Characterization of karst development and groundwater circulation in the middle part of the Jinshajiang fault zone
-
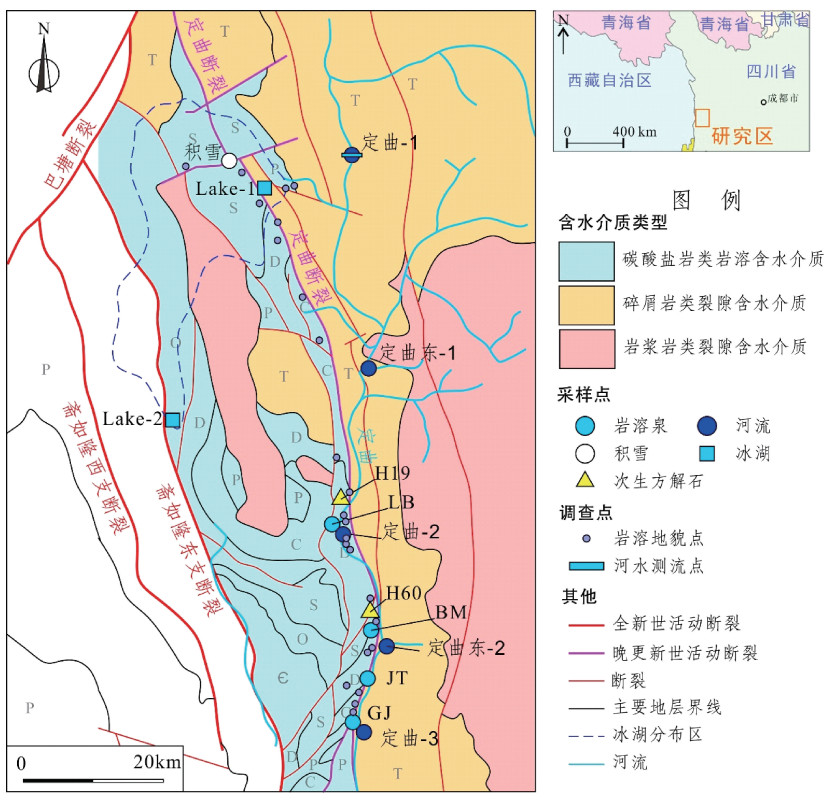
摘要:
金沙江断裂带中段碳酸盐岩分布区水文地质结构复杂、岩溶水量丰富, 是工程地质安全的重要威胁之一。文章在岩溶地貌和水文地质调查的基础上, 采用水化学和新型同位素测年与示踪的方法, 研究了金沙江断裂带中段岩溶发育特征, 分析了岩溶水补给、径流和排泄过程。结果表明: 岩溶空间分布和地下水补给、径流、排泄均受构造控制; 在垂向上主要存在3个高程级别的岩溶发育分区, 其中二级和三级顶部岩溶的发育时间分别为晚中新世至晚更新世和上新世至晚更新世; 岩溶水补给区海拔4400~4600 m, 主要补给源为大气降水和冰湖水, 水中228Ra/226Ra数据显示非定曲断裂控制范围内水源难以形成跨断裂影响范围的补给; 岩溶水循环速度快, 岩溶大泉的85Kr年龄<15 a, 且基本没有年龄较大的地下水混合; 径流过程中碳酸盐岩溶蚀和阳离子交换作用不充分。在工程中应充分考虑活动断裂影响下岩溶水径流通道空间分布、高水压影响和特殊天气条件带来的地质灾害威胁。
Abstract:The complex hydrogeological structure and abundant karst water in the carbonate rock distribution area in the Jinshajiang fault zone's middle section are essential threats to engineering safety. Based on karst landform and hydrogeological investigations, the article presents the karst development characteristics in the Jinshajiang fault zone's middle section, and analyzes the recharge source, runoff process, and discharge characteristics of karst water using the methods of hydrochemical and new isotopic dating and tracing. The results show that structures control the spatial distribution of karst and the groundwater circulation in the study area. There are mainly three elevation-level karst development zones in the vertical direction. The development time of the second elevation-level karst is from the late Miocene to the late Pleistocene, and the top of the third elevation-level karst is from the Pliocene to the late Pleistocene. The karst water recharge area is at an elevation of 4400~4600 m. The primary recharge sources are atmospheric precipitation and glacial lake water. The 228Ra/226Ra data in the water shows that it is difficult for water sources under the control of a non-fixed-curvature fault to form recharge across the affected area of the fault. The karst water circulates fast, the 85Kr age of the karst spring is < 15 a, and there is basically no older groundwater mixing. Carbonate rock dissolution and cation exchange are not sufficient during groundwater runoff. In the engineering project, the spatial distribution of karst water runoff channels under the control of active faults, the influence of high-water-pressure and the threat of geological disasters caused by special weather conditions should be fully considered.
-
图 3 研究区不同高程的岩溶地貌
a—第一级岩溶,溶洞,海拔约5000 m;b—第二级岩溶,溶洞(样品编号H19),海拔约4050 m;c—第三级岩溶,溶洞(样品编号H60),海拔约3600 m;d—波密泉(样品编号BM),海拔约3550 m;e—根久泉(样品编号GJ;据马剑飞等,2022a修改),海拔约3450 m;f—定曲泉(样品编号LB),海拔约3670 m
Figure 3. Karst landforms at different elevations in the study area
(a) The first-elevation-level krast (Krast cave at 5000 m); (b) The second-elevation-level (Krast cave at 4050 m; Sample H19); (c) The third-elevation-level (Krast cave at 3600 m; Sample H60); (d) The Bomi Spring at 3550 m (Sample BM); (e) The Genjiw Spring at 3450 m (Sample GJ; Modified from Ma et al., 2022b); (f) The Dingqu Spring at 3670 m (Sample LB)
图 7 水样T值与TDS和85Kr关系图
a—水样TDS与氚值(T)关系;b—岩溶泉85Kr活度与氚值(T)关系(图中虚线表示根据基于延迟输入函数的活塞流模型计算出的过去几十年的混合分数,实线表示年轻水占50%和99%时的模型计算值;Avrahamov et al., 2018)
Figure 7. T value vesus TDS value and 85Kr value in the water sample
(a) TDS value vesus T value in the water sample; (b) 85Kr value vesus T value in the karst springs The dashed lines are mixing lines between an old, T and 85Kr free component and groundwater of different ages. The solid lines are the calculated values by the model when the young water accounts for 50% and 99% based on Avrahamov et al., 2018.
图 8 研究区主要岩溶泉多期流量(GJ、BM部分数据源自Ma et al., 2022b)
Figure 8. Multi-flow of main karst springs in the study area (Parts of GJ, BM data are from Ma et al., 2022b)
表 1 不同高程次生方解石的230Th年龄
Table 1. 230Th age of secondary calcite at different elevations
样品编号 高程/m 230Th年龄/a BP H19 4050 36737±11667 H60 3600 14298±903 表 2 水化学和同位素测试结果
Table 2. Test results of hydrochemical components and isotopes
水体类型 数据项/样品编号* 水化学指标 同位素指标 TDS Ca2+ Mg2+ K+ Na+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- pH δD δ18O T /mg·L-1 /‰ /‰ TU 岩溶泉 最大值 207.00 54.83 10.86 0.91 5.75 0.30 9.15 223.50 7.89 -142.00 -18.90 4.70 最小值 90.00 22.06 7.44 0.16 0.25 0.17 1.35 102.80 7.71 -146.00 -19.50 4.20 平均值 162.50 42.67 9.66 0.58 3.31 0.22 6.91 175.85 7.82 -143.25 -19.08 4.40 变异系数 0.31 0.33 0.16 0.54 0.69 0.32 0.54 0.29 0.01 -0.01 -0.02 0.06 河水 最大值 251.00 68.62 11.83 1.50 3.35 1.05 91.31 138.90 8.16 -135.00 -17.90 7.00 最小值 52.00 10.65 0.84 0.58 1.61 <0.1 7.58 36.28 7.68 -142.00 -18.80 4.30 平均值 139.20 35.18 5.52 0.89 2.17 — 42.21 84.75 7.89 -138.80 -18.34 5.56 变异系数 0.67 0.73 0.83 0.41 0.31 — 0.94 0.57 0.02 -0.02 -0.02 0.23 湖水 Lake-1 69.00 18.39 2.83 0.51 0.97 0.10 6.08 66.45 7.35 -127.00 -16.60 8.10 Lake-2 9.00 1.37 0.10 0.08 0.25 0.15 < 0.20 12.08 7.44 降雨 4月降雨 9.00 1.31 0.18 0.17 0.33 0.21 0.30 12.08 7.70 -79.00 -10.00 10.00 9月降雨 15.00 1.79 0.22 0.08 0.33 1.40 2.00 12.02 6.74 积雪 积雪 10.00 2.11 0.05 0.08 0.09 0.35 1.50 11.42 7.38 -177.00 -24.10 7.20 “*”该列中岩溶泉和河水列出的为数据的统计值;湖水、降雨和积雪列出的为采样编号,其所在行的数据是样品的测试值 表 3 岩溶泉补给高程计算值
Table 3. Calculated values of the karst water recharge elevation
岩溶泉编号 补给高程h/m δ18O=-0.0028h -3.93① δ18O=-0.0033h-4.29② δ18O=-0.0023h-10.011③ δD=-0.0195h-67.813③ δ18O=-0.0018h-6.86④ GJ 5346 4427 3865 3804 6689 LB 5561 4609 4126 4010 7022 JT 5382 4458 3908 3856 6744 BM 5346 4427 3865 3804 6689 注:①李维杰等,2018;来自川东、渝、滇、黔等四地监测数据;②姚檀栋等,2009;以青海、西藏监测台站为主;③张磊等,2021;来自道孚-康定-石棉-西昌数据;④于津生等,1980;来自渝、黔、川、藏东等地数据 表 4 研究区主要水体226Ra和228Ra活度
Table 4. 226Ra and 228Ra activity in the water samples from the study area
水样编号 226Ra活度/dpm·100 L-1 228Ra活度/dpm·100 L-1 228Ra/226Ra GJ 6.27±1.07 7.18±2.38 0.91 BM 8.75±1.06 7.00±1.97 3.07 LB 7.56±0.98 4.28±1.91 0.80 Lake-1 3.95±0.78 5.27±1.97 0.57 Lake-2 9.57±1.11 29.42±2.70 1.34 定曲-2 14.95±1.16 13.56±2.13 1.14 -
AVRAHAMOV N, YECHIELI Y, PURTSCHERT R, et al., 2018. Characterization of a carbonate karstic aquifer flow system using multiple radioactive noble gases (3H-3He, 85Kr, 39Ar) and 14C as environmental tracers[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 242: 213-232. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.09.009 BOLLHÖFER A, SCHLOSSER C, SCHMID S, et al., 2019. Half a century of Krypton-85 activity concentration measured in air over Central Europe: Trends and relevance for dating young groundwater[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 205-206: 7-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2019.04.014 CLARK I D, FRITZ P, 1997. Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press. DONAHUE J, 1965. Laboratory growth of Pisolite grains[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 35(1): 251-256. doi: 10.1306/74D7123A-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D FAN H B, ZHANG Y H, HE S Y, et al., 2018. Hazards and treatment of karst tunneling in Qinling-Daba mountainous area: overview and lessons learnt from Yichang-Wanzhou railway system[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77(19): 679. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-7860-1 GAO C, LIU S Y, FENG J D, et al., 2021. Monitoring atmospheric 85Kr by atom counting[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 233: 106604. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2021.106604 GAO Q Z, CUI Z J, LIU G N, et al., 2000. The fission track ages of the cavernous recrystalline calcites in Tibet plateau and their geomorphologic significance[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 20(3): 61-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) GAO Q Z, CUI Z J, TAO Z, et al., 2002. The nature, formation age and genetic environment of the Palaeokarst on the Qinghai-Xizang plateau[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 57(3): 267-274. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2002.03.002 GAUTAM V K, KOTHARI M, SINGH P K, et al., 2022. Analysis of groundwater level trend in Jakham River Basin of Southern Rajasthan[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 10(1): 1-9, doi: 10.19637/j.cnki.2305-7068.2022.01.001. JIANG Z C, ZHANG J, HUANG C, et al., 2019. Causes of formation and geo-scientific significance of karst gorge group in Xiangxi geopark[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 38(2): 269-275. (in Chinese with English abstract) KANG X B, YANG S F, GUAN Z D, et al., 2021. Distribution of soluble rock strata and development of karst landforms in the Batang area, west Sichuan plateau[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 40(3): 381-388. (in Chinese with English abstract) KONG F C, YANG Y K, MA Y J, et al., 2021. The distribution and sources of radium isotopes in Da Qaidam Salt Lake[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 33(2): 632-646. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18307/2021.0227 LANG L, LIU J A, ZHONG Q Q, et al., 2020. Water mixing in the northern slope of the South China Sea as traced by 226Ra and 228Ra[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 39(4): 511-521. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI C S, DING J F, LIAO Y K, et al., 2020. Experimental study on karst dissolution action mechanism under tunnel excavation condition[M]//LI C S, DING J F, LIAO Y K, et al. Groundwater chemical kinetics and fractal characteristics of karst tunnel. Singapore: Springer: 117-148. LI S C, WANG X T, XU Z H, et al., 2021. Numerical investigation of hydraulic tomography for mapping karst conduits and its connectivity[J]. Engineering Geology, 281: 105967. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105967 LI W J, WANG J L, WANG J L, 2018. Characteristics of the stable isotopes in precipitation and the source of water vapor in different terrain in the southwest region[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 27(5): 1132-1142. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201805020 LI X Q, MA J F, ZHANG C C, et al., 2021. Evolution regularity of the plateau tectonic karst and the relevant karst groundwater circulation mode in Mount Genie and Zaya sections along the Sichuan-Xizang railway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 48(5): 34-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIAO F, WANG G C, YI L X, et al., 2020. Applying radium isotopes to estimate groundwater discharge into Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 585: 124782. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124782 LOOSLI H H, LEHMANN B E, SMETHIE JR W M, 2000. Noble gas radioisotopes: 37Ar, 85Kr, 39Ar, 81Kr[M]//COOK P G, HERCZEG A L. Environmental tracers in subsurface hydrology. Boston: Springer: 379-396. LU Y R, 1999. Study on the evolution of karst hydrogeological environment and its engineering effect[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) LUO W Y, 2019. Characteristics of water-thermal hazard and hydrogeological route selection in typical sections of Sichuan-Tibet Railway[C]//Proceedings of Seminar on construction technology of Sichuan-Tibet Railway project. Xi'an: China Railway Society. (in Chinese with English abstract) LUO X, JIAO J J, WANG X S, et al., 2017. Groundwater discharge and hydrologic partition of the lakes in desert environment: Insights from stable 18O/2H and radium isotopes[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 546: 189-203, doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.01.017. LUO X, JIAO J J, MOORE W S, et al., 2018. Significant chemical fluxes from natural terrestrial groundwater rival anthropogenic and fluvial input in a large-river deltaic estuary[J]. Water Research, 144: 603-615. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.07.004 MA J F, LI X Q, ZHANG C C, et al., 2022a. Recharge source, mode and development potential of typical tectonic karst groundwater in the eastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J/OL]. Geology in China, (2022-08-22). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20220822.1417.016.html. (in Chinese with English abstract) MA J F, FU C C, ZHANG C C, et al., 2022b. Plateau tectonic karst development characteristics and underground conduits identification in the northern part of Kangding[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 41(1): 288-299. (in Chinese with English abstract) MA J F, LI X Q, LIU F, et al., 2022a. Application of hydrochemical and isotopic data to determine the origin and circulation conditions of karst groundwater in an alpine and gorge region in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau: a case study of Genie Mountain[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 81(10): 291, doi: 10.1007/s12665-022-10414-9. MA J F, LI X Q, ZHANG C C, et al., 2022b. Identification of origin and runoff of karst groundwater in the glacial lake area of the Jinsha River fault zone, China[J]. Scientific Reports, 12(1): 14661. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18960-9 MU W P, 2018. Mechanism of water inrush on faults of coal seam floor and prediction of dewatering rate from karst aquifers in Beiyangzhuang mine[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract) QIN Y L, WU J L, ZHAN H Y, et al., 2021. Discussion on the correlation between active fault and geological disaster distribution in the Ganzi area, western Sichuan Province, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(3): 463-474. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHEN J F, SHI Y H, YU Q C, et al., 1991. On the formation condition and prediction-method of karst caves in carbonate rocks[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 16(1): 61-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHI X D, KANG X B, XU M, et al., 2019. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution laws of karst grounderwater in the slope zone of the canyon area, Sichuan-Yunnan Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(11): 2975-2984. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.11.019 SICHUAN LOCAL CHRONICLES COMPILATION COMMITTEE, 1996. Annals of Sichuan province [M]. Chengdu: Chengdu Cartographic Publishing House: 127. (in Chinese) TESFALDET Y T, PUTTIWONGRAK A, ARPORNTHIP T, 2020. Spatial and temporal variation of groundwater recharge in shallow aquifer in the Thepkasattri of Phuket, Thailand[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 8(1): 10-19. WANG D J. 2021. Development characteristics of plateau karst and influences on the engineering in a tunnel area of southeast Tibet[J]. Tunnel Construction, 41(6): 996-1006. (in Chinese with English abstract) WENG J T, RU J W, 1982. Cave pearls[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1(1): 58-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIA J W, ZHU M, 2020. Study on tectonic characteristics and activity of middle section of Jinshajiang Main Fault Zone[J]. Yangtze River, 51(5): 131-137, 159. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU H H, HU B, LIU W L, et al., 2020. Study on karst water drainage path in plateau karst area[J]. Yangtze River, 51(11): 128-133. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20190833 XU Y P, XIANG X Q, YANG G L, 2020. Study on recharge, runoff and drainage of karst groundwater in Nanjiang Grand Canyon in Kaiyang[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 51(2): 53-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) XUE Y G, KONG F M, LI S C, et al., 2021. Water and mud inrush hazard in underground engineering: genesis, evolution and prevention[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 114: 103987. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2021.103987 YANG Z H, WU R A, GUO C B, et al., 2022. Geo-hazard effects and typical landslide characteristics of the Batang fault zone in the Western Sichuan[J]. Geology in China, 49(2): 355-368. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Z P, JIANG Y W, LI B, et al., 2020. Study on the mechanism of deep and large fracture propagation and transfixion in karst slope under the action of mining[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(4): 459-470. (in Chinese with English abstract) YAO T D, ZHOU H, YANG X X, 2009. Indian monsoon influences altitude effect of δ18O in precipitation/river water on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(16): 2724-2731, doi: 10.1007/s11434-009-0497-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) YOUNG M B, GONNEEA M E, FONG D A, et al., 2008. Characterizing sources of groundwater to a tropical coastal lagoon in a karstic area using radium isotopes and water chemistry[J]. Marine Chemistry, 109(3-4): 377-394. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2007.07.010 YU J S, ZHANG H B, YU F J, et al., 1980. Oxygen isotopic composition of meteoric water in the eastern part of Xizang[J]. Geochimica, 9(2): 113-121. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG C C, LI X Q, MA J F, et al., 2021. Formation model of geothermal water in Chaya of Tibet: perspective from hydrochemistry and stable isotopes[J]. Geoscience, 35(1): 199-208. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG D, 1994. Distribution of Tibetan karren and their morphogenetic analysis[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 13(3): 270-280. ZHANG D, SHI C X, 2002. CO2 partial pressure, karst dissolution rate and karst micro-landforms on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 76(4): 566-570. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG L, GUO L S, LIU S W, et al., 2021. Characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes of hot springs in Xianshuihe-Anninghe fault zone, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 37(2): 589-598. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Y S, GUO C B, LI X Q, et al., 2021. Key problems on hydro-engineering-environmental geology along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway corridor: current status and development direction[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 48(5): 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAO T S, GAO R X, 1985. Concealed karst development in eastern part of lower Liaohe river plain, Liaoning Province, and its hydrogeological significance[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 4(3): 257-266. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHONG L M, XU M, WU M L, et al., 2018. Development of deep karst under the coupling of multistage flow systems: a case of southern part of the Zhongliang Mountain anticline of the parallel barrier structure in Eastern Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 45(1): 45-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) 高全洲, 崔之久, 刘耕年, 等, 2000. 青藏高原洞穴次生方解石的裂变径迹年代及地貌学意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 20(3): 61-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200003012.htm 高全洲, 崔之久, 陶贞, 等, 2002. 青藏高原古岩溶的性质、发育时代和环境特征[J]. 地理学报, 57(3): 267-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB200203001.htm 蒋忠诚, 张晶, 黄超, 等, 2019. 湘西地质公园岩溶峡谷群成因及其地学意义[J]. 中国岩溶, 38(2): 269-275. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201902016.htm 康小兵, 杨四福, 管振德, 等, 2021. 川西高原巴塘地区可溶岩地层分布与岩溶地貌发育特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 40(3): 381-388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202103002.htm 孔凡翠, 杨英魁, 马玉军, 等, 2021. 大柴旦盐湖中镭同位素分布特征来源及示踪意义[J]. 湖泊科学, 33(2): 632-646. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX202102028.htm 郎琳, 刘建安, 钟强强, 等, 2020. 226Ra和228Ra对南海北部陆坡水团的示踪作用[J]. 海洋环境科学, 39(4): 511-521. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYHJ202004003.htm 李维杰, 王建力, 王家录, 2018. 西南地区不同地形降水稳定同位素特征及其水汽来源[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 27(5): 1132-1142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY201805020.htm 李向全, 马剑飞, 张春潮, 等, 2021. 川藏铁路格聂山和察雅段构造岩溶发育规律及岩溶地下水循环模式研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 48(5): 34-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202105004.htm 卢耀如, 1999. 岩溶水文地质环境演化与工程效应研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 罗文艺, 2019. 川藏铁路水-热灾害特征及典型段落水文地质选线探析[C]//川藏铁路工程建造技术研讨会. 西安: 中国铁道学会. 马剑飞, 李向全, 张春潮, 等, 2022a. 青藏高原东部典型构造岩溶地下水补给来源、模式及开发利用潜力[J/OL]. 中国地质, (2022-08-22). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20220822.1417.016.html. 马剑飞, 付昌昌, 张春潮, 等, 2022b. 康定北部高原构造岩溶发育特征与地下水径流带识别[J]. 地质科技通报, 41(1): 288-299. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202201031.htm 穆文平, 2018. 北阳庄矿煤层底板断层突水机理与岩溶水疏降水量预测[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京). 秦宇龙, 吴建亮, 詹涵钰, 等, 2021. 川西甘孜地区活动断裂与地质灾害分布相关性探讨[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(3): 463-474. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.03.042 沈继方, 史毅虹, 于青春, 等, 1991. 碳酸盐岩中岩溶洞穴的形成条件及预测方法初探[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 16(1): 61-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX199101007.htm 史箫笛, 康小兵, 许模, 等, 2019. 川滇高原斜坡地带峡谷区岩溶水化学特征及演化规律[J]. 地质学报, 93(11): 2975-2984. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201911019.htm 四川省地方志编纂委员会, 1996. 四川省志·地理志(上下册)[M]. 成都: 成都地图出版社: 127. 王杜江. 2021. 藏东南某隧址区高原型岩溶发育特征及工程影响[J]. 隧道建设, 41(6): 996-1006. 翁金桃, 茹锦文, 1982. 穴珠[J]. 中国岩溶, 1(1): 58-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198201010.htm 夏金梧, 朱萌, 2020. 金沙江主断裂带中段构造特征与活动性研究[J]. 人民长江, 51(5): 131-137, 159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE202005022.htm 许汉华, 胡斌, 刘文连, 等, 2020. 高原岩溶区岩溶水排泄路径研究[J]. 人民长江, 51(11): 128-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE202011022.htm 徐一萍, 向喜琼, 杨根兰, 2020. 开阳南江大峡谷岩溶地下水补径排研究[J]. 水利水电技术, 51(2): 53-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJWJ202002005.htm 杨志华, 吴瑞安, 郭长宝, 等, 2022. 川西巴塘断裂带地质灾害效应与典型滑坡发育特征[J]. 中国地质, 49(2): 355-368. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202202001.htm 杨忠平, 蒋源文, 李滨, 等, 2020. 采动作用下岩溶山体深大裂隙扩展贯通机理研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(4): 459-470. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.04.039 姚檀栋, 周行, 杨晓新, 2009. 印度季风水汽对青藏高原降水和河水中δ18O高程递减率的影响[J]. 科学通报, 54(15): 2124-2130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200915003.htm 于津生, 张鸿斌, 虞福基, 等, 1980. 西藏东部大气降水氧同位素组成特征[J]. 地球化学, 9(2): 113-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX198002000.htm 张春潮, 李向全, 马剑飞, 等, 2021. 基于水化学及稳定同位素的西藏察雅地下热水成因研究[J]. 现代地质, 35(1): 199-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202101022.htm 章典, 师长兴, 2002. 青藏高原的大气CO2含量、岩溶溶蚀速率及现代岩溶微地貌[J]. 地质学报, 76(4): 566-570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200204023.htm 张磊, 郭丽爽, 刘树文, 等, 2021. 四川鲜水河-安宁河断裂带温泉氢氧稳定同位素特征[J]. 岩石学报, 37(2): 589-598. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202102016.htm 张永双, 郭长宝, 李向全, 等, 2021. 川藏铁路廊道关键水工环地质问题: 现状与发展方向[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 48(5): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202105001.htm 赵天石, 高瑞袖, 1985. 辽宁省下辽河平原东部隐伏岩溶发育规律及水文地质意义[J]. 中国岩溶, 4(3): 257-266. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198503007.htm 钟玲敏, 许模, 吴明亮, 等, 2018. 多级水流系统耦合下深部岩溶分异研究: 以川东隔挡式构造区中梁山背斜南段为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 45(1): 45-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201801007.htm -





 下载:
下载: