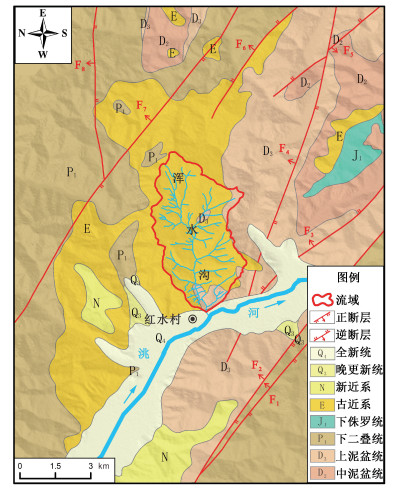
Genesis mechanism and disaster-causing significance of the mud-coated gravel in the Hunshui gully, Min County, Gansu Province
-
摘要:
2020年8月, 甘东南地区持续降雨且伴随多个强降雨过程, 岷县梅川镇浑水沟暴发泥石流, 左岸方家山滑坡失稳下滑, 严重威胁沟口成兰铁路安全。基于野外调查、遥感解译和室内测试结果, 分析泥包砾的形态结构、矿物组成以及堆积特征, 研究泥包砾形成的地质环境和机制, 探讨泥包砾的灾害意义。研究结果表明: 泥包砾分布于浑水沟流通区下游及堆积区, 呈球形且具多层结构, 由石英、方解石、黏土矿物等组成, 其形成主要受控于流域第四系黄土和古近系泥岩中的黏土矿物, 而较缓的沟道、岸坡黄土滑坡和崩塌的发育以及适宜的水动力条件, 促进了泥包砾的形成和自生加大; 泥石流冲击力随着泥包砾粒径的增大而增大, 再起动所需临界泥石流流速相较于块石较小; 泥包砾是古近系泥岩与泥石流共同作用的结果, 具有加剧泥石流危害的作用, 因此亟需治理浑水沟泥石流以保证成兰铁路的安全运营。
Abstract:In August 2020, due to the continuous rainfall in southeast Gansu, especially the heavy rainfall processes, debris flows broke out in the Hunshui gully. The left bank of the Fangjiashan landslide was destabilized and sliding, seriously threatening the safety of the Chengdu-Lanzhou Railway at the mouth of the gully. Based on the field investigation results, remote sensing interpretation, and laboratory tests, we studied the mud-coated gravel's morphology, mineral composition, and accumulation characteristics, analyzed the geological environment and mechanism for its formation and discussed its disaster-causing significance. The results show that mud-coated gravels are distributed in the lower reaches of the circulation area and the accumulation area. It presents a spherical and multi-layered structure composed of quartz, calcite, clay minerals, etc. Its formation is mainly controlled by the clay minerals in the Quaternary loess and Paleogene mudstone in the basin. The slow-moving gullies, landslides, and collapses developed on the bank slope as well as appropriate hydrodynamic conditions, promoted the formation and autogenesis of the mud-coated gravel. The impact force of debris flow increases with the particle size of mud-coated gravel, and the critical velocity required for restarting a debris flow is smaller than that of block rock. Mud-coated gravel is the result of the joint action of the Paleogene mudstone and debris flow, and it can aggravate the debris flow hazard. Therefore, it is urgent to control the debris flows in the Hunshui gully to ensure the safe operation of the Chengdu-Lanzhou Railway.
-
Key words:
- mud-coated gravel /
- debris flow /
- clay mineral /
- formation mechanism /
- impact force /
- threshold velocity
-
表 1 泥包砾、滑坡体前缘及风化层矿物成分及黏土矿物含量测试结果表
Table 1. Test results of the mineral composition and clay mineral content in the mud-coated gravel, in the front of the landslide mass and in the weathered layer
样品编号 矿物种类和含量/% 黏土矿物总量/% 黏土矿物相对含量/% 混层比S/% 石英 钾长石 斜长石 方解石 伊蒙混层 伊利石 高岭石 绿泥石 伊蒙混层 泥包砾1(外) 61.8 3.2 3.0 12.2 19.8 53.1 34.0 6.7 6.2 50.3 泥包砾1(中) 46.4 0.2 1.1 26.6 25.7 58.9 31.4 5.0 4.7 49.8 泥包砾1(内) 18.5 0.7 1.6 41.7 37.5 67.2 24.8 3.1 4.9 45.1 泥包砾2(外) 57.0 2.6 2.1 19.3 19.0 39.4 44.3 6.6 9.7 50.0 泥包砾2(中) 45.9 0.8 1.1 29.1 23.1 51.8 35.1 6.7 6.4 44.6 泥包砾2(内) 34.4 0.7 1.3 33.3 30.3 57.9 28.7 7.5 5.9 45.1 泥包砾3(外) 37.6 19.2 11.8 12.5 14.8 41.8 40.1 8.0 10.1 45.3 泥包砾3(内) 19.0 1.8 2.6 20.8 29.6 37.6 47.2 4.0 11.0 50.1 泥包砾4(外) 43.2 12.4 2.2 19.7 20.0 31.5 53.3 6.9 8.3 50.4 泥包砾4(内) 35.8 1.0 4.6 19.6 39.0 44.7 41.2 5.9 8.2 50.2 泥包砾5(外) 49.1 4.7 4.7 16.3 25.2 46.6 38.1 8.3 7.0 44.8 泥包砾5(内) 48.5 4.0 2.2 16.3 29.0 52.7 36.4 5.6 5.3 45.2 崩滑体前缘1 35.5 1.3 2.3 28.1 32.8 52.3 35.7 3.5 8.5 35.5 崩滑体前缘2 40.3 1.7 2.6 24.3 31.1 50.5 37.4 4.8 7.3 40.3 风化层1 54.3 1.7 3.3 13.3 27.4 47.3 34.6 8.5 9.6 54.3 风化层2 52.9 1.3 2.7 18.5 24.6 42.5 42.8 6.9 7.8 52.9 表 2 浑水沟不同地层灾害发育面积及占比
Table 2. Proportion of landslide and collapse areas in different strata of the Hunshui gully
灾害类型 灾害总面积/m2 古近系(E) 泥盆系(D) 发育面积/m2 占比/% 发育面积/m2 占比/% 滑坡 2530 2530 100 0 0 崩塌 1320 1200 90.9 120 9.1 -
CHEN C Y, REN J W, MENG G J, et al., 2013. Division, deformation and tectonic implication of active blocks in the eastern segment of Bayan Hlar block[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(12): 4125-4141. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/cjg20131217 CUI L, LEI X F, ZHAO F H, et al., 2011. Study on stability evaluation of surrounding rock based on weighted average method[J]. Coal Engineering(6): 77-78, 81. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0959.2011.06.031 DENG H, CHEN N S, HU G S, et al., 2011. Calculation of dynamics parameters of Sanyanyu gully in Zhouqu, Gansu[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science), 30(4): 833-838. (in Chinese with English abstract) DING X L, LIU S M, 2006. Distribution law and prevention measures of geological disasters in Minxian county[J]. Scientific & Technical Information of Gansu, 35(5): 46-47. (in Chinese) GE W P, 2013. Discussion on the relationship between regional landform and seismogenic structure of the Minxian-Zhangxian MS6.6 earthquake[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 35(4): 840-847. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2013.04.840 HE W G, ZHENG W J, WANG A G, et al., 2013. New activities of Lintan-Dangchang fault and its relations to Minxian-Zhangxian MS6.6 earthquake[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 35(4): 751-760. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2013.04.751 HE W S, FANG D, LIU X N, et al., 2003. Critical condition for starting motion of gravel[J]. Sichuan Water Power, 22(1): 64-65, 69. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2184.2003.01.023 HE X Y, 2014. Experimental study on the shock characteristics of debris flow considering different slurry viscosity and gradation particles[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University. (in Chinese with English abstract) HE X Y, CHEN H K, TANG H M, 2016. Experimental study on the energy distribution characteristics of impacting signals of debris flow considering the slurry viscosity and particle collision[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 35(6): 64-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU G S, CHEN N S, DENG M F, et al., 2011. Analysis of the characteristics of impact force of massive stones of the Sanyanyu debris flow gully in Zhouqu, Gansu Province[J]. Earth and Environment, 39(4): 478-484. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU L, XIN P, WANG T, et al., 2021. Centrifuge model tests on the near-horizontal slide of hard soil-soft rock landslides[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(1): 73-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI C Y, FU H L, CAI H L, et al., 2009. Water character of flowering sheet stone[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 6(1): 74-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2009.01.015 LI J F, 2021. Comparative study on formulas of pebble starting velocity[J]. Yangtze River, 52(11): 201-206, 218. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI P Z, GAO Y, GUO M J, 2015. Research status and development trend of debris-flow impact Force[J]. Structural Engineers, 31(1): 200-206. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI X B, XU G B, 1985. Characteristics of sediments of quaternary period Glaice in Pan Ji coal Mine Area[J]. Journal of Huainan Institute of Mining(1): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI X B, LIU H Q, ZHANG Z Y, et al., 2014. "Argillaceous parcel" Structure: A direct evidence of debris flow origin of deep-water massive sandstone of Yanchang Formation, Upper Triassic, the Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 32(4): 611-622. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIAO J B, LI X B, ZHAO H Z, et al., 2017. Genetic mechanism of mud-coated intraclasts within deep-water massive sandstone in Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 41(4): 46-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU D C, YOU Y, DU J, et al., 2019. Spatio-temporal distribution of the impact force of debris flow[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 51(3): 17-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU J J, MA C, LI C Y, 2020. Fundamental problems and prospects in the study of deposition dynamics of viscous debris flow in the gully-river junction[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(4): 544-555. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Y, YOU Y, WANG H F, et al., 2020. Research status and discussion on granular flow impact force[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 40(5): 714-723. (in Chinese with English abstract) LUO L Y, 2011. Research on geometric shapes influencing on incipient motion of gravel[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University. (in Chinese with English abstract) SUN X W, LIU Y P, 2018. Debris flow characteristics and its impact force test in the engineering areas of Dagu and Jiexu hydropower stations in Tibet[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 16(2): 167-172. (in Chinese with English abstract) TIAN L Q, 1994. Genetic classification of accumulational landforms of channel viscous debris folw[J]. Mountain Research, 12(1): 9-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Y B, 2019. Debris flow impact forces on bridge piers[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG H J, WEI F Q, HU K H, et al., 2016. Rheological parameters of debris flow slurries with different maximum grain sizes[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 47(7): 884-890. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG W Y, LI H Y, 1988. Environmental engineering geology in Nanguanling area of Dalian[C]//Selected papers of the third national engineering geology conference (vol. 2). Chengdu: Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press. (in Chinese) YU X B, CHEN X Q, WANG D Z, et al., 2017. Study on the impact rule of viscous debris flow to check dams[J]. Yellow River, 39(3): 37-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZANG X L, LIN G Y, 2011. Discussion on nomenclature of soil layer in Shenyang area[J]. Science & Technology Information(5): 36. (in Chinese) ZENG C, SU Z M, LEI Y, et al., 2015. An experimental study of the characteristics of impact forces between debris flow slurry and large-sized particles[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 36(7): 1923-1930, 1938. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG B, TIAN Q J, WANG A G, et al., 2021. Studies on new activity of Lintan-Dangchang Fault, West Qinling[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(1): 72-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Z T, YAO Y L, 1989. Research on starting velocity of the bed gravel in upper Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute(2): 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHENG W J, YUAN D Y, HE W G, et al., 2013. Geometric pattern and active tectonics in Southeastern Gansu province: Discussion on seismogenic mechanism of the MinxianZhangxian MS6.6 earthquake on July 22, 2013[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(12): 4058-4071. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU H J, WANG X, YUAN Y, et al., 2014. Rapid-assessing methods of loss in extremely heavy rainfall disaster chain in semiarid region: a case study on a flash flood debris flow in Minxian county, Gansu province[J]. Arid Zone Research, 31(3): 440-445. (in Chinese with English abstract) 陈长云, 任金卫, 孟国杰, 等, 2013. 巴颜喀拉块体东部活动块体的划分、形变特征及构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(12): 4125-4141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201312017.htm 崔亮, 雷学峰, 赵飞虎, 等, 2011. 基于加权平均法的围岩稳定性评价研究[J]. 煤炭工程(6): 77-78, 81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MKSJ201106031.htm 邓虎, 陈宁生, 胡桂胜, 等, 2011. 甘肃舟曲三眼峪沟泥石流动力学特征参数计算[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 30(4): 833-838. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQJT201104030.htm 丁晓莉, 刘世梅, 2006. 岷县地质灾害分布规律及防治措施[J]. 甘肃科技纵横, 35(5): 46-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZKQ200605036.htm 葛伟鹏, 2013. 岷县漳县6.6级地震发震构造与区域地形地貌特征关系讨论[J]. 地震工程学报, 35(4): 840-847. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ201304019.htm 何文贵, 郑文俊, 王爱国, 等, 2013. 临潭-宕昌断裂新活动特征与岷县漳县MS6.6地震关系研究[J]. 地震工程学报, 35(4): 751-760. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ201304006.htm 何文社, 方铎, 刘兴年, 等, 2003. 砾卵石起动临界条件[J]. 四川水力发电, 22(1): 64-65, 69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCSL200301023.htm 何晓英, 2014. 浆体与级配颗粒组合条件下泥石流冲击特性实验研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学. 何晓英, 陈洪凯, 唐红梅, 2016. 泥石流浆体与固体颗粒冲击信号能量分布研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 35(6): 64-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ201606011.htm 胡桂胜, 陈宁生, 邓明枫, 等, 2011. 甘肃舟曲三眼峪沟泥石流粗大颗粒冲击力特征分析[J]. 地球与环境, 39(4): 478-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201104007.htm 胡乐, 辛鹏, 王涛, 等, 2021. 硬土软岩滑坡近水平滑移的离心机模型试验研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(1): 73-82. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.01.008 李昌友, 傅鹤林, 蔡海良, 等, 2009. 风化板岩水理特性研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 6(1): 74-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD200901014.htm 李江峰, 2021. 卵石起动流速公式对比研究[J]. 人民长江, 52(11): 201-206, 218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE202111033.htm 李培振, 高宇, 郭沫君, 2015. 泥石流冲击力的研究现状[J]. 结构工程师, 31(1): 200-206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGGC201501031.htm 李祥碧, 徐广标, 1985. 潘集矿区第四纪冰川沉积物的特征[J]. 淮南矿业学院学报(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLGB198501000.htm 李相博, 刘化清, 张忠义, 等, 2014. 深水块状砂岩碎屑流成因的直接证据: "泥包砾"结构: 以鄂尔多斯盆地上三叠统延长组研究为例[J]. 沉积学报, 32(4): 611-622. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201404001.htm 廖建波, 李相博, 赵惠周, 等, 2017. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组深水块状砂岩"泥包砾"结构成因机制[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 41(4): 46-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201704006.htm 刘道川, 游勇, 杜杰, 等, 2019. 泥石流冲击力的时空分布特征[J]. 工程科学与技术, 51(3): 17-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLH201903003.htm 刘晶晶, 马春, 李春雨, 2020. 粘性泥石流入汇区河床堆积动力学研究的问题与展望[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(4): 544-555. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.04.047 刘洋, 游勇, 王海帆, 等, 2020. 颗粒流冲击力研究现状及讨论[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报, 40(5): 714-723. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXK202005005.htm 罗羚源, 2011. 卵砾石几何形状对起动的影响研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学. 孙兴伟, 刘云鹏, 2018. 大古与街需水电站工程区泥石流基本特征及冲击力试验研究[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报, 16(2): 167-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSJS201802032.htm 田连权, 1994. 沟道粘性泥石流堆积地貌的成因分类[J]. 山地研究, 12(1): 9-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA401.001.htm 王友彪, 2019. 泥石流对桥墩冲击力研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学. 杨红娟, 韦方强, 胡凯衡, 等, 2016. 不同上限粒径泥石流浆体的流变参数变化规律[J]. 水利学报, 47(7): 884-890. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB201607007.htm 杨文远, 李宏义, 1988. 大连南关岭地区环境工程地质问题[C]//全国第三次工程地质大会论文选集(下卷). 成都: 成都科技大学出版社. 于献彬, 陈晓清, 王道正, 等, 2017. 黏性泥石流浆体对拦砂坝冲击规律研究[J]. 人民黄河, 39(3): 37-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RMHH201703012.htm 臧秀玲, 林国友, 2011. 沈阳地区土层定名探讨[J]. 科技信息(5): 36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJXX201105022.htm 曾超, 苏志满, 雷雨, 等, 2015. 泥石流浆体与大颗粒冲击力特征的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 36(7): 1923-1930, 1938. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201507018.htm 张波, 田勤俭, 王爱国, 等, 2021. 西秦岭临潭-宕昌断裂第四纪最新活动特征[J]. 地震地质, 43(1): 72-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ202101005.htm 张植堂, 姚于丽, 1989. 长江上游河床卵石起动流速表达式的讨论[J]. 长江科学院院报(2): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJKB198902000.htm 郑文俊, 袁道阳, 何文贵, 等, 2013. 甘肃东南地区构造活动与2013年岷县-漳县MS6.6级地震孕震机制[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(12): 4058-4071. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201312011.htm 周洪建, 王曦, 袁艺, 等, 2014. 半干旱区极端强降雨灾害链损失快速评估方法: 以甘肃岷县"5·10"特大山洪泥石流灾害为例[J]. 干旱区研究, 31(3): 440-445. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHQJ201403010.htm -





 下载:
下载: