Determination of the northeast section of the Nanyuan–Tongxian fault in Beijing and research on its Quaternary activity
-
摘要: 南苑−通县断裂是北京凹陷与大兴凸起的边界断裂,也是1665年北京$ 6{\dfrac{1}{2}}$级地震的主要控震断裂,其活动性对北京市土地规划利用和地质灾害预测有着重要意义。文章通过高精度重力、纵波和横波地震综合物探剖面以及钻孔联合地质剖面探测方法,调查研究了南苑−通县断裂带北东段的几何特征及其活动性。研究结果显示,南苑−通县断裂经过通州区平家疃村后转为近东西向,倾向北,倾角56°~75°;北东段新生代活动呈正断层属性,推测上断点埋深约为21.6 m,为晚更新世活动断裂。文章论证了南苑−通县断裂北东段的活动时代与中段、南西段不同,为首都地区国土空间规划及防灾减灾体系建设提供了重要的地质依据。Abstract: The Nanyuan–Tongxian fault is the boundary fault between the Beijing depression and the Daxing uplift, also the primary seismic-controlling fault of the Beijing M $ 6{\dfrac{1}{2}}$ earthquake in 1665. Its activity is of great significance to land planning and geological disaster prediction in Beijing. Using high-precision gravity, longitudinal-wave and shear-wave seismic comprehensive exploration profiles, and composite borehole geological profiles, this study investigated the geometric characteristics and activity of the northeastern section of the Nanyuan–Tongxian fault. The results show that after passing through Pingjiatuan Village in Tongzhou District, the fault turns to a nearly east-west direction, trending north with a dip angle of 56° to 75°. The new activity in the northeastern section exhibits characteristics of a normal fault, with an estimated buried depth of about 21.6 m, indicating it as a late Pleistocene active fault. The findings demonstrate that the activity age of the northeast section of the Nanyuan–Tongxian fault differs from that of the middle and southwestern sections, providing crucial geological foundations for the spatial planning and disaster reduction systems in the Beijing region.
-
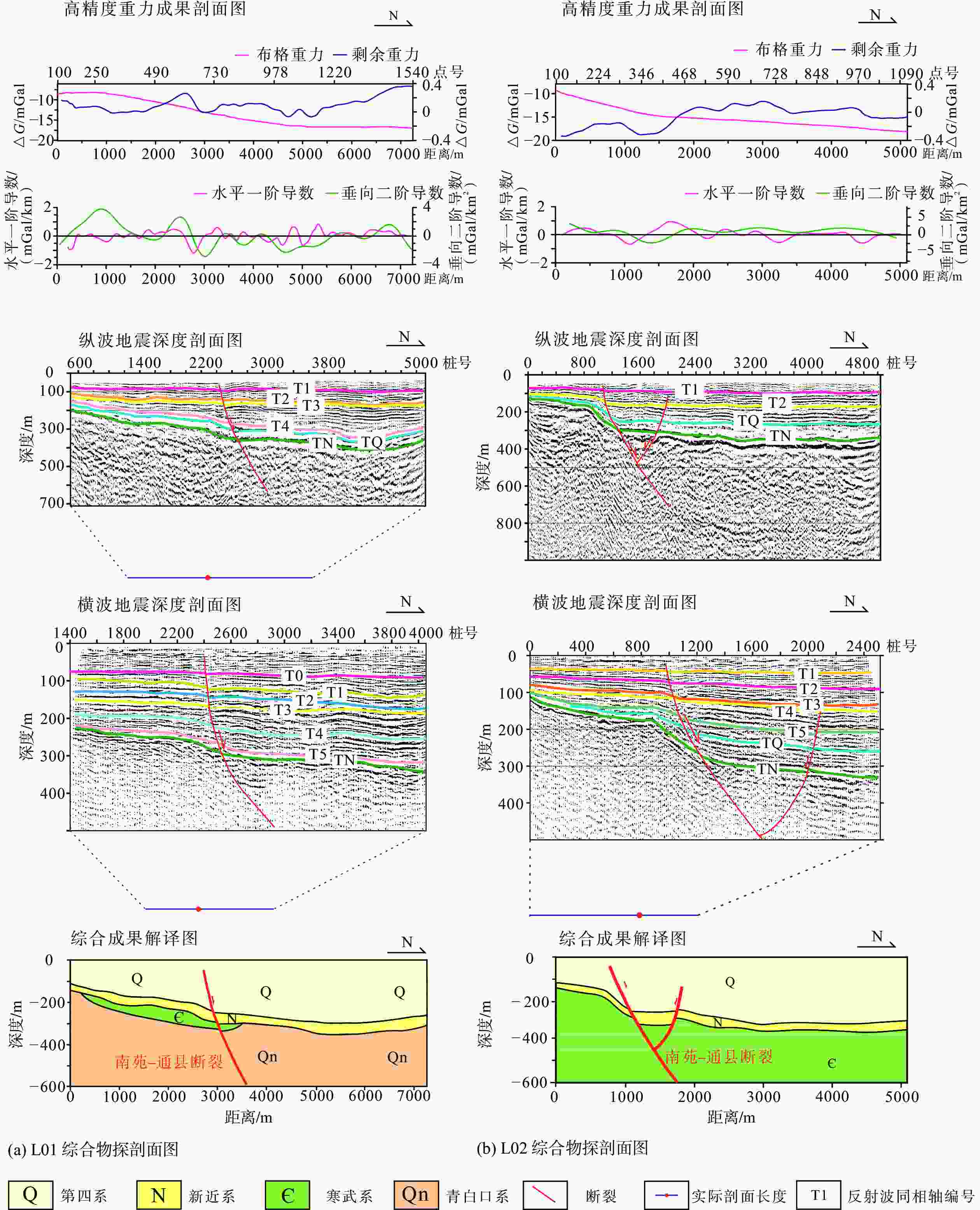
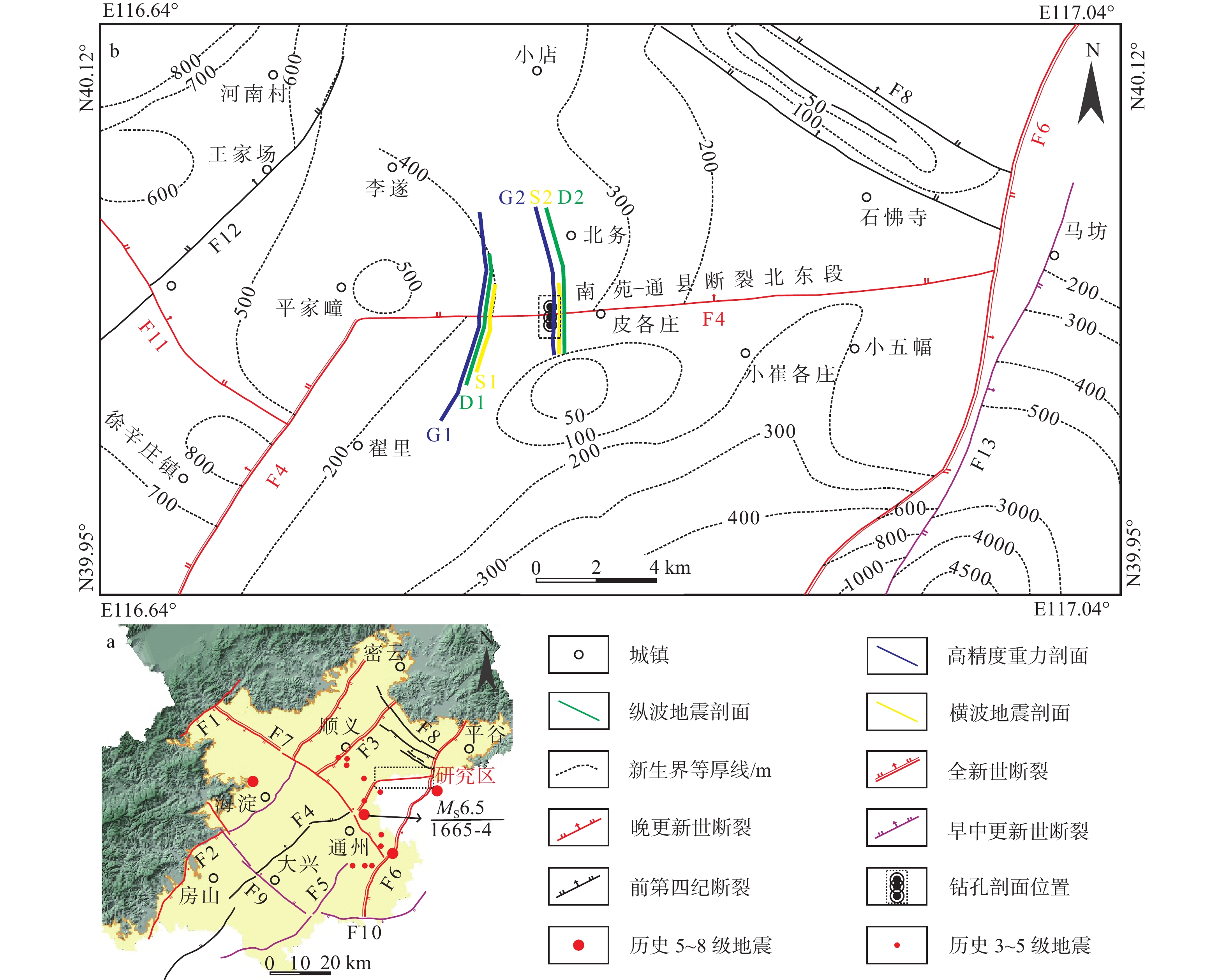
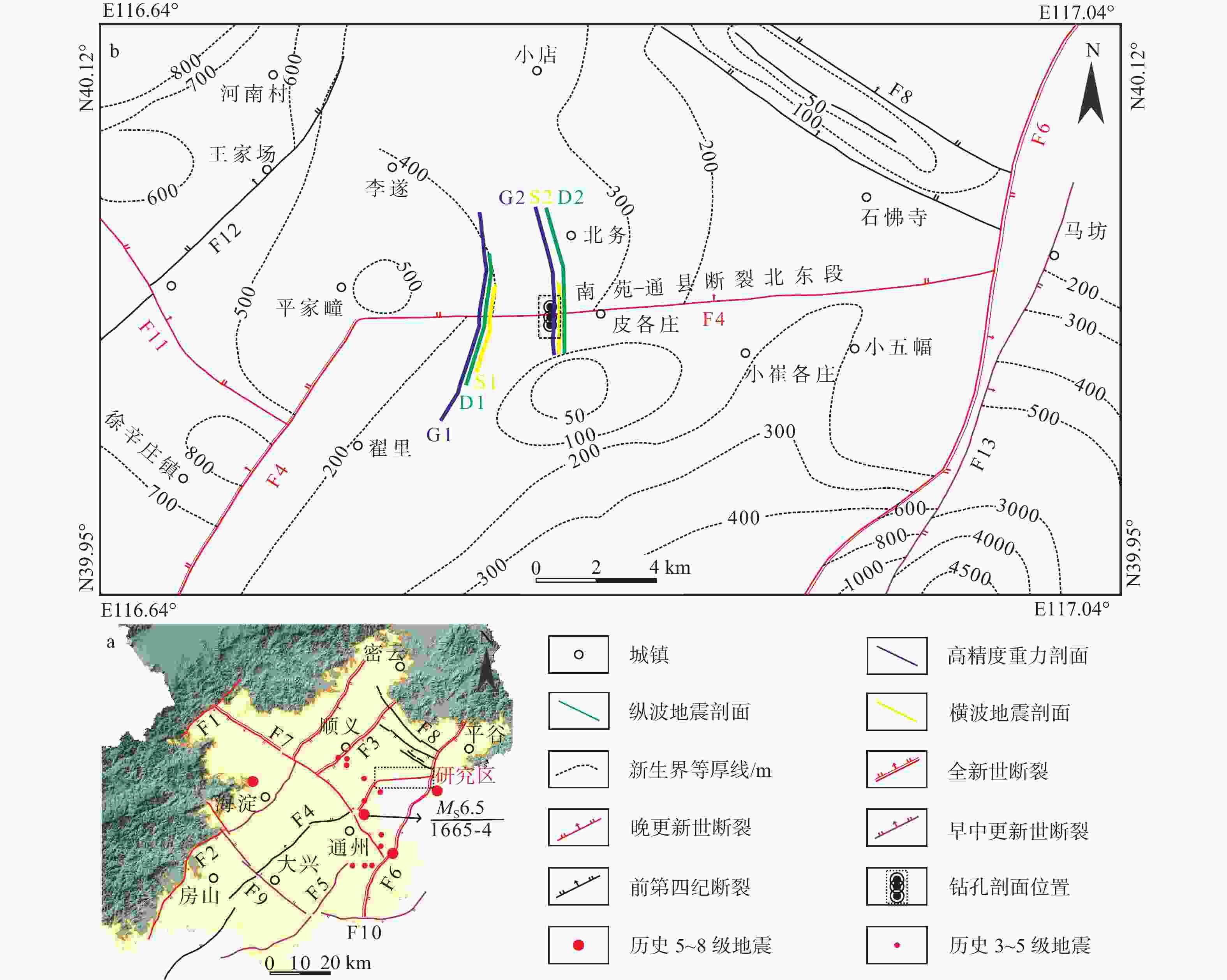
图 1 研究区地质构造简图
F1—南口山前断裂;F2—黄庄−高丽营断裂;F3—顺义断裂;F4—南苑−通县断裂;F5—礼贤断裂;F6—夏垫断裂;F7—南口−孙河断裂;F8—二十里长山断裂;F9—永定河断裂;F10—桐柏断裂;F11—李桥断裂;F12—楼梓庄断裂;F13—西集断裂a—北京市平原区主要断裂分布图;b—南苑−通县断裂北东段断裂分布图及工作部署图
Figure 1. Schematic map of geological structure in the study area
(a) Distribution map of major faults in the plain area of Beijing; (b) Distribution map and work deployment map of Nanyuan–Tongxian fault F1–Nankou piedmont fault; F2–Huangzhuang–Gaoliying fault; F3–Shunyi fault; F4–Nanyuan–tongxian fault; F5–Lixian fault; F6–Xiadian fault; F7–Nankou–Sunhe fault; F8–Ershilichangshan fault; F9–Yongdinghe fault; F10–Tongbai fault; F11–Liqiao fault; F12–Louzizhuang fault; F13–Xiji fault
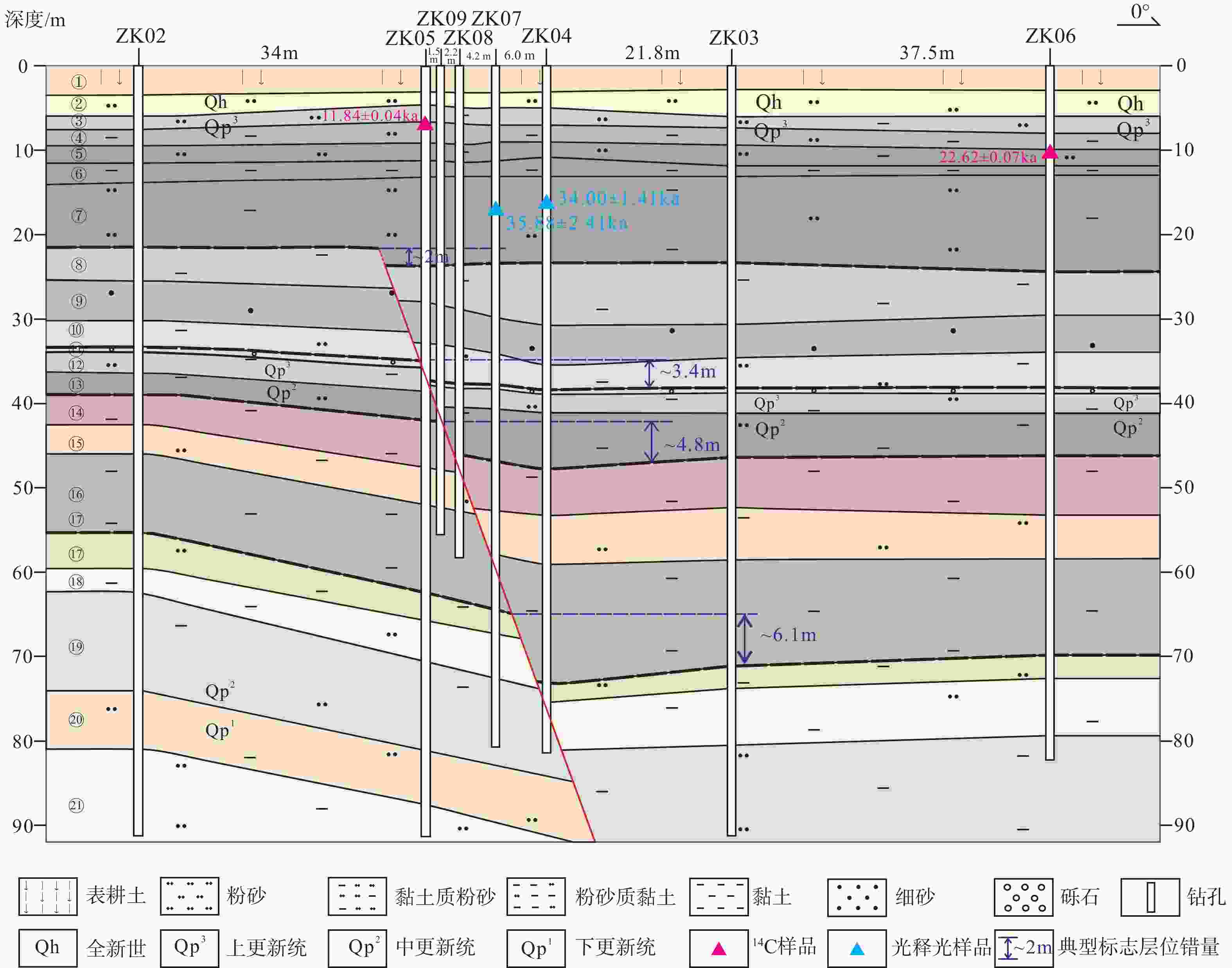
表 1 碳十四样品测试结果一览表
Table 1. Test Results of 14C Samples
样品编号 岩性 取样深度/m 年龄/ka 置信度 ZK05–6.7 含有机质灰色黏土质粉砂 6.7 11.84±0.04 95.4% ZK06–10.1 含有机质灰色黏土质粉砂 10.1 22.62±0.07 95.4% 表 2 光释光样品测试结果一览表
Table 2. Test results of OSL samples
样品编号 取样深度/m 环境剂量率
/(Gy/ka)等效剂量
/Gy年龄/ka 测试方法 ZK04(16.0—16.2) 16.0~16.2 3.04±0.13 103.3±0.2 34.00±1.41 SAR ZK07(16.8—17.0) 16.8~17.0 3.15±0.13 113.2±6.1 35.88±2.41 SAR -
[1] BAI L Y, LI X, QIN H M, et al. , 2018. Study on the cyclic stratigraphy activity of Nankou-Sunhe fault in Beijing plain since Quaternary and its tectonic significance[J]. Geoscience, 32(2): 270-278. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] CAO X W, MA X M, HU D G, 2017. Application of the resistivity tomography method to detection of active faults northeast of the Hainan island[J]. Geology and Exploration, 53(5): 1001-1009. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] FANG T M, LIU H, LIU Y, et al. , 2016. Fundamental geological survey situations and development trend in Beijing's urbanization process[J]. Land and Resources Information(4): 52-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] FENG C J, 2014. Study on the present in situ stress field beneath the capital circle region[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] GAO X L, WANG Q, LI Y D, et al. , 1986. On correlations between transgressions and climatic phases since late Middle-Pleistocene based on data of drilling hole P8 in Tianjin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 6(1): 53-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] HE F B, 2019. Study on geometry and kinematics of the Nankou-Sunhe fault and its relationship with ground fissures[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administrator. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7] HE F B, XU X W, HE Z J, et al. , 2020. Research on Neogene-Quaternary stratigraphic structure and shallow tectonic features in the north section of Daxing fault zone based on shallow seismic reflection profiling[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(4): 893-908. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] HE F B, 2021. Geological survey of twelve faults such as Lixian Beijing plain[R]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Geological Survey. (in Chinese) [9] HUANG X, CHEN G, LI Z L, et al. , 2012. The study on Nanyuan-Tongxian fault in Beijing Daxing planning town[J]. Urban Geology, 7(4): 15-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] HUANG X M, WANG L M, XU J, et al. , 1991. Characteristics of Neotectonic movement in Beijing area[J]. Seismology and Geology, 13(1): 43-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration, 1978. A compilation of researches of Beijing seismic and geological campaign[M]. Beijing: Beijing Earthquake and Geology Office. (in Chinese) [12] JIANG W L, 2007. Active fault detection and seismic risk assessment in Beijing[R]. Beijing: Institute of Geology China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese) [13] LEI X D, QI B S, GUAN W, et al. , 2021. Research on the faults identification based on gravity anomaly in Beijing plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 64(4): 1253-1265. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] LI Z F, LI Y B, ZHOU B G, et al. , 2021. New insight on the holocene activity of the Eastern marginal fault of Daxing uplift, Beijing plain[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(6): 1671-1681. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] LIU B J, HU P, CHEN Y, et al. , 2009. The crustal shallow structures and buried active faults revealed by seismic reflection profiles in Northwestern area of Beijing plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(8): 2015-2025. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] NI J B, LIU X, ZHANG X L, et al. , 2023. Quaternary stratigraphic division and sedimentary characteristics of borehole TB02 in the Southeast margin of Beijing plain, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 45(1): 68-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] SUN Y H, 2021. Beijing regional geology[R]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Geological Survey. (in Chinese) [18] TIAN T T, WU Z H, ZHANG K Q, et al. , 2013. Overview of Quaternary dating methods and their application in neotectonics and active tectonics research[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 19(3): 242-266. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] WANG C Q, JIA L Y, HU D G, et al. , 2022. Quaternary activity characteristics of the Maniao-Puqian fault in the Jiangdong new district of Haikou[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(2): 403-417. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] XU X W, YU G H, RAN Y K, et al. , 2015. An introduction to urban active faults in China[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 380-403. (in Chinese) [21] YUN L, ZHANG J, WANG J, et al. , 2021. Discovery of active faults in the southern Beishan area, NW China: implications for regional tectonics[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(2): 195-207. (in Chinese with English abstract) [22] ZHANG L, BAI L Y, CAI X M, et al. , 2014. An analysis of the activity of the Northwest part of Nankou-Sunhe fault[J]. Geology in China, 41(3): 902-911. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] ZHANG X L, ZHANG L, CAI X M, et al. , 2016. A study of structure and activity characteristics of the northern segment of Huangzhuang-Gaoliying fault in Beijing plain area[J]. Geology in China, 43(4): 1258-1265. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] ZHAO J R, ZHANG X K, ZHANG C K, et al. , 2004. Deep structural features of the Sanhe-Pinggu strong earthquake area imaged by wide angle reflection / refraction and deep seismic reflection profiling[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 47(4): 736-744. doi: 10.1002/cjg2.3544 [25] ZHAO L, LI Y M, CUI W J, et al. , 2018. Disaster characteristics and influence factors for ground fissures at Songzhuang village in Beijing[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 26(6): 1600-1610. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] ZHAO L, LI Y M, LUO Y, et al. , 2021. An extension-dominant 9-km-long ground failure along a buried geological fault on the eastern Beijing Plain, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 289: 106168. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106168 [27] ZHAO Y, LI R J, WEI B, et al. , 2019. Magnetostratigraphy of borehole PGZ05 in Southern Daxing uplift, Beijing plain[J]. Geoscience, 33(1): 56-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28] ZHAO Z H, ZHU H J, 2003. The main characteristics of geological environment and present situation of geological hazard in plain area of Shunyi, Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 14(2): 61-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) [29] 白凌燕, 李潇, 秦浩敏, 等, 2018. 北京平原南口—孙河断裂南段第四纪活动性及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 32(2): 270-278. [30] 曹新文, 马秀敏, 胡道功, 2017. 电阻率层析成像技术在琼东北活动断裂探测中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 53(5): 1001-1009. doi: 10.13712/j.cnki.dzykt.2017.05.016 [31] 方同明, 刘鸿, 刘予, 等, 2016. 北京城市化过程基础地质工作现状及发展趋势[J]. 国土资源情报(4): 52-56. [32] 丰成君, 2014. 首都圈地区现今地应力环境研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院. [33] 高秀林, 王强, 李玉德, 等, 1986. 从天津P8孔看中更新世末期以来海侵期、气候期对比问题[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 6(1): 53-64. [34] 国家地震局地球物理研究所, 1978. 北京市地震地质会战研究成果汇编[M]. 北京: 北京市地震地质会战办公室. [35] 何付兵, 2019. 南口—孙河断裂几何学、运动学特征及与地裂缝关系研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所. [36] 何付兵, 徐锡伟, 何振军, 等, 2020. 利用浅层地震反射剖面探测研究大兴断裂北段新近纪—第四纪的构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 42(4): 893-908. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.04.008 [37] 何付兵, 2021. 北京平原区礼贤等十二条断裂地质调查[R]. 北京: 北京市地质调查研究所. [38] 黄骁, 陈刚, 李哲琳, 等, 2012. 南苑—通县断裂大兴规划新城段的研究[J]. 城市地质, 7(4): 15-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2012.04.004 [39] 黄秀铭, 汪良谋, 徐杰, 等, 1991. 北京地区新构造运动特征[J]. 地震地质, 13(1): 43-51. [40] 江娃利, 2007. 北京市活断层探测与地震危险性评价[R]. 北京: 中国地震局地壳应力研究所. [41] 雷晓东, 戚帮申, 关伟, 等, 2021. 北京平原区断裂构造重力异常识别研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(4): 1253-1265. doi: 10.6038/cjg2021O0210 [42] 李正芳, 李彦宝, 周本刚, 等, 2021. 北京平原大兴凸起东缘断裂全新世活动的新认识[J]. 地震地质, 43(6): 1671-1681. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.06.018 [43] 刘保金, 胡平, 陈颙, 等, 2009. 北京平原西北部地壳浅部结构和隐伏活动断裂: 由地震反射剖面揭示[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(8): 2015-2025. [44] 倪敬波, 刘晓, 张晓亮, 等, 2023. 北京平原区东南缘钻孔TB02第四纪地层划分与沉积特征[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 45(1): 68-79. doi: 10.19814/j.jese.2022.04014 [45] 孙永华, 2021. 北京市区域地质志[R]. 北京: 北京市地质调查研究院. [46] 田婷婷, 吴中海, 张克旗, 等, 2013. 第四纪主要定年方法及其在新构造与活动构造研究中的应用综述[J]. 地质力学学报, 19(3): 242-266. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2013.03.002 [47] 王超群, 贾丽云, 胡道功, 等, 2022. 海口市江东新区马袅-铺前断裂第四纪活动特征[J]. 地质学报, 96(2): 403-417. doi: 10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2022109 [48] 徐锡伟, 于贵华, 冉勇康, 等. 2015. 中国城市活动断层概论: 20个城市活动断层探测成果[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 380-403. [49] 云龙, 张进, 王驹, 等, 2021. 甘肃北山南部活动断裂的发现及其区域构造意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(2): 195-207. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.02.019 [50] 张磊, 白凌燕, 蔡向民, 等, 2014. 北京平原南口—孙河断裂带北西段活动性分析[J]. 中国地质, 41(3): 902-911. [51] 张晓亮, 张磊, 蔡向民, 等, 2016. 北京平原区黄庄—高丽营断裂北段结构特征及活动特点研究[J]. 中国地质, 43(4): 1258-1265. doi: 10.12029/gc20160412 [52] 赵龙, 李玉梅, 崔文君, 等, 2018. 北京宋庄地裂缝灾害特征及影响因素分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 26(6): 1600-1610. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017-426 [53] 赵勇, 李瑞杰, 魏波, 等, 2019. 北京大兴凸起南部PGZ05钻孔剖面第四纪磁性地层学[J]. 现代地质, 33(1): 56-62. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.01.06 [54] 赵忠海, 朱红军, 2003. 北京市顺义平原区地质环境的主要特征及地质灾害现状[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 14(2): 61-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2003.02.013 -




 下载:
下载: