Factors inducing the Xigouwan landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area and the influence of antecedent precipitation
-
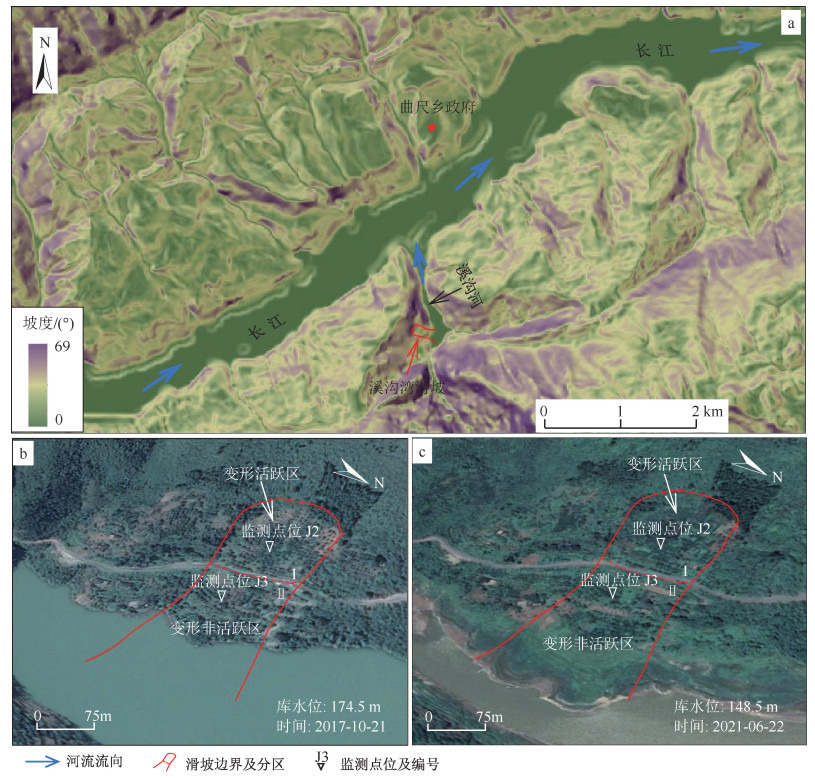
摘要:
多年来的监测数据表明溪沟湾滑坡加速变形时总伴随着季节性降雨和库水位变动, 难以辨别滑坡变形的主导诱发因素, 对风险分析带来了挑战。鉴于此, 论文首先采用邻域粗糙集模型中的属性约简算法, 对溪沟湾滑坡活跃区和非活跃区日变形速率与降雨、库水位和库水位变动速率因素之间的相关性进行了系统分析, 计算结果表明溪沟湾滑坡活跃区变形主要受过去7日降雨因素影响, 并与短期库水位变化率因素存在关联性, 滑坡非活跃区的微弱变形与过去3日库水位变化率因素存在关联性。然后, 结合滑坡变形特征, 研究发现诱发溪沟湾滑坡活跃区剧烈变形的过去7天平均降雨量在20 mm左右, 库水位下降因素对其变形存在影响, 但影响较小, 而溪沟湾滑坡非活跃区的微弱变形主要受库水位波动影响。最后, 通过对溪沟湾滑坡进行渗流-力学数值计算分析, 结果揭示了溪沟湾滑坡活跃区受长历时前期降雨作用的变形机理。数值分析过程中, 当降雨强度由1 mm/d增至20 mm/d, 降雨造成滑坡体内部孔隙水压逐渐增大, 内部水位抬升并不断向滑坡活跃区延伸, 导致活跃区滑坡体由稳定状态降至欠稳定状态, 进而引发溪沟湾滑坡活跃区变形加剧。此外, 数值模拟结果也表明库水位下降因素对滑坡活跃区内部渗流场影响较小, 对其稳定性影响有限, 而库水位变动对滑坡非活跃区内部渗流场影响较大, 说明滑坡非活跃区的微弱变形主要受库水位波动影响。论文针对溪沟湾滑坡变形诱发因素的综合分析结果, 有助于对该滑坡进行风险预警, 可将过去7日平均降雨量20 mm作为诱发溪沟湾滑坡活跃区剧烈变形预警阀值之一。
Abstract:Monitoring data over the years have shown that seasonal rainfall and reservoir level changes have always accompanied the accelerated deformation of the Xigouwan landslide, which makes it difficult to identify the dominant triggering factors of landslide deformation and poses a challenge to risk analysis. Given this, this paper analyzed the correlation between the daily deformation rate of the active and inactive areas in the Xigouwan landslide and rainfall, reservoir level, and the change rate of reservoir level by applying the attribute reduction algorithm of the neighborhood rough set model. The calculation results showed that the deformation in the active area was mainly affected by the rainfall in the past seven days. It was also related to the short-term change rate of reservoir water level in some ways. The weak deformation in the inactive area was related to the change rate of reservoir water level in the past three days. Then, based on the landslide deformation characteristics, it was further obtained that the average rainfall in the past seven days inducing severe deformation in the active area was about 20 mm. The decline of the reservoir water level influenced its deformation, but the effect was small. The reservoir level change affected the weak deformation in the inactive area with negligible influence, while the weak deformation in the inactive area was mainly influenced by the reservoir level change. Finally, the seepage-mechanics numerical analysis of the Xigouwan landslide reveals the deformation mechanism of the active area under long-duration early rainfall. As the rainfall intensity increased from 1 mm/d to 20 mm/d, the pore water pressure at the bottom of the landslide body gradually increased. The internal reservoir level rose and extended to the active area, which caused the landslide body in the active area to go from a stable state to an under-stable state, leading to large deformation in the active area. In addition, the numerical simulation results further showed that the decline of the reservoir level had little effect on the internal seepage field and the stability in the active area. The reservoir level change greatly influenced the internal seepage field in the inactive area, indicating that the weak deformation in the inactive area was mainly affected by the reservoir level change. The complete analysis results of factors inducing the Xigouwan landslide in this paper can help provide early warning. The average rainfall of 20 mm in the past seven days can be used as one of the early warning thresholds for severe deformation in the active area of the Xigouwan landslide.
-
图 10 前期降雨引发的溪沟湾滑体内部渗流场状况
a—前期降雨强度为1 mm/d时;b—前期降雨强度为12 mm/d时;c—前期降雨强度为20 mm/d时
Figure 10. Seepage feilds in the Xigouwan landslide body caused by antecedent rainfall
(a) Antecedent rainfall intensity at 1 mm/d; (b) Antecedent rainfall intensity at 12 mm/d; (c) Antecedent rainfall intensity at 20 mm/d
图 12 库水位下降引发的溪沟湾滑体内部渗流场状况
a—前期降雨强度为1 mm/d时;b—前期降雨强度为12 mm/d时;c—前期降雨强度为20 mm/d时
Figure 12. Seepage field in the Xigouwan landslide body caused by the drawdown of the reservoir level
(a) Antecedent rainfall intensity at 1 mm/d; (b) Antecedent rainfall intensity at 12 mm/d; (c) Antecedent rainfall intensity at 20 mm/d
表 1 溪沟湾滑坡形变信息系统属性指标
Table 1. Attribute index of the information system for the Xigouwan landslide deformation
条件属性C 指标 描述 指标 描述 a1 当日降雨量 a9 过去15日平均库水位 a2 过去3日平均降雨量 a10 过去30日平均库水位 a3 过去7日平均降雨量 a11 当日库水位变动率 a4 过去15日平均降雨量 a12 过去3日平均库水位变动率 a5 过去30日平均降雨量 a13 过去7日平均库水位变动率 a6 当日库水位 a14 过去15日平均库水位变动率 a7 过去3日平均库水位 a15 过去30日平均库水位变动率 a8 过去7日平均库水位 决策属性D a16 J2监测点位日位移速率 a17 J3监测点位日位移速率 表 2 溪沟湾滑坡体物质物理力学参数
Table 2. Physical and mechanical parameters of the Xigouwan landslide body
部位 容重/(KN/m3) 黏聚力/kPa 摩擦角/(°) 渗透系数/(m/d) 孔隙比 滑体 21 13 33 2.16 1.22 滑带 18 18 16 0.1 0.67 -
BISHOP A W, MORGENSTERN N, 1960. Stability coefficients for earth slopes[J]. Géotechnique, 10(4): 129-153. doi: 10.1680/geot.1960.10.4.129 DAI Z W, YIN Y P, WEI Y J, et al., 2016. Deformation and failure mechanism of Outang landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 24(1): 44-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) GEO-SLOPE International Ltd, 2012. Stability modeling and seepage modeling with GeoStudio[M]. Calgary, Alberta, Canada. GU D M, HUANG D, YANG W D, et al., 2017. Understanding the triggering mechanism and possible kinematic evolution of a reactivated landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Landslides, 14(6): 2073-2087. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0845-4 HAN X D, FU J, LI Y Y, et al., 2021. A study of the early identification and risk assessment of the Jiangdingya landslide in Zhouqu county[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 48(6): 180-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU Q H, YU D R, LIU J F, et al., 2008. Neighborhood rough set based heterogeneous feature subset selection[J]. Information Sciences, 178(18): 3577-3594. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2008.05.024 HU X L, WU S S, ZHANG G C, et al., 2021. Landslide displacement prediction using kinematics-based random forests method: a case study in Jinping Reservoir Area, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 283: 105975. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105975 HUANG D, KUANG X B, LUO S L, 2019. A study of the deformation characteristics and reactivation mechanism of the Outang landslide near the Three Gorges Reservoir of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 46(5): 127-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG D, LUO S L, ZHONG Z, et al., 2020. Analysis and modeling of the combined effects of hydrological factors on a reservoir bank slope in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 279: 105858. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105858 JANBU N, 1954. Application of composite slip surface for stability analysis[C]. Proceedings of European conference on stability of earth slopes, 3: 43-49. LI D, JIANG Y, BAO Y W Y, 2020. Attribute reduction of variable precision neighborhood rough sets based on attribute quality[J]. Journal of Sichuan Normal University (Natural Science), 43(4): 560-568. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Y, UTILI S, MILLEDGE D, et al., 2021. Chasing a complete understanding of the failure mechanisms and potential hazards of the slow moving Liangshuijing landslide[J]. Engineering Geology, 281: 105977. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105977 MORGENSTERN N R, PRICE V E, 1965. The analysis of the stability of general slip surfaces[J]. Géotechnique, 15(1): 79-93. doi: 10.1680/geot.1965.15.1.79 PAWLAK Z, 2002. Rough sets and intelligent data analysis[J]. Information Sciences, 147(1-4): 1-12. doi: 10.1016/S0020-0255(02)00197-4 RAO H, WANG J S, ZHAO Z M, et al., 2021. An analysis of rainfall infiltration of expansive soil slope based on the finite element software custom constitutive model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 48(1): 154-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHANG M, LIAO F, MA R, et al., 2021. Quantitative correlation analysis on deformation of Baijiabao landslide between rainfall and reservoir water level[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 29(3): 742-750. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHENG K, BIAN X F, DONG H, et al., 2020. Attribute reduction of mixed data based on neighborhood rough set combination metrics[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 37(2): 234-239. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2020.02.036 SONG K, WANG F W, YI Q L, et al., 2018. Landslide deformation behavior influenced by water level fluctuations of the Three Gorges Reservoir (China)[J]. Engineering Geology, 247: 58-68. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.10.020 TAN L Y, HUANG R Q, FENG X L, et al., 2020. Monitoring features and induced mechanism analysis of typical landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area of Chongqing[J]. Geological Review, 66(S1): 171-174. (in Chinese with English abstract) TAN L Y, HUANG R Q, PEI X J, 2021. Deformation characteristics and inducing mechanisms of a super-large bedding rock landslide triggered by reservoir water level decline in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 40(2): 302-314. (in Chinese with English abstract) TANG H M, WASOWSKI J, JUANG C H, 2019a. Geohazards in the three Gorges Reservoir Area, China-Lessons learned from decades of research[J]. Engineering Geology, 261: 105267. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105267 TANG M G, XU Q, YANG H, et al., 2019b. Activity law and hydraulics mechanism of landslides with different sliding surface and permeability in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 260: 105212. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105212 WANG H Q, FENG C J, QI B S, et al., 2020. Analysis of the stability of the Lisizhuang landslide in Shunping County, Hebei Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(4): 595-603. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIANG L, WANG S M, WANG L, 2014. Response of typical hydrodynamic pressure landslide to reservoir water level fluctuation: Shuping landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir as an Example[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 22(5): 876-882. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIN P, WANG T, LIU J M, et al., 2022. The geological structure and sliding mode of the slopes in the Yigong landslide source area, Tibet[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(6): 1012-1023. XU B, 2019. Research on heuristic attribute reduction algorithm for neighbourhood rough set[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Normal University. (in Chinese with English abstract) YAN G Q, YI W, TONG S A, et al., 2018. Stability analysis prediction and deformation mechanism of Baijiabao landslide in Three Gorges Reservoirs Area[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 34(5): 29-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) YAN J K, HUANG J B, LI H L, et al., 2020. Study on instability mechanism of shallow landslide caused by typhoon and heavy rain[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(4): 481-491. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG X L, CHEN H M, LI T R, et al., 2021. Neighborhood rough sets with distance metric learning for feature selection[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 224: 107076. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107076 YAO W M, LI C D, ZUO Q J, et al., 2019. Spatiotemporal deformation characteristics and triggering factors of Baijiabao landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir region, China[J]. Geomorphology, 343: 34-47. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.06.024 ZHANG C Y, YIN Y P, YAN H, et al., 2021a. Reactivation characteristics and hydrological inducing factors of a massive ancient landslide in the three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 292: 106273. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106273 ZHANG K, ZHANG K, BAO R, et al., 2021. Intelligent prediction of landslide displacements based on optimized empirical mode decomposition and K-Mean clustering[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 42(1): 211-223 (in Chinese with English abstract). ZHANG X Y, FAN Y R, Yang J L, 2021b. Feature selection based on fuzzy-neighborhood relative decision entropy[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 146: 100-107. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2021.03.001 ZHAO N H, HU B, YAN E C, et al., 2019. Research on the creep mechanism of Huangniba landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of China considering the seepage-stress coupling effect[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 78(6): 4107-4121. doi: 10.1007/s10064-018-1377-4 ZHENG W B, LI J J, HE Q H, 2019. Attribute reduction algorithm for neighborhood rough sets with variable precision based on attribute importance[J]. Computer Science, 46(12): 261-265. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU W, WANG K W, WEI D, et al., 2017. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of deformation influencing factors of Baijiabao landslide[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University (Natural Sciences), 39(5): 6-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) 代贞伟, 殷跃平, 魏云杰, 等, 2016. 三峡库区藕塘滑坡变形失稳机制研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 24(1): 44-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201601008.htm 韩旭东, 付杰, 李严严, 等, 2021. 舟曲江顶崖滑坡的早期判识及风险评估研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 48(6): 180-186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202106020.htm 黄达, 匡希彬, 罗世林, 2019. 三峡库区藕塘滑坡变形特点及复活机制研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 46(5): 127-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201905018.htm 李冬, 蒋瑜, 鲍杨婉莹, 2020. 基于属性质量度的变精度邻域粗糙集属性约简[J]. 四川师范大学学报(自然科学版), 43(4): 560-568. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCSD202004023.htm 饶鸿, 王金淑, 赵志明, 等, 2021. 基于有限元软件自定义本构模型的膨胀土边坡降雨入渗分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 48(1): 154-162. 尚敏, 廖芬, 马锐, 等, 2021. 白家包滑坡变形与库水位、降雨相关性定量化分析研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 29(3): 742-750. 盛魁, 卞显福, 董辉, 等, 2020. 基于邻域粗糙集组合度量的混合数据属性约简算法[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 37(2): 234-239. 谭淋耘, 黄润秋, 冯晓亮, 等, 2020. 三峡重庆库区典型滑坡监测特征与诱发机制[J]. 地质论评, 66(S1): 171-174. 谭淋耘, 黄润秋, 裴向军, 2021. 库水位下降诱发的特大型顺层岩质滑坡变形特征与诱发机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 40(2): 302-314. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202102007.htm 王惠卿, 丰成君, 戚帮申, 等, 2020. 河北省顺平县李思庄滑坡稳定性分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(4): 595-603. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.04.052 向玲, 王世梅, 王力, 2014. 动水压力型滑坡对库水位升降作用的响应: 以三峡库区树坪滑坡为例[J]. 工程地质学报, 22(5): 876-882. 辛鹏, 王涛, 刘甲美, 等, 2022. 西藏易贡滑坡源区坡体赋存的地质结构及其滑动模式[J]. 地质力学学报, 28(6): 1012-1023. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2022072 徐波, 2019. 邻域粗糙集的启发式属性约简算法研究[D]. 成都: 四川师范大学. 闫国强, 易武, 童时岸, 等, 2018. 三峡库区白家包滑坡变形机理及稳定性分析预测[J]. 科技通报, 34(5): 29-34. 闫金凯, 黄俊宝, 李海龙, 等, 2020. 台风暴雨型浅层滑坡失稳机理研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(4): 481-491. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.04.041 张凯, 张科, 保瑞, 等, 2021. 基于优化经验模态分解和聚类分析的滑坡位移智能预测研究[J]. 岩土力学, 42(1): 211-223. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202101024.htm 郑文彬, 李进金, 何秋红, 2019. 基于属性重要度的变精度邻域粗糙集属性约简算法[J]. 计算机科学, 46(12): 261-265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJA201912039.htm 朱伟, 王孔伟, 魏东, 等, 2017. 白家包滑坡变形影响因素定性及定量分析[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版), 39(5): 6-11. -





 下载:
下载: