新理论为生产勘探提供了全新支撑和指导,而矿山生产勘探也验证了创新理论实用价值,探明了中型铜矿床并共生铁矿,伴生金银资源(方维萱,2012;方维萱等,2018)。
1.2 成矿蚀变−构造岩相分类方案
在矿集区和矿田尺度上,成矿蚀变−矿田构造岩相的划分方法如下:以基本填图单位并加载重要构造岩相事件信息、或者经过解剖建相后作为独立构造岩相学填图单元,用于恢复矿田构造−古地理单元。在1∶5万或1∶1万地质填图中清晰或放大标示,其可用于有效地圈定找矿靶区,进行深部探测和找矿预测。对重要的构造岩相事件进行解剖建相研究后,筛选特定构造岩相学独立填图单元,经过大比例尺构造岩相学填图,圈定成岩成矿事件范围,最终圈定找矿靶位。主要原理是成岩成矿过程与相关构造岩相体、围岩蚀变体系、矿石类型和蚀变岩类型之间有十分密切关系,不同构造岩相记录了它们形成过程、瞬态成矿流体−蚀变岩−岩石之间的构造−物理−化学相互作用,通过解析研究可揭示并恢复它们的识别标志、形成机制与演化模式。对于构造岩相学独立填图单元和相关构造岩相体进行立体填图和建模预测,有助于实现矿集区和矿田尺度上的构造岩相学填图理论和技术创新。
在矿集区和矿田尺度上,成矿蚀变−构造岩相类型的划分原则包括:①成矿系统与地球动力学系统的识别;②岩石组合、岩石组构、标型矿物和标型矿物组合类型;③蚀变岩类型、蚀变作用类型、围岩蚀变系统;④热力作用类型和成矿流体运移的驱动力类型;⑤构造应力场结构、构造样式、构造组合和变形构造序列;⑥特殊的前置限定语,包括特殊的结构和构造、有特殊意义的示相矿物、具有特定构造−流体动力学意义的矿物与结构、岩石的颜色和结构构造等,如多孔状硅化脉、马牙状方解石化等;⑦双重前置限定命名,如火山岩命名时,采用碱性玄武质熔岩、碱性钛铁质苦橄岩、酸性长英质凝灰岩等命名,研究不同类型火山岩与岩浆成分等特征,揭示矿田尺度上的岩浆成分和火山岩岩相学与金属成矿之间关系。采用碎裂状白云岩、白云岩质碎裂岩、白云岩质超碎裂岩、长英质糜棱岩、绢英质糜棱岩、大理岩质糜棱岩、碳质糜棱岩、黑云母糜棱岩等不同的前置限定语,对碎裂岩和糜棱岩进行前置限定,表述岩石和成分在岩相学上遭受构造应力变形变质的程度变化规律,为野外划分构造岩相学类型和确定独立填图单元提供依据。对矿集区−矿田尺度的变形构造岩相释义是指能够揭示矿田构造岩相的成矿流体−构造−岩相多重耦合结构、构造变形机制和演化历史的构造岩相样式的总和。与成矿蚀变−构造岩相的区别主要是变形构造岩相类型和特征主要用于识别和筛分构造岩相变形层次和重建构造岩相变形序列,其划分原则、划分方案和识别原理是重要理论研究和技术创新的方向。
变形构造岩相类型划分方案是基于构造岩类型、构造型相和变形变质岩相特征研究而厘定的,依据构造岩相学独立填图单元,开展立体构造岩相学填图,以圈定和预测变形构造岩相带在地表延伸分布规律,基于协同学原理并采用多种勘查方法,探测和预测它们的深部延深规模。根据构造型相、成岩作用方式和强度、岩石组合和地球化学动力学等要素,进行变形构造岩相分类,主要类型包括:①节理−裂隙相;②碎裂岩化相−碎裂岩相;③构造角砾岩相−构造热液角砾岩相;④构造片岩相;⑤构造千枚岩相/斑点状构造千枚岩相;⑥糜棱岩化相−糜棱岩相;⑦构造片麻岩相;⑧构造混合岩相;⑨构造岩块/构造岩片(如坍塌构造岩块、蛇绿混杂岩岩片);⑩古/岩溶构造相带;⑪侵入岩岩脉(枝、墙等);⑫复合型构造−热液蚀变岩相。其中,一级命名方法主体为构造+岩相的复合命名;节理−裂隙相、构造岩块/构造岩片等均以特定的构造型相进行命名,以研究和揭示特定的构造型相在地质演化历史中的作用。在对矿床尺度的复合型构造−热液岩相研究基础上,选定特定的构造−蚀变岩类型和组合,作为矿田尺度上矿化蚀变−构造岩相类型进行研究,实现在矿田构造岩相尺度上对比研究、深部探测和建模预测。
2. 重要矿田的成矿蚀变−构造岩相模型与形成机制
2.1 IOCG型矿田与主岛弧带和弧相关盆地
不同岛弧构造带和弧相关盆地具有不同构造岩相学和金属成矿规律,如:在大洋板块(洋中脊)俯冲消减环境下,从南美安第斯的中生代沟−弧−盆构造系统,演替成为新生代的沟−弧−盆−山−原构造系统。在智利海岸山带的主岛弧带、弧前盆地、弧间盆地和弧后盆地内,火山喷发−岩浆侵入作用形成了完全不同的构造岩相格架。
在智利—玻利维亚地区,从西到东,中生代构造分带特征是:海岸山带前侏罗纪岛弧基底构造→侏罗纪—白垩纪主岛弧带(IOCG成矿带)→中生代弧后盆地(IOCG成矿带)→西科迪勒拉前陆冲断带→前志留纪褶皱构造带→侏罗纪—白垩纪高原弧后断陷盆地带→东科迪勒拉后陆冲断带(造山型锑−金矿床)→弧后前陆盆地,其中:①在智利侏罗纪—白垩纪主岛弧带内,矿田构造岩相以火山穹隆、弧内盆地、岩浆热液角砾岩筒、钙碱性侵入岩和阿卡塔玛脆韧性剪切带为主,矿田构造岩相形成机制是以火山喷发穹隆化—次火山岩侵入—岩浆叠加侵位等综合叠加作用为主,岩浆热液角砾岩筒是岩浆气成隐爆−坍塌−成岩成矿热液充填蚀变而成。②智利侏罗纪—白垩纪弧后盆地位于中生代主岛弧带东侧,宽80~150 km,矿田构造岩相以盆内碳酸盐岩系、膏盐层和含膏砾岩层、钙碱性侵入岩系、岩浆热液角砾岩筒、矽卡岩相−矽卡岩化相带为主。矿田构造岩相的形成机制是以火山喷发穹隆—次火山岩侵入—岩浆叠加侵位—岩浆热液交代矽卡岩相−热液角砾岩相等综合叠加作用为主,形成了智利白垩纪斑岩型铜钼−浅成低温热液金银矿床−IOCG成矿带。③在玻利维亚,形成了侏罗纪—白垩纪弧后前陆盆地内的锡多金属成矿带−曼陀型铜银多金属矿床。
在南美安第斯新生代沟−弧−盆−山−原系统内:①智利中央盆地属弧前山间盆地,形成了钾盐−芒硝−锂矿田和砂砾岩型铜矿床(“异地型”铜矿床)。②新生代斑岩铜金钼−浅成低温热液金银多金属成矿带,受深成岩浆弧和幔型断裂带控制,斑岩铜金钼矿田受岩浆热液蚀变体系控制,在斑岩铜金钼矿田内,形成了浅成低温热液金银多金属矿床;浅成低温热液金银多金属矿田受火山断陷盆地、火山穹隆构造和壳型断裂带等复合控制。③在玻利维亚−阿根廷新生代弧后高原盆地内,形成了铜−锂−硝石−硼矿田和成矿带。④在玻利维亚高原两侧造山带内,形成了斑岩型银锡多金属矿床和造山型金锑矿床。
火山岩区的成矿作用受火山热液和原岩控制,构造−蚀变岩填图有助于揭示(次)火山热液喷流通道系统,为深部找矿预测提供依据。在沟−弧−盆−山−原、洋中脊(有限洋盆)、大陆裂谷盆地3类地球动力学体制下,火山岩系、火山机构和火山地热系统十分发育。在智利中生代弧后盆地内,发育了由火山沉积盆地等负向构造和火山穹隆构造等组成的正向构造单元。
(1)在弧后盆地内发育生物碎屑灰岩−石灰岩−凝灰岩等岩石组合,形成于浅海相沉积环境中;富铁质闪长岩床沿侏罗系生物碎屑灰岩和石灰岩等顺层侵入,富铁质闪长岩上下盘发育矽卡岩相(如石榴子石透闪石矽卡岩)、矽卡岩化相(如方柱石矽卡岩化结晶灰岩)和大理岩相,形成了含铜铁似层状矽卡岩相;偏碱性富铁闪长岩切层侵入于钙碱性火山岩系内,伴有区域性钠长石化相、青磐岩化相和铁矿化,形成含铁铜岩浆热液角砾岩筒,如智利科皮亚波GV铁铜矿区和仙多明格IOCG矿床等。
(2)在主岛弧带内,火山喷发作用持续形成了火山口及其周围的火山堆积物,火山口相(增生的火山锥体)以熔结火山集块岩、熔结火山角砾岩和熔结凝灰熔岩为主,火山锥顶扇体以粗火山碎屑岩为主,如沉火山角砾岩、火山角砾岩、火山集块岩。火山喷发通道相分布于火山口相体内。火山锥外扇体常位于火山穹隆构造周缘台地,由缓倾斜火山碎屑岩层(火山碎屑流相)和火山沉积岩层(如凝灰岩等)组成了远端火山沉积相,垂向上可叠置火山锥外扇体和冲刷水道沉积。
(3)在火山穹隆构造中心(成矿系统中心相),白垩纪酸性流纹岩和花岗岩侵位,形成了岩浆隐爆角砾岩相(筒)、电气石岩浆隐爆角砾岩(筒)、电气石钾长石热液隐爆角砾岩,它们是IOCG成矿系统的中心相物质,具有同岩浆侵入期脆韧性剪切带中的构造热液角砾岩相特征,归属铁氧化物铜金型(IOCG)矿床储矿岩相学类型。
(4)总体垂向蚀变分带特征是:上部黏土化−绢云母化−赤铁矿化蚀变相带,中部钾质蚀变相带 (电气石−铁质)+热液角砾岩化相带,下部钠质蚀变相(铁质)−热液角砾岩化带。围绕二长斑岩−二长闪长岩舌状侵入体形成电气石蚀变岩相带,属于气成高温热液蚀变中心相。大型—超大型IOCG 矿床具有多期蚀变相系叠加特征,不同成因的热液角砾岩化相带发育、异时同位多期蚀变岩相叠加和气成高温热液蚀变相发育等是寻找大型—超大型IOCG矿床的重要标志。
(5)成矿系统根部相,以磷灰石铁质辉长岩、碱性铁质闪长岩脉群、铁质苦橄岩−铁质安山岩、钛铁辉长岩−钛铁质闪长岩和二长岩−二长斑岩为主。
2.2 沉积岩型(SSC型)铜矿床−IOCG型铁铜矿田与陆缘裂谷盆地
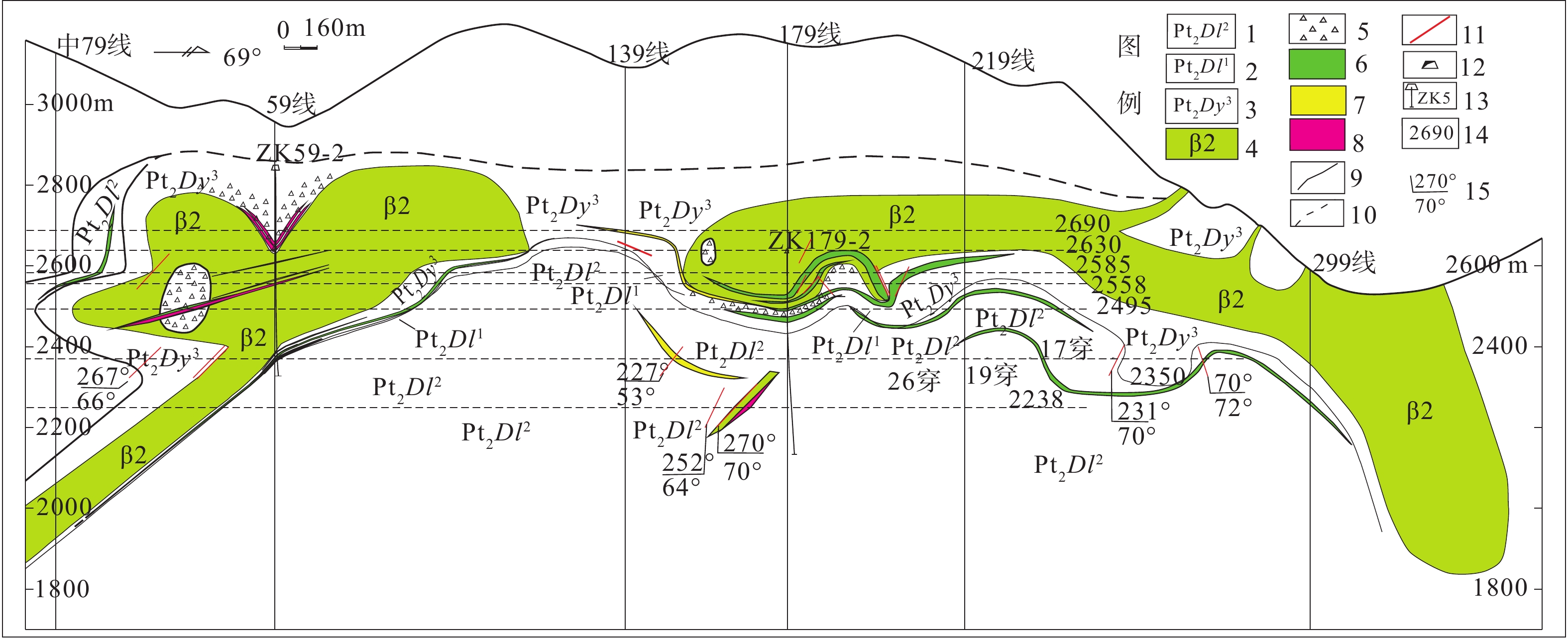
在云南东川滥泥坪−汤丹铁铜矿田,探明的SSC型铜矿床有滥泥坪铜矿床、白锡腊铜矿床、汤丹−马柱硐铜矿床、白锡腊深部IOCG型铜矿床4处(图1,图2)。汤丹−马柱硐三级局限火山热水沉积洼地和火山热水沉积岩相、盆地变形构造岩相(斜歪紧闭向斜)是SSC型铜矿床的储矿构造岩相(图1)。在汤丹−马柱硐SSC型铜矿区内,正常的火山热水沉积层序结构特征是:①因民期垂向相序从下到上依次为火山浊流沉积岩相→局限洼地热水沉积岩相(热水沉积岩亚相/硅质白云岩亚相)→混合潮坪相沉积岩相(凝灰质沉积岩亚相+热水沉积岩亚相)→碱性钛铁质辉绿辉长岩岩枝;马柱硐矿段储矿相体为火山热水沉积成因的硅质白云岩、钠长石白云岩、粗面质凝灰岩和粗面质白云岩等,它们组成了因民期末期衰竭火山口洼地内的火山热水沉积岩相,也是热水沉积成矿系统的中心相;同时格林威尔期碱性钛铁质辉长岩岩枝,对马柱硐型铜矿床具有叠加成矿作用。②落雪期的垂向相序结构从下到上依次为混合潮坪相沉积岩相(凝灰白云岩+硅质钠长石岩+硅质白云岩)→潮坪相硅质白云岩−钠质白云岩→浅海局限碳酸盐岩台地相(准同生白云质角砾岩+硅质白云岩),中下部代表了三级沉积盆地中的热水沉积、火山喷发沉积和低温白云岩等混合同生沉积过程,为东川式火山热水沉积−改造型铜矿的保存提供了条件。这种落雪期垂向相序结构,反映了火山热衰竭过程以热水沉积增强和火山喷发沉积物向上减弱到消失的活动过程。在藻硅质白云岩内的铜矿成矿中,有富CO2热水沉积作用存在,盆地稳定热沉降过程表现为热水沉积成因的白云石含量不断增加。③火山热水隐爆角砾岩相−火山热水喷流口相与富矿包(富矿囊),深部1560中段46#—60#勘探线(图1),有利于铜矿质堆积成矿,该盆地为热水喷流沉积成矿中心相。1650中段富矿囊段(图1)的岩性为含铜硅质热液角砾岩,被斑铜矿、黄铜矿胶结,铜品位约10%。地层产状:175°∠82°。角砾状钠长碧玉岩为火山热水喷流通道口相标志,热水喷流沉积形成“牛眼”状构造,边部以黄铜矿为主,核部以斑铜矿、辉铜矿为主;角砾状碧玉岩的胶结物为斑铜矿和辉铜矿,在边部可见热水同生沉积硅质角砾岩和硅质岩,沿层面有条带条纹状辉铜矿的浑圆状同生角砾,长轴(D)为13 cm,短轴(d)为8 cm,外缘热液胶结物为黄铜矿和斑铜矿,由热水隐爆−同生沉积作用形成的富矿体物质组成。④黑山期盆地中心相+火山喷发沉积相+层状辉长岩侵入相,层状碱性钛铁质辉绿辉长岩侵入相属格林威尔期顺层侵位,导致了黑山组地层发生层间褶曲变形,形成桃园型铜矿床。⑤在格林威尔期近南北向挤压收缩作用下,汤丹碱性钛铁质辉绿辉长岩床(1069±25 Ma;LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄)侵位。在晋宁期自西向东区域挤压应力作用下,叠加了较强的斜冲走滑作用,马柱硐型热液脉带状铜矿体形成于该压扭性断裂下部。⑥马柱硐型铜矿体赋存于因民期三级热水沉积洼地中,汤丹同生断裂、隐伏岩枝产状由陡变缓部位、S-L构造透镜体顶部+断裂流体叠加部位等,它们是马柱硐型铜矿体定位的构造岩相空间。马柱硐型铜矿床属火山热水同生沉积−岩浆热液叠加改造型铜矿床。
 图 1 汤丹铜矿床(SSC型)4号构造岩相学实测纵剖面1—震旦系陡山沱组;2—中元古界东川群落雪组二段;3—中元古界东川群落雪组一段; 4—中元古界东川群因民组三段;5—古元古界汤丹岩群平顶山组;6—铁质板岩;7—白云岩; 8—泥粉砂质板岩;9—碱性铁质辉绿辉长岩枝(墙);10—铜矿体(SSC型铜矿床);11—低品位铜矿体; 12—推测铜矿体;13—地质界线; 14—推测地质界线;15—断层;16—推测断层; 17—地质产状;18—中段标高和海拔高度Figure 1. Measured No.4 longitudinal profiles of tectonic lithofacies in the Tangdan copper deposits (SSC-type)1−Sinian Doushantuo Formation; 2−the Second of member at Luoxue Formation of Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 3−the first member at Luoxue Formation of Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 4−the three member at Yinming Formation of Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 5−Pingdingshan Formation of Palaeoproterozoic Tangdan Rock Group; 6−irony slate; 7−dolomite; 8−argillaceous-silty slate; 9−alkaline Fe-rich diabase-gabbro apophyse or dike; 10−copper orebody(SSC-type copper deposit);11−copper orebody with low-grades; 12−presumed copper orebody;13−geological line; 14−presumable geological line;15−faults; 16−presumed faults; 17−geological occurrence; 18−adit level and above the sea level
图 1 汤丹铜矿床(SSC型)4号构造岩相学实测纵剖面1—震旦系陡山沱组;2—中元古界东川群落雪组二段;3—中元古界东川群落雪组一段; 4—中元古界东川群因民组三段;5—古元古界汤丹岩群平顶山组;6—铁质板岩;7—白云岩; 8—泥粉砂质板岩;9—碱性铁质辉绿辉长岩枝(墙);10—铜矿体(SSC型铜矿床);11—低品位铜矿体; 12—推测铜矿体;13—地质界线; 14—推测地质界线;15—断层;16—推测断层; 17—地质产状;18—中段标高和海拔高度Figure 1. Measured No.4 longitudinal profiles of tectonic lithofacies in the Tangdan copper deposits (SSC-type)1−Sinian Doushantuo Formation; 2−the Second of member at Luoxue Formation of Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 3−the first member at Luoxue Formation of Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 4−the three member at Yinming Formation of Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 5−Pingdingshan Formation of Palaeoproterozoic Tangdan Rock Group; 6−irony slate; 7−dolomite; 8−argillaceous-silty slate; 9−alkaline Fe-rich diabase-gabbro apophyse or dike; 10−copper orebody(SSC-type copper deposit);11−copper orebody with low-grades; 12−presumed copper orebody;13−geological line; 14−presumable geological line;15−faults; 16−presumed faults; 17−geological occurrence; 18−adit level and above the sea level白锡腊矿段IOCG矿床是隐伏矿找矿预测实例,经生产勘探验证最终证实:东川元古宙裂谷盆地在格林威尔期,形成了岩浆叠加侵入构造系统和斜歪倒转复式背斜,碱性钛铁质辉长岩类形成拱形岩体超覆侵入构造(图2)和隐伏IOCG矿床。碱性钛铁质辉长岩类侵入体(1067±20 Ma,1047±15 Ma;锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄)斜切东川群因民组三段和落雪组,对东川型铜矿床形成了岩浆热液叠加成矿作用。从上到下构造岩相依次为:格林威尔三段→落雪组二段→落雪组一段,上为岩浆侵入构造系统,下为东川群倒转层序与岩浆叠加改造地层系统。在299勘探线(图2),因切割深度较大,出露于地表沟系中,这种碱性钛铁质辉长岩−碱性钛铁质辉绿岩岩枝位于次级拱形顶部,在地表见其周缘发育岩浆隐爆角砾岩相带和因民组三段残留构造岩块。推测这种侵入岩体的岩枝状扩展侵位机制,可能为被断裂系统切破的“膨胀气球”,或者因“膨胀气球”近地表形成断裂释压,热应力破裂导致形成了热力断裂带,这些断裂带连通了侵入岩体与因民组三段,形成了构造−岩浆−热流体耦合作用,最终导致因民组在构造−岩浆−热流体耦合作用最强烈部位形成了坍塌角砾岩相带和构造岩块带,并组成了坍塌次火山机构。被断裂带刺破的“膨胀气球”导致了侵入构造系统热能量和热物质释放,形成了岩浆隐爆角砾岩相带和岩浆热液角砾岩构造系统;因属开放的侵入构造系统,对IOCG矿床形成不利,仅形成了蚀变和分散矿化。在侵入岩体顶面岩凸和岩凹构造上,碱性钛铁质辉长岩类侵入岩→岩浆隐爆角砾岩相带(岩浆热液角砾岩构造系统)→因民组双“膨胀气球”之间形成的岩凹构造对IOCG矿体的形成有利(图2),如59勘探线形成的岩凹构造,这种小型岩凹构造在北西向(ZK59-3)已消失。从59线(ZK59-1和ZK59-2)呈现北东向延伸到139线和179线,主要为侵入岩体顶面之上形成的岩浆隐爆角砾岩相带。在岩凹构造中,形成了岩浆热液角砾岩构造系统,IOCG矿体定位于其中。但岩凸构造和平缓的侵入岩体顶面对成矿不利。③侵入岩体中心和下部有利于形成IOCG矿体,主要在侵入岩体中心部分发育。
 图 2 白锡腊−中老龙IOCG型和SSC型铜矿床实测构造岩相学纵剖面1—中元古界东川群落雪组二段;2—中元古界东川群落雪组一段;3—中元古界东川群因民组三段;4—碱性铁质辉绿辉长岩枝;5—热液角砾岩相;6—铜矿体(SSC型铜矿床);7—低品位铜矿体;8—铁铜矿体(IOCG型铁铜矿床);9—地质界线;10. —推测地质界线;11—断层;12—穿脉垂直投影面;13—坑内钻孔及编号;14—中段标高和海拔高度;15—地质产状Figure 2. Measured longitudinal profiles of tectonic lithofacies for IOCG-type and SSC-type copper deposits from Baixila to Zhonglaolong1−the second of member of the Luoxue Formation of the Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 2−the first member of the Luoxue Formation of the Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 3−the third member of the Yinming Formation of the Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 4−alkaline Fe-rich diabase-gabbro apophyse; 5−hydrothermal breccia facies; 6−copper orebody (SSC-type copper deposit); 7−low-grade copper orebody; 8−Fe-Cu orebody (IOCG-type deposit); 9−geological boundary; 10−inferred geological boundary; 11−fault; 12−transverse drift (vertical projection); 13−adit-in drillhole and its number; 14−adit elevation and altitude
图 2 白锡腊−中老龙IOCG型和SSC型铜矿床实测构造岩相学纵剖面1—中元古界东川群落雪组二段;2—中元古界东川群落雪组一段;3—中元古界东川群因民组三段;4—碱性铁质辉绿辉长岩枝;5—热液角砾岩相;6—铜矿体(SSC型铜矿床);7—低品位铜矿体;8—铁铜矿体(IOCG型铁铜矿床);9—地质界线;10. —推测地质界线;11—断层;12—穿脉垂直投影面;13—坑内钻孔及编号;14—中段标高和海拔高度;15—地质产状Figure 2. Measured longitudinal profiles of tectonic lithofacies for IOCG-type and SSC-type copper deposits from Baixila to Zhonglaolong1−the second of member of the Luoxue Formation of the Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 2−the first member of the Luoxue Formation of the Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 3−the third member of the Yinming Formation of the Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 4−alkaline Fe-rich diabase-gabbro apophyse; 5−hydrothermal breccia facies; 6−copper orebody (SSC-type copper deposit); 7−low-grade copper orebody; 8−Fe-Cu orebody (IOCG-type deposit); 9−geological boundary; 10−inferred geological boundary; 11−fault; 12−transverse drift (vertical projection); 13−adit-in drillhole and its number; 14−adit elevation and altitude拱形岩体超覆侵入构造的储矿构造岩相类型共有4种,分别是:①岩凹构造“膨胀气球”对IOCG矿体形成有利,岩凸构造对成矿不利;②侵入岩体中心和下部有利于形成IOCG矿体;③因民组三段有利于形成岩浆热液角砾岩构造系统和IOCG矿体(图2中59线);④对落雪组中的火山热水沉积型铜矿,形成了较强的岩浆热液叠加成矿作用(图2中179线)。
2.3 浅成低温热液型银铅锌矿田与陆相火山机构、火山岩岩相类型
火山负向构造包括火山口湖盆(多形成于火山口顶部和塌陷火山机构内)、火山堰塞湖盆、火山喷气湖盆、破火山机构宽浅湖盆4种构造岩相结构。火山正向构造包括盾状火山隆起(由平缓的熔岩相组成)、锥状火山隆起(发育寄生火山锥)、穹状火山隆起(熔岩穹丘)、半环状破火山机构(半环状火山隆起+坍陷火山口洼地)、复式半环形火山穹隆(半环状火山隆起+充填塌陷火山口)+次火山岩侵入相(岩脉、岩枝、岩墙和小岩株等)5种构造岩相结构。
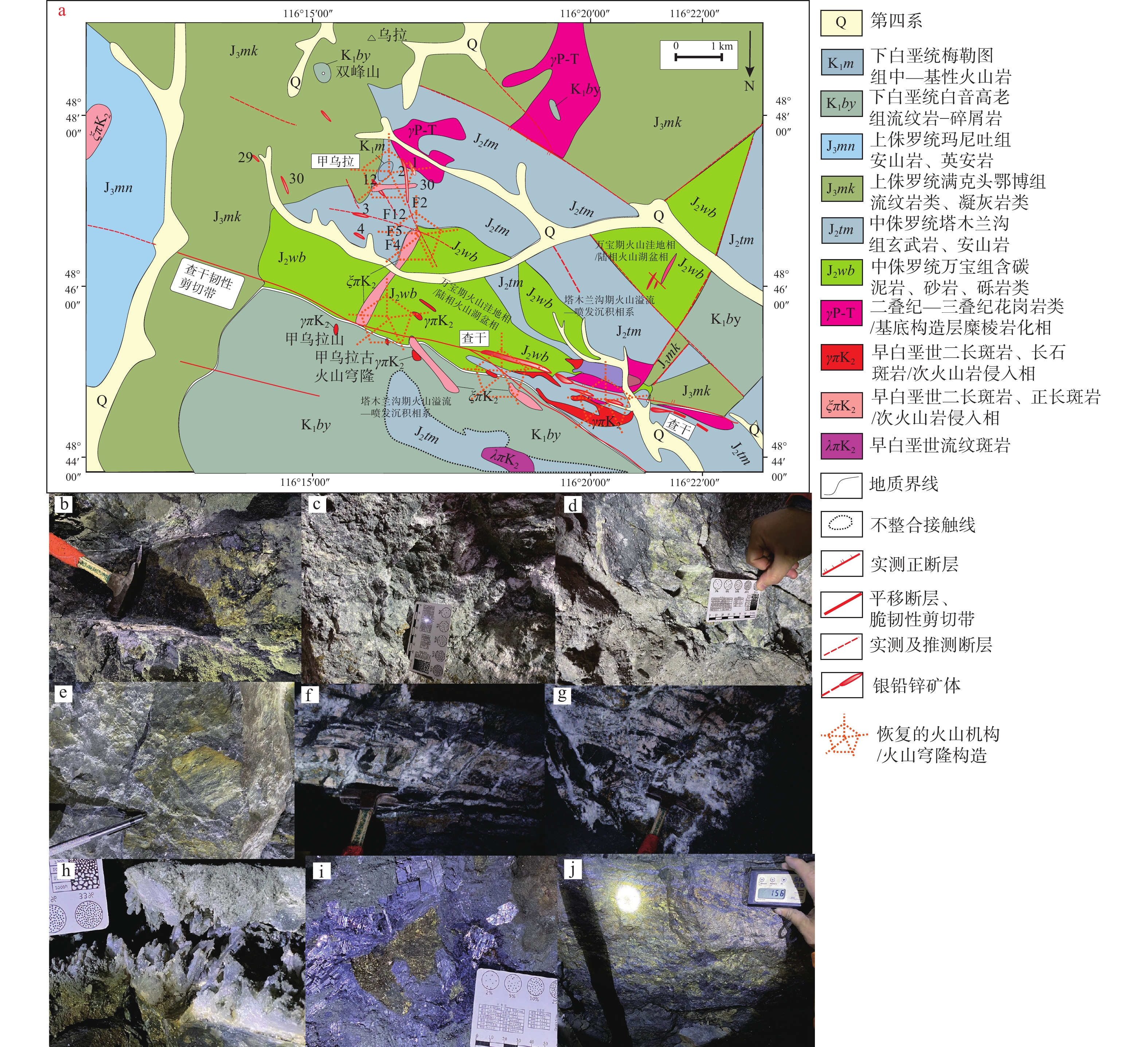
内蒙古甲查银多金属矿田构造组合由基底隆起、火山穹隆构造、次火山岩侵入构造、火山断陷洼地、涡轮状−放射状断裂−裂隙系统、火山隐爆角砾岩筒和热液角砾岩相7种构造样式组成。它们构造岩相特征分别是:①基底隆起以三叠纪糜棱岩相−糜棱岩化相和韧性剪切带为前侏罗纪基底构造层标志,它们构成了出露的基底隆起(图3)或隐伏基底隆起。②万宝期火山洼地湖盆以万宝组(J2wb)呈角度不整合覆盖于二叠纪—三叠纪岛弧造山带之上为构造岩相分界标志,以含火山物质的碎屑岩系为主,属于陆相火山断陷湖盆相。万宝期早期火山洼地湖盆相分布于北东向和北西向断裂交汇部位(图3a),万宝组内发育脆韧性剪切带(糜棱岩化相)、层间褶皱和热液角砾岩相;组内的断裂和褶皱构造带形成于满克头鄂博期前,是脉带状银铅锌矿脉带的有利储矿构造岩相,也是寻找热液角砾岩筒型银铅锌矿的主攻目标。还有两个设计验证钻孔均已经揭露了深部银铅锌矿体。③安山质火山穹隆机构以塔木兰沟组(J2tm)以玄武−安山质火山岩系为主体,为陆相火山穹隆构造形成期。下部为灰色和灰紫色玄武安山岩、安山玄武岩,局部为玄武质集块岩,以火山熔岩相和火山集块岩相(近火山口相)为主。上部为安山岩、安山质熔岩、火山角砾岩夹少量火山碎屑岩,以火山熔岩相、火山角砾岩相和火山碎屑岩相为主。安山岩类常见气孔晶洞中充填有玛瑙、蛋白石、燧石等,显示陆相火山喷发作用为主。从下到上的总体火山相序结构恢复为:火山爆发相(火山集块岩相)→火山喷溢相(火山熔岩相)→火山喷发沉积相(火山角砾岩相)→火山沉积岩(火山碎屑岩相)→火山热液蚀变相(青磐岩化相),青磐岩化相的发育强度能够揭示和圈定火山热液蚀变作用的强度和中心部位。④火山岩−次火山岩带受北西向和北东向隐伏基底断裂带控制。现今残余的塔木兰沟组总体呈现北西向展布,暗示控制火山穹隆构造为北西向基底断裂带,与主体北东向重力异常带内叠加北西向扭曲重力梯度异常带所揭示的北西向基底断裂带相一致。⑤次火山岩带总体受北西向、北东向和近南北向隐伏基底断裂带控制,也是次火山热液成矿能量−物质供给中心,以发育岩浆热液隐爆角砾岩、火山隐爆角砾岩和涡轮状−放射状断裂−裂隙系统为成岩成矿系统中心相标志。⑥满克头鄂博组(J3mk)与塔木兰沟组呈火山喷发不整合接触或断层接触,呈现外围环绕式相体空间拓扑学结构,也是隐伏火山穹隆构造岩相标志。塔木兰沟组(J2tm)被白音高老组(K1by)呈角度不整合覆盖(图3a),火山洼地+火山穹隆定型于玛尼吐期末,也是次火山岩叠加成岩成矿重要时期。
 图 3 甲查银多金属矿田火山机构与矿田构造岩相图a—甲乌拉−查干银多金属矿田构造岩相图;b—e、h—j为甲乌拉银多金属矿床;f—g为查干银多金属矿床;b—540 m中段铅锌硫化物充填交代脉与边部菱沸石−铁绿泥石相;c—580 m中段石膏−蒙脱石−钾伊利石相;d—580 m中段伊蒙混层−伊利石相;e—475 m中段细脉状和微脉状闪锌矿方铅矿硫化物充填在伊利石热液角砾岩相中。 f—怡圣园西端18号矿体300 m中段216勘探线主巷道掌子面富银菱锰矿铁锰碳酸盐热液角砾岩相;g—怡圣园西端18号矿体300 m中段216勘探线主巷道掌子面富银菱锰矿铁锰碳酸盐热液角砾岩相;h—200 m中段5′—7′线含闪锌矿方铅矿马牙状石英脉;i—伟晶状方铅矿结晶核相;j—200 m中段5′—7′线2号矿体巨晶状方铅矿结晶核相的外缘中心相(具有海绵陨铁结构的铁闪锌矿−磁黄铁矿−黄铜矿矿石,磁化率151~114×10−3SI)Figure 3. Mapping of volcanic edifice and ore-field tectonic lithofacies in the Jia–Cha Ag-polymetallic orefield(a) Tectonic lithofacies map of the Jiawula–Chagan Ag-polymetallic orefield; Fig.3b to 3e and 3h to 3i are photos from the Jiawula Ag-polymetallic deposit and Fig.3f to 3g are photos from the Chagan Ag-polymetallic deposit; (b) Chabasite-daphnite facies along both sides of the filling−replacement veins of Pb-Zn-sulfides at 540 m level; (c) Gypsum-semctite-K-illite facies at 580 m level; (d) Facies of illite-smectite formation and illite at 580 m level; (e) Fine-veined and microveined sphalerite-galena sulfides veins filling in lithofacies of illite hydrothermal breccia at 475 m level; (f) Fe-Mn-carbonate hydrothermal breccia lithofacies of Ag-rich rhodochrosite from No.18 orebody in the 216 exploration line at the tunnel face of 300 m level; (g) Fe-Mn-carbonate hydrothermal breccia lithofacies of Ag-rich rhodochrosite from No.18 orebody in the 216 exploration line at the tunnel face of 300 m level; (h) Sphalerite-galena sulfides quartz veins in horse-teeth-shape in the 5′–7′ exploration line at 200 m level; (i) Crystalline nuclear lithofacies of pegmatitic galena in the 5′–7′ exploration line at 200 m level; (j) Marmatite-pyrrhotite-chalcopyrite ores in sideronitic texture around crystalline nuclear lithofacies of pegmatitic galena in the 5′–7′ exploration line at 200 m level; magnetic susceptibility is from 151×10−3 to 114×10−3SI
图 3 甲查银多金属矿田火山机构与矿田构造岩相图a—甲乌拉−查干银多金属矿田构造岩相图;b—e、h—j为甲乌拉银多金属矿床;f—g为查干银多金属矿床;b—540 m中段铅锌硫化物充填交代脉与边部菱沸石−铁绿泥石相;c—580 m中段石膏−蒙脱石−钾伊利石相;d—580 m中段伊蒙混层−伊利石相;e—475 m中段细脉状和微脉状闪锌矿方铅矿硫化物充填在伊利石热液角砾岩相中。 f—怡圣园西端18号矿体300 m中段216勘探线主巷道掌子面富银菱锰矿铁锰碳酸盐热液角砾岩相;g—怡圣园西端18号矿体300 m中段216勘探线主巷道掌子面富银菱锰矿铁锰碳酸盐热液角砾岩相;h—200 m中段5′—7′线含闪锌矿方铅矿马牙状石英脉;i—伟晶状方铅矿结晶核相;j—200 m中段5′—7′线2号矿体巨晶状方铅矿结晶核相的外缘中心相(具有海绵陨铁结构的铁闪锌矿−磁黄铁矿−黄铜矿矿石,磁化率151~114×10−3SI)Figure 3. Mapping of volcanic edifice and ore-field tectonic lithofacies in the Jia–Cha Ag-polymetallic orefield(a) Tectonic lithofacies map of the Jiawula–Chagan Ag-polymetallic orefield; Fig.3b to 3e and 3h to 3i are photos from the Jiawula Ag-polymetallic deposit and Fig.3f to 3g are photos from the Chagan Ag-polymetallic deposit; (b) Chabasite-daphnite facies along both sides of the filling−replacement veins of Pb-Zn-sulfides at 540 m level; (c) Gypsum-semctite-K-illite facies at 580 m level; (d) Facies of illite-smectite formation and illite at 580 m level; (e) Fine-veined and microveined sphalerite-galena sulfides veins filling in lithofacies of illite hydrothermal breccia at 475 m level; (f) Fe-Mn-carbonate hydrothermal breccia lithofacies of Ag-rich rhodochrosite from No.18 orebody in the 216 exploration line at the tunnel face of 300 m level; (g) Fe-Mn-carbonate hydrothermal breccia lithofacies of Ag-rich rhodochrosite from No.18 orebody in the 216 exploration line at the tunnel face of 300 m level; (h) Sphalerite-galena sulfides quartz veins in horse-teeth-shape in the 5′–7′ exploration line at 200 m level; (i) Crystalline nuclear lithofacies of pegmatitic galena in the 5′–7′ exploration line at 200 m level; (j) Marmatite-pyrrhotite-chalcopyrite ores in sideronitic texture around crystalline nuclear lithofacies of pegmatitic galena in the 5′–7′ exploration line at 200 m level; magnetic susceptibility is from 151×10−3 to 114×10−3SI甲查银铅锌矿田内形成了次火山岩侵入构造和岩浆隐爆角砾岩筒,属于岩浆叠加侵入构造系统和成矿−储矿构造岩相类型。结合已发表的成岩成矿年龄测试成果(李铁刚等,2014;戴蒙等,2016;杨梅等,2017;曹鹏等,2018;牛斯达等,2020),经大比例尺构造岩相学填图和构造岩相学变形筛分认为:①晚侏罗世成岩成矿期内的次火山岩侵入体序列为闪长玢岩(J3δπ)→石英二长斑岩(J3ηoπ;152.2±1.5 Ma)→石英斑岩(J3Oπ;150.1±1.8 Ma)→正长斑岩(148.8±2.2 Ma) →富碱花岗斑岩(146.4±1.6 Ma)→二长斑岩(145.3±1.9 Ma)。②早白垩世成岩−成矿热液事件序列为富碱花岗斑岩的岩浆热液活动期(143.1±3.9 Ma)。③甲乌拉银铅锌矿床成矿年龄为153 ± 2 Ma(闪锌矿Rb-Sr等时线年龄;曹鹏等,2018)、143.0 ± 2.0 Ma(闪锌矿Rb-Sr等时线年龄;李铁刚等,2014),与晚侏罗世石英二长斑岩(J3ηoπ;152.2±1.5 Ma)和早白垩世石英二长斑岩(K1ηoπ;143 Ma)的形成年龄吻合,推测绢云母化蚀变相(137±3 Ma~131.88 Ma)的形成年龄属于成矿流体的延续时限。
该矿床的垂向成矿蚀变−构造岩相分带特征明显,揭示了“浆−气−液”分级隐爆式成矿流体侵位机制,从上到下依次为:①近地表铁锰化蚀变帽内,银次生富集成矿作用发育,形成了Ag>500 g/t的富矿块,属银次生富集成矿中心;②顶部伊利石−硅化帽或硅化−伊利石化蚀变帽,位于碎裂岩化相蚀变安山岩中,蚀变组合为高龄石−蒙脱石−伊蒙混层−硅化(图3b、3c、3d),前者以银金矿体为主,后者以银矿体为主;③上部硅化−伊利石化蚀变相(图3e);④中部铁锰碳酸盐化蚀变相内形成了富银(>1000 g/t)矿块(图3f、3g);⑤下部马牙状硅化角砾岩相+伟晶状方铅矿硫化物相,形成了银铅锌富矿体,也是成矿中心相(图3h、3i、3g),铁闪锌矿磁黄铁矿矿脉原位磁化率>100×10−3 SI,属于高磁化率相和低视电阻率相;⑥深部铁闪锌矿−磁铁矿矿浆角砾岩相,新发现了铁闪锌矿磁铁矿矿浆角砾岩型铁锌矿石和铅锌硫化物磁黄铁矿型矿石,它们属高磁化率相和低视电阻率相,蚀变组合为金云母−铁绿泥石−阳起石化;⑦构造岩相水平分带显著,银多金属矿体两侧多具有对称式蚀变−成矿−构造岩相分带,中心相是粉末状伊利石−马牙状硅化蚀变带,为铅锌硫化物蒙脱石−伊蒙混层黏土化蚀变相。
2.4 斑岩型金铜钼矿田+浅成低温热液金银矿床与深成岩浆弧
不少学者在斑岩型铜金钼矿床研究方面取得了丰硕成果(Sillitoe,2005,2010;Hou and Cook,2009;刘飞等,2017;陈华勇等,2019)。Lowell and Guilbert(1970)首次建立了岛弧环境下钙碱性斑岩系统与斑岩铜矿围岩蚀变分带模型,得到了广泛应用。基于红外光谱探测技术,结合室内构造岩相学鉴定和X射线粉晶衍射定量分析等综合手段,进行斑岩型铜金钼矿田成矿蚀变−构造岩相填图也成为当前重要的发展方向(陈华勇等,2019)。
岩浆热液成矿系统控制了深成岩浆弧区成矿系统和围岩蚀变体系,斑岩铜钼金矿床、浅成低温热液型金银多金属矿床和铁氧化物铜金(IOCG)型矿床,三者呈现矿田尺度上的区域成矿分带(李建旭等,2011),表现为:①斑岩型铜金钼矿床沿幔型断裂带呈带状和线带状分布,斑岩铜成矿系统包括网脉−细脉型、热液角砾岩型和蚀变围岩型(Cooke et al.,2004),有学者将矿田内矽卡岩型、产于碳酸盐岩中的交代脉状、产于沉积岩中的微细浸染状、高硫型和低硫型浅成低温热液型金银多金属归入斑岩成矿系统内(Sillitoe,2010)。②斑岩型铜钼金矿床+浅成低温热液型铜金矿床+“异地”铜矿床矿田模型。在深成岩浆弧与造山期构造隆升过程相互耦合结构下,在钙碱性斑岩成矿系统上部可叠置或嵌入浅成低温热液成矿系统,顶部岩帽为多孔状硅化帽并发育晶腺晶洞,外侧依次是石英−明矾石蚀变相(高级泥化相)、石英−高岭石±迪开石蚀变相(泥化相),最外缘相为赤铁矿化−碳酸盐化−绿泥石化相(青磐岩化蚀变相)。蚀变体系的根部相沿断裂带延深,相变为石英−叶腊石±硬水铝石±红柱石±刚玉带,岩帽及高硫型金银多金属矿体位于深部斑岩铜钼金矿床之上可达1000 m(Sillitoe,2010);斑岩成矿系统停息后,持续的造山作用将两类成矿系统剥蚀,在附近的陆相盐沼湖盆内形成“异地”铜矿床或席状次生矿体。如蒙古国南戈壁省奥玉陶勒盖斑岩铜金钼矿床之上嵌入了高硫化型铜金矿体,发育次生席状铜金矿体。③智利科皮亚波IOCG成矿带−Salvador斑岩矿床均形成于板块汇聚构造岩浆演化过程,晚白垩世—古新世弧后盆地发生构造反转后,斑岩和浅成低温热液成矿作用增强,富金斑岩型−斑岩铜钼矿床系统,如智利Inco de Oro和Andacollo 白垩纪斑岩铜金矿床。④成矿蚀变−构造岩相填图和深部预测是寻找热液角砾岩和隐伏斑岩型铜钼金矿床有效方法,进行大比例尺构造岩相学填图,有助于寻找隐伏斑岩型铜钼金矿床。
2.5 银铜铅锌−菱铁矿−重晶石矿田与陆缘拉分断陷盆地
与含油气沉积盆地(杨树锋等,2022)不同,金属成矿盆地在构造岩相学类型上具有显著的差别(Huang et al.,2018;方维萱,2020,2022a,2022b,2023)。热水沉积岩相形成于陆缘裂谷盆地、弧后裂谷盆地、洋中脊或有限洋盆、弧−盆系统、陆缘伸展盆地和湖相盆地内。对于SEDEX型银铜铅锌−菱铁矿−重晶石矿田而言,它们受控于三级热水沉积盆地和同生断裂相带。热水沉积岩相系是储矿构造岩相,可划分为热水同生沉积岩相、热水准同生交代岩相、热水同生蚀变岩相、热水爆炸−液压致裂角砾岩相、热卤水准同生渗滤交代岩相与热流柱构造有关的热流体隐爆−液压致裂角砾岩相,包括17种构造岩相学类型。它们多经历了碎裂岩相、糜棱岩相和热流体改造−叠加−再造成岩相,需进行构造岩相学变形史研究和构造岩相学变形筛分。采用构造岩相学独立填图单元进行填图,有助于重建古热水流体成岩成矿系统及物质组成,其构造岩相分带特征为根部相→喷口相→中心相→过渡相→远端相(方维萱,2023)。SEDEX型重晶石−毒重石−铅锌−磷−锰矿田多形成于陆缘裂谷盆地内,在震旦纪—寒武纪和寒武纪—志留纪期间,扬子地块周缘形成了陆缘裂谷盆地,最终以碱性苦橄岩−钾镁煌斑岩−碱性辉绿岩等幔源岩浆的侵位为标志,陆缘裂谷盆地最终封闭并保存了矿田构造岩相。
在成矿蚀变−构造岩相岩类型方面,热水沉积岩相系与古沉积水体深度和后期盆地变形改造作用密切相关。在热水沉积岩相内,普遍发育似层状热水同生蚀变岩相,以热水喷口通道相内发育的热流体隐爆角砾岩相为特征。①深水型热水沉积岩相,以硅质岩、富碳质岩、重晶石岩、冰长石凝灰岩、钾伊利石凝灰岩等为主;②半深水型热水沉积岩相,以硅质岩、硫化物岩、铁白云石硅质岩、铁白云岩和含炭生物灰岩为主;③浅水型热水沉积岩相,以凝灰质白云岩、硅质白云岩、硅质岩和伊利石凝灰岩等为主,如云南东川铜矿床等;在局限海湾盆地内,浅水型热水沉积−蒸发岩系以石膏岩−膏质盐岩−膏质白云岩−天青石石膏岩−天青石岩−热液岩溶白云岩组合为构造岩相标志,可细分为沉积型、构造型、热液型、坍塌岩(盐)溶角砾岩型,如新疆乌拉根−康西砂砾岩型铅锌矿田;④在盆地变形过程中,构造−热事件导致盆内发生了烃矿源岩的生烃成矿作用,富烃类和富CO2-H2S型非烃类还原性成矿流体沿盆内层间滑动构造带和切层断裂带运移,形成了沥青化蚀变相、褪色化蚀变相和碎裂岩化相带紧密同体共生,它们与铜铅锌硫化物相是盆内蚀变−成矿−构造岩相的主要物质组成,见于新疆塔西萨热克等砂砾岩型铜多金属矿床和乌拉根超大型砂砾岩型铅锌矿床;⑤在盆内岩浆叠加期,岩浆−构造−热事件形成了较为广泛的面状和带状蚀变体。
2.6 脆韧性剪切带型金矿田与陆内造山带
在大陆造山带和断块隆升造山区内,脆性剪切带、韧−脆性剪切带、脆韧性剪切带和韧性剪切带对金矿田控制作用显著,但具有不同的构造岩相学样式和组合,蚀变类型差异较大。
卡林型金矿田多形成于面状断块隆升造山区内和不同造山带挟持区,如陕西镇安和凤县南部、川西北—甘南、滇黔桂等沉积盆地区,脆性剪切带、韧−脆性剪切带、层间滑动构造、断褶构造带及其共生的切层和似层状破碎蚀变带均为成矿−储矿构造岩相带,节理−裂隙相(包括膝折和破碎带等)和伴生的蚀变岩相为主要储矿构造岩相,低温蚀变岩相组合包括碳酸盐化蚀变相(碳酸盐化脉和网脉、碳酸盐化热液角砾岩等)、面状和网脉状黏土化蚀变相、面状和脉状硅化蚀变相等,发育低温Hg-As-Sb-Fe硫化物蚀变相等。在碳酸盐岩区,热液岩溶作用(去碳酸盐化相)发育,形成团斑状和巨晶状白云石化相和方解石化相等。
造山型金矿田定位于压剪性脆韧性剪切带,受陆内造山带形成的构造−热流柱驱动和控制,以脆韧性剪切带内发育黄铁矿−硅化蚀变相和黄铁矿−绢云母−硅化蚀变相为储矿构造岩相学特征,斑点状菱铁矿千枚岩、斑点状铁白云石千枚岩和斑点状黑云母千枚岩为构造−热流柱的构造岩相学记录。如陕西丁家林−四川太阳坪−四川董家院北东向金矿带,该区未见早三叠世后的岩浆活动,金矿田受北东向递进脆−韧性剪切带控制,形成于后龙门山陆−陆碰撞型逆冲推覆造山带内。含矿地层志留系黄坪组中部层间流体活动强烈,地壳浅部富 Fe-Mg-CO32−型构造流体活动形成了斑点状铁碳酸盐千枚岩相,强应变带发育构造片岩相和初糜棱岩相,富 SiO2型流体和构造分异成岩作用形成了流变状糜棱岩相。强烈的构造成岩作用及造山带流体的大规模排泄,形成了糜棱岩相、流变状糜棱岩相和菱铁矿铁白云石网脉相。金矿储矿构造岩相特征是蚀变糜棱岩相和脆性蚀变碎裂岩相叠加于先存构造岩相之上。
在大陆造山带隐伏岩浆侵入区上方,隐伏岩浆−构造−热事件(热流柱构造)对含金脆韧性剪切带型金矿田的控制作用显著,如陕西八卦庙金矿田内的八卦庙、丝毛岭和柴蚂3个金矿床,均受到绢云母−绿泥石型脆韧性剪切带和隐伏花岗岩底拱侵位形成的岩浆−构造−热流柱控制,伴有造山带尺度大规模流体运移的构造−蚀变岩岩相学记录。该金矿田垂向成矿蚀变−构造岩相分带模型是:浅部斑点状千枚岩相(斑点状铁绿泥石千枚岩+斑点状铁碳酸盐千枚岩)+钠长斑岩脉岩相→深部斑点状黑云母千枚岩+斑点状电气石千枚岩+含金蚀变糜棱岩。在八卦庙—八方山深部,印支期铁白云石钠长斑岩脉切层。在八方山铜铅锌矿床深部,大理岩化相逐渐增加,结合区域上的硼化探异常(指示电气石蚀变相)、闪长玢岩和花岗斑岩脉发育特征,推测这些成矿蚀变−构造岩相特征均为隐伏花岗岩−热流柱构造。
在云南哀牢山造山带,墨江金镍多金属矿田受超大型脆韧性剪切带+石炭纪蛇绿混杂岩带+花岗岩热流柱构造控制,成矿蚀变−构造岩相以蚀变糜棱岩相+含金脆韧性剪切带+含金镍绿色蚀变岩相为特色,垂向成矿分带特征是:顶部为红土型金矿和金镍矿床,发育铬高岭石、多水铬高岭石、铬蒙脱石、铬埃洛石等;上部蚀变岩型金镍矿+含金石英脉金矿,赋存在脆韧性剪切带与蛇绿混杂岩接触部位,发育镍绿泥石化、蛇纹石化、滑石化、铬伊利石、铬绿泥石、硅化等;中部蚀变岩型金矿+含金石英脉型金矿,赋存于金厂岩组糜棱岩化硅质岩和脆韧性剪切带内,发育黄铁矿化、硅化、铬绢云母、含铬绢云母、铬伊利石;下部含金石英脉型金矿,赋存于金厂岩组糜棱岩化硅质岩和脆韧性剪切带内,以黄铁矿化和硅化为主。
金钼多金属矿田受多层次多期叠加脆韧性剪切带控制,如小秦岭金钼多金属矿田垂向分带为:①下部以C型韧性剪切带(S//C面理)为主,发育黄铁矿−钾化蚀变岩和黄铁矿−硅化钾化蚀变岩,以厚大金矿体和平行矿体为主组成了蚀变岩型金矿体,如小秦岭葫芦沟钾质蚀变岩型金矿床;②中部发育S-C型含金脆韧性剪切带,中心部位以碎裂状含金硫化物石英脉为主,两侧多以蚀变岩型金矿为主,如含金黄铁矿钾长蚀变岩和黄铁绢云蚀变岩等,二者在垂向和水平方向相互交替分布,发育含金黄铁绢英岩、含金黄铁绢英岩化蚀变相、含金银绿泥石化蚀变岩和褪色化蚀变岩相,蚀变带规模仍受脆韧性剪切带控制,如小秦岭Q2142脉金银多金属矿体;③上部以S型含金石英脉为主,受压剪性或张剪性断裂带控制显著,顶部为含金石英脉尖灭部位,铁锰碳酸盐化蚀变相发育,如小秦岭岳王庙地区含金石英脉。
2.7 砂砾岩型天青石−铅锌矿田和铜多金属矿田与盆−山−原镶嵌区
在南疆盆−山−原镶嵌区内,形成了萨热克铜多金属−煤(铀)矿田、乌拉根铅锌−天青石−铀矿田、加斯—巴什布拉克铜−铀矿田和阿克莫木天然气田,呈现金属矿产−煤−铀−天然气同盆富集特征,包括下侏罗统—中侏罗统煤系烃矿源岩、库孜贡苏组紫红色铁质杂砾岩、克孜勒苏群第五岩性段紫红色铁质硅质细砾岩−紫红色铁质长英质细砾岩、阿尔塔什组底砾岩、含膏白云岩和气成热水沉积岩相等,它们是多种矿产同盆共存与富集成藏成矿的基础,将它们作为1∶5万地质填图中的构造岩相学独立填图单元,能够揭示重大构造岩相学事件及在空间域—时间域—物质域多重耦合结构。萨热克铜多金属−煤(铀)矿田赋存于萨热克巴依次级盆地内,形成了下侏罗统—中侏罗统煤系烃矿源岩。晚侏罗世(库孜贡苏运动)时区内发生了构造反转和区域性抬升,盆地演化为山间尾闾湖盆,形成了库孜贡苏组紫红色铁质杂砾岩,纳米级氧化相态Cu-Pb-Zn-Mo-Ag成矿物质被铁质胶结物吸附富集。在下白垩统克孜勒苏群第三岩性段硅质细砾岩、砂砾岩和砂岩中,形成了砂砾岩型铅锌矿床和砂岩型铜矿床,克孜勒苏群上部缺失。形成机制主要为:①山间尾闾湖盆发生了构造反转和递进变形,对冲式基底型逆冲推覆作用,形成了构造−热事件驱动的富烃类和富CO2-H2S型非烃类还原性热流柱构造,第一期成矿蚀变−构造岩相以库孜贡苏组紫红色铁质杂砾岩中碎裂岩(化)相、沥青化蚀变相、褪色化蚀变蚀变相、铁锰碳酸盐化蚀变相和辉铜矿化为主,主成矿期为166.3±2.8 Ma(辉铜矿Re-Os等时线法);②构造−热事件成岩成矿作用,在136±2.6 Ma~116±2.1 Ma(辉铜矿Re-Os模式年龄)继续增强,属早白垩世构造变形−热事件的产物,导致克孜勒苏群第三岩性段形成了碎裂岩化相、节理−裂隙相和褶皱,缺少克孜勒苏群上部地层;③晚白垩世—古近纪幔源热流柱构造,形成于盆内岩浆叠加期,在地层中热响应记录的绿泥石蚀变相形成温度达到了430~480 ℃;放射状变碱性辉长岩脉群(79.87 Ma±1.80~41.11±1.63 Ma;全岩K-Ar法)穿切了侏罗系煤系烃矿源岩并形成了生烃成矿事件,周缘发育硅化−碳酸盐化蚀变相、褪色化蚀变相和铜矿体,脉带状辉铜矿沥青化蚀变相沿断裂破碎带分布。碱性辉绿辉长岩脉群(58.03±1.20 Ma)与岩浆热液叠加成矿年龄(58.6±2.0 Ma;辉铜矿Re-Os等时线年龄)一致,揭示它们是铅锌与铜多金属矿田共生分异机制。
乌拉根砂砾岩型天青石−铅锌矿田,产于西南天山中生代—新生代山前挤压−伸展转换盆地中,形成了侏罗系煤系烃矿源岩。下白垩统克孜勒苏群粗碎屑岩系发育齐全,第五岩性段紫红色铁质硅质细砾岩和长英质细砾岩、含砾粗砂岩是乌拉根铅锌矿床和帕克布拉克天青石矿床的主要赋存层位,其次为古近系阿尔塔什组底砾岩、含砾白云岩和白云质岩溶角砾岩等。早白垩世晚期,西南天山造山带发生了垂向隆升,在萨热克和托帕地区缺失克孜勒苏群第四和第五岩性段,乌拉根局部缺失上白垩统。热流柱构造及其成岩成矿机制如下:①该期构造−热事件由西南天山山前冲断褶皱带形成,导致下侏罗统—中侏罗统煤系烃矿源岩发生了大规模生烃成矿作用,形成了富烃类和富CO2-H2S型非烃类还原性热流柱构造;在克孜勒苏群第五岩性段,发育了碎裂岩化相、节理−裂隙相、褪色化蚀变相、沥青化蚀变相、铁锰碳酸盐化蚀变相、铅锌硫化物化和黄铁矿化。②古近纪富Sr-SO42−型气成高温热流柱构造,起源最大深度约3.56~5.38 km,在阿尔塔什组天青石化角砾状白云岩内,天青石形成温度最高在480~478 ℃,该高温热流柱构造在上升运移过程中,穿越了侏罗系煤系烃矿源岩并导致生烃成矿作用;进入乌拉根盆地后,与盆地内海水、盆地流体和沉积物发生了气成热液准同生交代作用,导致了天青石和铅锌矿质大规模富集沉淀。③山前冲断褶皱带形成的构造−热事件和富Sr-SO42−型气成高温热流柱,穿越了煤系烃矿源岩并导致生烃成矿作用,它们在乌拉根前挤压−伸展转换盆地内相互耦合作用强烈,形成了原地构造−流体分层效应(重质油→轻质油→含烃盐水→气烃+甲烷→CO2)、冠羽状热储构造和似层状热储构造层。
2.8 电气石岩浆隐爆角砾岩筒与金属成矿
在智利月亮山IOCG矿田和海南儋州丰收钨铯铷多金属矿田,电气石岩浆隐爆角砾岩筒是重要的成矿蚀变−构造岩相,对铁铜、锡铜钨铯铷多金属富集成矿较为有利。在甘南合作地区录斗艘金矿床内,含金电气石隐爆角砾岩筒是甘肃辰州矿产开发有限责任公司新发现的金矿床类型,电气石岩浆隐爆角砾岩筒为成矿流体运移通道相、成矿−储矿构造岩相和成矿流体运移驱动力,具有“三位一体”构造岩相作用。石英闪长斑岩侵入于下二叠统和三叠系火山岩内,形成的角岩−角岩化相包括黑云母−白云母石英角岩、红柱石−石英角岩等。金矿体产于电英岩与石英闪长斑岩接触部位的蚀变带内或电英岩内。金矿体呈筒柱状和锥状,坑道控制最大直径约35~75 m,控制垂深>88 m,金平均品位8.30~8.94 g/t。在录斗艘金矿区发育电气石化、黄铁矿化、硅化、绢云母化、毒砂化、辉锑矿化、碳酸盐化、黄铜矿化。
在录斗艘金矿床内,电气石隐爆角砾岩筒由电英岩、石英电气石岩、气孔状电气石热液角砾岩、扁平状电气石热液隐爆角砾岩、电气石岩浆隐爆角砾岩共5种蚀变岩类组成,具有明显的水平分带和垂直分带特征。①从中心相到外缘相的水平分带为:电气石化二长斑岩岩帽和穹顶)岩浆隐爆角砾岩相→气孔状电气石热液隐爆角砾岩相(角砾为蚀变二长斑岩)→扁平状流体化电气石热液角砾相→电英岩质热液角砾岩相→电气石伊利石蚀变岩相→电气石黑云母闪长斑岩相,金富矿体赋存在二长斑岩岩帽穹顶周缘。②从深部到浅部垂向分带为:二长斑岩侵入相→电气石岩浆隐爆角砾岩相→二长斑岩岩帽穹顶相和电气石隐爆角砾岩相→电气石岩浆隐爆角砾岩相+电气石热液角砾岩相→扁平状流体化电气石热液角砾岩相+毒砂黄铁矿电气石岩相。金矿体在四中段分布最广,呈“下小上大”的气囊状构造。二长斑岩角砾含量从浅部到深部逐渐增加,并出现岩帽和岩墙,指示了深部存在隐伏二长斑岩岩体,并与金矿体具有密切关系。③二中段V3脉东沿脉巷道内含金电英岩发育,采场存隆矿石均为含金电英岩。在空间上,电气石热液隐爆角砾岩型金矿体位于隐爆角砾岩中或其附近;在成因上,由浅成—超浅成中酸性侵入岩及其电气石岩浆隐蔽爆破作用所形成的热液角砾岩化相,二长斑岩和闪长斑岩等是电气石隐爆角砾岩筒形成的决定性因素。二长斑岩角砾含量从浅部到深部逐渐增加,推测录斗艘矿区深部存在隐伏二长斑岩岩体,且与金矿体具有密切关系。
3. 深部隐蔽矿田构造岩相识别探测、解析建相和形成机制
电气石热流柱构造、岩浆气囊构造、复合岩溶构造岩相是3种新类型的成矿蚀变−构造岩相。在老厂矿田黄茅山和卡房矿田,地表发育大理岩、大理岩化结晶灰岩、碎裂岩化大理岩和电气石热液岩溶大理岩;沿断裂带发育碎裂岩化结晶灰岩、白云岩质碎裂岩和白云岩质超碎裂岩等组成的碎裂岩相。深部隐蔽构造岩相释义是指出露于地表但难以识别和隐伏于地表至5000 m以浅、采用常规方法技术难以直接识别和探测的构造岩相类型,也称复杂构造岩相体。如热流柱构造是起源于地球内部(包括地表、陆壳、地幔、软流圈等)热流体垂向运移过程,热流体系统与围岩之间发生过超临界流体—化学反应—热力作用—固流作用—围岩固体五重耦合反应结构,富高挥发性组分、富烃类(CH4等)和富非烃类组分(F、Cl、B、CO2、H2S等)的热流体柱,在构造−地层−岩石的多重耦合反应下,发生了垂向热储构造和垂向热流体色层分异作用、层状热储构造和岩相分异作用、循环对流热储构造和固−流−热耦合反应作用。如电气石热流柱构造、富H2S-CO2型非烃类热流柱构造、富CH4烃类热流柱构造、富NH3 −类热流柱构造。
在个旧东区,从上到下的垂向分带结构是(图4):①顶部层间锡多金属矿床(层间硫化矿和层间氧化矿)+白云岩型锡矿床赋存在卡房段第6岩性层内(复合岩溶构造岩相;图4),受下伏的电气石热液岩溶大理岩相、碎裂状铁皂石大理岩相和隐伏花岗岩突起复合控制,高热流垂向热驱动导致CO2垂向运移和逃逸。②脉带型锡多金属矿床受切层断控型岩溶构造岩相带控制,含锡多金属碳酸盐质热液角砾岩筒受断裂带交汇处和CO2型热流柱构造的复合控制。③锡石−电气石细脉带型锡矿床受电气石热流柱构造控制。④锡钨铜−铌钽矿床受岩浆气囊构造控制显著。⑤蚀变花岗岩型锡铜钨矿床受隐伏花岗岩内的深部热流体房控制。
3.1 岩浆气囊构造与锡铜钨成矿蚀变−构造岩相
岩浆气囊构造主要分布在花岗岩和闪长岩侵入体的边部—顶部,或闪长岩岩被之下的岩滴构造和岩凹构造部位,如个旧东区岩浆气囊构造在马拉格矿田白砂冲、大红坡和马拉格地区出露,长英电气石岩脉扎根于赤铁矿电气石二长斑岩体内,因富含赤铁矿、电气石、含锂电气石、白云母、黄玉、斧石等示相矿物,指示属强酸性的氧化态侵入岩体。
在云南个旧锡铜钨铯铷多金属矿集区,岩浆气囊构造的宏观构造岩相学特征是以云英岩化蚀变和云英岩、伟晶状白云母岩、电英岩化和电气石岩浆隐爆角砾岩、黑/金云母蚀变岩和黑云母热液角砾岩等为标志。通过大比例尺蚀变构造岩相学填图,可圈定侵入岩体边部—顶部岩浆气囊构造(岩浆隐爆角砾岩筒)。在岩浆气囊构造内,“浆—气—液”三相态物质相互作用强烈,形成了钨锡铜−铌钽−铯铷等关键矿产有关的成矿蚀变构造岩相(方维萱等,2021)。从侵入岩体内部→岩浆气囊构造带→围岩,垂向分带规律是:①岩浆气囊构造底部或旁侧为隐伏花岗岩突起,以电气石二长斑岩+电气石二长花岗岩+浅色二长花岗岩为主。云英岩和伟晶状白云母岩位于侵入岩体边—顶部或岩凹、岩滴或岩被之下,有利于形成岩浆气囊构造(环状岩帽和岩羽构造;图4)。岩帽状云英岩分布在花岗岩突起顶部,发育似伟晶岩壳。云英岩和伟晶状白云母岩呈岩羽构造,穿切进入围岩而尖灭为黏土化蚀变脉,W-Sn-Mo-Cu-Nb-Ta-Rb-Cs-B-F原生异常发育,W-Nb-Ta-Rb-Cs富集成矿。②底部或旁侧以黑云母闪长岩−黑云母电气石闪长岩、电气石花岗岩−电气石二长斑岩等为主;电英岩和电气石岩浆隐爆角砾岩在这些侵入岩体边部—顶部发育。向上进入地层围岩系统内,以电气石热液角砾岩相和脉带状电气石蚀变相为主。W-Sn-Mo-Bi-F-B化探异常为主。③外缘相带以碎裂岩化大理岩、碎裂岩化白云岩、碎裂岩化角岩等为主,发育石英−白钨矿网脉、赤铁矿−铁锰碳酸盐−锡石网脉或硫化物−锡石网脉。④纳米成矿效应以瞬态超临界作用为特色,基于化合物和矿物中O-H、C-H、H-N、C-O等共价键振动的组合频和倍频在350~2500 nm 波长区间有明显的吸收特征(Cloutis,1989;修连存等,2007)。基于这些原理,对黏土矿物种类和含烃类蚀变矿物进行识别,进行岩浆气囊构造与蚀变岩相分带探测识别和圈定。
3.2 电气石热流柱构造与锡石−电气石脉带型矿床
电气石热流柱属高氧化态、强酸性的地球化学岩相学类型。电气石热流柱的垂向分带从下到上为:电气石化等粒花岗岩+电气石二长斑岩+电气石浅色花岗岩→电气石岩浆隐爆角砾岩筒→电气石热液隐爆角砾岩筒→赤铁矿电气石大脉带→锡石硫化物电气石网脉带→电气石热液岩溶大理岩(图4)。电气石热流柱可以驱动CO2向上运移和逃逸,因电气石热流柱具有高氧化态和强酸性特征。电气石热液岩溶作用发育,在电气石热液岩溶大理岩相和碎裂状铁皂石大理岩相上方,驱动CO2向上运移和逃逸并形成了CO2型热流柱。
在老厂矿田不同深度上:①根部相以岩浆隐爆角砾岩相为主,形成了电气石岩浆隐爆角砾岩、电气石钠基伊利石隐爆角砾岩和岩浆隐爆角砾岩等,通过大比例尺矿田蚀变岩构造岩相填图,有助于圈定侵入岩体顶部和周缘的富气残浆中心和成岩−成矿中心。其形成机制可能是以岩浆隐爆作用和岩浆气囊构造封闭−再度隐爆开启作用,它们为电气石热流柱向上运移驱动力。②向上演化为气成热液隐爆角砾岩和岩浆射气角砾岩相,多呈筒状、羽状或冠羽状热液隐爆角砾岩体,岩浆隐爆角砾岩相−气成热液隐爆角砾岩−岩浆射气角砾岩相,它们是岩浆气囊构造(magmatic gasbag structure)物质组成,如个旧老厂05花岗岩突起顶部发育电气石钠基伊利石隐爆角砾岩。钠基伊利石指示了岩浆内生水和盆地流体来源的H2O共同气化,岩浆射气+气成高温流体射流−射气可能是电气石热液(隐爆)角砾岩形成机制和向上运移的驱动力。③向上依次相变为高温热液角砾岩类→中—低温热液角砾岩类→低温液压致裂热液角砾岩类,这是热流场驱动的降温过程、盆地流体加热−循环对流作用过程的记录。④在个旧老厂矿田和高松矿田内,隐伏花岗岩岩突和岩凹之上,受断裂带控制的铁锰碳酸盐质热液角砾岩筒发育,它们是重要的矿田储矿构造岩相类型。垂向构造岩相分带显著,依次为:含绿柱石电气石铁锰碳酸盐化热液角砾岩→赤铁矿铁锰碳酸盐化浑圆状热液角砾岩→赤铁矿铁锰碳酸盐化液压致裂角砾岩。
3.3 电气石热液岩溶大理岩相和碎裂岩化铁皂石大理岩相
大理岩相−大理岩化相总体呈带状—放射状—冠羽状,围绕隐伏花岗岩突起周缘发育垂向和水平分带,从下到上垂向分带模型是:①深部大理岩相带,环带状和穹帽状矽卡岩化大理岩相与大理岩化相,紧邻隐伏花岗岩周缘300~500 m范围分布(图4),穿层脉状矽卡岩沿大理岩相内断裂带充填,两侧矽卡岩化作用显著;网脉状电气石化大理岩呈穿层分布。②中部大理岩化相带,似层状−穹帽状大理岩相−铁锰碳酸盐化白云岩相带,分布在隐伏花岗岩周缘500~1200 m范围,铁锰碳酸盐化白云岩相主要受切层断裂带控制,具有内核层间破碎带→赤铁矿化碎裂状大理岩±铁锰碳酸盐化热液岩溶大理岩→外缘碎裂状大理岩。③浅部铁锰碳酸盐化相+断控型大理岩化相,断控型铁锰碳酸盐化热液角砾岩→赤铁矿化碎裂状结晶灰岩→白云岩质碎裂岩、赤铁矿化碎裂状白云岩和赤铁矿化碎裂状白云质灰岩。在电气石热流柱和电气石热液岩溶大理岩之上,断控型热液岩溶构造岩相带内,发育伟晶状铁锰碳酸盐化蚀变岩和巨晶状铁锰碳酸盐化热液角砾岩,它们是CO2型热流柱构造顶部岩帽−构造岩相带。
3.4 复合岩溶构造岩相与层间锡多金属矿床
个旧东区发育多期次岩溶作用同位叠加的复合岩溶构造岩相(方维萱,2022b),采用近红外矿物波谱仪,现场识别微纳米级示相矿物(沸石、菱锌矿、伊利石、皂石、蛇纹石、钠闪石等)和同位叠加成岩作用。①中三叠世—晚三叠世,准同生期灰质岩溶角砾岩以富锌镁低温热水渗滤交代作用为主,形成了沸石白云岩和沸石白云石岩溶角砾岩;②在侏罗纪—早白垩世盆地改造变形期,富锰镁盆地流体形成了似层状白云岩、切层不规则富锰白云岩、网脉状−脉状锰白云石化;③在岩浆热液岩溶作用外缘带,示相矿物组合为赤铁矿−方解石−钾/镁伊利石−利蛇纹石型,中部岩浆热液蚀变相带以黑云母−钾伊利石−高岭石型示相矿物为主;大理岩相−大理岩化相内,示相矿物组合是铁皂石−方解石−锰白云石−电气石型和角闪石−电气石−蛇纹石型;④在古近纪表生岩溶作用相带内,岩溶洞穴中形成了紫红色铁质钙屑砂岩和紫红色铁质钙屑砂砾岩等沉积岩层,发育水锌矿−含铜水锌矿−菱锌矿−石膏−胆矾型示相矿物组合,与晚白垩世末期—古近纪期间干旱蒸发气候密切有关;⑤在新近纪表生岩溶作用相带,示相矿物为方解石−石膏−赤铁矿,缺失锰白云石和白云石、电气石等热液矿物信息。
4. 结论
(1)在活动陆缘构造上,智利科皮亚波地区IOCG型矿田受主岛弧带−弧相关盆地及岩浆叠加−盆地变形样式复合控制,而云南东川沉积岩型铜矿床(SSC型)+IOCG型铁铜矿田受陆缘裂谷盆地、盆地变形构造样式和岩浆叠加侵入构造系统复合控制。内蒙古甲查浅成低温热液型银铅锌矿田受火山洼地、火山穹隆构造、火山岩岩相类型和火山热液隐爆角砾岩的复合控制,而深成岩浆弧控制了蒙古国南戈壁斑岩型金铜钼−浅成低温热液金银矿田。
(2)大陆构造演化上,秦岭热水沉积型(SEDEX)银铜铅锌−菱铁矿−重晶石矿田受陆缘拉分盆地内三级热水沉积盆地、同生断裂带和热水沉积岩相控制,造山带内不同层次的脆韧性剪切带控制了金矿田和金钼多金属矿田定位。在南疆盆−山−原镶嵌区内,侏罗系煤系烃矿源岩是金属矿田和天然气气田的成矿成藏物质供给源区;乌拉根砂砾岩型天青石−铅锌矿田受山前挤压−伸展转换盆地、气成热流柱构造和山前冲断褶皱带的复合控制;萨热克铜多金属田赋存于旱地扇杂砾岩,对冲式厚皮型逆冲推覆断裂带和幔源热流柱带复合控制。
(3)提出了矿田成矿蚀变−构造岩相类型的新划分方法和划分原则方案,首次划分确定了12种变形构造岩相类型;认为电气石热流柱构造岩相、岩浆气囊构造岩相、复合岩溶构造岩相等是成矿蚀变−构造岩相的3种新类型,在形成机制上,它们均与气相−流体−固体−岩石多相态耦合作用密切有关。
-
图 1 汤丹铜矿床(SSC型)4号构造岩相学实测纵剖面
1—震旦系陡山沱组;2—中元古界东川群落雪组二段;3—中元古界东川群落雪组一段; 4—中元古界东川群因民组三段;5—古元古界汤丹岩群平顶山组;6—铁质板岩;7—白云岩; 8—泥粉砂质板岩;9—碱性铁质辉绿辉长岩枝(墙);10—铜矿体(SSC型铜矿床);11—低品位铜矿体; 12—推测铜矿体;13—地质界线; 14—推测地质界线;15—断层;16—推测断层; 17—地质产状;18—中段标高和海拔高度
Figure 1. Measured No.4 longitudinal profiles of tectonic lithofacies in the Tangdan copper deposits (SSC-type)
1−Sinian Doushantuo Formation; 2−the Second of member at Luoxue Formation of Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 3−the first member at Luoxue Formation of Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 4−the three member at Yinming Formation of Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 5−Pingdingshan Formation of Palaeoproterozoic Tangdan Rock Group; 6−irony slate; 7−dolomite; 8−argillaceous-silty slate; 9−alkaline Fe-rich diabase-gabbro apophyse or dike; 10−copper orebody(SSC-type copper deposit);11−copper orebody with low-grades; 12−presumed copper orebody;13−geological line; 14−presumable geological line;15−faults; 16−presumed faults; 17−geological occurrence; 18−adit level and above the sea level
图 2 白锡腊−中老龙IOCG型和SSC型铜矿床实测构造岩相学纵剖面
1—中元古界东川群落雪组二段;2—中元古界东川群落雪组一段;3—中元古界东川群因民组三段;4—碱性铁质辉绿辉长岩枝;5—热液角砾岩相;6—铜矿体(SSC型铜矿床);7—低品位铜矿体;8—铁铜矿体(IOCG型铁铜矿床);9—地质界线;10. —推测地质界线;11—断层;12—穿脉垂直投影面;13—坑内钻孔及编号;14—中段标高和海拔高度;15—地质产状
Figure 2. Measured longitudinal profiles of tectonic lithofacies for IOCG-type and SSC-type copper deposits from Baixila to Zhonglaolong
1−the second of member of the Luoxue Formation of the Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 2−the first member of the Luoxue Formation of the Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 3−the third member of the Yinming Formation of the Mesoproterozoic Dongchuan Group; 4−alkaline Fe-rich diabase-gabbro apophyse; 5−hydrothermal breccia facies; 6−copper orebody (SSC-type copper deposit); 7−low-grade copper orebody; 8−Fe-Cu orebody (IOCG-type deposit); 9−geological boundary; 10−inferred geological boundary; 11−fault; 12−transverse drift (vertical projection); 13−adit-in drillhole and its number; 14−adit elevation and altitude
图 3 甲查银多金属矿田火山机构与矿田构造岩相图
a—甲乌拉−查干银多金属矿田构造岩相图;b—e、h—j为甲乌拉银多金属矿床;f—g为查干银多金属矿床;b—540 m中段铅锌硫化物充填交代脉与边部菱沸石−铁绿泥石相;c—580 m中段石膏−蒙脱石−钾伊利石相;d—580 m中段伊蒙混层−伊利石相;e—475 m中段细脉状和微脉状闪锌矿方铅矿硫化物充填在伊利石热液角砾岩相中。 f—怡圣园西端18号矿体300 m中段216勘探线主巷道掌子面富银菱锰矿铁锰碳酸盐热液角砾岩相;g—怡圣园西端18号矿体300 m中段216勘探线主巷道掌子面富银菱锰矿铁锰碳酸盐热液角砾岩相;h—200 m中段5′—7′线含闪锌矿方铅矿马牙状石英脉;i—伟晶状方铅矿结晶核相;j—200 m中段5′—7′线2号矿体巨晶状方铅矿结晶核相的外缘中心相(具有海绵陨铁结构的铁闪锌矿−磁黄铁矿−黄铜矿矿石,磁化率151~114×10−3SI)
Figure 3. Mapping of volcanic edifice and ore-field tectonic lithofacies in the Jia–Cha Ag-polymetallic orefield
(a) Tectonic lithofacies map of the Jiawula–Chagan Ag-polymetallic orefield; Fig.3b to 3e and 3h to 3i are photos from the Jiawula Ag-polymetallic deposit and Fig.3f to 3g are photos from the Chagan Ag-polymetallic deposit; (b) Chabasite-daphnite facies along both sides of the filling−replacement veins of Pb-Zn-sulfides at 540 m level; (c) Gypsum-semctite-K-illite facies at 580 m level; (d) Facies of illite-smectite formation and illite at 580 m level; (e) Fine-veined and microveined sphalerite-galena sulfides veins filling in lithofacies of illite hydrothermal breccia at 475 m level; (f) Fe-Mn-carbonate hydrothermal breccia lithofacies of Ag-rich rhodochrosite from No.18 orebody in the 216 exploration line at the tunnel face of 300 m level; (g) Fe-Mn-carbonate hydrothermal breccia lithofacies of Ag-rich rhodochrosite from No.18 orebody in the 216 exploration line at the tunnel face of 300 m level; (h) Sphalerite-galena sulfides quartz veins in horse-teeth-shape in the 5′–7′ exploration line at 200 m level; (i) Crystalline nuclear lithofacies of pegmatitic galena in the 5′–7′ exploration line at 200 m level; (j) Marmatite-pyrrhotite-chalcopyrite ores in sideronitic texture around crystalline nuclear lithofacies of pegmatitic galena in the 5′–7′ exploration line at 200 m level; magnetic susceptibility is from 151×10−3 to 114×10−3SI
-
[1] CAO P, REN Y S, HOU Z S, et al. , 2018. Ore-forming fluid characteristics and mineralization age of the Jiawula Pb-Zn (Ag) Deposit in Manzhouli area[J]. Gold, 39(9): 5-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] CHEN H Y, ZHANG S T, CHU G B, et al. , 2019. The short wave infrared (SWIR) spectral characteristics of alteration minerals and applications for ore exploration in the typical skarn-porphyry deposits, Edong ore district, eastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(12): 3629-3643. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.12.04 [3] CHEN X H, CHEN Z L, YANG N, 2009. Study on regional mineralizations and ore-field structures: building of mineralizing tectonic systems[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 15(1): 1-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] CHEN Z L, CHEN B L, 2012. Thinking, steps and practice of research on orefield structure in geomechanics[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 34(4): 208-215. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] CLOUTIS E A, 1989. Spectral reflectance properties of hydrocarbons: remote-sensing implications[J]. Science, 245(4914): 165-168. doi: 10.1126/science.245.4914.165 [6] COOKE D R, WILSON A J, DAVIES A G S, 2004. Characteristics and genesis of porphyry copper-gold deposits[R]. Hobart: University of Tasmania: 17-34. [7] DAI M, YAN G S, LIU C, et al. , 2016. The zircon U-Pb geochronology and the geochemistry of magmatic rocks and their constraints on the mineralization of Jiawula Pb-Zn-Ag deposit, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(5): 266-280. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] FANG W X, LIU Y L, ZHANG S L, et al. , 2009. Three types of continental geodynamics and metallogenic models for IOCG (Iron-oxide copper gold deposits) from the global view[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 39(3): 404-413. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] FANG W X, 2012. R&D on new mapping technology of geochemical lithofacies in prediction and exploration for Iron-Oxide Copper Gold deposits (IOCG)[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 27(10): 1178-1184. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] FANG W X, LIU X Y, LIU Y L, et al. , 2012. Trial applications of lithofacies mapping in the Baixila Fe-Cu Ore district, Dongchuan, Yunnan, and their achievements of prospecting predication[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 32(1): 101-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.5846/stxb201011021569 [11] FANG W X, DU Y L, LI J X, et al. , 2018. Large scale structural petrography mapping technology and prospecting prediction[M]. Beijing: Geology Press: 1-394. (in Chinese) [12] FANG W X, 2019. Magmatic intrusive tectonic system I: tectonic lithofacies mapping and ore-predication[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 43(3): 473-506. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] FANG W X, 2020. Classification and types of diagenetic lithofacies systems in the Sedimentary Basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 39(11): 1692-1714. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] FANG W X, GUO Y Q, JIA R X, et al. , 2021. On relationship between the superimposed mineralization systems and the zoning patterns of vertical tectonic lithofacies in the Gejiu concentration area of Sn-Cu-W and three rare metals in Yunnan[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(4): 557-584. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] FANG W X, 2022a. On research methodology for deformation history of tectonic lithofacies in sedimentary basin and their application[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(1): 1-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] FANG W X, 2022b. On tectonic lithofacies of hypogene paleokarst unconformable tectonic systems and metallic mineralization[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(7): 2585-2610. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] FANG W X, 2023. Hydrothermal sedimentary lithofacies and their tectono-palaeogeography[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 25(3): 525-553. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] HAN R S, WANG F, HU Y Z, et al. , 2014. Metallogenic tectonic dynamics and chronology constrains on the Huize-type (HZT) germanium-rich silver-zinc-lead deposits[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 38(4): 758-771. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] HOU Z Q, COOK N J, 2009. Metallogenesis of the Tibetan collisional orogen: a review and introduction to the special issue [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 36(1-3): 2-24HOU Z Q, YANG Z M, LU Y J, et al. , 2015. A genetic linkage between subduction- and collision-related porphyry Cu deposits in continental collision zones [J]. Geology, 43(3): 247-250. doi: 10.1130/G36362.1 [20] HOU Z Q, CHEN J, ZHAI M G, 2020. Current status and frontiers of research on critical mineral resources [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 65(33): 3651-3652. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-1417 [21] HU R Z, WEN H J, YE L, et al. , 2020. Metallogeny of critical metals in the Southwestern Yangtze Block [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 65(33): 3700-3714. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0274 [22] HUANG J H, CHEN H Y, HAN J S, et al. , 2018. Alteration zonation and short wavelength infrared (SWIR) characteristics of the Honghai VMS Cu-Zn deposit, Eastern Tianshan, NW China [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 100: 263-279. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.02.037 [23] LI J X, FANG W X, LIU J J, 2011. Types and characteristics of regional tectonics and ore-field structures of iron oxide-copper-gold deposits in Chile [J]. Geology and Exploration, 47(2): 323-332. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] LI T C, FANG W X, WANG L, et al. , 2022. Application of integrated geophysical method in prospecting: a case study of the magnetite-type IOCG deposits in the Moon Mountain exploration area, Copiapo, Chile [J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(1): 22-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] LI T G, WU G, LIU J, et al. , 2014. Rb-Sr isochron age of the Jiawula Pb-Zn-Ag deposit in the Manzhouli area and its geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(1): 257-270. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] LI SZ, LIU LJ, SUO YH, et al. , 2023. Carbon Tectonics: A new paradigm for Earth system science [J]. China Science Bullet, 68(4): 309 –338. doi: 10.1360/TB-2022-0741 [27] LIU F, WANG L, HAN R S, et al. , 2017. Ore-field structural system and its ore-controlling processes of the Beiya porphyry gold polymetallic deposit in northwestern Yunnan, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 24(6): 208-224. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28] LOWELL J D, GUILBERT J M, 1970. Lateral and vertical alteration-mineralization zoning in porphyry ore deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 65(4): 373-408. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.65.4.373 [29] LÜ G X, ZHANG B L, HU B Q, et al. , 2020. Classification and application effect of structural deformation lithofacies in the orefield [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 39(11): 1669-1680. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30] LÜ Q T, MENG G X, YAN J Y, et al. , 2019. Multi-scale exploration of mineral system: concept and progress: a case study in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt[J]. Geology in China, 46(4): 673-689. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31] LÜ Z C, CHEN H, MI K F, et al. , 2022. The theory and method of ore prospecting prediction for exploration area: case studies of the Lala copper deposit in Sichuan, Muhu-Maerkantu manganese ore deposit in Xinjiang and Aonaodaba tin-polymetallic deposit in Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(5): 842-865. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] MAO J W, WU S H, SONG S W, et al. , 2020. The world-class Jiangnan tungsten belt: geological characteristics, metallogeny, and ore deposit model [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 65(33): 3746-3762. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0370 [33] NIU S D, LI S R, GUO J, 2020. 40Ar-39Ar ages of the sericite in the Jiawula Pb-Zn-Ag deposit, Inner Mongolia and their geological significance[J]. Geology and Exploration, 56(1): 59-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34] SILLITOE R H, 2005. Supergene oxidized and enriched porphyry copper and related deposits [M]//HEDENQUIST J W, THOMPSON J F H, GOLDFARB R J, et al. One hundredth anniversary volume. Littleton: Society of Economic Geologists: 723-768. [35] SILLITOE R H, 2010. Porphyry copper systems [J]. Economic Geology, 105(1): 3-41. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.105.1.3 [36] XIAO W J, SONG D F, ZHANG J E, et al. , 2022. Anatomy of the structure and evolution of subduction zones and research prospects [J]. Earth Science, 47(9): 3073-3106. (in Chinese with English abstract) [37] XIU L C, ZHENG Z Z, YU Z K, et al. , 2007. Mineral analysis technology application with near infrared spectroscopy in identifying alteration mineral [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(11): 1584-1590. (in Chinese with English abstract) [38] YANG M, SUN J G, WANG Z Y, et al. , 2017. Petrogenesis and geological significance of the alkali-rich granite porphyry in the Jiawula Cu-Ag-Pb-Zn deposit in the Western slope of the great Xing’an range: zircon U-Pb dating and geochemical characteristics [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 47(2): 477-496. (in Chinese with English abstract) [39] YANG S F, JIA C Z, CHEN H L, et al. , 2022. Core theories of sedimentary basin structure and the related key research techniques: frontiers and development directions [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 29(6): 10-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) [40] YANG X K, LIU W, FAN Y, et al. , 2015. Type classification and Qinghai example analysis of orefield structure and magma-thermodynamic structure [J]. Journal of Earth sciences and Environment, 37(1): 24-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) [41] ZHAI Y S, 2007. Earth system, metallogenic system to exploration system [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(1): 172-181. (in Chinese with English abstract) [42] ZHANG B L, LYU G X, YU J G, et al. , 2021. Geophysical data interpretation of the tectonic deformation lithofacies belts in the ore field: application in ore prospecting [J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(4): 542-556. (in Chinese with English abstract) [43] ZHANG S M, WANG G H, ZHAO S B, et al. , 2022. The Main magmstic-thermodynamic Structures and their controls on ore formation in Beishan, Inner Mongolia [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 46(4): 691-709. (in Chinese with English abstract) [44] ZHENG Y, 2022. Large-scaled structure-alteration-mineralization mapping of the hydrothermal deposits: basic principle and precautions[J]. Earth Science, 47(10): 3603-3615. (in Chinese with English abstract) [45] ZHOU Y Z, CHEN S, ZHANG Q, et al. , 2018. Advances and prospects of big data and mathematical geoscience [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(2): 255-263. (in Chinese with English abstract) [46] ZOU C C, WANG C S, PENG C, et al. , 2023. Development of the Chinese continental scientific deep drilling: perspectives and suggestions[J]. Geoscience, 37(1): 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) [47] 曹鹏, 任云生, 侯召硕, 等, 2018. 满洲里地区甲乌拉铅锌(银)矿床成矿流体特征及成矿时代[J]. 黄金, 39(9): 5-12. doi: 10.11792/hj20180902 [48] 陈华勇, 张世涛, 初高彬, 等, 2019. 鄂东南矿集区典型矽卡岩-斑岩矿床蚀变矿物短波红外(SWIR)光谱研究与勘查应用[J]. 岩石学报, 35(12): 3629-3643. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.12.04 [49] 陈宣华, 陈正乐, 杨农, 2009. 区域成矿与矿田构造研究: 构建成矿构造体系[J]. 地质力学学报, 15(1): 1-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.01.001 [50] 陈正乐, 陈柏林, 2012. 地质力学矿田构造研究思路、步骤与实践[J]. 自然杂志, 34(4): 208-215. [51] 戴蒙, 严光生, 刘翠, 等, 2016. 内蒙古甲乌拉铅锌银矿区岩浆岩年代学、地球化学特征及其对成矿的约束[J]. 地学前缘, 23(5): 266-280. [52] 方维萱, 柳玉龙, 张守林, 等, 2009. 全球铁氧化物铜金型(IOCG)矿床的3类大陆动力学背景与成矿模式[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 39(3): 404-413. [53] 方维萱, 2012. 论铁氧化物铜金型(IOCG)矿床地球化学岩相学填图新技术研发[J]. 地球科学进展, 27(10): 1178-1184. [54] 方维萱, 杨新雨, 柳玉龙, 等, 2012. 岩相学填图技术在云南东川白锡腊铁铜矿段深部应用试验与找矿预测[J]. 矿物学报, 32(1): 101-114. [55] 方维萱, 杜玉龙, 李建旭, 等, 2018. 大比例尺构造岩相学填图技术与找矿预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-394. [56] 方维萱, 2019. 岩浆侵入构造系统Ⅰ: 构造岩相学填图技术研发与找矿预测效果[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 43(3): 473-506. [57] 方维萱, 2020. 论沉积盆地内成岩相系划分及类型[J]. 地质通报, 39(11): 1692-1714. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2020.11.003 [58] 方维萱, 郭玉乾, 贾润幸, 等, 2021. 论云南个旧锡铜钨三稀金属矿集区叠加成矿系统与垂向构造岩相学结构的关系[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(4): 557-584. [59] 方维萱, 2022a. 论沉积盆地构造岩相变形史研究方法及应用[J]. 地质力学学报, 28(1): 1-21. [60] 方维萱, 2022b. 深成古岩溶不整合构造系统构造岩相学与金属成矿[J]. 地质学报, 96(7): 2585-2610. [61] 方维萱, 2023. 论热水沉积岩相及其构造古地理[J]. 古地理学报, 25(3): 525-553. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2023.03.035 [62] 韩润生, 王峰, 胡煜昭, 等, 2014. 会泽型(HZT)富锗银铅锌矿床成矿构造动力学研究及年代学约束[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 38(4): 758-771. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2014.04.003 [63] 侯增谦, 陈骏, 翟明国, 2020. 战略性关键矿产研究现状与科学前沿[J]. 科学通报, 65(33): 3651–3652. [64] 胡瑞忠, 温汉捷, 叶霖, 等, 2020. 扬子地块西南部关键金属元素成矿作用[J]. 科学通报, 65(33): 3700-3714. [65] 李建旭, 方维萱, 刘家军, 2011. 智利铁氧化物-铜-金矿床区域定位构造-矿田构造类型与特征[J]. 地质与勘探, 47(2): 323-332. [66] 李天成, 方维萱, 王磊, 等, 2022. 综合地球物理方法找矿应用: 以智利科皮亚波地区月亮山磁铁矿型IOCG矿床为例[J]. 地质力学学报, 28(1): 22-35. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222802 [67] 李铁刚, 武广, 刘军, 等, 2014. 大兴安岭北部甲乌拉铅锌银矿床Rb-Sr同位素测年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 30(1): 257-270. [68] 李三忠, 刘丽军, 索艳慧, 等, 2023. 碳构造: 一个地球系统科学新范式[J]. 科学通报, 68(4): 309 –338. [69] 刘飞, 王雷, 韩润生, 等, 2017. 滇西北北衙斑岩型金多金属矿田构造体系及其控矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 24(6): 208-224. [70] 吕古贤, 张宝林, 胡宝群, 等, 2020. 矿田构造变形岩相分类与应用效果[J]. 地质通报, 39(11): 1669-1680. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2020.11.001 [71] 吕庆田, 孟贵祥, 严加永, 等, 2019. 成矿系统的多尺度探测: 概念与进展: 以长江中下游成矿带为例[J]. 中国地质, 46(4): 673-689. doi: 10.12029/gc20190401 [72] 吕志成, 陈辉, 宓奎峰, 等, 2022. 勘查区找矿预测理论与方法及其应用案例[J]. 地质力学学报, 28(5): 842-865. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222816 [73] 毛景文, 吴胜华, 宋世伟, 等, 2020. 江南世界级钨矿带: 地质特征、成矿规律和矿床模型[J]. 科学通报, 65(33): 3746-3762. [74] 牛斯达, 李胜荣, 郭健, 2020. 内蒙古甲乌拉铅锌银矿绢云母40Ar-39Ar年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 56(1): 59-67. doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2020.01.006 [75] 肖文交, 宋东方, 张继恩, 等, 2022. 俯冲带结构演变解剖与研究展望[J]. 地球科学, 47(9): 3073-3106. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.9.dqkx202209001 [76] 修连存, 郑志忠, 俞正奎, 等, 2007. 近红外光谱分析技术在蚀变矿物鉴定中的应用[J]. 地质学报, 81(11): 1584-1590. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.11.013 [77] 杨梅, 孙景贵, 王忠禹, 等, 2017. 大兴安岭西坡甲乌拉铜银铅锌矿床富碱花岗斑岩的成因及其地质意义: 锆石U-Pb定年和地球化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 47(2): 477-496. [78] 杨树锋, 贾承造, 陈汉林, 等, 2022. 沉积盆地构造核心理论和关键技术方法: 前沿与发展方向[J]. 地学前缘, 29(6): 10-23. [79] 杨兴科, 刘渭, 范阅, 等, 2015. 矿田构造与岩浆-热力构造的类型划分及青海实例分析[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 37(1): 24-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2015.01.003 [80] 翟裕生, 2007. 地球系统、成矿系统到勘查系统[J]. 地学前缘, 14(1): 172-181. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.01.017 [81] 张宝林, 吕古贤, 余建国, 等, 2021. 矿田构造变形岩相带的地球物理资料解译与找矿应用[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(4): 542-556. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.04.047 [82] 张善明, 王根厚, 赵士宝, 等, 2022. 北山内蒙地区主要岩浆‒热力构造类型及控矿作用分析[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 46(4): 691-709. [83] 郑义, 2022. 热液矿床超大比例尺构造-蚀变-矿化填图: 基本原理与注意事项[J]. 地球科学, 47(10): 3603-3615. [84] 周永章, 陈烁, 张旗, 等, 2018. 大数据与数学地球科学研究进展: 大数据与数学地球科学专题代序[J]. 岩石学报, 34(2): 255-263. [85] 邹长春, 王成善, 彭诚, 等, 2023. 中国大陆科学深钻发展的若干思考与建议[J]. 现代地质, 37(1): 1-14. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 方维萱,郭玉乾,李天成. 滇东地区裂谷盆地内火山—侵入岩序列与金属成矿. 地质学报. 2024(06): 1776-1802 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 谭威,罗玉川,林明钟,曾育龙,王虎,林健,曾兴宝. 塞尔维亚Timok成矿带北段成矿规律及找矿方向. 地质与勘探. 2024(06): 1272-1283 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术




